Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MS2 - NMAS Definition
Încărcat de
Varun PersadDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MS2 - NMAS Definition
Încărcat de
Varun PersadDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
be similar, but the actual number and sizes of horizontal scale, which represents sieve size openings
particles in the mixture are not similar and the in inches (millimeters) raised to the 0.45 power,
resulting volumetrics in the compacted mixture and a vertical scale that represents percent passing.
will be different. An important feature of the 0.45 power chart is the
Field-produced mixtures with significantly maximum density line. The maximum density line
different aggregate specific gravities than those plots as a straight line from the maximum aggregate
used in the mix design will also yield different size to the origin of the chart.
hot mix volumetric properties. This is one of the The maximum aggregate size is typically the largest
reasons why most specifications require a new mix sieve size through which 100 percent of the aggregate
design when the source (and characteristics) of any will pass. The maximum aggregate size is defined
of the mix ingredients are changed. as one sieve size larger than the nominal maximum
aggregate size (NMAS). The NMAS is defined as one
3.2.3.1 Plotting gradations sieve size larger than the first sieve size to retain
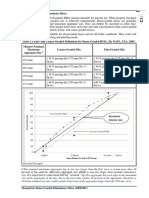
In the early 1960s, the Bureau of Public Roads more than 10 percent of the aggregate gradation.
(today’s FHWA) introduced a gradation chart (see The maximum density line was developed for
Figure 3.7) which is an especially useful tool in rounded, uncrushed materials. The maximum
evaluating aggregate gradations. The chart uses a density condition for crushed particles typically
FIGURE 3.7 0.45 Power Chart Showing Several Maximum Density Lines (MDLs) for Various Top Sizes
Maximum Density Lines for Different Top Sizes
100
90
80
70
60
Percent Passing
25mm (1")
50 19.0mm (¾")
12.5mm (½")
40 9.5mm (⅜")
4.75mm (#4)
30
20
10
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
4.75mm 2.5 9.5mm312.5mm3.5 19mm4 25mm4.5
Sieve Size
Chapter 3 Materials Selection and Aggregate Batching 25
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gradation and Size AggregatesDocument9 paginiGradation and Size AggregatesAnthony DelarosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marshall Method of Mix Design (Compatibility Mode)Document34 paginiMarshall Method of Mix Design (Compatibility Mode)Farah MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials of Construction Laboratory: Sieve Analysis of Aggregate (ASTM C136Document38 paginiMaterials of Construction Laboratory: Sieve Analysis of Aggregate (ASTM C136Mohammed JberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chip Seal 2Document14 paginiChip Seal 2phat nguyen tienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2.2-Unbound Pavement MaterialsDocument24 paginiChapter 2.2-Unbound Pavement MaterialsAbel MulugetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mamarshall Mix Design MethodDocument31 paginiMamarshall Mix Design MethodZul StudiozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Publication 1558676872 PDFDocument13 paginiPublication 1558676872 PDFHenok MebrateÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Duhok College of Engineering Civil Department 2 Year, 2017-2018Document11 paginiUniversity of Duhok College of Engineering Civil Department 2 Year, 2017-2018Dakheel malekoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESAL and Traffic DesignationDocument1 paginăESAL and Traffic DesignationTAN DAYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspal Bab ViiDocument5 paginiAspal Bab ViiFebrinaDianKurniasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Superpave Aggregate RequirementsDocument17 pagini2 - Superpave Aggregate RequirementsMuhammad FaheemÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM D2940 Agregates For Base CourseDocument1 paginăASTM D2940 Agregates For Base Courseتوفيق عبداللهÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dry Mix DesignDocument7 paginiDry Mix DesignNeeraj ChaubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Superpave-4Document124 pagini1 - Superpave-4Hozayen HozayenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sieve Analysis:: Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 10Document17 paginiSieve Analysis:: Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 10Mahmoud HosnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coarse Aggregate Angularity NumberDocument5 paginiCoarse Aggregate Angularity NumberMohammad Tarequl AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sand & AggregateDocument75 paginiSand & AggregateCBIT CIVIL A1Încă nu există evaluări
- D 448 - 03 Rdq0oc1sruqDocument4 paginiD 448 - 03 Rdq0oc1sruqel kevinsio el kevinsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS 594.1-92 - Hot Rolled Asphalt For Roads and Other Paved Areas (Spec For Constituent Materials and Asphalt Mixtures)Document21 paginiBS 594.1-92 - Hot Rolled Asphalt For Roads and Other Paved Areas (Spec For Constituent Materials and Asphalt Mixtures)Michael VeneerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 Experimental Determination of The Aluminium Thin Sheets Diameter To ADocument6 pagini2013 Experimental Determination of The Aluminium Thin Sheets Diameter To AL ZhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marshall Stability TestDocument10 paginiMarshall Stability TestBVS NAGABABUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sieve Analysis and Fineness Modulus SamplingDocument15 paginiSieve Analysis and Fineness Modulus SamplingExcel MigsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aggregates For Asphalt Concrete 880Document2 paginiAggregates For Asphalt Concrete 880melvinkorahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mix Design For BSM-foam - Feb 2012Document14 paginiMix Design For BSM-foam - Feb 2012Alan FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- تكنولوجيا الخرسانة و خواصها و اختباراتهاDocument18 paginiتكنولوجيا الخرسانة و خواصها و اختباراتهاalbfaragÎncă nu există evaluări
- ML12153A333Document67 paginiML12153A333HKDOCUMENTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aggregates: CE 201 Engineering MaterialsDocument17 paginiAggregates: CE 201 Engineering MaterialsMahadi HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scar RowDocument22 paginiScar RowMr.WasgehtsiedasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mix Design 8 2Document6 paginiMix Design 8 2Eulogio JameroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 703 Aggregates - ASTM E11Document9 paginiSection 703 Aggregates - ASTM E11Azim De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cement: A) Brand 2. Aggregates: A) Fine Aggregate B) Coarse Aggregate The Characteristics of Materials Are Given in Table 1 To 3Document7 paginiCement: A) Brand 2. Aggregates: A) Fine Aggregate B) Coarse Aggregate The Characteristics of Materials Are Given in Table 1 To 3Praneeth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical 2 (Sieve Analysis Test)Document8 paginiPractical 2 (Sieve Analysis Test)Ddeqz Elina Bueno IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elongation and Flakiness Index TEST FOR AGGREGATEDocument2 paginiElongation and Flakiness Index TEST FOR AGGREGATEQuality JamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marshall Stability TestDocument10 paginiMarshall Stability Testanon_789699787Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 2B Determination of Flakiness Index of Coarse Aggregate AimDocument3 paginiExperiment No. 2B Determination of Flakiness Index of Coarse Aggregate AimTanmaya butaneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effect of Volumetric Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixture To Wheel Track Rutting With Respect To EN and BS Rutting Test MethodsDocument9 paginiThe Effect of Volumetric Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixture To Wheel Track Rutting With Respect To EN and BS Rutting Test MethodsthanoseeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpreting Asphalt Test Results: Danny Gierhart, P.E. Asphalt Institute Regional Engineer Tuttle, OklahomaDocument65 paginiInterpreting Asphalt Test Results: Danny Gierhart, P.E. Asphalt Institute Regional Engineer Tuttle, OklahomaMaríaAlejandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB2017 15 How Much Adhesive Will I NeedDocument2 paginiTB2017 15 How Much Adhesive Will I NeedAs PireÎncă nu există evaluări
- 31 LatesteDocument10 pagini31 Latesteabhiram_23355681Încă nu există evaluări
- Materials TestDocument20 paginiMaterials TestDanish MohdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gradation of AggregatesDocument28 paginiGradation of AggregatesDane BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact Behavior of AM Honeycomb StructuresDocument13 paginiImpact Behavior of AM Honeycomb StructuresSeçkin KoçÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Mix Design Aci 211 - Workshop 2017 PRDP PDFDocument39 paginiConcrete Mix Design Aci 211 - Workshop 2017 PRDP PDFChuckie EntocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subgrade Stabilization Filter Analysis Report : Design ParametersDocument1 paginăSubgrade Stabilization Filter Analysis Report : Design ParametersCub_7_illasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subgrade Stabilization Filter Analysis Report : Design ParametersDocument1 paginăSubgrade Stabilization Filter Analysis Report : Design ParametersCub_7_illasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0921344904000643 Main PDFDocument10 pagini1 s2.0 S0921344904000643 Main PDFpoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aggregates: Nilanjan MitraDocument10 paginiAggregates: Nilanjan MitrassriramiitÎncă nu există evaluări
- T-117 Segregation Causes CuresDocument24 paginiT-117 Segregation Causes CuresLuiz Fernando Oliveira Martins100% (2)
- Experiment No 4 Abrasion Value Los AngelesDocument6 paginiExperiment No 4 Abrasion Value Los Angelesfaiz19aaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AggregateDocument27 paginiAggregateSangkhayanon PhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 EnglishDocument3 pagini4 Englishananabutaleb40Încă nu există evaluări
- Astm D1557Document1 paginăAstm D1557tarekismailsabryÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02a - Aggregate GradationDocument28 pagini02a - Aggregate Gradationsiva jagathguru2184Încă nu există evaluări
- Tarea 2 (Granulometria)Document6 paginiTarea 2 (Granulometria)Danny MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grading of AggregatesDocument14 paginiGrading of AggregatesShakil KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conventional Asphalt Mix Design: Prof. P. K. Bhuyan Dept. of Civil Engg. NIT RourkelaDocument43 paginiConventional Asphalt Mix Design: Prof. P. K. Bhuyan Dept. of Civil Engg. NIT RourkelaSatya Prakash SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Woven Wire Mesh TableDocument4 paginiWoven Wire Mesh Tabledilip matalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perforated Panel of ALPOLICfrDocument4 paginiPerforated Panel of ALPOLICfrTran The AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perhitungan Mix Design Beton (ACI 211.4R-93)Document14 paginiPerhitungan Mix Design Beton (ACI 211.4R-93)Silvester Hadiaman ZalukhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solucionario BerrDocument182 paginiSolucionario Berrnellyscribd100% (2)
- Alt 1 Unit 1 Test Study Guide KeyDocument5 paginiAlt 1 Unit 1 Test Study Guide Keyapi-297435275Încă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Planting Density On Canopy Parameter, Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Kinnow MandarinDocument5 paginiEffect of Planting Density On Canopy Parameter, Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Kinnow MandarinPrabhdeep DhaliwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bs en 12390 7 Testing Hardened Concrete Part 7 Density of HardenedDocument12 paginiBs en 12390 7 Testing Hardened Concrete Part 7 Density of Hardenedញ៉ាន ណាឃីមÎncă nu există evaluări
- التربةDocument118 paginiالتربةali hashemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Onkar SinghDocument18 paginiThermodynamics Onkar SinghSaurabh JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superpave Mix D 11Document15 paginiSuperpave Mix D 11Markos MikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soil Mechanics and FoundationDocument64 paginiSoil Mechanics and Foundationmir imran100% (1)
- High Precision Balances ManualDocument19 paginiHigh Precision Balances ManualManishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Road Network Upgrading ProjectDocument18 paginiRoad Network Upgrading ProjectDominto MicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expansion FactorDocument11 paginiExpansion FactornambiduraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Properties of WoodDocument31 paginiPhysical Properties of WoodJohn SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Back-Pressure Tests On. Gas-Condensate Wells: As - OndeisateDocument9 paginiBack-Pressure Tests On. Gas-Condensate Wells: As - OndeisateAura Cristina Villafañe GeraldinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unfrozen Composition Data, Initial Freezing Point, and Specific Heats of Foods PDFDocument4 paginiUnfrozen Composition Data, Initial Freezing Point, and Specific Heats of Foods PDFroxanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported By: CclexDocument43 paginiReported By: CclexJoey MelencionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cargo Calculations - Tanker WorkDocument24 paginiCargo Calculations - Tanker WorkVasil Raykov100% (1)
- Calibration of Pouring CylinderDocument16 paginiCalibration of Pouring CylinderAnonymous drBWfwhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo IsopentaneDocument51 paginiThermo IsopentaneIrwan JanuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Pharmacy - 4th Edition PDFDocument339 paginiPhysical Pharmacy - 4th Edition PDFZahra Ahmed Alzaher79% (14)
- Research On Gas Migration Properties in A Saturated Bentonite/sand Mixture Under Exible Boundary ConditionsDocument14 paginiResearch On Gas Migration Properties in A Saturated Bentonite/sand Mixture Under Exible Boundary ConditionsmazharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partition Curve - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument38 paginiPartition Curve - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsnarendrasinghsjsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barton Automatic Tank Gauging System User ManualDocument12 paginiBarton Automatic Tank Gauging System User ManualSatit hunsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P6 1 Bump Up WSDocument4 paginiP6 1 Bump Up WSAmjadÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPE Paper DenSCRETEDocument9 paginiSPE Paper DenSCRETEeng7mohamed7hashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAD FileDocument24 paginiCAD FileNilanjan SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravity of GravityDocument25 paginiGravity of Gravitydrgopibams1100% (1)
- Assignmnents ICE 4TH Sem Construction TechnologyDocument7 paginiAssignmnents ICE 4TH Sem Construction TechnologyPawan SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zinc Dust Pigment For Paints - Specification: Indian StandardDocument16 paginiZinc Dust Pigment For Paints - Specification: Indian StandardDevesh Kumar PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 1 131 2021W2 HydrostaticsDocument8 paginiWorksheet 1 131 2021W2 HydrostaticseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Mechanics: Elastic BehaviorDocument9 paginiBone Mechanics: Elastic BehaviorpillaiyarmuruganÎncă nu există evaluări