Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Performance Based Wind Analysis of Diagrid Structural Systems
Încărcat de
Shubham patelTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Performance Based Wind Analysis of Diagrid Structural Systems
Încărcat de
Shubham patelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Performance Based Wind Analysis of Diagrid Structural Systems
Prepared By: Patel Shubham R. Roll No. Guided By: Dr. Paresh V. Patel , Prof & Head, Civil Engineering Department
M.Tech (CASAD) Sem IV 17MCLC16 CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
Push over Analysis of G+50 storey Diagrid Structural systems under Development of Wind Performance Assessment Approach
Introduction Static and Dynamic wind load
Performance Level
Advancement in construction techniques, lack of urban land and availability of Building Element Collapse Prevention Life Safety (LS) Limited Operations Fully Operational
computational tools has facilitated the development of tall building. Design of Tall Building Configuration: (CP) (LO) (FO)
buildings are sensitive to lateral load, specifically wind load. Current wind design Plan dimension = 36m× 36m
Storm Level (MRI 10,000 years 700-1700 years 50-100 years 1-10 years
Story height = 3.6m Range)
approach is inefficient to provide accurate and reliable method for computing the
Steel grade = Fe 250 General Overall Building Survives Repair likely Minor repair of All systems
performance of the building systems during extreme wind. The primary intention No stories = 50 Building but unrepairable required before building requiredimportant to
of this approach is to keep the structural system under elastic condition, but allow- Total height = 180 m Performance occupancy normal operational
ing some controlled in-elasticity in structural component. All these facts put a Steel tube grade = Yt310 remain functional
great emphasis on using a dependable wind design and assessment approach Grade of concrete = 25N/mm2 Significant cost and Minor disruption to Access and egress
describing the performance of high-rise building subjected to strong wind storms. Slab thickness = 150mm time to repair access and egress unaffected
Live load = 2.5 N/mm2 Access and egress Immediate Access and egress
Wind speed =39m/s comparison but occupancy unaffected
Typhoon Cyclone generally expected
Mangkhut Fani functional
Hong Odisha,
kong, 2018 Relocation of Significant Continuous occu-
2018 occupants likely occupant pancy and use of
Static Dynamic required within discomfort during the building
Wind Wind load building storm event expected
In this study carried out wind performance-based engineering approach for G+50 load Severe level of All MEP and other Minor effect
storey building with diagrid structural system and evaluated the performance of occupant discom- systems repairable
fort expected
the building under nonlinear static, dynamic and time history analysis. Wind load
time history data are acquired using TPU (Tokyo Polytechnic University) Aerody- Peak Floor Comfort Limit PFA Comfort Limit
namic database. For evaluation of performance of Diagrid structural systems push- Acceleration < 5 mg Imperceptible to most occupants
Wind Time History Analysis < 5 mg Not Perceptible 5-15 mg Perceptible range to most occupants
over analysis is carried out using software SAP2000.
5-15 mg Threshold of
20-25 mg Target range for office building occupancy
Perceptibility
Objective of Study 15-50 mg Annoying > 28 mg Annoying range for most occupants
50-150 mg Very Annoying > 40 mg Very annoying and difficult walking for most
To perform nonlinear static, dynamic and Time History analysis of Diagrid
> 150 mg Intolerable occupants
structural systems.
To develop Wind Time History data for Non linear Time history Analysis of
diagrid structural system.
Analytically investigate the characteristics of the uncertain nonlinear dynamic
response of Diagrid Structural Systems under extreme wind events using soft-
ware SAP2000.
Scope of Work
Developing a reliable analytical model to conduct nonlinear wind response
history analysis using Software SAP2000. Conclusion
Perform nonlinear analysis of G+50 storey diagrid structural systems using The performance-based engineering approach as implemented in this study can assures efficient
point load wind Time history data. diagnostics of existing buildings as well efficient wind design of new buildings.
It is shown that the wind performance assessment is able to provide a full spectrum of serviceability
Derivation of Hinge properties of Diagrid Structural systems for non linear status, despite the current serviceability check only based on 1-10 MRI winds. This is critical for the
buildings designated to accommodate people during extreme winds to assure their acceptable
analysis.
serviceability performances.
Evaluate performance of the building under stated level of wind storm by References
adopting wind performance assessment approach available in literature's. Alireza,M et al.(2019), ("Performance A ssessment of an existing 47-Story High Rise Building under Extreme Wind
loads"), Journal of Structural Engineering, Vol-145(1), pp:04018232.
Chang, F. (1973), ("Human response to motions in tall buildings"), Journal of Structural Engineering, Vol-99 (6),
pp. 1259-1272.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Static Vs Dynamic Analysis PDFDocument11 paginiStatic Vs Dynamic Analysis PDFj_herndzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenDocument11 paginiCause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenRony LesbtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyundai SL760Document203 paginiHyundai SL760Anonymous yjK3peI7100% (3)
- SDS ERSA Rev 0Document156 paginiSDS ERSA Rev 0EdgarVelosoCastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Based Seismic Evaluation-IEI-AUG2015Document10 paginiPerformance Based Seismic Evaluation-IEI-AUG2015cinithaserc appuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dec 2-7 Week 4 Physics DLLDocument3 paginiDec 2-7 Week 4 Physics DLLRicardo Acosta Subad100% (1)
- Transportation of CementDocument13 paginiTransportation of CementKaustubh Joshi100% (1)
- 611-Article Text-2571-1-10-20221213Document7 pagini611-Article Text-2571-1-10-20221213BUSH RCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asian Journal of Civil EngineeringDocument16 paginiAsian Journal of Civil EngineeringKaushik GondaliyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Response of Seismic LoadingDocument6 paginiA Review On Response of Seismic LoadingFatuma SulymanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection of Suitable Bracing System ForDocument10 paginiSelection of Suitable Bracing System ForNazish AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach Trestle DesignDocument6 paginiApproach Trestle DesignmanjucadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ruiz - Taflanidis - Giaralis - Lopez Garcia - ES - 2018Document15 paginiRuiz - Taflanidis - Giaralis - Lopez Garcia - ES - 2018Hisham TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Comparison Between Static and Dynamic Analysis Subjected To Wind and Earthquake LoadDocument6 paginiStudy of Comparison Between Static and Dynamic Analysis Subjected To Wind and Earthquake LoadAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Response Reduction Factor and Ductility Factor of RC Braced FrameDocument10 paginiEvaluation of Response Reduction Factor and Ductility Factor of RC Braced Framewidayat81Încă nu există evaluări
- Shape Effects of Wind Induced Response On Tall Buildings Using CFDDocument4 paginiShape Effects of Wind Induced Response On Tall Buildings Using CFDerpublicationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shruti 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1276 012033Document10 paginiShruti 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1276 012033Manikanta SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Study On Seismic Analysis of High-Rise Building by Using SoftwareDocument8 paginiReview Study On Seismic Analysis of High-Rise Building by Using SoftwareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0141029619312106 MainDocument10 pagini1 s2.0 S0141029619312106 Mainvincenzo.gattulliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1670 Evaluation Techniques of Damping in BuildingsDocument9 pagini1670 Evaluation Techniques of Damping in BuildingsApetsi AmpiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamic Mitigation by Corner Modification On Square Model Under Wind Loads Employing CFD and Wind TunnelDocument19 paginiAerodynamic Mitigation by Corner Modification On Square Model Under Wind Loads Employing CFD and Wind TunnelPACAO ANDRES. BARROS DIAZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Study of Static and Dynamic PDFDocument11 paginiComparative Study of Static and Dynamic PDFovikbasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- C StrucPerformance Gerges July131 PDFDocument3 paginiC StrucPerformance Gerges July131 PDFAbdulqader Al SheekhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aravindh PPTDocument12 paginiAravindh PPTpandiarajkgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Evaluation of Shear-Wall On Existing Irregular Building Under Seismic LoadingsDocument6 paginiPerformance Evaluation of Shear-Wall On Existing Irregular Building Under Seismic LoadingsMahhhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Wind Pressure On R.C Tall Buildings Using Gust Factor Method IJERTV3IS070871Document9 paginiEffect of Wind Pressure On R.C Tall Buildings Using Gust Factor Method IJERTV3IS070871Khushroo LankerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhaarini ImplantDocument19 paginiDhaarini ImplantDhaarini SriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 597-Article Text-2583-1-10-20180206Document6 pagini597-Article Text-2583-1-10-20180206Andrzej BąkałaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of Transmission Line Towers in Comparsion With Wind AnalysisDocument7 paginiAnalysis and Design of Transmission Line Towers in Comparsion With Wind AnalysismulualemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review On Design and Analysis of Residential Building by Using Different MaterialsDocument6 paginiReview On Design and Analysis of Residential Building by Using Different MaterialsBiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- (2003) The Height of Precision PDFDocument8 pagini(2003) The Height of Precision PDFjose antonio carazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Study On The Evaluation of Wind Load On Buildings Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and IS: 875 (Part-3)Document3 paginiComparative Study On The Evaluation of Wind Load On Buildings Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and IS: 875 (Part-3)Jay KasodariyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Engineering SoftwareDocument7 paginiAdvances in Engineering SoftwareGuillermo WyssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Response of Tall Building G 21 Under SeiDocument6 paginiResponse of Tall Building G 21 Under Seiamlan jyoti ChakravortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Response Modification Factor For RC Frames With Non Uniform DimensionsDocument21 paginiSeismic Response Modification Factor For RC Frames With Non Uniform DimensionsMahmoood IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness of Using Tuned-Mass Dampers in Reducing Seismic RiskDocument17 paginiEffectiveness of Using Tuned-Mass Dampers in Reducing Seismic RiskFoudilYouyouÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Investigation On Optimal Outrigger Locations FoDocument21 paginiAn Investigation On Optimal Outrigger Locations FoAbir DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of Flat Slabs in Commercial Building by UsingDocument5 paginiAnalysis and Design of Flat Slabs in Commercial Building by Usingheyiamadam2Încă nu există evaluări
- Tid in Mdof - Wenai ShenDocument17 paginiTid in Mdof - Wenai ShenAbdul BasitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Analysis of A Multistorey Building With and Without DamperDocument4 paginiComparative Analysis of A Multistorey Building With and Without Damperfharak patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irjet V9i44664Document7 paginiIrjet V9i44664Sayan DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Study of Multistorey Building Using Various Types of DampersDocument32 paginiComparative Study of Multistorey Building Using Various Types of DampersJayant ShaligramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ali 2018Document6 paginiAli 2018rosendo rojas barraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Investigation On Optimal Outrigger Locations For Hybrid Outrigger System Under Wind and Earthquake ExcitationDocument20 paginiAn Investigation On Optimal Outrigger Locations For Hybrid Outrigger System Under Wind and Earthquake Excitationgosiw71340Încă nu există evaluări
- C StructuralDesign DenoonDocument3 paginiC StructuralDesign DenoonmendoncajamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ware House DesignDocument8 paginiWare House DesignJay-Jay JapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irjet V5i8206 PDFDocument7 paginiIrjet V5i8206 PDFmustafazahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Energy: Francesco Balduzzi, Alessandro Bianchini, Ennio Antonio Carnevale, Lorenzo Ferrari, Sandro MagnaniDocument9 paginiApplied Energy: Francesco Balduzzi, Alessandro Bianchini, Ennio Antonio Carnevale, Lorenzo Ferrari, Sandro Magnanim.wijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijert Ijert: Design and Development of Material Handling CraneDocument8 paginiIjert Ijert: Design and Development of Material Handling CraneAnonymous PufNjgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of Transmission ToweDocument6 paginiAnalysis and Design of Transmission ToweDominic Kibet-TooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Economic Analysis of Low Rise High Rise BuildingDocument4 paginiComparative Economic Analysis of Low Rise High Rise BuildingJaskiratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring Wind Characteristics and Structural Performance of A Supertall Building During A Landfall TyphoonDocument16 paginiMonitoring Wind Characteristics and Structural Performance of A Supertall Building During A Landfall TyphoonAnonymous sQGjGjo7oÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Seismic Analysis of High-Rise Building by Using SoftwareDocument9 paginiStudy On Seismic Analysis of High-Rise Building by Using SoftwaremonaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Response of Performance Base Designed Building: A ReviewDocument11 paginiSeismic Response of Performance Base Designed Building: A Reviewengomar nadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relationship of Strength Reduction Factor and Maximum Ductility Factor For Seismic Design of One Storey Industrial Steel FramesDocument16 paginiRelationship of Strength Reduction Factor and Maximum Ductility Factor For Seismic Design of One Storey Industrial Steel Frameshence roringÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1664815906805geam 166 MarchelliDocument8 pagini1664815906805geam 166 MarchelliROBBY GAMER08Încă nu există evaluări
- Demountable Precast Connection Test ReportDocument16 paginiDemountable Precast Connection Test ReportAsjid MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Assessment On Susceptibility of High-Rise Reinforced Concrete Buildings To Wind-Induced Motions Based On Various International CodesDocument7 paginiComparative Assessment On Susceptibility of High-Rise Reinforced Concrete Buildings To Wind-Induced Motions Based On Various International CodesGermar PorquerinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methodologies To Mitigate Wind-Induced Vibration of Tall BuildingsDocument25 paginiMethodologies To Mitigate Wind-Induced Vibration of Tall BuildingsVAIDEHI SHARMA100% (1)
- Wind and Seismic Analysis and Design of Multistoried Building (G+30) by Using Staad ProDocument8 paginiWind and Seismic Analysis and Design of Multistoried Building (G+30) by Using Staad ProSuresh GSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energies 13 02552 v2Document18 paginiEnergies 13 02552 v2PeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vibration Control of Super-Tall Buildings Using Combination of Taperingmethod and TMD System - 11.12.19Document9 paginiVibration Control of Super-Tall Buildings Using Combination of Taperingmethod and TMD System - 11.12.19ভেতো বাঙালিÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Tall RCC Building With Gust Factor and Pushover Anaylysis On EtabsDocument4 paginiDesign of Tall RCC Building With Gust Factor and Pushover Anaylysis On EtabsUGCJOURNAL PUBLICATION100% (1)
- 2017 Finite Element Modlelling PR Prestress Concrete Poles Undert Downburst and TornadoesDocument13 pagini2017 Finite Element Modlelling PR Prestress Concrete Poles Undert Downburst and TornadoesChandara KOEMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gallium Nitride-enabled High Frequency and High Efficiency Power ConversionDe la EverandGallium Nitride-enabled High Frequency and High Efficiency Power ConversionGaudenzio MeneghessoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Annexure-II Previous PO Mail Correspondence With TOYO PDFDocument4 pagini3 Annexure-II Previous PO Mail Correspondence With TOYO PDFShubham patelÎncă nu există evaluări
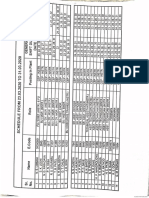
- Duty ScheduleDocument1 paginăDuty ScheduleShubham patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Annexure - V - Commercial Offer For Spares For Silica AnalyzerDocument1 pagină7 Annexure - V - Commercial Offer For Spares For Silica AnalyzerShubham patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torsion in Beams - Limit State of CollapseDocument23 paginiTorsion in Beams - Limit State of Collapsesubhajit284Încă nu există evaluări
- Two Pile GroupDocument12 paginiTwo Pile GroupJammy KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistic RegressionDocument7 paginiLogistic RegressionShashank JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manhole Head LossesDocument11 paginiManhole Head Lossesjoseph_mscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 AssignmentDocument2 paginiChapter 11 AssignmentsainothegamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Consolidated Data On Learners' Grade Per QuarterDocument4 paginiDepartment of Education: Consolidated Data On Learners' Grade Per QuarterUsagi HamadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Kebutuhan Bahan Ajar Berbasis EDocument9 paginiAnalisis Kebutuhan Bahan Ajar Berbasis ENur Hanisah AiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPI Unit 4Document155 paginiMPI Unit 4Dishant RathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keeping Track of Your Time: Keep Track Challenge Welcome GuideDocument1 paginăKeeping Track of Your Time: Keep Track Challenge Welcome GuideRizky NurdiansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- D E S C R I P T I O N: Acknowledgement Receipt For EquipmentDocument2 paginiD E S C R I P T I O N: Acknowledgement Receipt For EquipmentTindusNiobetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Job DescriptionDocument13 paginiJurnal Job DescriptionAji Mulia PrasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Systems Project: IITB CPUDocument7 paginiDigital Systems Project: IITB CPUAnoushka DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSWIP-WP-19-08 Review of Welding Procedures 2nd Edition February 2017Document6 paginiCSWIP-WP-19-08 Review of Welding Procedures 2nd Edition February 2017oberai100% (1)
- Etag 002 PT 2 PDFDocument13 paginiEtag 002 PT 2 PDFRui RibeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of Porosity - Permeability Relationship in Sandstone Petrophysical PropertiesDocument61 paginiImportance of Porosity - Permeability Relationship in Sandstone Petrophysical PropertiesjrtnÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM EFATEX Rev D2 3 1 2018 PDFDocument20 paginiSM EFATEX Rev D2 3 1 2018 PDFGuilhermePlacidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectroscopic Methods For Determination of DexketoprofenDocument8 paginiSpectroscopic Methods For Determination of DexketoprofenManuel VanegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Quality Dimensions of A Philippine State UDocument10 paginiService Quality Dimensions of A Philippine State UVilma SottoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothDocument111 paginiRankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothphysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MLX90614Document44 paginiMLX90614ehsan1985Încă nu există evaluări
- BDocument28 paginiBLubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JO 20221109 NationalDocument244 paginiJO 20221109 NationalMark Leo BejeminoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Documentation Report On School's Direction SettingDocument24 paginiDocumentation Report On School's Direction SettingSheila May FielÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE162P MODULE 2 LECTURE 4 Analysis & Design of Mat FoundationDocument32 paginiCE162P MODULE 2 LECTURE 4 Analysis & Design of Mat FoundationPROSPEROUS LUCKILYÎncă nu există evaluări
- LC For Akij Biax Films Limited: CO2012102 0 December 22, 2020Document2 paginiLC For Akij Biax Films Limited: CO2012102 0 December 22, 2020Mahadi Hassan ShemulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Over BrahmaputraDocument38 paginiBridge Over BrahmaputraRahul DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Ethics in Practice ShorterDocument79 paginiEngineering Ethics in Practice ShorterPrashanta NaikÎncă nu există evaluări