Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
9054 Exp4 Bernoulli's Theorem
Încărcat de
Konem SolutionsDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
9054 Exp4 Bernoulli's Theorem
Încărcat de
Konem SolutionsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No.
EXPERIMENT No. 4
1.0 Title:
To study and verify Bernoulli’s Theorem.
2.0 Prior Concepts:
Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy, Pressure Energy, Total Energy, Types of
Fluid.
3.0 New Concepts:
Proposition 1: Energy
Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. It exists in various forms and can change
from one from to another. The different forms of energy of flowing liquid are i) Potential
Energy (Potential Head) ii) Kinetic Energy (Velocity Head) iii) Pressure Energy (Pressure
Head).
Concept Structure:
Prospositon 2 : Potential Energy ( Potential Head)
It is the energy possessed by a liquid particle by virtue of its position it is due to configuration
or position above some suitable height or datum line. it is denoted by z.
Proposition 3 : Kinnetic Energy (Velocity Head)
IT is the energy possessb by a liquid particle by vertue of it is due to the velocity of flowing
liquid and is measured as V Where ‘v’ is the velocity of flow and ‘g’ is acceleation due to
2
gravity ( 9 = 9.8 1m / S2 ) 2g
Propositon 4 : Pressure Energy ( Pressure )
It is the energy possessed by a liquid particle by virtue of its existing pressure. It is due to the
pressure of liquid and measured as p / w. where ‘p’ is intensity of pressure and ‘w’ is the
specific weight of liquid.
Propositon 5 : Total Energy (Total Head)
It is the sum of potential energy, kinetic energy and the pressure energy. It is denoted ad E and
mathematically it is expressed as E = potential energy + kinectic energy + pressure energy. E
= Z + ( V2 / 29) + ( P/ W)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 26
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
Bernoulli’s Theorem:
This theorem states that, for an ideal, incompressible fluid when the flow is steady and
continuous then the sum of pressure energy, kinetic energy and potential energy is con-
stant.
Mathematically it is expressed as
(p/W)+(V2/2g)+ Z = constant
where p/W = Pressure Energy
V2/2g = Kinetic Energy
Z = Potential Energy
Bernoulli’s theorem can also be stated as for a steady incompressible and ideal fluid, the
total energy at any point of fluid is constant.
4.0 Learning Objectives:
Intellectual Skills:
¾ To understand concept of total energy.
¾ To understand the application of Bernoulli’s theorem.
Motor Skills:
¾ Ability to calculate potential energy, kinetic energy or velocity head, pressure
energy or pressure head.
¾ Ability to take and read observations.
¾ Ability to adjust flow rate through pipe.
5.0 Apparatus:
Piezometer, scale, measuring cylinder, collecting tank, stopwatch etc.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 27
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
1.0 Figure:
The apparatus consists of an inlet tank and outlet tank connected by a flow channel. The
channel tapers for a length of 20 cm and gradually enlarges in a length of 35 cm, On top of
the flow channel piezometer tubes are fixed at a distance of 5 cm for the measurement of
pressure head. To calculate the flow, into the inlet tank and out of the outlet valves are
provided. The flow can be of obtained by controlling inlet and outlet valves suitably. After a
while a steady state will be reached.
7.0 Stepwise Procedure:
•Open the valve so that the water can accumulate in the tube.
After raising water in piezometer attached at various point, open the outlet valve in such a way
that level of water rising up remains the same.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 28
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
Litre
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 29
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Litre
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 30
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
10.0 Result:
The total energy head is found to be …………….. m of water
11.0 Conclusion:
• The value of total energy head is ……………. (same/different) at different points.
• The reason for not getting the total energy head constant is / are
……………………………………………………….( the flow is not steady/ frictional losses
in pipe/ turbulent flow / loss of energy due to centrifugal force / all of above)
Student shall write conclusion under guidance of teacher keeping in view the value of total
energy at diferent points.
.......................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................................
11.0 Questions:
Write answers to Q……,Q……,Q……,Q……,Q……
(Teacher shall allot the questions)
1. Define energy and its types for moving fluids.
2. What do you understand by the term total head of a moving fluid.
3. What do you understand by the term pressure head and velocity head.
4. Derive Bernoulli’s Equation.
5. State the Limitations of the Bernoulli’s theorem.
6. Name some practical applications of Bernoulli’s Theorem
7. Sketch any application of Bernoulli’s thermo.
8. Water is flowing through a tapered pipe having end diameters of 150 mm and 50 mm
respectively. Find the discharge at the larges end velocity head at the smaller end, if
the velocity of water at the larger end is 2 m/s. What do you understand by the term
discharge?
9. What do you understand by the term continuity equation?
10. What are the various types of flow lines?
11. What is ‘separation’ of liquid?
12. What is the effect of ‘separation’ on flowing liquid?
13. What is the assumption of Bernoulli’s theorem?
14. For which type of flow Bernoulli’s Equation is applicable?
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 31
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
15. How is piezometric head of a flow represented?
16. Draw HGL based on experimental values.
17 Draw TEL based on experimental values.
18 A 300mmX 150mm venturimeter is provided in a vertical pipeline carrying oil of spe-
cific gravity 0.9, the flow being upwards. The difference in elevations of the throat sec-
tion and entrance section of the venturimeter is 300mm.The differential U-tube mer-
cury manometer shows a gauge deflection of 250mm.Calculate i) discharge of oil ii)
pressure difference between entrance and the throat section.
(Space for answers)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 32
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
Signature of teacher
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 33
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery [9054] Experiment No. 4
Number of tubes Vs p/w +z
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION 34
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- (UNISIM (BEHAS) - Introduction To Aerospace) EAS105 - Lab2Document29 pagini(UNISIM (BEHAS) - Introduction To Aerospace) EAS105 - Lab2Mohd Ashraf Mohd IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series & Parallel Pump TestDocument22 paginiSeries & Parallel Pump TestIkhwan Z.100% (23)
- Receipt of Lab Report Submission (To Be Kept by Student)Document4 paginiReceipt of Lab Report Submission (To Be Kept by Student)Dylan YongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Formulas Sheet PDFDocument4 paginiPhysics Formulas Sheet PDFAdvyth Vaman AkalankamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 37 PDFDocument26 paginiChapter 37 PDFSamara CardenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9047 - Exp1 - Water Contents of Given Soil Sample by Oven Drying MethodDocument7 pagini9047 - Exp1 - Water Contents of Given Soil Sample by Oven Drying MethodKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final FMHM LAB MANUAL Manual of 1Document67 paginiFinal FMHM LAB MANUAL Manual of 1Motee SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- IndexDocument31 paginiIndexAnonymous l5X3VhTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me Lab 1 Exp. Group 1 VenturiDocument4 paginiMe Lab 1 Exp. Group 1 VenturiJerome BalatbatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manuals He Lab ManalsDocument146 paginiManuals He Lab ManalsNIKHIL DHIMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment and Reporting Writing: Hydraulics & Pneumatic LabDocument45 paginiExperiment and Reporting Writing: Hydraulics & Pneumatic Lababpt meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment and Reporting Writing: Hydraulics & Pneumatic LabDocument47 paginiExperiment and Reporting Writing: Hydraulics & Pneumatic Lababpt meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Lab: State Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research, KalamasseryDocument53 paginiFluid Mechanics Lab: State Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research, KalamasseryAeronautical Engineering HODÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpDocument19 paginiFluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpCik Tiem Ngagiman89% (65)
- Experiment 5 - Group 2Document16 paginiExperiment 5 - Group 2Arrianna PeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMHM Lab ManualDocument34 paginiFMHM Lab ManualMuhammad AdnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocument24 paginiFluid Mechanics and Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M94% (18)
- Lab1 - Verification of Bernoullis PrincipleDocument20 paginiLab1 - Verification of Bernoullis PrincipleAbenezer Tasew0% (1)
- Product Manual EIE - Bernoullis Theorm ApparatusDocument11 paginiProduct Manual EIE - Bernoullis Theorm ApparatusRavi ParikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heads and Efficiencies of Hydraulic Turbines: Visvesvaraya Technological University, BelagaviDocument13 paginiHeads and Efficiencies of Hydraulic Turbines: Visvesvaraya Technological University, BelagaviJûstîn TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bernaullis ExptDocument5 paginiBernaullis Exptsagar2407mÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 PB PDFDocument9 pagini3 PB PDFFuLin LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM&HM Lab Manual For PrintDocument94 paginiFM&HM Lab Manual For PrintAjithkumar K.TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demonstration On Bernoulli's TheoremDocument22 paginiDemonstration On Bernoulli's TheoremMahe RukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albao Laboratory 1Document65 paginiAlbao Laboratory 1Shaun Patrick AlbaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021-ME-12,13,16 # OEL ReportDocument8 pagini2021-ME-12,13,16 # OEL ReportMuhammad FurqanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics LAB: Government Engineering College Jagdalpur, BASTAR (C.G.) - 494005Document35 paginiFluid Mechanics LAB: Government Engineering College Jagdalpur, BASTAR (C.G.) - 494005Md. Sahinur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4 Formal ReportDocument14 paginiLab 4 Formal ReportMohd Haikal ShukorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Test of Centrifugal PumpDocument10 paginiPerformance Test of Centrifugal Pumpcha100% (1)
- Bournelli ExperimentDocument10 paginiBournelli ExperimentUsamaIjazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Lab. ENME 312: Methods of Measurement of Flow Rate of Liquids and GasesDocument10 paginiFluid Mechanics Lab. ENME 312: Methods of Measurement of Flow Rate of Liquids and GasesAhmad Haikal Mohd HalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi MeterDocument8 paginiConservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi Meterdist2235Încă nu există evaluări
- Mahatma Gandhi Mission'S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering CollegeDocument61 paginiMahatma Gandhi Mission'S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering CollegeRathodNarenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3Document6 paginiExperiment 3nurasamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Open ChannelDocument13 pagini11 Open ChannelshahqazwsxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical and Experimental Study of Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine at Different Number of BladeDocument9 paginiNumerical and Experimental Study of Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine at Different Number of BladeBung HaFiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Sheet Exp 01Document4 paginiLab Sheet Exp 01TusherAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 2204 - FMM 2 Marks With AnswerDocument22 paginiME 2204 - FMM 2 Marks With AnswerMohan Prasad.M100% (1)
- LAB (Flowmeter Demonstration)Document40 paginiLAB (Flowmeter Demonstration)Nurul AinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impulse TurbineDocument15 paginiImpulse TurbineHazwan JamhuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM&HM Lab Manual For PrintDocument92 paginiFM&HM Lab Manual For Printsanthu086Încă nu există evaluări
- Free Force VortexDocument25 paginiFree Force VortexAbdul MuqeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gatpu Me152l c3 Experiment 1Document18 paginiGatpu Me152l c3 Experiment 1Dikimbie Aldrei GatpuÎncă nu există evaluări
- B45 Hydraulicsand Hydraulic MachineryDocument7 paginiB45 Hydraulicsand Hydraulic MachineryRa BalamuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraullic Machines Lab ManualDocument43 paginiFluid Mechanics and Hydraullic Machines Lab Manualm udaya kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids 2 Lab Report 4 FinalDocument9 paginiFluids 2 Lab Report 4 FinalJay-ar BensOnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro TurbineDocument3 paginiHydro TurbinebassamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Laboratory Civil Engineering Department Sultan Azlan Shah Polytechnic Experiment: 2 Title: Impact of Jet TestDocument8 paginiHydraulic Laboratory Civil Engineering Department Sultan Azlan Shah Polytechnic Experiment: 2 Title: Impact of Jet TestAzrol Azmir Long100% (3)
- Lec-7 - Bernoulli EquationDocument23 paginiLec-7 - Bernoulli Equationwww.muhammadshahzaib72Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 Notes 18ME81Document25 paginiModule 4 Notes 18ME81thrilok SuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measurement of The Fluid Flow Load On A Globe Valve Stem Under Various Cavitation ConditionsDocument16 paginiMeasurement of The Fluid Flow Load On A Globe Valve Stem Under Various Cavitation ConditionsbayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group A Experiment 1Document11 paginiGroup A Experiment 1مرتضى كاظم غانمÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aim and ObjectiveDocument6 paginiAim and ObjectiveSaanvi MalhotraÎncă nu există evaluări
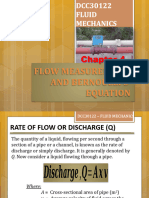
- Chapter 4 - Flow Measurement and Bernoulli's EquationDocument38 paginiChapter 4 - Flow Measurement and Bernoulli's EquationDark DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab VortexDocument22 paginiLab VortexaminsubriÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Lab VivaDocument20 paginiFM Lab VivaXanely D'souza50% (2)
- SpiraxSarco The Steam and Condensate Loop Block 1 14Document498 paginiSpiraxSarco The Steam and Condensate Loop Block 1 14mirceablaga86100% (1)
- Form No. .. Rs. 100/-: Page 1 of 10Document10 paginiForm No. .. Rs. 100/-: Page 1 of 10Konem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-20ma Loop Current Transmitter XTR116UDocument9 pagini4-20ma Loop Current Transmitter XTR116UKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sony SpeciDocument1 paginăSony SpeciKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yuken Servo Electro Hydraulic Valve - Eic-H-1011Document11 paginiYuken Servo Electro Hydraulic Valve - Eic-H-1011Konem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine Westerbeke Technical ManualDocument116 paginiMarine Westerbeke Technical ManualKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Engine Test Rig Development and MethodologyDocument16 paginiExperimental Engine Test Rig Development and MethodologyKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No - 14Document8 paginiExperiment No - 14Konem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9051 - Exp2 - Active and Passive Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagini9051 - Exp2 - Active and Passive Electronic ComponentsKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 123 Reynolds ApparatusDocument5 pagini123 Reynolds ApparatusKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9049 - Exp1 - Piezometer and U-Tube ManometerDocument5 pagini9049 - Exp1 - Piezometer and U-Tube ManometerKonem Solutions100% (1)
- 9047 - Exp1 - Bulk Density and Dry Density of A Soil in The Field by Core Cutter MethodDocument8 pagini9047 - Exp1 - Bulk Density and Dry Density of A Soil in The Field by Core Cutter MethodKonem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ie Irodov LN 1Document7 paginiIe Irodov LN 1ChandrikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choose The Correct Answer From A, B, or CDocument3 paginiChoose The Correct Answer From A, B, or CInsideBest10Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Spherical ValveDocument34 paginiHydrodynamic Calculation Spherical ValveEng-CalculationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- EM WavesDocument22 paginiEM WavesJane Reyes100% (1)
- HW3 SolutionDocument12 paginiHW3 SolutionmanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Sizing Spreadsheet Equation SheetDocument3 paginiGeneral Sizing Spreadsheet Equation SheetNellaiappa1975 DuraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Document9 paginiAssignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Parth PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7th ScienceDocument22 pagini7th ScienceSandeep BorseÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExamDocument16 paginiExamnicolas dionisio ordonez barruetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and Energy Formula SheetDocument3 paginiWork and Energy Formula SheetimkushofficialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manning Equation Calculator Open Channel Flow Software: Lmno Engineering Home Page (More Calculations)Document2 paginiManning Equation Calculator Open Channel Flow Software: Lmno Engineering Home Page (More Calculations)Chris van RensburgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hertz'S Experiments: Do Physics OnlineDocument3 paginiHertz'S Experiments: Do Physics OnlineVeerareddy VippalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECOR 1048A Midterm SolutionsDocument6 paginiECOR 1048A Midterm Solutionsdanielmacintyre31Încă nu există evaluări
- Line Single PhaseDocument2 paginiLine Single PhasehussamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Trilogy WavesDocument9 paginiPhysics Trilogy WavesisheanesuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transverse and Longitudinal WavesDocument4 paginiTransverse and Longitudinal Wavesnhipol_95Încă nu există evaluări
- Flight Dynamics: Y.K.SinhaDocument10 paginiFlight Dynamics: Y.K.SinhaVenkateshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serway Physics II Example Questions Chapter 7Document1 paginăSerway Physics II Example Questions Chapter 7AizuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.4.1.5 Newtons Laws of MotionDocument96 pagini3.4.1.5 Newtons Laws of Motionprashyam20Încă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/01Document18 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/01Nicole TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maxwell's Equations and Electromagnetic WavesDocument37 paginiMaxwell's Equations and Electromagnetic WavesAwadh AlharthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newtonian PhysicsDocument299 paginiNewtonian PhysicsdarcasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 8Document47 paginiCH 8Antoine Dumont NeiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Juma Yousuf Alaydi Dr. Juma Yousuf Alaydi Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Islamic University Islamic UniversityDocument18 paginiDr. Juma Yousuf Alaydi Dr. Juma Yousuf Alaydi Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Islamic University Islamic UniversityMohamed NasserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waterhammer Analysis John Parmakain Charts PDFDocument13 paginiWaterhammer Analysis John Parmakain Charts PDFdaskirÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAQ Ans 2Document3 paginiSAQ Ans 2Shaikh Usman AiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of The Modern Family of HeliDocument32 paginiDesign of The Modern Family of Heli邓帅Încă nu există evaluări
- 4: Mechanics 1 - Topic Questions Paper 4: Year Series Paper NumberDocument8 pagini4: Mechanics 1 - Topic Questions Paper 4: Year Series Paper NumberrobinsonÎncă nu există evaluări