Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
12 Biology Notes Ch08 Human Health and Disease
Încărcat de
rohit403Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
12 Biology Notes Ch08 Human Health and Disease
Încărcat de
rohit403Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CBSE
Class 12 Biology
Revision Notes
CHAPTER- 08
HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE
The state of complete physical, mental and social well beings is called health. Health simply
does not simply means disease free condition or physical fitness. Health is affected by-
a. Genetic disorders – the defect which child inherits from it parents.
b. Infection from microbes or other organisms.
c. Life style- includes food and water we take, exercise and rest.
Good health can be maintained by
Balanced diet.
Personal hygiene
Regular exercise
Awareness about the disease and their effect
Immunization against the infectious disease
Proper disposal of wastage
Control of vectors
Maintenance of hygienic food and water.
Disease - Diseases can be broadly grouped into infectious and non-infectious.
a) Infectious disease -Diseases which are easily transmitted from one person to another, are
called infectious diseases e.g AIDS, common cold, malaria, tuberculosis etc
b) Non-infectious disease – Diseases which cannot transmitted from one person to another,
are called non- infectious diseases e.g cancer, hypertension, diabetes etc.
Common Diseases in Humans:
The disease causing microorganisms like bacteria, virus, fungus, protozoa, helminthes
are called pathogen.
The pathogen can enter the body by various means and multiply and interfere with
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 1 / 11
normal vital activities resulting in morphological and functional damage.
Name of
Causal organisms Symptoms Effects
disease /test
Typhoid / Sustained high fever,
Salmonella typhi
Widal test weakness, stomach pain,
Streptococcus
Alveoli get filled with fluid
pneumoniae and Fever, chills, cough and
Pneumonia leading to severe problems
Haemophilus headache.
in respiration.
influenzae
Nasal congestion and
Common Infect the nose and
Rhino viruses discharge, sore throat,
cold respiratory passage.
cough and headache.
Plasmodium (P. Parasite multiply within
The chill and high fever
Malaria vivax, P. malaria and lever cells and then attack
recurring 3 to 4 days.
P. falciparum) the RBCs.
Amoebiasis Constipation, abdominal
Entamoeba
or Amoebic pain, cramps, stool with Infect the large intestine.
histolytica
dysentery mucous and blood clot.
Healthy person get
Internal bleeding, muscular
Ascariasis Ascaris (Helminthes) infected through water,
pain, fever, anemia etc.
vegetable etc.
Wuchereria (W.
Elephantiasis Inflammation in the lower Lymphatic vessels of lower
bancrofti and W.
or filariasis limb and genital organs. limbs get blocked.
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 2 / 11
malayi)
Microsporum, Appearance of dry, scaly
Infects the skin, nail and
Ring worms Trichophyton and lesions on various part of
scalp.
Epidermophyton body.
Life cycle of plasmodium : Plasmodium enters the human body as small sporozoites
through the bite of infected female anopheles mosquito and multiplies within the lever cells.
Later attacks the RBCs resulting the rapture with release of toxic substance, haemozoin,
which is responsible for high fever and chill recurring every three to four days.
Malarial parasite requires two hosts, human and anopheles mosquito to complete their life
cycle. Female anopheles is vector of this disease to human beings.
Flowchart to show lifecycle of Plasmodium
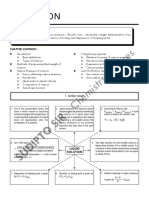
Immunity – the ability of host cells to fight the disease causing microorganism due to
immune system is called immunity. There are two types of immunity-
Innate immunity - non-specific types of defence presents at the time of birth and provide
different kinds of barriers to the entry of foreign agents into the body. it consists of four
types of barrier-
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 3 / 11
a. Physical barrier- skin, mucus coating of epithelium lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal
and urogenital tract.
b. Physiological barrier- acid in stomach and saliva in mouth.
c. Cellular barrier- leucocytes, neutrophils, monocytes.
d. Cytokine barriers- virus infected cells secretes protein called interferon.
No Innate Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity
1 Present from birth itself Develops during life time
The immunity remains throughout
2 Can be short lived or lifelong.
life.
Contact or exposure with pathogen or
3 Contact with pathogen or its antigen is essential.
its antigen is not essential.
Acquired immunity cannot be passed to the next
4 Innate immunity is inheritable.
generation except for a brief period to neonates.
It protects the individuals from
It protects the individuals from pathogens present
5 contraction of diseases of other
on other members of the same species.
organisms.
Acquired Immunity- pathogen specific defence characterised by memory. When our body
encounters a pathogen first time produces a response called primary response of low
intensity. Subsequent encounter by same pathogen produce highly intensified response
called secondary response or anamnestic response due to memory of first encounter.
Primary and secondary responses are carried out with the help of B-lymphocytes and T-
lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes produce army of protein called antibodies each having two light
and two heavy chains.
It involves two types of lymphocytes –
B lymphocytes: Show humoral immune response (HI)
T lymphocytes: Show cell mediated immunity (CMI)
Structure of an Antibody:
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 4 / 11
The antibodies are protein molecules called immunoglobulins and are of various
types like IgA, IgM, IgE, IgG.
Each antibody molecule consists of four polypeptide chains, two are long called heavy
chains and other two are short called light chains. Both are arranged in the shape of
‘Y’, hence an antibody is represented as H2L2.
On the basis of production of antibodies, immunity can be further categorised as –
Active immunity: Body produces its own antibodies against antigens
Passive immunity: Readymade antibody is transferred from one individual to another
Colostrum (contains antibodies IgA) is an example of passive immunity provided by
the mother to her child.
Different types of antibodies produce in blood include IgA, IgM, IgEete. They are called
humoral immune response due to presence in blood.
Human immune system can distinguish between self and foreign molecules or foreign
bodies. Sometimes, due to genetic or unknown reasons, the body attack self-cells. This results
in damage to the body and called auto-immune disease. Rheumatoid arthritis is due to this
effect
Allergies – the exaggerated response of immune system to certain antigens present in the
environment is called allergy. The substance to which such immune response is produced is
called allergens. The antibodies produced due to these are IgE types. Allergy is due to
secretion of chemicals like histamine and serotonin from the mast cells.
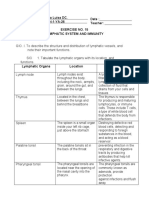
Immune system in the body- the human immune system includes lymphoid organs, tissue,
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 5 / 11
cells and soluble molecules like antibodies.
Lymphoid organs are the organs where origin and maturation and proliferation of
lymphocytes occur. Primary lymphoid organs include bone marrow and thymus.
After maturation lymphocytes migrate to secondary lymphoid organ like spleen, lymph
nodes, tonsils, peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix. They provide the sites for
interaction lymphocyte with antigens.
There is lymphoid tissue also located within the lining of respiratory, digestive and
urogenital tract called mucosal associated lymphoid tissue ( MALT). It constitute 50% of
lymphoid tissues in human body.
AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) was first reported in 1981. It is caused by HIV
(human Immuno deficiency virus), a retrovirus. Transmission of HIV virus occurs by-
a. Sexual contact with infected person
b. Transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products
c. Sharing infected needles as in intravenous drug abusers
d. Infected mother to her child through placenta.
Replication of retrovirus in Macropahges
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 6 / 11
AIDS/HIV does not spread by physical contact. It spread only through body fluids. There is
always time lag between infection and appearance of symptoms that may vary from 5-10
years.
Diagnostic test for AIDS is ELISA (enzyme-linked Immuno-sorbent assay). The treatment of
this disease with anti-retroviral drug is partially effective and just prolonged the life but not
prevents the death.
Cancer is one of the most dreaded diseases of human beings and is a major cause of death all
over the world. Normal cells show a property called contact inhibition by virtue of which
contact with other cells inhibit their uncontrolled growth. Cancer cells lost this property.
Cell
Normal Cells Cancer Cells
Characteristics
Cancer cells have a large variety of sizes
Normal cells have uniform and shapes
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 7 / 11
Morphology shapes and sizes The nucleuses have irregular structure
and have relatively small cytoplasm.
Cells stop dividing when too
much of its kind are present.
These cells grow and divide in a
controlled manner and follow a Cancer cells don’t stop growing resulting
Reproduction
predictable life cycle. to appearance of a tumor ( a cluster of
and Cell Death
mutant cells)
Normal cells undergo the process
of apoptosis – self destruction if
they detect abnormalities and
damage in their organelles.
Normal cells communicate with
Cancer cells do not communicate with
Communication each other for proper
each other
functioning.
Cancer cells lose the molecules that keep
cells bonded together.
These cells have external
Adhesion and
membranes that allow them to These cells have the ability to invade or
Invasion
bond with other cells. spread to other parts of the body by
travelling through the blood stream or
the lymphatic system – metastasis.
Cancer cells do not mature, and undergo
apoptosis. Instead these cells become
Normal cells start out as
Specialization immature cells and mature with immature overtime.
certain specialized functions. Cancer cells are primitive and they don’t
have specialized functions.
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 8 / 11
Normal cells recognize signals.
Cancer cells don’t recognize signals.
Signal They know when there are
Hence these cells erratically reproduce
Recognition enough new cells and stops
mutated cells.
dividing.
Cancerous cells continue to divide giving rise to masses of cells called tumors. There are two
kind so tumors-
(a) Benign tumors
(b) Malignant tumors
Benign Tumor Malignant Tumor
1. It remains confined to the affected
1. It also spreads to other organs of the body.
organ.
2. Rate of growth is usually slow. 2. Rate of growth is usually rapid.
3. There is no latent stage. 3. There is latent stage.
4. The cancer cells migrate to other sites of the
4. It causes limited damage to the body.
body.
5. There is no metastasis. 5. There is metastasis.
6. It is non-cancerous. 6. It is cancerous.
Causes of cancer – cancerous neoplastic cell may be induced by physical, chemical and
biological agents called carcinogens. Cancer causing viruses called oncogenic virus have
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 9 / 11
gene called viral oncogenes. Several genes called cellular oncogenes (c-onc) or proto
oncogenes have been identified in normal cells which, when activated under certain
conditions, could lead to oncogenic transformation of the cells.
Cancer detection and diagnosis-cancer detection is based on biopsy and histopathological
study of the tissues, blood and bone marrow test for increased cell counts. Radiography, CT
(computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to cancers of
internal organs.
Treatment of Cancer-
1. Surgical – cancerous tissues are surgically removed.
2. Radiotherapy – tumor cells are irradiated lethally by radiation.
3. Chemotherapy – drugs are used to kill cancerous cells, but shows side effects like hair
loss, anemia, etc.
4. Immunotherapy – patients are given with alpha-interferon which activate their immune
system and help in destroying the tumor
Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
Commonly abused drugs include opioids, cannabinoids and coca alkaloids obtained from
flowering plants and a few from fungi.
Opioids are the drugs which bind to specific opioids receptors present in our central nervous
system and gastrointestinal tract. Heroin commonly called smack is chemically
diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound. It is extracted
from the latex of poppy plant (Papaversomniferum).Generally taken by snorting and
injection, heroin is a depressant and slows down body functions.
Cannabinoids are a group of chemicals which interact with cannabinoid receptors present in
the brain. Natural cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescence of the plant cannabis
sativa. They include marijuana, hashish, charas and gangja. They generally taken by
inhalation and oral ingestion, these are known for their effects on cardiovascular system of
the body.
Coca alkaloid or cocaine is obtained from coca plant Erythroxylum coca, native to South
America. It interferes with the transport of the neuro-transmitter dopamine. Cocaine,
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 10 / 11
commonly called coke or crack is usually snorted. It has a potent stimulating action on
central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy.
Adolescence and Drug abuse
Adolescence is the period during which the child becomes matured.
It is between 12 – 18 years of age.
Causes of drug abuse –
Curiosity
Adventure
Excitement
Experimentation
Stress or pressure to excel in examination
Effects of drug/alcohol abuse –
Reckless behaviour
Malicious mischief
Violence
Drop in academic performance
Depression, isolation, aggressiveness, etc.
Dependence is the tendency of the body to manifest a characteristic and unpleasant
withdrawal syndrome if regular dose of drug/alcohol is abruptly discontinued that includes
anxiety, shakiness, nausea and sweating.
Prevention avoid undue peer pressure, education & counselling, seeking helps from parents
and peers, seeking professional and medical help etc.
Material downloaded from www.vidyakul.com. 11 / 11
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NBP Planners For Branches (Weekdays) - NEET-2024Document4 paginiNBP Planners For Branches (Weekdays) - NEET-2024monikakansal213100% (1)
- Aakash FTS 2024Document2 paginiAakash FTS 2024Tanmay COC50% (2)
- Classplusapp - NEET CHEM-Ch 4Document37 paginiClassplusapp - NEET CHEM-Ch 4Muhammad Ali100% (1)
- Allen Handbook ChemistryDocument4 paginiAllen Handbook Chemistrys1672snehil6353Încă nu există evaluări
- Year and Contributions NCERTDocument3 paginiYear and Contributions NCERTchannel of dhyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 26 E19 20 Respiration in Plants Enzyme 1589118408Document43 pagini26 E19 20 Respiration in Plants Enzyme 1589118408Allen Chryso67% (3)
- Final Test Series For NEET-2023 (XII & RM) Code-B - Phase-01Document3 paginiFinal Test Series For NEET-2023 (XII & RM) Code-B - Phase-01Aorpopi DrawsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360Document10 paginiClass 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Xi Cbse Mind Maps BiologyDocument22 paginiClass Xi Cbse Mind Maps BiologyShreyash VishwakarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chintu Notes 2.0 (Class XI+XII)Document362 paginiChintu Notes 2.0 (Class XI+XII)Heshwanth Reddy100% (2)
- Class XI: Biology at EaseDocument7 paginiClass XI: Biology at EaseSomya Kataria0% (1)
- Chemistry Class 12 Revision MaterialDocument52 paginiChemistry Class 12 Revision Materialkrish dabhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesDocument22 paginiNotes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesVanshika JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases (OneNoteDocument10 paginiBreathing and Exchange of Gases (OneNoteKajal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus of NCERT Booster Test Series - NEET-2024Document1 paginăSyllabus of NCERT Booster Test Series - NEET-2024mohduwais695Încă nu există evaluări
- Aakash Test Planner: Aiats Test For Class-Xi (Medical)Document3 paginiAakash Test Planner: Aiats Test For Class-Xi (Medical)Bharat GelotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7Document11 paginiEquilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7Kanishk RanjitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakash FTS 2023 ScheduleDocument2 paginiAakash FTS 2023 Scheduleluxurythanks 1M50% (2)
- +1 CBSE - BOTANY CDF MATERIAL (01-48) .pmd-1 PDFDocument48 pagini+1 CBSE - BOTANY CDF MATERIAL (01-48) .pmd-1 PDFcernpaul100% (1)
- Practice Test 12 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET 2024Document17 paginiPractice Test 12 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET 2024Pandey 14Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Important Questions With SolutionsDocument41 paginiCBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Important Questions With SolutionsDimpal BisenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timetable For NEET Preparation in 1 Month PDFDocument3 paginiTimetable For NEET Preparation in 1 Month PDFAstha Agrawal100% (1)
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes ThermodynamicsDocument11 paginiClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes ThermodynamicsAivenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: By: Dr. Anand ManiDocument130 paginiMolecular Basis of Inheritance: By: Dr. Anand ManiIndu Yadav100% (3)
- NCERT Maps ChemistryDocument62 paginiNCERT Maps ChemistrySagnik Bhunia100% (1)
- Ncert Booster Test Series: (For NEET-2021)Document20 paginiNcert Booster Test Series: (For NEET-2021)Swaraj Mukherjee0% (1)
- Mechanical Propeties of Solids (58 - 96)Document39 paginiMechanical Propeties of Solids (58 - 96)Abdul Musavir100% (1)
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDocument6 paginiClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwanaastha.sawlaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution: STR Ycl AssesDocument40 paginiSolution: STR Ycl AssesArka DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 Performance Enhancement Sheet PDFDocument3 pagini16 Performance Enhancement Sheet PDFSARA50% (2)
- Plant Growth and Development: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenDocument12 paginiPlant Growth and Development: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenBipin GhimireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 1: PhysicsDocument17 paginiNeet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 1: PhysicsMangesh VeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5Document34 paginiBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5SDO BSNL NALAGARHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xam Idea Biology Class 12 Term II For 2022 ExamDocument314 paginiXam Idea Biology Class 12 Term II For 2022 ExamAadithS mtpprep100% (2)
- ElectrochemistryDocument78 paginiElectrochemistryNik Muhammad Firdaus100% (1)
- Class 12 Physics Notes For Alternating CurrentDocument12 paginiClass 12 Physics Notes For Alternating CurrentPrashant KoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 paginiCBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsNada NavasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakash NBTS Test 05 SolutionDocument9 paginiAakash NBTS Test 05 Solutiondnamazing1702Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument81 paginiPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationRayan100% (1)
- Mind Maps - One Stop NEETDocument1 paginăMind Maps - One Stop NEETVidya KolliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsDocument22 paginiOrganic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsLiza DahiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amines 1Document21 paginiAmines 1Gowri ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Practical Book Class 12Document77 paginiChemistry Practical Book Class 12Hendra GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MLL Chemistry 2024Document6 paginiMLL Chemistry 2024prembabumahawar782Încă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Line by LineDocument162 paginiNCERT Line by LineAyushi Chandel 12-C,530% (1)
- Periodic Classification - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document1 paginăPeriodic Classification - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Harsh Singh RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 Chemistry Ch-3.Chemical KineticsDocument41 paginiClass 12 Chemistry Ch-3.Chemical Kineticskarnan karupiah0% (1)
- Reaction Mechanism IIDocument21 paginiReaction Mechanism IIFilmode100% (2)
- Class 12th Chemistry Practical FileDocument17 paginiClass 12th Chemistry Practical Filevivek mishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic of Chemistry For Class 12 by Bharat PanchalDocument11 paginiBasic of Chemistry For Class 12 by Bharat PanchalNemantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties (@Document20 paginiClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties (@LONE WOLFÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS Project File Class 12Document29 paginiPHYSICS Project File Class 12S.r.Siddharth45% (20)
- Last Leap For NEET - 2020Document3 paginiLast Leap For NEET - 2020K Geeth Sagar0% (3)
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument17 paginiChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryRavi Kumar50% (4)
- SHM Formula Sheet @cbseinfiniteDocument6 paginiSHM Formula Sheet @cbseinfiniteRekha JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Pointer XiiDocument407 paginiBrain Pointer XiiJaynee EdwardsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Med-RM Bot SP-1 Ch-3 The Living WorldDocument24 paginiMed-RM Bot SP-1 Ch-3 The Living Worldkrish masterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio and Images Phy Edcn Class XIIDocument35 paginiBio and Images Phy Edcn Class XIIoREpTiONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Chap 08Document10 paginiNotes Chap 08umamahfarooq75Încă nu există evaluări
- Laporan Bulanan Rekapitulasi Hasil Deteksi Dini Hepatitis B Pada Ibu HamilDocument1 paginăLaporan Bulanan Rekapitulasi Hasil Deteksi Dini Hepatitis B Pada Ibu HamilShanty SulamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vaccine-Preventable Diseases and Their VaccinesDocument7 paginiVaccine-Preventable Diseases and Their VaccinesgosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S193897360800072X MainDocument8 pagini1 s2.0 S193897360800072X MainItsAnimal DudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocument14 paginiEPI Vaccines HandoutsStephen Pilar PortilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 in 10 Infants Worldwide Did Not Receive Any Vaccinations in 2016Document2 pagini1 in 10 Infants Worldwide Did Not Receive Any Vaccinations in 2016YennyIrdayaniNasutionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flu Assessment Screening and Consent FormDocument2 paginiFlu Assessment Screening and Consent FormMatt GunnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis Grant ProposalDocument9 paginiTuberculosis Grant Proposalselina_kollsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immuno DiagnosisDocument28 paginiImmuno Diagnosisbaker samuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithm Immunisation Status Jan2020Document1 paginăAlgorithm Immunisation Status Jan2020Afsan BulbulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mumps: Resurgence of A Once-Dormant Disease: Published Ahead-Of-PrintDocument4 paginiMumps: Resurgence of A Once-Dormant Disease: Published Ahead-Of-Printanindya nandiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument13 paginiToxic Shock SyndromeodessayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autoimmune Disease - Why and Where It OccursDocument7 paginiAutoimmune Disease - Why and Where It OccursdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Urticaria Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument5 paginiChronic Urticaria Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsOgy SkillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabies 052612Document80 paginiRabies 052612May Grace Noriega RolleÎncă nu există evaluări
- VaginitisDocument16 paginiVaginitisMae Christelle Hamoy100% (2)
- Infectious Diseases and NanomaterialsDocument123 paginiInfectious Diseases and NanomaterialsSohail LatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature Sensitivity of Vaccines: March 2014Document12 paginiTemperature Sensitivity of Vaccines: March 2014Sergio de Jesús Jaime RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook For Vaccine and Cold Chain HandlersDocument128 paginiHandbook For Vaccine and Cold Chain HandlersRyza Jazid Baharuddin NurÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 MonocytopoiesisDocument8 pagini6 MonocytopoiesisVannisa Dwi NovianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lizzy Hiv AssignmentDocument7 paginiLizzy Hiv Assignmentapi-376826833Încă nu există evaluări
- RSV Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Identification TreatmentDocument1 paginăRSV Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Identification Treatmentapi-350983586Încă nu există evaluări
- Daniel Santiago Rincón PinzónDocument2 paginiDaniel Santiago Rincón PinzónYANDRA YINNETH RINCON PINZONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Undergraduate Course Catalogue - 2017Document362 paginiUndergraduate Course Catalogue - 2017Anonymous nlfbWzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunoassay Premium Plus - Level 3 (Ia Premium Plus 3)Document24 paginiImmunoassay Premium Plus - Level 3 (Ia Premium Plus 3)concocdocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review HDocument62 paginiReview HStephanie Louisse Gallega HisoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument10 paginiChronic PyelonephritisSuthar Keval CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument14 paginiCase Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaRachelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1526931449Document123 pagini1526931449Lika KipshidzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imci Pre TestDocument7 paginiImci Pre TestericÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 10 LABORATORY EXERCISE - Lymphatic Immune SystemDocument7 paginiWEEK 10 LABORATORY EXERCISE - Lymphatic Immune SystemEricka ElloÎncă nu există evaluări