Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 12
Încărcat de
Jannibee Estrera0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
341 vizualizări7 paginiManagement science
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentManagement science
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
341 vizualizări7 paginiChapter 12
Încărcat de
Jannibee EstreraManagement science
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 7
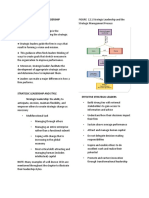
CHAPTER 12: STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP FIGURE 12.
1 Strategic Leadership and the
Strategic Management Process
INTRODUCTION
● Effective strategic leadership is the
foundation for successfully using the strategic
management process.
● Strategic leaders guide the firm in ways that
result in forming a vision and mission.
● This guidance often finds leaders thinking of
ways to create goals that stretch everyone in
the organization to improve performance.
● Moreover, strategic leaders facilitate the
development of appropriate strategic actions
and determine how to implement them.
● Leaders can make a major difference in how a
firm performs.
STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP AND STYLE
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC LEADERS
Strategic leadership: the ability to
anticipate, envision, maintain flexibility, and • Build strong ties with external
empower others to create strategic change as stakeholders to gain access to
necessary information and advice
• Multifunctional task • Understand how their decisions impact
their firm
• Managing through others
• Sustain above-average performance
• Managing an entire enterprise
rather than a functional subunit • Attract and manage human capital
• Coping with change that is • Do not delegate decision-making
increasing in the global responsibilities
economy
• Inspire and enable others to do
• Most critical skill: attracting and excellent work and realize their
managing human (includes potential
intellectual) capital
• Promote and nurture innovation
NOTE: Many examples of well-known CEOs are through transformational leadership
mentioned throughout the chapter to illustrate
their leadership styles.
THE ROLE OF TOP-LEVEL MANAGERS • Composed of key individuals who are
responsible for selecting and implementing
● Managers use their discretion when making
firm’s strategies; usually includes officers of
strategic decisions
the corporation (VP and above) and BOD
● Primary factors that determine the
TOP MANAGEMENT TEAM, FIRM
amount of a manager’s decision-making
PERFORMANCE, AND STRATEGIC CHANGE
discretion
Heterogeneous team: individuals with varied
• External environmental sources
functional backgrounds, experiences, and
• Organization’s characteristics education
• Manager’s characteristics A HETEROGENEOUS TEAM
FACTORS AFFECTING MANAGERIAL • Introduces a variety of perspectives
DISCRETION
• Has a greater propensity for strong
competitive action
• “Outside of the box thinking," leads to
more creative decision making,
innovation, and strategic change
• Offers various areas of expertise to
identify environmental opportunities,
threats, or the need for change
• Promotes debate, which leads to better
strategic decisions, and higher firm
performance
• May take longer to reach consensus
Team members: bring a variety of strengths,
capabilities, and knowledge and provide
effective strategic leadership when faced with
TOP MANAGEMENT TEAMS complex environments and multiple
stakeholder relationships to manage
Top Management Teams
THE CEO AND TOP MANAGEMENT TEAM
• Help avoid potential problem of CEO POWER
making decisions alone: managerial
hubris Higher performance is achieved when the board
of directors (BOD) is more directly involved in
• Hubris: excessive pride leading shaping strategic direction
to a feeling of invincibility
A powerful CEO may:
Hubris can magnify the effects
of decision-making biases • Appoint sympathetic outside
board members
• Have inside board members • This decision impacts company
who report to the CEO performance and the ability to embrace
change in today's competitive landscape
• Have long tenure, thus have
greater influence on board • Succession, top management team
decisions composition, and strategy are intimately
related
• Be virtually independent of
oversight by the BOD EFFECTS OF CEO SUCCESSION AND TOP
MANAGEMENT TEAM COMPOSITION ON
• May also hold the position of
STRATEGY
chairman of the board (CEO
duality)
CEO Duality – CEO serves as CEO and BOD
• More common in the United
States
• Occurs most often in the largest
firms
• Increased shareholder activism
recently brought the practice Benefits of Internal Managerial Labor Market
under scrutiny
• Continuity
• Criticized for causing poor
performance and slow response • Continued commitment
to change
• Familiarity
BALANCE OF POWER BETWEEN THE BOD AND
• Reduced turnover
TOP MANAGEMENT IMPACTED BY:
• Retention of “private knowledge”
• Resource abundance
• Favored when the firm is performing
• Environmental volatility and
well
uncertainty
Benefits of External Managerial Labor Market
MANAGERIAL SUCCESSION
• Long tenure with the same firm is
DEFINITION: preselect and shape the skills of
thought to reduce innovation
tomorrow’s leaders
• Outsiders bring diverse knowledge
• Internal managerial labor market:
bases and social networks, which offer
opportunities for managerial positions
the potential for synergy and new
to be filled from within the firm
competitive advantages
• External managerial labor market:
• Fresh paradigms
opportunities for managerial positions
to be filled by candidates from outside
of the firm
Note: Opportunity cost for firms: Women as Effectively Managing the Firm’s Resource
strategic leaders have been somewhat Portfolio
overlooked
• Most important task - effectively managing
KEY STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP ACTIONS the firm’s portfolio of resources
Certain actions characterize effective strategic • Resources defined as financial, human,
leadership social, and organizational capital
• These actions interact with each other • Effective strategic leaders manage
their firm’s resource portfolio by:
• The most effective strategic leaders
create options as the foundation for • Organizing the resources
making effective decisions into capabilities
EXERCISE OF EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC • Structuring the firm to
LEADERSHIP facilitate using those
capabilities
• Managing each type of
resource as well as the
integration of resources,
e.g., using financial capital
to enhance human capital
capabilities (training and
development)
• Choosing strategies through
KEY STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP ACTIONS which the capabilities are
successfully leveraged to
Determining Strategic Direction create value for customers
● The strategic direction is framed within the Exploiting and Maintaining Core Competencies
context of the conditions (i.e., opportunities
and threats) strategic leaders expect their firm Core competencies
to face in the next 3-5 years
• Resources and capabilities that serve as
● Ideal long-term strategic direction has two a source of competitive advantage for a
parts: firm over its rivals
■ Core ideology • Relate to an organization’s functional
skills, such as manufacturing, finance,
■ Envisioned future marketing, and research and
● Serves as a guide to a firm’s strategy development
implementation process, including motivation, • Leadership must verify that the firm’s
leadership, employee empowerment, and competencies are emphasized when
organizational design implementing strategy
• Firms must continuously • Strong organizational culture may
develop/change their core be a competitive advantage
competencies to prevail over
ENTREPRENEURIAL MIND-SET
competitors
Source of growth and innovation
Developing Human Capital and Social Capital
May be encouraged and promoted by
• Human capital: knowledge and skills of strategic leaders
a firm’s entire workforce, requiring An organizational culture can encourage (or
investment in training and development discourage) strategic leaders from pursuing
(or not pursuing) entrepreneurial
• Social capital: relationships inside and
opportunities
outside the firm that help it accomplish
tasks and create value for customers Fostering an Entrepreneurial Mind-Set: Five
and shareholders Dimensions
• Cooperative strategies, e.g., strategic • Autonomy- Employees are allowed to take
alliances, may leverage complementary actions that are free of organizational
resources to develop social capital constraints; permits individuals and groups
to be self-directed
• Firms with strong social capital can
access multiple capabilities, providing • Innovativeness - Reflects a firm’s tendency
them with important flexibility to take to engage in and support new ideas,
advantage of opportunities and respond novelty, experimentation, and creative
to challenges processes that may result in new products,
services, or technological processes
• Social capital created through alliances
is pivotal to: Cultures with a tendency toward
innovativeness encourage employees to
o Large multinational firms when
think beyond existing knowledge,
entering new foreign markets
technologies, and parameters to find
o Entrepreneurial firms for creative ways to add value
resource access, venture
• Risk taking - Reflects a willingness by
capital, or other types of
employees and their firm to accept risks
resources
when pursuing entrepreneurial
Sustaining an Effective Organizational Culture opportunities
• Organizational culture: the complex set Examples of RISKS
of ideologies, symbols, and core values
Assuming significant levels of debt
shared throughout the firm
Allocating large amounts of resources to
• Influences the way business is
projects that may not be completed
conducted
• Helps regulate and control employees’
behavior • Proactiveness - Ability to be a market
leader rather than a follower
Proactive organizational cultures constantly Actions that foster an ethical organizational
use processes to anticipate future market culture:
needs and to satisfy them before
• Establish and communicate ethics-
competitors learn how to do so
related goals
• Revise, update, and disseminate code of
• Competitive aggressiveness - Propensity to conduct
take actions that allow the firm to
• Develop and implement methods and
consistently and substantially outperform
procedures to use in achieving firm’s
its rivals.
ethical standards
KEY STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP ACTIONS
• Create/use specific reward systems that
Sustaining an Effective Organizational Culture recognize acts of courage
CHANGING THE ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE • Create a working environment where all
AND RESTRUCTURING are treated with dignity
• More difficult to change culture than Establishing Balanced Organizational Controls
maintain it
Controls: formal, information-based
• Sometimes change must occur procedures used by managers to maintain
or alter patterns in organizational activities
• Effective strategic leaders recognize
when change in culture is needed Controls help strategic leaders:
• Requires effective ● Build credibility
communicating and problem
● Demonstrate the value of strategies to
solving
the firm’s stakeholders
• Selecting the right people
● Promote and support strategic change
• Engaging in effective
● Financial Controls
performance appraisals
• Focus on short-term financial outcomes
• Measuring individual
performance toward goals that • Produce risk-averse managerial
fit with new values decisions because financial outcomes
may be caused by events beyond
• Using appropriate reward
managers’ direct control
systems
● Strategic Controls
Emphasizing Ethical Practices
• Focus on the content of strategic
• Effectiveness of strategy
actions rather than their outcomes
implementation processes increases
when based on ethical practices • Encourage decisions that incorporate
moderate and acceptable levels of risk
• Ethical practices create social capital
and goodwill for the firm
THE BALANCED SCORECARD STRATEGIC CONTROLS AND FINANCIAL
CONTROLS IN A BALANCED SCORECARD
• Framework to evaluate if firms have
FRAMEWORK
achieved the appropriate balance
among the strategic and financial
controls to attain the desired level of
firm performance
• Most appropriate for evaluating
business-level strategies; it can also be
used with the other strategies firms
implement (e.g., corporate-level,
international, and cooperative)
• Prevents overemphasis of financial
controls at the expense of strategic
controls
THE BALANCED SCORECARD
● Premise is that firms jeopardize their
future performance when financial controls
are emphasized at the expense of strategic
controls
● This is because financial controls focus on
historical outcomes, and do not address
future performance drivers
● An overemphasis on financial controls
may promote managerial behavior that
sacrifices long-term, value-creating
potential for short-term performance gains
● An appropriate balance of strategic
controls and financial controls, rather than
an overemphasis on either, allows firms to
achieve higher levels of performance
Four perspectives of the balanced scorecard
Financial
Customer
Internal Business Processes
Learning and Growth
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter 8Document34 paginiChapter 8Tayba AwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Income Taxation Answer Key Only 1 1Document60 paginiIncome Taxation Answer Key Only 1 1Paul Justin Sison Mabao88% (32)
- Rent To Own ContractDocument5 paginiRent To Own Contractjepoy100% (1)
- Mott Macdonald Case StudyDocument4 paginiMott Macdonald Case StudyPanthrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Control Systems, Transfer Pricing, and Multinational ConsiderationsDocument30 paginiManagement Control Systems, Transfer Pricing, and Multinational Considerationsjudelyn sanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of SAP Status CodesDocument19 paginiList of SAP Status Codesmajid D71% (7)
- Home Replication StrategyDocument5 paginiHome Replication StrategyChau Hoang100% (19)
- CH 10 ImDocument24 paginiCH 10 Imprabu06051984Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles of ManagementDocument48 paginiPrinciples of ManagementAdaitaChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9Document21 paginiChapter 9Vidgezxc Loria100% (1)
- CH 11 Strategy Monitoring Kel 7Document3 paginiCH 11 Strategy Monitoring Kel 7IBGA AGASTYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAR-Midterm ExamDocument19 paginiFAR-Midterm ExamTxos Vaj100% (1)
- Pidsbk04 AgricultureDocument220 paginiPidsbk04 AgricultureMaer Pohane100% (2)
- Chapter 7 Measuring and Controlling Assets EmployedDocument62 paginiChapter 7 Measuring and Controlling Assets Employedshital_vyas198786% (7)
- Bbap2103 Akaun PengurusanDocument10 paginiBbap2103 Akaun PengurusanEima AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14: Case Study Mary Barra's Leadership Guides General Motors Through A Crisis and Toward ProfitabilityDocument3 paginiChapter 14: Case Study Mary Barra's Leadership Guides General Motors Through A Crisis and Toward ProfitabilityMuller Graphy100% (1)
- Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership Leadership - Two Capabilities That Are Marks of A Successful Leadership 1. Overcoming Barriers To ChangeDocument3 paginiChapter 11: Strategic Leadership Leadership - Two Capabilities That Are Marks of A Successful Leadership 1. Overcoming Barriers To ChangecaicaiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 Creating and Managing Organizational CultureDocument41 paginiCH 7 Creating and Managing Organizational Culturezeid100% (1)
- CH4 David SMCC16ge Ppt04Document41 paginiCH4 David SMCC16ge Ppt04Yanty IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH01 Nature and Purpose of Management Consulting (2 Files Merged)Document15 paginiCH01 Nature and Purpose of Management Consulting (2 Files Merged)Madielyn Santarin Miranda100% (2)
- Case Study Tiger BrandDocument2 paginiCase Study Tiger Brandreza cellia0% (1)
- Chapter 7-Dealing With Management and Operation Issues (Strategy Implementation)Document78 paginiChapter 7-Dealing With Management and Operation Issues (Strategy Implementation)Maria Cassandra O. Ramos0% (2)
- Capital Gains TaxDocument5 paginiCapital Gains TaxJAYAR MENDZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9Document5 paginiChapter 9Jenny Pearl Lastrilla100% (1)
- Different Approaches To Corporate GovernanceDocument13 paginiDifferent Approaches To Corporate Governancekim cheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 - International StrategyDocument2 paginiChapter 8 - International StrategyAgung Jati PramonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No 2 BPDocument2 paginiAssignment No 2 BPBernadette AnicetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Understanding StrategiesDocument31 paginiChapter 2 - Understanding StrategiesSarah Laras WitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By: Talha Daud Roll No: 38 BBA 7 Question No.1Document1 paginăSubmitted By: Talha Daud Roll No: 38 BBA 7 Question No.1talhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Governance - Christine Mallin - Chapter 9 - Directors Performance and RemunerationDocument4 paginiCorporate Governance - Christine Mallin - Chapter 9 - Directors Performance and RemunerationUzzal Sarker - উজ্জ্বল সরকার100% (4)
- Summary Chapter 11 - STRUCTURE AND CONTROLS WITH ORGANIZATIONDocument5 paginiSummary Chapter 11 - STRUCTURE AND CONTROLS WITH ORGANIZATIONHenny Zahrany100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Strategy Formulation Corporate StrategyDocument23 paginiChapter 7 Strategy Formulation Corporate StrategyJm Fernando WenceslaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Concept of Cost Attach Is The Theory Based On The Assumption That The Value in Any CommodityDocument1 paginăThe Concept of Cost Attach Is The Theory Based On The Assumption That The Value in Any CommodityAlexius Julio BrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransDocument18 paginiTransFajri SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - PlanningDocument15 paginiChapter 2 - PlanningHidayu AfiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8Document12 paginiChapter 8Shuvo SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap01 Determinants of CultureDocument15 paginiChap01 Determinants of CultureAnthea Jacelyn MelanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cbstm01 Chapter 1 10Document137 paginiCbstm01 Chapter 1 10Samantha AzueloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume Sistem Pengendalian ManajemenDocument49 paginiResume Sistem Pengendalian ManajemenAldilla Yasmin InasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rais12 SM ch13Document32 paginiRais12 SM ch13Edwin MayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 - Global HRMDocument33 paginiChapter 8 - Global HRMFinn NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Gitman - pmf13 - PPT 07 GE Stock Valuation To 50Document51 paginiFinal Gitman - pmf13 - PPT 07 GE Stock Valuation To 50asimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Darson Securities PVT LTD Internship ReportDocument90 paginiDarson Securities PVT LTD Internship Report333FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Audit Statutory Audit 1) AppointmentDocument3 paginiInternal Audit Statutory Audit 1) AppointmentSamiksha AngreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal Myob PT DinamikaDocument5 paginiSoal Myob PT DinamikaRaden Andini AnggreaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix - B. Solutions To Self-Test ProblemsDocument30 paginiAppendix - B. Solutions To Self-Test ProblemsjuanggamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Accounting: A Business PartnerDocument24 paginiManagement Accounting: A Business PartnerIsbah IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Market StakeholdersDocument3 paginiProduct Market Stakeholdersqaqapataqa100% (1)
- Questions - Chapter 2Document3 paginiQuestions - Chapter 2Mohammad Salim HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Management, The Controller, and Cost AccountingDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Management, The Controller, and Cost Accountingdekambas100% (1)
- Mgt210 Case 3Document4 paginiMgt210 Case 3Saidul Alam Rahat 1721598Încă nu există evaluări
- Meyerson S Bakery Is Considering The Addition of A New LineDocument1 paginăMeyerson S Bakery Is Considering The Addition of A New LineLet's Talk With HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BaskinRobins José MorenoDocument1 paginăBaskinRobins José MorenoJosef Moreno100% (1)
- Capital Structure (WordDocument32 paginiCapital Structure (Wordrashi00100% (1)
- MGT 531Document5 paginiMGT 531rizwan aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No.9 (BP)Document3 paginiAssignment No.9 (BP)Bernadette AnicetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of The Case Study :multicultural and Multinational Teams at IBMDocument5 paginiAnalysis of The Case Study :multicultural and Multinational Teams at IBMnabeel088Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 19 - Professional Conduct, Independence, and Quality ControlDocument18 paginiChapter 19 - Professional Conduct, Independence, and Quality ControlBlake CrusiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Krishna G. Palepu, Paul M. Healy, Erik Peek - Business Analysis and Valuation - IFRS Edition-Cengage Learning (2013) - Chapter 5 PDFDocument58 paginiKrishna G. Palepu, Paul M. Healy, Erik Peek - Business Analysis and Valuation - IFRS Edition-Cengage Learning (2013) - Chapter 5 PDFTrần BetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Components of Corporate Strategy?Document7 paginiWhat Are The Components of Corporate Strategy?Madhan RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No.10Document3 paginiAssignment No.10Bernadette AnicetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategy - Chapter 11Document9 paginiStrategy - Chapter 1132_one_two_threeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kunci Jawaban ICAEW Part 2Document4 paginiKunci Jawaban ICAEW Part 2Dendi RiskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 (BP)Document3 paginiAssignment 1 (BP)Bernadette AnicetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adm650 Chapter 7 Leadership - Entrepreneurship May Sapura Revised Mac2023Document63 paginiAdm650 Chapter 7 Leadership - Entrepreneurship May Sapura Revised Mac2023Arya zllkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeadershipDocument28 paginiLeadershipbijuajitheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of Strategy - 6 - Strategy Implementation & ControlDocument42 paginiElements of Strategy - 6 - Strategy Implementation & ControlAyush JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12Document1 pagină12Jannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To End-of-Chapter Three ProblemsDocument13 paginiSolutions To End-of-Chapter Three ProblemsAn HoàiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finman AssignmentDocument1 paginăFinman AssignmentJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Quality Management and Just-In-Time Production SystemDocument30 paginiTotal Quality Management and Just-In-Time Production SystemJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Development in Asia Chapter 6 - International Trade and InvestmentDocument40 paginiEconomic Development in Asia Chapter 6 - International Trade and InvestmentJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic DevelopmentDocument25 paginiEconomic DevelopmentJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Development in Asia Chapter 2 - Growth and The Asian ExperienceDocument61 paginiEconomic Development in Asia Chapter 2 - Growth and The Asian ExperienceJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Development in Asia Chapter 3 - The Asian Crisis and Recent DevelopmentsDocument52 paginiEconomic Development in Asia Chapter 3 - The Asian Crisis and Recent DevelopmentsJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Development in Asia Chapter 3 - The Asian Crisis and Recent DevelopmentsDocument52 paginiEconomic Development in Asia Chapter 3 - The Asian Crisis and Recent DevelopmentsJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diosdado P. Macapagal: Prepared By: Jannibee L. Estrera BSA-2Document7 paginiDiosdado P. Macapagal: Prepared By: Jannibee L. Estrera BSA-2Jannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12Document7 paginiChapter 12Jannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11Document12 paginiChapter 11Jannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- HistoryDocument17 paginiHistoryJannibee EstreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Godown Creation in Tally 9 Tutorial Youtube PDFDocument3 paginiGodown Creation in Tally 9 Tutorial Youtube PDFKristinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pfrs 1Document8 paginiPfrs 1Jenne LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Price and Return ModelsDocument38 paginiPrice and Return Modelsnoir_weizzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project ReportBanty Kumar VermaDocument126 paginiProject ReportBanty Kumar VermagunjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership Development at Hindustan Unilever Limited FinalDocument10 paginiLeadership Development at Hindustan Unilever Limited FinaldurdenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consolidated Edison Co. v. NLRB, 305 U.S. 197 (1938)Document26 paginiConsolidated Edison Co. v. NLRB, 305 U.S. 197 (1938)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 8Document64 paginiCH 8Anonymous 0cdKGOBBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyDocument48 paginiAug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyBuildersLineMonthlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Products Services FCPO EnglishDocument16 paginiProducts Services FCPO EnglishKhairul AdhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nestle CSRDocument309 paginiNestle CSRMaha AbbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mission Statement: SBI Articulates Nine Core ValuesDocument6 paginiMission Statement: SBI Articulates Nine Core ValuesPaneer MomosÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCG MatrixDocument1 paginăBCG MatrixFritz IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roles & Responsibilities of A Maintenance Engineer - LinkedInDocument4 paginiRoles & Responsibilities of A Maintenance Engineer - LinkedInEslam MansourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mms-Ente-Case StudyDocument2 paginiMms-Ente-Case Studyvivek ghatbandheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alliance Governance at Klarna: Managing and Controlling Risks of An Alliance PortfolioDocument9 paginiAlliance Governance at Klarna: Managing and Controlling Risks of An Alliance PortfolioAbhishek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oracle Payables Invoice Gateway Documentation SuplementDocument121 paginiOracle Payables Invoice Gateway Documentation SuplementRolando Eduardo Erazo DuronÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSC Economics Essay QuestionsDocument5 paginiHSC Economics Essay QuestionsYatharth100% (1)
- w9 - L2 - Review For Lecture Midterm 2Document14 paginiw9 - L2 - Review For Lecture Midterm 2Rashid AyubiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Technology in Transportation (Aviation) : Nor Shahirah Afiqah Binti Mat Shater Nazira Binti BahronDocument15 paginiPhysics Technology in Transportation (Aviation) : Nor Shahirah Afiqah Binti Mat Shater Nazira Binti Bahronjustin milangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Funds FlowDocument5 paginiFunds FlowSubha KalyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum ViateDocument1 paginăCurriculum ViateOssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rural Marketing ManualDocument21 paginiRural Marketing ManualRahul Verma RVÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Commerce?: Comprehensive DefinitionDocument31 paginiWhat Is Commerce?: Comprehensive Definitionmuhammad riazÎncă nu există evaluări