Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Archivo Resuelto de La Tarea
Încărcat de
ingrid chicanganaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Archivo Resuelto de La Tarea
Încărcat de
ingrid chicanganaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Name Class Date
34.3 The Reproductive System
Lesson Objectives
Describe the effects the sex hormones have on development.
Name and discuss the structures of the male reproductive system.
Name and discuss the structures of the female reproductive system.
Describe some of the most common sexually transmitted diseases.
Lesson Summary
Sexual Development Hormones released by the ovaries and testes cause sexual
development during puberty, a period of rapid growth and sexual maturation that usually
starts between the ages of 9 and 15. At the end of puberty, the male and female reproductive
organs are fully developed and become fully functional.
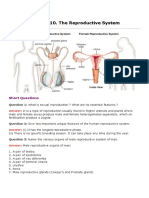
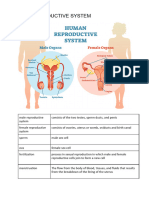
The Male Reproductive System The main role of the male reproductive system is to
make and deliver sperm.
The testes are the main organs of the male system. Two testes are held in an external sac
called the scrotum. The testes make sperm in tiny tubes called seminiferous tubules.
The sperm mature and are stored in an epididymis. A tube called a vas deferens carries
sperm from each testis to the urethra within the penis.
Along the way, secretions of several glands form a nutrient-rich fluid called seminal fluid.
The combination of sperm and seminal fluids is called semen. Semen leaves the body
through the urethra. Contractions eject semen from the penis in a process called
ejaculation.
A mature sperm cell consists of a head that contains the nucleus, a midpiece that is
packed with mitochondria, and a flagellum that propels the sperm.
The Female Reproductive System The main roles of the female reproductive
system are to make eggs and prepare the female body to nourish an embryo.
The ovary is the main organ of the female system. Each ovary has thousands of follicles,
which are clusters of cells that surround an egg. A mature egg moves through the
Fallopian tube to the uterus, which is connected to the outside of the body by the vagina.
Beginning in puberty, the female body goes through a menstrual cycle, a series of events
that prepares the body to care for a fertilized egg. The menstrual cycle has four phases:
Follicular phase: An egg matures in its follicle.
Ovulation: The mature egg is released from the ovary.
Luteal phase: The follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum.
Menstruation: The lining of the uterus falls away and leaves the body through the
vagina if the egg is not fertilized.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases A disease spread during sexual contact is called a
sexually transmitted disease (STD). Bacteria and viruses can cause STDs. Chlamydia,
syphilis, gonorrhea, and AIDS are STDs.
Name VALENTINA OROZCO CHICANGANA Class Date
Sexual Development
For Questions 1–3, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
A 1. Male and female embryos are nearly identical until the
A. second week of development. C. third month of development.
B. seventh week of development. D. fifth month of development.
C 2. Which hormone, when produced in an embryo, triggers a male pattern of
development?
A. testosterone C. estrogen
B. progesterone D. adrenalin
D 3. The period of human development that includes rapid growth and sexual
maturation is called
A. adolescence. C. maturity.
B. childhood. D. puberty.
The Male Reproductive System
For Questions 4–8, match each structure of the male reproductive system with its
description.
Structure Description
A 4. epididymis A. External sac that holds male gonads
C 5. scrotum B. The primary male reproductive organ
E 6. seminiferous tubule C. Structure in which sperm mature
B 7. testis D. Structure in which meiosis occurs
D 8. vas deferens E. The tube through which sperm travel to the
urethra
For Questions 9–12, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words.
9. The seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethal gland produce a
nutrient-rich fluid called seminal fluid.
10. Sperm mixed with the seminal fluid is called semen.
11. Signals from the brain and the nervous system cause sperm to be ejaculated.
12. The seminal fluid of a sperm cell contain mitochondria that supply energy to the
mitochondria ,which propels the sperm forward.
The Female Reproductive System
For Questions 13–16, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words.
13. The primary reproductive organs of females are the OVUM .
14. The function of a(n) UTERUS is to help an egg mature.
15. Only about OVARY of the 400,000 eggs a female is born with develop into a
mature ovum.
16. The structure of the female reproductive system in which the embryo develops is called
the UTERUS .
Name Class Date
For Questions 17–20, match each phase of the menstrual cycle with the correct event.
Phase Event
C 17. Follicular phase A. An unfertilized egg leaves the body.
B 18. Ovulaton B. The egg travels through a Fallopian tube.
A 19. Luteal phase C. An egg within a follicle develops.
D 20. Menstruation D. An egg is released from an ovary.
21. Complete the concept map to explain what the outcomes of a menstrual cycle can be.
Mature ovum
enters the
Fallopian tube
No sperm are in female tract
The sperm are in
female tract
Fertilization
menstruation could result
happens, it is
when the ovule
does not
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
For Questions 22–24, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change
the underlined word or words to make the statement true.
F 22. AIDS is the most common bacterial STD.
T 23. Chlamydia damages the reproductive tract and can cause infertility.
F 24. Hepatitis B and genital herpes are viral STDs.
Apply the Big idea
25. How is the menstrual cycle an example of the body’s use of negative feedback?
THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE IS A SERIE THE CHANGES OF THE NATURE
FORM THAT OCCURS IN THE SYSTEM REPRODUCTATOR FEMANE, BUT THE
REGULATION OF THE TEMPERATURE BODILY AND THE REGULATION OF THE
PH IN THE BLOOD ARE EXAMPLES OF THE NEGATIVE FEEDBACK.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Reproductive System TestDocument12 paginiReproductive System TestVân vui vẻÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction - Enrichment Drill - SVDocument6 paginiReproduction - Enrichment Drill - SVdasharrath sathish kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roads to Family: All the Ways We Come to BeDe la EverandRoads to Family: All the Ways We Come to BeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Document15 paginich-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Turani SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Illustrated Book of Medicine: The Making of MeDe la EverandThe Illustrated Book of Medicine: The Making of MeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade5 Q2 W1Document17 paginiGrade5 Q2 W1george.carbaquilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 1 and 2Document8 paginiScience: Quarter 2 - Module 1 and 2Lena Beth Tapawan Yap100% (1)
- Daug - Activity No.1 - Reproductive SystemDocument3 paginiDaug - Activity No.1 - Reproductive SystemFRANCINE JULIA DAUGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temporary Module1 Science5Document10 paginiTemporary Module1 Science5Lena Beth Tapawan YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4Document95 paginiScience Form 3 Chapter 4Eric Chew100% (1)
- Mod 2 7 For Students PDFDocument118 paginiMod 2 7 For Students PDFpetergomez0119Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Class-12 Chapter-3Document9 paginiBiology Class-12 Chapter-3mokanrajan141106Încă nu există evaluări
- ST#1 Science 5 Quarter 2Document1 paginăST#1 Science 5 Quarter 2John Rick BelenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repro Q N A PDFDocument8 paginiRepro Q N A PDFtrust zimunyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastery Test in Science 5Document3 paginiMastery Test in Science 5Klent ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Exam Gender and SocietyDocument7 paginiMidterm Exam Gender and SocietyJazmin Ace PrepotenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci10 Quarter 3 Module 1 NO ANSWER KEYDocument30 paginiSci10 Quarter 3 Module 1 NO ANSWER KEYNiña Miles TabañagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 2nd Quarter ExamDocument3 paginiScience 5 2nd Quarter ExamLouie Ric FiscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction System: By: Maharini, S.PD Anik Rahmawati, S.PD SMP Negeri 1 PonorogoDocument31 paginiReproduction System: By: Maharini, S.PD Anik Rahmawati, S.PD SMP Negeri 1 PonorogoYu HasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Periodical Test I Science ReviewerDocument7 pagini1st Periodical Test I Science Reviewercatherine tamayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3RD Q Module 1 Quiz 1 Reproductive SystemDocument1 pagină3RD Q Module 1 Quiz 1 Reproductive Systemsinunuc nhs100% (1)
- Summative Test Reproductive SystemDocument28 paginiSummative Test Reproductive SystemManilyn PenafloridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive System Answer KeyDocument7 paginiReproductive System Answer Keyapi-209542414Încă nu există evaluări
- EnglishDocument11 paginiEnglishLaili Dwi Alvi SyahriniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 - Biology - Human ReproductionDocument10 paginiClass 12 - Biology - Human ReproductionAstha SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesDocument138 paginiGrade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesLulo NnenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3Document27 paginiNCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3Me RahaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remedial QUIZDocument2 paginiRemedial QUIZsinunuc nhsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 paginiHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd QTR Multiple Choice Work Sheet BIO X LearnersDocument11 pagini3rd QTR Multiple Choice Work Sheet BIO X LearnersIan DibÎncă nu există evaluări
- sCIENCE 7Document3 paginisCIENCE 7Julien PitogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 paginiA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceI AM ANONYMOUSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDocument33 paginiReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 paginiThe Human Reproductive SystemEhr WinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 - Q2 PT 2022-2023Document6 paginiScience 5 - Q2 PT 2022-2023Mary Grace V. CanlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci10-q3-Male and Female Repro SystemDocument71 paginiSci10-q3-Male and Female Repro SystemDani Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- tJISjCwWKppIrfVbBOdL PDFDocument31 paginitJISjCwWKppIrfVbBOdL PDFBharati GulajkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ran Ii - Reproductive - 083648Document17 paginiRan Ii - Reproductive - 083648joykibaki066Încă nu există evaluări
- Human Reproduction: Points To RememberDocument9 paginiHuman Reproduction: Points To RememberPREM277272Încă nu există evaluări
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 paginiHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Reproduction QuestionareDocument4 paginiHuman Reproduction QuestionarePRATAP SEEMTOSH SINGH100% (1)
- Science 6 1.3Document3 paginiScience 6 1.3Thùy Võ Ngọc PhươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 paginiHuman Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFAubrey EuropeÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.ing YenishacDocument3 paginiB.ing YenishacYenisha CherinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction in HumansDocument4 paginiReproduction in HumansIsra OmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yr 8 WK 2 Bio NoteDocument3 paginiYr 8 WK 2 Bio Notesedrick ocheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draft Exam01Document13 paginiDraft Exam01Hannah Pegalan AlegarmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 2 - Weekly Test #1 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument2 paginiQuarter 2 - Weekly Test #1 - Human Reproductive SystemmagnojoanmaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcement Form 3 Science MT AugustDocument5 paginiReinforcement Form 3 Science MT AugustAisha SuhaylaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Ahmad Shafie B. Basari Class: No. Matrix: 09104 Teacher: Azizah YahyaDocument31 paginiName: Ahmad Shafie B. Basari Class: No. Matrix: 09104 Teacher: Azizah YahyaShafie BasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 paginiReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionDocument17 paginiImportant Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionYuvraj MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument3 paginiReproduction in Animalsdakshsri24Încă nu există evaluări
- Appreciation EvaluationDocument6 paginiAppreciation EvaluationJorge GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 paginiReproductive SystemAnnie Mae LamparaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Document27 paginiMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Assessment Test in Science Grade 5Document5 paginiFirst Assessment Test in Science Grade 5Gilami DiamondÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE 5-Human Reproductive SystemDocument54 paginiSCIENCE 5-Human Reproductive SystemKIMBERLY CHRISTINE ESPANOLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Malformations of The Female Genital TractDocument7 paginiCongenital Malformations of The Female Genital TractDo le QuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Injection ContraceptionDocument3 paginiInjection ContraceptionEzyan SyaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- PUERPERIUMDocument58 paginiPUERPERIUMPencenk Azznew100% (4)
- Analysis of Cesarean Section Rate - According To Robson's 10-Group ClassificationDocument4 paginiAnalysis of Cesarean Section Rate - According To Robson's 10-Group ClassificationMahavir GemavatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka: Dwina Retna Martuti, Dr. Riris Andono Ahmad, MPH, PHD Dr. Hanevi Djasri, MarsDocument5 paginiDaftar Pustaka: Dwina Retna Martuti, Dr. Riris Andono Ahmad, MPH, PHD Dr. Hanevi Djasri, MarsNENA RISKI HARIYATIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chorionic Villus Sampling: Ashique Palliyal 09M2385Document15 paginiChorionic Villus Sampling: Ashique Palliyal 09M2385Sanjay Kumar SanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PartoghraphDocument60 paginiPartoghraphharley dela cruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duration of Postpartum Magnesium Sulphate For The.7Document8 paginiDuration of Postpartum Magnesium Sulphate For The.7Tegar Dwi Prakoso NurdionoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Narrative Report On Child DeliveryDocument3 paginiMedical Narrative Report On Child DeliveryMelona BenidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aub Pogs CPGDocument39 paginiAub Pogs CPGVenz Timothy Wesley LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE - Reproductive System (Male & Female)Document6 paginiWEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE - Reproductive System (Male & Female)Lance KennethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Golden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas City: College of NursingDocument2 paginiGolden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas City: College of NursingJoseph Mandigma100% (1)
- TetekDocument4 paginiTetekasoly giovanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age of Gestation: First TrimesterDocument4 paginiAge of Gestation: First TrimesterBenjamin GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterine CancerDocument20 paginiUterine CancerAjurs UrsabiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Mrs Rajbr Kaur Lecturer OBGDocument20 paginiNursing Care Plan: Mrs Rajbr Kaur Lecturer OBGKavi rajput91% (23)
- IUFD For 4th Year Medical StudentsDocument19 paginiIUFD For 4th Year Medical StudentsDegefaw BikoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems of The PassengerDocument11 paginiProblems of The PassengerShanon France100% (1)
- Breastfeeding PresentationDocument27 paginiBreastfeeding Presentationapi-485081343Încă nu există evaluări
- IUGA Scoring SystemDocument40 paginiIUGA Scoring SystemBudi Iman SantosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intrauterine Drug Delivery SystemsDocument32 paginiIntrauterine Drug Delivery SystemsAhmad ThantowiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Genitalia PDFDocument57 paginiFemale Genitalia PDFElleÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDL Introduction STEM - SanchezDocument3 paginiRDL Introduction STEM - SanchezErik Maximus SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mola HidatidosaDocument30 paginiMola HidatidosajackyploesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibnu Sina Hospital, Tuesday, April 19th, 2022 (Period April 10th - 17th, 2022)Document4 paginiIbnu Sina Hospital, Tuesday, April 19th, 2022 (Period April 10th - 17th, 2022)MirahAvishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Estrus Cycle in BuffaloesDocument31 paginiStudy of Estrus Cycle in BuffaloesMUHAMMAD AWAISÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annotated Bibliography The Embryo ImbroglioDocument8 paginiAnnotated Bibliography The Embryo Imbroglioapi-242000092Încă nu există evaluări
- Konsep Normal Pada PersalinanDocument25 paginiKonsep Normal Pada PersalinanFitri RitongaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOAL Masuk 2018Document142 paginiSOAL Masuk 2018Yoza FirdaozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gynaecology Passmed PlabDocument49 paginiGynaecology Passmed PlabDoctor daveÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouDe la EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (62)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDe la EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (392)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDe la EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDe la EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (516)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)De la EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (378)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDe la Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDe la EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (811)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowDe la EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (390)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDe la EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDe la EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDe la EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (38)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDe la EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (15)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDe la EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDe la EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondDe la EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDe la EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (215)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDe la EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (65)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDe la EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (397)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldDe la EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineDe la EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (17)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDe la EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (115)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightDe la EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)