Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ASSIGNMENT ON Tenses
Încărcat de
kRn prEtTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ASSIGNMENT ON Tenses
Încărcat de
kRn prEtDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ASSIGNMENT ON
TENSES
SUBJECT:
English (Language)
DEPARTMENT:
Computer Science (Part-1, 1st Semester)
SUBMITTED TO:
Respected, Sir Abdullah Joyo
SUBMITTED BY:
Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi
DATE: 4th February 2014
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 1
TENSES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TENSES
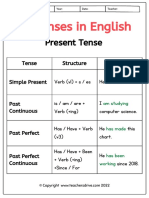
Present Tense
Present Indefinite Tense
Present Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Tense
Past Indefinite Tense
Past Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Tense
Future Indefinite Tense
Future Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 2
PRESENT INDEFINITE TENSE
TENSE: A grammatical category of verbs used to express distinctions of time.
PRESENT TENSE: The verb tense expressing action in the present time.
PRESENT INDEFINITE TENSE: It is used to express an action in present time, habitual or
usual actions or daily event or universal fact. It is used to express an action in present time which
is usually done on a regular basis. For example a student says, “I go to school”. It is a daily
activity of a student to go to school, so such actions are expressed by present simple tense.
Another example is, “I work in a factory”. It tells about a usual action of a person that he works in
a factory on regular basis.
Rules: 1st form of verb or base verb is used as main verb in sentence
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + 1st form of verb (or base verb) + Object
Note: If the subject in a sentence is “he, she, it, singular or proper noun” then “s” or “es”
is added to the first form of verb or base form in the sentence.
Negative Sentences:
Subject + Do not/Does not + 1st form of verb (or base form) + object
Note: In negative sentence auxiliary verb “do or does” along with “not” is used. If the
subject in a sentence is “he, she, it, singular or proper noun”, then “Does not” is used after
subject in sentence. If subject is “I, we, they, you or plural” then “Do not” is used after
subject in sentence. “s” or “es” is not added to main verb in negative sentence.
Interrogative Sentence:
Do/Does + Subject + 1st for of verb (or base verb) + Object?
Note: If the subject in a sentence is “he, she, it, singular or proper noun” the sentence is
started with Auxiliary verb “Does”. If the subject in a sentence is “I, we, they, you or
plural” the sentence is started with auxiliary verb “Do”. “s” or “es” is not added to main
verb in Interrogative sentence.
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Do/Does + Subject + not +1st for of verb (or base verb) + Object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after every subject.
Present Indefinite Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I write a letter. I do not write a letter. Do I write a letter? Do I not write a letter?
We throw a ball. We do not throw a ball. Do we throw a ball? Do we not throw a ball?
He drinks milk. He does not drink milk. Does he drink milk? Does he not drink milk?
She sews clothes. She does not sew Does she sew Does she not sew
clothes. clothes? clothes?
It runs fast. It does not run fast. Does it run fast? Does it not run fast?
Aslam walks Aslam does not walk Does Aslam walk Does Aslam not walk
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You play cricket. You do not play Do you play cricket? Do you not play cricket?
cricket.
They work hard. They do not work Do they work hard? Do they work hard?
hard.
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 3
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE: It is used to express a continued or ongoing action at
present time. It expresses an action which is in progress at the time of speaking. For example, a
person says, “I am writing a letter”. It means that he is in the process of writing a letter right now.
Such actions which are happening at time of speaking are expressed by present continuous tense.
Present Continuous tense is also called Present progressive tense.
Rules: Auxiliary verb “am or is or are” is used in sentence. 1st form of verb or base verb + ing
(present participle) is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + am/is/are + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Note: If the subject is “I” then auxiliary verb “am” is used after subject in sentence.
If the subject is “He, She, It, singular or proper name” then auxiliary verb “is” is used after
subject in sentence. If subject is “You, They or plural” then auxiliary verb “are” is used
after subject in sentence. The participle “ing” is added to the 1st form of verb.
Negative Sentences:
Subject + am/is/are + not + (1st form of verb + ing) + object
Note: Rules for using auxiliary verbs (am or is or are) after subject in negative sentences
are same as mentioned above.
Interrogative Sentence:
Am/is/are + Subject + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object?
Note: For making interrogative sentences, the sentence is started with auxiliary verb
rather than putting auxiliary verb inside the sentence. If the subject is “I” the sentence
starts with auxiliary verb “am”. If the subject is “He, She, It, singular or proper name” the
sentence starts with auxiliary verb “is”. If subject is “You, They or plural” the sentence
starts with auxiliary verb “are”.
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Am/is/are + Subject + not+ (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after subject.
Present Continuous Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I am writing a letter. I am not writing a Am I writing a Am I not writing a
letter. letter? letter?
We are throwing a We are not throwing a Are we throwing a Are we not throwing a
ball. ball. ball? ball?
He is drinking milk. He is not drinking milk. Is he drinking milk? Is he not drinking milk?
She is sewing She is not sewing Is she sewing Is she not sewing
clothes. clothes. clothes? clothes?
It is running fast. It is not running fast. Is it running fast? Is it not running fast?
Aslam is walking Aslam is not walking Is Aslam walking Is Aslam not walking
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You are playing You are not playing Are you playing Are you not playing
cricket. cricket. cricket? cricket?
They are working They are not working Are they working Are they not working
hard. hard. hard? hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 4
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE: It is used to express an action which happened or completed in
past but usually the action which happened or completed at a short time before now (near past)
not a very long time before now. Specific time such as two years ago, last week or that day is
usually not used in the sentences of in this tense. It means that this tense expresses the action
whose time when it happened, is not exactly specified but it sounds to refer to some action that
happened or completed in near past.
Rules: Auxiliary verb “has or have” is used in sentence. 3rd form of verb (past participle) is used
as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + has/have + 3rd form of verb or past participle + subject
Note: If the subject is “He, She, It, singular or proper name” then auxiliary verb “has” is
used after subject in sentence. If subject is “You, They or plural” then auxiliary verb “have”
is used after subject in sentence.
Negative Sentences:
Subject + has/have + NOT + 3rd form of verb or past participle + subject
Note: Rules for using auxiliary verb “has or have” in negative sentence are same as
mentioned above.
Interrogative Sentence:
Has/have + Subject + 3rd form of verb or past participle + subject?
Note: Interrogative sentence starts with auxiliary verb. If the subject is “He, She, It,
singular or proper name” then the sentence starts with auxiliary verb “has”.
If subject is “You, They or plural” then the sentence starts with auxiliary verb “have”.
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Has/have + Subject + not + 3rd form of verb or past participle + subject?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after every subject.
Present Perfect Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I have written a I have not written a Have I written a Have I not written a
letter. letter. letter? letter?
We have thrown a We have not thrown a Have we thrown a Have we not thrown a
ball. ball. ball? ball?
He has drunk milk. He has not drunk milk. Has he drunk milk? Has he not drunk milk?
She has sewed She has not sewed Has she sewed Has she not sewed
clothes. clothes. clothes? clothes?
It has run fast. It has not run fast. Has it run fast? Has it not run fast?
Aslam has walked Aslam has not walked Has Aslam walked Has Aslam not walked
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You have played You have not played Have you played Have you not played
cricket. cricket. cricket? cricket?
They have worked They have not worked Have they worked Have they not worked
hard. hard. hard? hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 5
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE: It is used to express a continued or ongoing
action that started in past and is continued until now.
Note: If there is not time reference or sense of time reference then it is not Present perfect
continuous tense because there is no hint about the time of action when it started in past and it
seems just an ongoing action at present time which resembles “present Continuous tense. So the
reference of time differentiates between Present perfect continuous tense and Present continuous
tense.
Rules: An auxiliary verb “has been or have been” is used in sentence. 1st form of verb (base
verb) +ing (present participle) is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + has been/have been + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Note: If the subject is “He, She, It, singular or proper name” then auxiliary verb “has
been” is used after subject in sentence. If subject is “You, They or plural” then auxiliary
verb “have been” is used after subject in sentence.
Negative Sentences:
Subject + has not been/have not been + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Note: To make negative sentence, the word “not” is written between the auxiliary verbs,
so it becomes like “has not been or have not been”. The rule for using auxiliary verb “has
been or have been” in negative sentences is as same as mentioned above.
Interrogative Sentence:
Has/have + Subject + been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object?
Note: Interrogative sentence starts with auxiliary verb. If the subject is “He, She, It,
singular or proper name” then the sentence starts with auxiliary verb “has” and auxiliary
verb “been” is used after subject. If subject is “You, They or plural” then the sentence
starts with auxiliary verb “have” and “been” is used after subject
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Has/have + Subject +not+ been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after every subject.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I have been writing I have not been writing Have I been writing Have I not been writing
a letter. a letter. a letter? a letter?
We have been We have not been Have we been Have we not been
throwing a ball. throwing a ball. throwing a ball? throwing a ball?
He has been He has not been Has he been Has he not been
drinking milk. drinking milk. drinking milk? drinking milk?
She has been sewing She has not been Has she been sewing Has she not been
clothes. sewing clothes. clothes? sewing clothes?
It has been running It has not been running Has it been running Has it not been running
fast. fast. fast? fast?
Aslam has been Aslam has not been Has Aslam been Has Aslam not been
walking slowly. walking slowly. walking slowly? walking slowly?
You have been You have not been Have you been Have you not been
playing cricket. playing cricket. playing cricket? playing cricket?
They have been They have not been Have they been Have they not been
working hard. working hard. working hard? working hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 6
PAST INDEFINITE TENSE
PAST INDEFINITE TENSE: It is used to express an action that happened or completed in past,
usually a very little time before speaking, or action which is just completed. Time of action is not
specified in terms of long time ago or short ago but it make a sense that the action has done a
little time ago. For example, a person says, “I watched a movie”, it means the speaker of this
sentence watched a movie a little time ago or little time ago in the same day.
Rules: 2nd form of verb (past simple) is used as main verb in the positive sentences and base
form is used in negative and interrogative sentences.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PAST SIMPLE TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + 2nd form of verb (past simple) + object
Negative Sentences:
Subject + did not + 1st form of verb or base form + object
Note: In negative sentence “did not” is written and the 1st form of verb (base verb) is
used instead of using 2nd form (or past simple verb).
Interrogative Sentence:
Did + subject + 1st form of verb (or base verb) + object?
Note: Interrogative sentence starts with “did” and the 1st form of verb (base verb) is used
instead of using 2nd form (or past simple verb).
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Did + subject + 1st form of verb (or base verb) + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after subject.
Past Indefinite Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I wrote a letter. I did not write a letter. Did I write a letter? Did I not write a letter?
We threw a ball. We did not throw a Did we throw a ball? Did we not throw a
ball. ball?
He drank milk. He did not drink milk. Did he drink milk? Did he not drink milk?
She sewed clothes. She did not sew Did she sew clothes? Did she not sew
clothes. clothes?
It ran fast. It did not run fast. Did it run fast? Did it not run fast?
Aslam walked Aslam did not walk Did Aslam walk Did Aslam not walk
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You played cricket. You did not play Did you play cricket? Did you not play
cricket. cricket?
They worked hard. They did not work Did they work hard? Did they work hard?
hard.
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 7
PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE: It is used to express a continued or ongoing action in past, an
ongoing action which occurred in past and completed at some point in past. It expresses an
ongoing nature of an action in past. For example, “he was laughing.” This sentence shows ongoing
action (laughing) of a person which occurred in past. Past continuous tense is also called past
progressive.
Rules: Auxiliary verb “was or were” is used in sentence. 1st form of verb or base verb + ing
(present participle) is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + was/were + (1st form of verb or base verb +ing) +object
Note: If the subject is “he, she, It, I, singular or proper noun” then auxiliary verb “was” is
used. If subject is “you, we, they or plural” then auxiliary verb “were” is used.
Negative Sentences:
Subject + was/were + NOT + (1st form of verb or base verb +ing) +object
Note: Rules for using auxiliary verb after subject are same as mentioned above
Interrogative Sentence:
Was/were + Subject + (1st form of verb or base verb +ing) +object?
Note: The interrogative sentence starts with the auxiliary verb. If the subject is “he, she,
It, I, singular or proper noun” then the sentence starts with auxiliary verb “was”. If subject
is “you, we, they or plural” then the sentence starts with auxiliary verb “were”.
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Was/were + Subject +not + (1st form of verb or base verb +ing) +object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after subject.
Past Continuous Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I was writing a I was not writing a Was I writing a Was I not writing a
letter. letter. letter? letter?
We were throwing a We were not throwing Were we throwing a Were we not throwing
ball. a ball. ball? a ball?
He was drinking He was not drinking Was he drinking Was he not drinking
milk. milk. milk? milk?
She was sewing She was not sewing Was she sewing Was she not sewing
clothes. clothes. clothes? clothes?
It was running fast. It was not running fast. Was it running fast? Was it not running fast?
Aslam was walking Aslam was not walking Was Aslam walking Was Aslam not walking
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You were playing You were not playing Were you playing Were you not playing
cricket. cricket. cricket? cricket?
They were working They were not working Were they working Were they not working
hard. hard. hard? hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 8
PAST PERFECT TENSE
PAST PERFECT TENSE: It is used to express an action which has occurred in past (usually, a
long time ago) and action which has occurred in past before another action in past.
The students had gone before the teacher came. (The first part of sentence “The student has
gone” is sentence of past perfect tense, it says about an action which occurred before another
action in past which is “the teacher came”. The second part “the teacher came” is sentence of past
simple tense. So such a sentence which express an action in past before another action in past
comprises two parts where the first part of sentence is past perfect tense)
Rules: Auxiliary verb “had” is used in sentence. 3rd form of verb (past participle) is used as main
verb in sentence
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PAST PERFECT TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + had + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object
Negative Sentences:
Subject + had + not + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object
Note: “Not” is written after auxiliary verb in negative sentence.
Interrogative Sentence:
Had + subject + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object?
Note: Interrogative sentence starts with auxiliary verb “had”.
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Had + subject + not + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after subject.
Past Perfect Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I had written a I had not written a Had I written a Had I not written a
letter. letter. letter? letter?
We had thrown a We had not thrown a Had we thrown a Had we not thrown a
ball. ball. ball? ball?
He had drunk milk. He had not drunk milk. Had he drunk milk? Had he not drunk milk?
She had sewed She had not sewed Had she sewed Had she not sewed
clothes. clothes. clothes? clothes?
It had run fast. It had not run fast. Had it run fast? Had it not run fast?
Aslam had walked Aslam had not walked Had Aslam walked Had Aslam not walked
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You had played You had not played Had you played Had you not played
cricket. cricket. cricket? cricket?
They had worked They had not worked Had they worked Had they not worked
hard. hard. hard? hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 9
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE: It is used to express a continued or ongoing action
that started in past and continued until sometime in past. (Remember, an ongoing action in past
which continued till some time in past).
Note: If there is not time reference or sense of time reference, then it is not Past perfect
continuous tense because there is no hint about the time of action when it started in past or
continued for some time period, so it seems just an ongoing action in past which resembles “past
Continuous tense”. So the reference of time differentiates between Past perfect continuous
tense and past continuous tense.
Rules: An auxiliary verb “had been” is used in sentence. 1st form of verb (base verb) +ing
(present participle) is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + had been + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Note: If the subject is “He, She, It, singular or proper name” then auxiliary verb “has
been” is used after subject in sentence. If subject is “You, They or plural” then auxiliary
verb “have been” is used after subject in sentence.
Negative Sentences:
Subject + had not been + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Note: To make negative sentence, the word “not” is added inside auxiliary verb, so it
becomes “had not been”.
Interrogative Sentence:
Had + Subject + been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object?
Note: Interrogative sentence starts with auxiliary verb “had” and auxiliary verb “been” is
used after subject in sentence.
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Had + Subject +not+ been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after every subject.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I had been writing a I had not been writing Had I been writing a Had I not been writing
letter. a letter. letter? a letter?
We had been We had not been Had we been Had we not been
throwing a ball. throwing a ball. throwing a ball? throwing a ball?
He had been He had not been Had he been Had he not been
drinking milk. drinking milk. drinking milk? drinking milk?
She had been sewing She had not been Had she been Had she not been
clothes. sewing clothes. sewing clothes? sewing clothes?
It had been running It had not been Had it been running Had it not been running
fast. running fast. fast? fast?
Aslam had been Aslam had not been Had Aslam been Had Aslam not been
walking slowly. walking slowly. walking slowly? walking slowly?
You had been You had not been Had you been Had you not been
playing cricket. playing cricket. playing cricket? playing cricket?
They had been They had not been Had they been Had they not been
working hard. working hard. working hard? working hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 10
FUTURE INDEFINITE TENSE
FUTURE INDEFINITE TENSE: It is used to express an action which has not occurred yet and
will occur after saying or in future. For example, “I shall go to zoo tomorrow”, in this sentence the
person intend for tomorrow’s visit to zoo. In short, these sentences express actions which will be
done in future.
Rules: Auxiliary verbs “will/shall” are used in sentence. 1st form of verb or base form is used as
main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + shall/will + (1st form of verb or base form) + object
Negative Sentences:
Subject + shall/will +not + (1st form of verb or base form) + object
Note: To make negative sentence “not” is written after auxiliary verb in sentence.
Interrogative Sentence:
shall/Will + subject + (1st form of verb or base form) + object?
Note: Interrogative sentence starts with auxiliary verb “will”
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Shall/Will + subject + not + (1st form of verb or base form) + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after subject.
Future Indefinite Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I shall write a I shall not write a Shall I write a letter? Shall I not write a
letter. letter. letter?
We shall throw a We shall not throw a Shall we throw a Shall we not throw a
ball. ball. ball? ball?
He will drink milk. He will not drink milk. Will he drink milk? Will he not drink milk?
She will sew She will not sew Will she sew Will she not sew
clothes. clothes. clothes? clothes?
It will run fast. It will not run fast. Will it run fast? Will it not run fast?
Aslam will walk Aslam will not walk Will Aslam walk Will Aslam not walk
slowly. slowly. slowly? slowly?
You will play You will not play Will you play Will you not play
cricket. cricket. cricket? cricket?
They will work They will not work Will they work Will they work hard?
hard. hard. hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 11
FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE: It is used to express a continued or an ongoing action in
future. For example, “I will be waiting for you tomorrow”, it conveys ongoing nature of an action
(waiting) which will occur in future.
Rules: Auxiliary verbs “will be/shall be” are used in sentence. 1st form of verb + ing (present
participle) is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + will/Shall + be + (1st form of verb or base form +ing) + object
Negative Sentences:
Subject + will/Shall +not +be+ (1st form of verb or base form +ing) + object
Note: To make negative sentence “not” is written between auxiliary verbs “will
and be” in sentence.
Interrogative Sentence:
Will/shall + subject + be+ 1st form of verb or base form+ing (present participle) + object?
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Will/shall + subject + not + be+ 1st form of verb or base form+ing (present participle) + object?
Note: This type is same in rules with interrogative but “not” is added after subject.
Future Continuous Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I shall be writing a I shall not be writing a Shall I be writing a Shall I not be writing a
letter. letter. letter? letter?
We shall be We shall not be Shall we be Shall we not be
throwing a ball. throwing a ball. throwing a ball? throwing a ball?
He will be drinking He will not be drinking Will he be drinking Will he not be drinking
milk. milk. milk? milk?
She will be sewing She will not be sewing Will she be sewing Will she not be sewing
clothes. clothes. clothes? clothes?
It will be running It will not be running Will it be running Will it not be running
fast. fast. fast? fast?
Aslam will be Aslam will not be Will Aslam be Will Aslam not be
walking slowly. walking slowly. walking slowly? walking slowly?
You will be playing You will not be playing Will you be playing Will you not be playing
cricket. cricket. cricket? cricket?
They will be They will not be Will they be working Will they not be
working hard. working hard. hard? working hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 12
FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
FUTURE PERFECT TENSE: It is used to express an action which will occur in future and is
thought to be completed in future. It expresses a sense of completion of an action which will occur
in future. For example, “John will have gone tomorrow”. It shows a sense of completion of an
action (go) which will occur in future (tomorrow).
Rules: Auxiliary verb “will/shall have” is used in sentence. 3rd form of verb or past participle form
of verb is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + will/shall have + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object
Negative Sentences:
Subject + will/shall not have + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object
Interrogative Sentence:
Will/shall + Subject +have + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object?
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Will/shall + Subject +have+ not + 3rd form of verb or past participle + object?
Future Perfect Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I shall have written I shall not have written Shall I have written Shall I not have written
a letter. a letter. a letter? a letter?
We shall have We shall not have Shall we have Shall we not have
thrown a ball. thrown a ball. thrown a ball? thrown a ball?
He will have drunk He will not have drunk Will he have drunk Will he not have drunk
milk. milk. milk? milk?
She will have sewed She will not have Will she have sewed Will she not have
clothes. sewed clothes. clothes? sewed clothes?
It will have run fast. It will not have run Will it have run fast? Will it not have run
fast. fast?
Aslam will have Aslam will not have Will Aslam have Will Aslam not have
walked slowly. walked slowly. walked slowly? walked slowly?
You will have played You will not have Will you have played Will you not have
cricket. played cricket. cricket? played cricket?
They will have They will not have Will they have Will they not have
worked hard. worked hard. worked hard? worked hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 13
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE: It is used to express a continued or ongoing action
that will start in future and is thought to be continued till sometime in future. (Remember, an
ongoing action in future which will continue till some time in future).
Note: If there is not time reference or sense of time reference then it is not future perfect
continuous tense because there is no hint about the time of action when it will start in future and it
seems just an ongoing action in future which resembles “future Continuous tense. So the reference
of time differentiates between Future perfect continuous tense between future continuous tense.
Rules: An auxiliary verb “will/Shall have been” is used in sentence. 1st form of verb (base verb)
+ing (present participle) is used as main verb in sentence.
STRUCTURE OF SENTENCES IN FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Affirmative Sentence:
Subject + will/shall have been + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Negative Sentences:
Subject + will/shall not have been + (1st form of verb or base verb + ing) + object
Note: To make negative sentence, the word “not” is added inside auxiliary verb, so it
becomes “will not have been”.
Interrogative Sentence:
Will/Shall + Subject + have been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object + time
reference?
Note: Will + Subject + have been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object
Interrogative-Negative Sentence:
Will/Shall + Subject + have not been + (1st form of verb or base verb+ing) + object?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Affirmative Negative Sentence Interrogative Interrogative-
Sentence Sentence Negative Sentence
I shall have been I shall not have been Shall I have been Shall I have not been
writing a letter. writing a letter. writing a letter? writing a letter?
We shall have been We shall not have been Shall we have been Shall we have not been
throwing a ball. throwing a ball. throwing a ball? throwing a ball?
He will have been He will not have been Will he have been Will he have not been
drinking milk. drinking milk. drinking milk? drinking milk?
She will have been She will not have been Will she have been Will she have not been
sewing clothes. sewing clothes. sewing clothes? sewing clothes?
It will have been It will not have been Will it have been Will it have not been
running fast. running fast. running fast? running fast?
Aslam will have Aslam will not have Will Aslam have Will Aslam have not
been walking slowly. been walking slowly. been walking been walking slowly?
slowly?
You will have been You will not have been Will you have been Will you have not been
playing cricket. playing cricket. playing cricket? playing cricket?
They will have been They will not have Will they have been Will they have not been
working hard. been working hard. working hard? working hard?
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 14
DESIGNED BY: Syed Nazir Imam Kazmi Page 15
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Tenses: Assignment OnDocument15 paginiTenses: Assignment Onalina basharatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On TensesDocument10 paginiAssignment On TensesAbdul Waheed100% (9)
- Multiple Choice Test PDFDocument60 paginiMultiple Choice Test PDFInés Amaya Díaz100% (8)
- Part # 1 Present Tense Present Simple TenseDocument9 paginiPart # 1 Present Tense Present Simple TensekhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Sentence StructuresDocument20 paginiBasic Sentence StructuresCarla GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tense: Ali Honours Academy & Computer CollegeDocument20 paginiTense: Ali Honours Academy & Computer CollegeZubair AmjadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris-Felicia TambaDocument11 paginiTugas Bahasa Inggris-Felicia TambaIvon IdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 TensesDocument97 pagini16 TensesPutri IndriyantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 10 English Grammar - TensesDocument5 paginiCBSE Class 10 English Grammar - TensesSagara SwathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Tenses 82Document10 paginiBasics of Tenses 82aternos BullyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Final B.inggrisDocument24 paginiTugas Final B.inggrisLevin LombanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 TensesDocument21 pagini5 TensesMaría Isabel Montoro100% (1)
- Remedial ProgrammDocument100 paginiRemedial Programmye9449299Încă nu există evaluări
- Tense PresentationDocument53 paginiTense PresentationProlificÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trabalho de Ingles 3Document9 paginiTrabalho de Ingles 3Solange Bernardo MurrureÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Verb Tenses in Urdu PDFDocument18 paginiEnglish Verb Tenses in Urdu PDFSajid HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideDe la EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Present Tense: Power Mechanics DepartmentDocument5 paginiTypes of Present Tense: Power Mechanics DepartmentMohammed NoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Panama Vicepresidency of Research and Graduate Studies College of Humanities English DepartmentDocument28 paginiUniversity of Panama Vicepresidency of Research and Graduate Studies College of Humanities English DepartmentlingarajugowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TENSES Saliza & HaziqDocument42 paginiTENSES Saliza & HaziqSaliza HalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilDocument77 paginiA Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilSofia RaheelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Guide 3-2017 PDFDocument48 paginiGrammar Guide 3-2017 PDFRoberto Figueroa ZúñigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses Part - 1 Simple Present TenseDocument5 paginiTenses Part - 1 Simple Present Tensesiva kumar100% (1)
- Simple Present (Present Simple) : - IntroductionDocument23 paginiSimple Present (Present Simple) : - IntroductionSimona VinatoruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meeting 8Document13 paginiMeeting 8Fitri DelitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inbound 676430358566289743Document8 paginiInbound 676430358566289743LamijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VerbsDocument21 paginiVerbsDarah Faye MacatangayÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 1Document13 paginiEnglish 1Mifta PutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument16 paginiPresent Simple Vs Present ContinuousNisrine Idrissi ChouahdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb TenseDocument4 paginiVerb TenseFlorencia Rita Leonor MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs 2 Past Simple PDFDocument3 paginiCurs 2 Past Simple PDFELENAÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar I, 001: Chapter 1: PRESENT TIME 1.1. Simple Present and Present ProgressiveDocument58 paginiEnglish Grammar I, 001: Chapter 1: PRESENT TIME 1.1. Simple Present and Present ProgressiveChrista bella MugishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Grammar 1. Personal PronounsDocument17 paginiUnit 1: Grammar 1. Personal PronounsannisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Chapter 1Document15 paginiGrammar Chapter 1Obaid HashmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Indefinite in UrduDocument5 paginiPresent Indefinite in UrduSawabi Queen0% (1)
- Sesion 6 Present ContinuousDocument24 paginiSesion 6 Present ContinuousWalter Atao SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Tenes PDFDocument18 paginiAll Tenes PDFMuhammad QasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses: 1. Simple Present TenseDocument14 paginiTenses: 1. Simple Present TenseApe ApeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Say What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.De la EverandSay What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.Încă nu există evaluări
- ENGLISH GRAMMAR, TENSES TensesDocument65 paginiENGLISH GRAMMAR, TENSES Tensesmessiah sastryÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRESENT SIMPLE Vs PRESENT CONTINUOUSDocument85 paginiPRESENT SIMPLE Vs PRESENT CONTINUOUSmia100% (1)
- Past Indefinite Tense in Hindi: Just After Few Seconds To Many YearsDocument4 paginiPast Indefinite Tense in Hindi: Just After Few Seconds To Many YearsMohd Zakir HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument5 paginiThe Present Continuous Tenseapi-3718916100% (2)
- English GrammarDocument20 paginiEnglish Grammarsuga1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Document14 paginiUnit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Johana CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDocument4 paginiVerbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDelgado Maria AngelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abilities and Present Cont. LessonDocument11 paginiAbilities and Present Cont. LessonSilviaJerez96Încă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple ContinuousDocument8 paginiPresent Simple ContinuousJosmaツÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses 1Document3 paginiTenses 1SHAILLY SHARMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 001 - Simple PresentDocument5 pagini001 - Simple PresentRodrigo GodoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses Finger Method Book by Dogar Brothers PDFDocument31 paginiTenses Finger Method Book by Dogar Brothers PDFnaeemakhtaracma58% (12)
- Verb Tenses - NewDocument16 paginiVerb Tenses - NewSai AmruthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYKES - in TransitDocument5 paginiSYKES - in TransitJorge BulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Summary Passive Voice: Present Simple: For ExampleDocument8 paginiGrammar Summary Passive Voice: Present Simple: For ExampleYlenia BaldiviezoÎncă nu există evaluări
- There Are Five Basic Patterns Around Which Most English Sentences Are BuiltDocument8 paginiThere Are Five Basic Patterns Around Which Most English Sentences Are BuiltSusarla SuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbs TypesDocument24 paginiVerbs TypesSairamTirumalaiGovindarajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approfondimenti Grammaticali Corso Inglese ECMDocument26 paginiApprofondimenti Grammaticali Corso Inglese ECMAntonio PiazzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Verb?: Click Here To Find Out...Document26 paginiWhat Is A Verb?: Click Here To Find Out...jun pelorianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar Solution: Structure of All Tense, Structure of The Tense.Document10 paginiEnglish Grammar Solution: Structure of All Tense, Structure of The Tense.Georgy CarfrittÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Everyday: Higher-Level Ability and Understanding. Level 1. the VerbsDe la EverandEnglish Everyday: Higher-Level Ability and Understanding. Level 1. the VerbsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Future TensesDocument13 paginiFuture TensesDario NoditiÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar PortfolioDocument49 paginiEnglish Grammar PortfolioEduardo Wester Pérez75% (4)
- перфектDocument5 paginiперфектВікторія ЗахароваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb Tense Review 2 - The Perfect Tenses: Grammar Practice WorksheetsDocument11 paginiVerb Tense Review 2 - The Perfect Tenses: Grammar Practice Worksheetsgutiii67% (3)
- English TensesDocument4 paginiEnglish TensesHeena JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Tenses QuestionDocument18 pagini100 Tenses QuestionLllllkkkkk100% (1)
- Future TensesDocument3 paginiFuture TensesMadalina IordacheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Simple Present Tense ExampleDocument9 paginiFormula Simple Present Tense ExamplesalsaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NLP - Advanced Language Patterns MasteryDocument122 paginiNLP - Advanced Language Patterns MasteryShawn SooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfect Tenses: by Salsabila Naqiyyah Xiia1Document13 paginiPerfect Tenses: by Salsabila Naqiyyah Xiia1Salsabila NaqiyyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Future TensesDocument30 paginiSimple Future TensesElvis Aguilar JulcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 paginiPerfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaAura SkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 PPT 12 Tenses OverviewDocument78 paginiWeek 3 PPT 12 Tenses OverviewdewxoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future TensesDocument23 paginiFuture TensesFlorina ConstantinÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Tenses in A TabloDocument4 paginiAll Tenses in A Tabloahmtozkn100% (1)
- Future Continuous & Future PerfectDocument3 paginiFuture Continuous & Future PerfectVitor CamachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resumen Ingles Modulo 1Document28 paginiResumen Ingles Modulo 1Lo RaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Perfect SimpleDocument2 paginiPast Perfect SimpleIanGiorgianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review 4esoDocument100 paginiReview 4esoBea Ferreres GilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Future: FORM WillDocument8 paginiSimple Future: FORM WillNong PhotiwongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb Conjugation: Advanced Grammar and CompositionDocument25 paginiVerb Conjugation: Advanced Grammar and CompositionJhay B. MagtibayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses: We Need To Be Thorough With TensesDocument61 paginiTenses: We Need To Be Thorough With TensesRising the screen GenerationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Verb TenseDocument32 paginiUnderstanding Verb Tensenormi100% (1)
- Module English 9 Week 22 23Document7 paginiModule English 9 Week 22 23Louise GermaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECT IndirectDocument8 paginiDIRECT IndirectSyafi' AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Tense Exercise 1and2 Merged MergedDocument14 paginiFuture Tense Exercise 1and2 Merged MergedGavindu NishodaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Present Simple Tense SDocument2 pagini1 Present Simple Tense Srahma071295Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document8 paginiAssignment 3Evangelister MapesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 6, Q4Document13 paginiEnglish 6, Q4Lemuel MoradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of VerbsDocument84 paginiTypes of VerbsMario RosasÎncă nu există evaluări