Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Symbols
Încărcat de
anupama91Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Symbols
Încărcat de
anupama91Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Vishay Semiconductors
Symbols
Arrangement of Symbols The following table summarizes the rules given
above.
Letter symbols for current, voltage and power
Basic letter
(according to DIN 41 785, sheet 1)
Upper-case Upper-case
To represent current, voltage and power, a system of Electrical parameters inherent Electrical parameters of
basic letter symbols are used. Capital letters are used in the semiconductor devices external circuits and of circuits
for the representation of peak, mean, dc or root- except inductances and in which the semiconductor
mean-square values. Lower case letters are used for capacitances device forms only a part; all
the representation of instantaneous values which inductances and capacitances
vary with time. Subscript(s)
Capital letters are used as subscripts to represent Upper-case Upper-case
continuous or total values, while lower case letters are Small-signal values Static (dc) values
used to represent varying values.
The following table summarizes the rules given Examples:
above. RG Generator resistance
Basic letter GP Power gain
Upper-case Upper-case hFE DC forward current transfer ratio in
Instantaneous values which Maximum (peak) average
vary with time (mean) continuous (dc) or root-
common emitter configuration
mean-square (RMS) values rP Parallel resistance, damping resistance
Subscript(s)
Upper-case Upper-case Example for the use of Symbols
Varying component Continuous (without signal) or according to 41785 and IEC 148
alone,i.e.,instantaneous, total (instantaneous, average or
root-mean-square, maximum maximum) values b) Diode
or average values
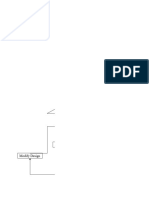
VF
Letter symbols for impedance, admittances,
VFSM
two-port parameters etc.
VFRM
For impedance, admittance, two-port parameters, VFWM
etc., capital letters are used for the representation of
external circuits of which the device is only a part.
Lower case letters are used for the representation of 0
electrical parameters inherent in the device. t
The rules are not valid for inductance and capaci- VRWM
tance. Both these quantities are denoted with capital VRRM
letters. VRSM
Capital letters are used as subscripts for the designa-
tion of static (dc) values, while lower case letters are VR 93 7796
used for the designation of small-signal values. Figure 1.
If more than one subscript is used (hFE, hfe), the letter
symbols are either all capital or all lower case. VF Forward voltage
If the subscript has numeric (single, double, etc.) as VR Reverse voltage
well as letter symbol(s) (such as h21E or h21e), the dif-
VFSM Surge forward voltage (non-repetitive)
ferentiation between static and small-signal value is
made only by a subscript letter symbol. VRSM Surge reverse voltage (non-repetitive)
Other quantities (values) which deviate from the VFRM Repetitive peak forward voltage
above rules are given in the list of letter symbols. VRRM Repetitive peak reverse voltage
VFWM Crest working forward voltage
VRWM Crest working reverse voltage
Document Number 84056 www.vishay.com
Rev. 1.2, 20-Jan-04 589
Vishay Semiconductors
List of Symbols RthJA Thermal resistance between junction and
A Anode ambient
a Distance (in mm) RthJC Thermal reistance between junction and case
C Capacitance, general rz Differential Z-resistance in breakdown region
(range) rz = rzj + rzth
Ccase Case capacitance
rzj Z-resistance at constant junction temperature,
CD Diode capacitance
inherent Z-resistance
Ci Junction capacitance
rzth Thermal part of the Z-resistance
CL Load capacitance
T Temperature, measured in centigrade
CP Parallel capacitance
T Absolute temperature, Kelvin temperature
F Noise figure
T Period duration
f Frequency
Tamb Ambient temperature (range)
fg Cut-off-frequency
Tcase Case temperature
IF Forward current
tfr Forward recovery time
iF Forward current, instantaneous total value
Tj Junction temperature
IFAV Average forward current, rectified current
TK Temperature coefficient
IFRM Repetitive peak forward current
TL Connecting lead temperature in the holder (sol-
IFSM Surge forward current, non-repetitive dering point) at the distance/(mm) from case
IFWM Crest working forward current tP Pulse duration (time)
IR Reverse current tp/T Duty cycle
iR Reverse current, instantaneous total value tr Rise time
IRAV Average reverse current trr Reverse recovery time
IRRM Repetitive peak reverse current ts Storage time
IRSM Non-repetitive peak reverse current Tsd Soldering temperature
IRWM Crest working reverse current Tstg Storage temperature (range)
IS Supply current V(BR) Breakdown voltage
IZ Z-operating current VF Forward voltage
IZM Z-maximum current VF Forward voltage, instantaneous total value
l Length (in mm), (case-holder/soldering point) VFAV Average forward voltage
LOCEP (local epitaxy) Vo Rectified voltage
A registrated trade mark of Vishay for a process ofepi- VFSM Surge forward voltage, non-repetitive
taxial deposition on silicon. Applications occur in
VFRM Repetitive peak forward voltage
planer Z-diodes. It has an advantage compared to the
normal process, with reduced reverse current. VFWM Crest working forward voltage
P Power VR Reverse voltage
Ptot Total power dissipation VR Reverse voltage, instantaneous total value
PV Power dissipation, general VRSM Surge reverse voltage, non-repetitive
Pvp Pulse-power dissipation VRRM Repetitive peak reverse voltage
Q Quality VRWM Crest working reverse voltage
Qrr Reverse recovery charge VZ Z-operating voltage
RF Forward resistance Zthp Thermal resistance – pulse operation
rf Differential forward resistance ηr Rectification efficiency
RL Load resistor ΔCD Capacitance deviation
rP Parallel resistance, damping resistance
RR Reverse resistance
rr Differential reverse resistance
rs Series resistance
www.vishay.com Document Number 84056
590 Rev. 1.2, 20-Jan-04
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Basic Definitions: VishayDocument5 paginiBasic Definitions: VishayAbhishek KushwahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polarity ConventionsDocument4 paginiPolarity Conventionsnicoka50Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Explanation: VishayDocument5 paginiPhysical Explanation: VishayAramitÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC-DC Converter - Design AspectsDocument15 paginiAC-DC Converter - Design Aspectsbishnu prasad muniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parallel RC Circuit Impedance Calculator - Electrical, RF and Electronics Calculators - Online Unit ConvertersDocument4 paginiParallel RC Circuit Impedance Calculator - Electrical, RF and Electronics Calculators - Online Unit ConvertersMRSUPERCOOLÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPS10170C: High Voltage Power Schottky RectifierDocument10 paginiSTPS10170C: High Voltage Power Schottky RectifierRicky Maulana FirdausÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 4 - Current and ResistanceDocument5 paginiChap 4 - Current and Resistancefareez fauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Explanation - General SemiconductorsDocument3 paginiPhysical Explanation - General SemiconductorsNarayanan RamanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Littelfuse Capacitance and Signal Integrity Application NoteDocument2 paginiLittelfuse Capacitance and Signal Integrity Application Notesujeet kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Opamp ApplicationsDocument5 paginiBasic Opamp ApplicationsNorbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014Document28 paginiSolved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014hshshdhdÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPS15L60C: DescriptionDocument8 paginiSTPS15L60C: DescriptioncqlÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Impedance Technical ReportDocument4 paginiHigh Impedance Technical Reportgovindaraj171Încă nu există evaluări
- UPS5817e3: Main Product CharacteristicsDocument4 paginiUPS5817e3: Main Product CharacteristicsSan DeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parameters of ThyristorsDocument5 paginiParameters of Thyristorsgarcia_drexÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBRF20100CTG Switch-Mode Schottky Power RectifierDocument4 paginiMBRF20100CTG Switch-Mode Schottky Power RectifierAlf IanÎncă nu există evaluări
- En CD00000695Document8 paginiEn CD00000695anhluc09vtÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Arte Da Eletronica 3oedicao (1) (0101-0150)Document50 paginiA Arte Da Eletronica 3oedicao (1) (0101-0150)Baba GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEMIKRON Technical Explanation Discrete Thyristors and Diodes EN 2005-04-15 Rev-00Document10 paginiSEMIKRON Technical Explanation Discrete Thyristors and Diodes EN 2005-04-15 Rev-00Izzudin YafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DatasheetDocument4 paginiDatasheetGrupo EpufmÎncă nu există evaluări
- STTH212: DescriptionDocument11 paginiSTTH212: DescriptionPablo Gonzalez RivielloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Explanation RectifiersDocument3 paginiPhysical Explanation RectifiersmixilopotstlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC-DC Converter - FDocument18 paginiAC-DC Converter - FBishnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- RectifierDocument76 paginiRectifierAbrar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthing Tool CalculatorDocument36 paginiEarthing Tool CalculatorJejomar ErebarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPS640C: Power Schottky RectifierDocument8 paginiSTPS640C: Power Schottky RectifierMax TeleÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC BUS CalculatorDocument4 paginiDC BUS CalculatorSandeeep_sonuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Generator Dan TrafoDocument3 paginiData Generator Dan TrafobudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied ElectricityDocument111 paginiApplied ElectricityYusif Ishaq Muhammad NazirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Explanation: RectifiersDocument3 paginiPhysical Explanation: RectifiersravindarsinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.AC Fundamental PDFDocument6 pagini2.AC Fundamental PDFTanishq MudaliarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1 General Device Data: 4.1.1 Analog InputsDocument4 pagini4.1 General Device Data: 4.1.1 Analog InputsEbrahim ArzaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Circuits LectureDocument30 paginiAC Circuits LectureYash MehraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loading Effects and Two-Port Networks Week 5 - 6Document31 paginiLoading Effects and Two-Port Networks Week 5 - 6منتصر الجعبريÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Note en 20230209 AKX00063Document12 paginiApplication Note en 20230209 AKX00063Bhakti MatsyapalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document13 paginiChapter 4Kishore SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triac (Bidirectional Triode Thyristor) : TMA126G-LDocument10 paginiTriac (Bidirectional Triode Thyristor) : TMA126G-LPedro RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet 2Document5 paginiDatasheet 2Roel GloriosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 5ke-1156012Document11 pagini1 5ke-1156012Ankadi Sikari ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT-PT ReqtsDocument32 paginiCT-PT Reqtsዛላው መና100% (1)
- Breaker Ratings: (Basic Insulation Level)Document1 paginăBreaker Ratings: (Basic Insulation Level)veljal6317Încă nu există evaluări
- Medium Power Diodes: Submitted By: Vikram 09235 Nikhil 09236 Vivek 09238 Prashant 09239Document14 paginiMedium Power Diodes: Submitted By: Vikram 09235 Nikhil 09236 Vivek 09238 Prashant 09239Vivek Kumar RuhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 920 325D LR 245176Document5 pagini920 325D LR 245176Avijit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (23001917 - Bulletin of The Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences) Selected Aspects of Modular Multilevel Converter Operation PDFDocument11 pagini(23001917 - Bulletin of The Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences) Selected Aspects of Modular Multilevel Converter Operation PDFnasiruddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Alina MirzaDocument44 paginiElectrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Alina MirzaMuhammad Zargham0% (1)
- Dioda Beban RDocument10 paginiDioda Beban RDamar Putra BriliawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Solved Problems Power Electronics Ashok KumarDocument65 paginiChapter 1 Solved Problems Power Electronics Ashok Kumarahmadus100% (2)
- Neutral Earth or GroundDocument3 paginiNeutral Earth or GroundAqeel � JZ Batch 22Încă nu există evaluări
- ACST4 Series: Ac Power Switch Asd™ AC Switch FamilyDocument9 paginiACST4 Series: Ac Power Switch Asd™ AC Switch FamilyMohsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Data - HVR International - Resistors For Compact CircuitryDocument2 paginiTechnical Data - HVR International - Resistors For Compact CircuitryNuma LumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.5ke33a DiodoDocument6 pagini1.5ke33a DiodocroquerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esdalc6v1 1u2Document11 paginiEsdalc6v1 1u2Aditya SrivatsavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture PPT 3-Diode Rating and RectificationDocument26 paginiLecture PPT 3-Diode Rating and RectificationAlex William JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsemi Power Diode Datasheet Notation AN1829Document12 paginiMicrosemi Power Diode Datasheet Notation AN1829scribddderÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPS80H100CY Schottky RectifierDocument10 paginiSTPS80H100CY Schottky RectifierAnonymous oyUAtpKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit1 - Ac FundamentalDocument18 paginiUnit1 - Ac FundamentalBlack spidey GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermistor ArduinoDocument16 paginiThermistor ArduinoJaume Segura GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet ST S5H100Document5 paginiDatasheet ST S5H100Maria Haro garateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cbse Syllabus For Class 11 Physics DownloadDocument7 paginiCbse Syllabus For Class 11 Physics Downloadgohn goneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic 24V "Hybrid" Underground Swing Gate Automation: HeadquartersDocument2 paginiHydraulic 24V "Hybrid" Underground Swing Gate Automation: HeadquartersHanan SFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetism and MotorsDocument7 paginiElectromagnetism and Motorsi don't have enough money for chicken nuggetsÎncă nu există evaluări
- (A) MARTIN 2003 - What Is Field TheoryDocument50 pagini(A) MARTIN 2003 - What Is Field TheoryDiego Maganhotto CoraiolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relay SettingDocument7 paginiRelay Settingsumitsharma2010Încă nu există evaluări
- AP - Generator Circuit-Breakers (EN) A - 1VCP000643 - 2017.03 PDFDocument48 paginiAP - Generator Circuit-Breakers (EN) A - 1VCP000643 - 2017.03 PDFenrique zamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extensive Review On Laminated Bus Bar For Low and High Power ApplDocument7 paginiExtensive Review On Laminated Bus Bar For Low and High Power ApplMANGAL KUMAR MOHAPATRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Analysis SyllabusDocument4 paginiNetwork Analysis SyllabusAyushnaitik PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1Document3 paginiTutorial 1A SкÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter One: Basic Concepts and UnitsDocument93 paginiChapter One: Basic Concepts and UnitsAmir ShakirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1.2-Energy Sources Test ReviewDocument4 paginiUnit 1.2-Energy Sources Test Reviewsmcowell662100% (1)
- MV Solution Up To 6.4 MVA: Medium Voltage Station For Decentralized PV Systems With 1500 V String InvertersDocument4 paginiMV Solution Up To 6.4 MVA: Medium Voltage Station For Decentralized PV Systems With 1500 V String InvertersDoan Anh TuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC Syllabus Kerala University (2003 Scheme)Document57 paginiEC Syllabus Kerala University (2003 Scheme)joyasams75% (4)
- Chrysler Charging SystemDocument23 paginiChrysler Charging SystemFred Passeau100% (1)
- HV9910BDB7 HV9910B PFC 40W LED Driver Demoboard: Specifications General DescriptionDocument5 paginiHV9910BDB7 HV9910B PFC 40W LED Driver Demoboard: Specifications General DescriptionNT372Încă nu există evaluări
- Fresnel Diffraction PDFDocument31 paginiFresnel Diffraction PDFassefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- isoMED427P DB enDocument6 paginiisoMED427P DB enMirwansyah TanjungÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Seminar Topic Report On Stability of High-Rise Building Bachelor of Technology IN Civil EngineeringDocument7 paginiA Seminar Topic Report On Stability of High-Rise Building Bachelor of Technology IN Civil Engineeringmrcopy xeroxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additive and Subtractive Polarity - An Electrician's Guide To Single Phase TransformersDocument4 paginiAdditive and Subtractive Polarity - An Electrician's Guide To Single Phase TransformersDeoudrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Periodic Test in Science 8 I. Multiple Choice: Department of EducationDocument3 paginiFirst Periodic Test in Science 8 I. Multiple Choice: Department of EducationRaymond Bugagao100% (1)
- Friction Lesson PlanDocument6 paginiFriction Lesson PlanmichelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- GyroscopeDocument4 paginiGyroscopeBlack PigeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises: 4.1 Motion Is RelativeDocument4 paginiExercises: 4.1 Motion Is RelativeamilcarsoaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- FLOW 3D Maritime Brochure WebDocument4 paginiFLOW 3D Maritime Brochure WebBovyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Dynamics Exam - 2008Document5 paginiStructural Dynamics Exam - 2008yusufhargeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SENSORSDocument31 paginiSENSORSKenani SaningaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program: M.A./M.Sc. (Mathematics) M.A./M.Sc. (Previous) Paper Code:MT-05 Mechanics Section - C (Long Answers Questions)Document9 paginiProgram: M.A./M.Sc. (Mathematics) M.A./M.Sc. (Previous) Paper Code:MT-05 Mechanics Section - C (Long Answers Questions)AjeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nichrome Wire Heating Element Design Basics PDFDocument7 paginiNichrome Wire Heating Element Design Basics PDFInfant RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- RF Mosfet BasicsDocument21 paginiRF Mosfet BasicsStephen Dunifer100% (5)