Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using A Customized Matrix Technique - A Case Report
Încărcat de
Muchlis Fauzi ETitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using A Customized Matrix Technique - A Case Report
Încărcat de
Muchlis Fauzi EDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CASE REPORT
Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using a Customized
Matrix Technique - A Case Report
Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi1, Afaf Zia2, Ashok Kumar3, Sharique Alam4
1,2,4Assistant Professor, 3Professor & Chairman, Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Dr. Z.A. Dental College, A.M.U Aligarh
*Corresponding Author:
E-mail: mukhtarandrabi@gmail.com
Abstract:
Correction of midline diastemas without much preparation of the teeth is one of the challenges in clinical esthetic
dentistry. While excellent aesthetics are possible with indirect restorations, there may be unnecessary tooth structure removed in
order to achieve the desired results. This may affect the long term success of the restoration, when dealing with younger patients.
Whenever possible, tooth material augmentation versus tooth material amputation allows for a more conservative treatment
option. Many innovative therapies have been used, varying from restorative procedures to surgery (frenectomies) and
orthodontics. The size of the diastema is an important determinant when selecting the mode of treatment as well as the material
for correction. When a larger space closure is needed, orthodontics may be indicated to allow for a more aesthetic outcome.
When a small diastema with teeth in proper orthodontic alignment, no preparation of the tooth structure is necessary and direct
composite bonding may yield the desired result. The following case report shows a restorative protocol using direct composite
resin build up when addressing the midline diastema.
Keywords: Diastema closure, Direct resin, Customized matrix
Introduction: techniques mentioned; direct composite veneers,
The midline diastema is a space between the indirect composite veneers, porcelain laminate
maxillary central incisors.1 The incidence of veneers, all ceramic crowns, metal ceramic crowns
diastemas varies greatly with age and race.The space and composite crowns.9
can be a normal growth characteristic during the The increased patient demand for minimally
primary and mixed dentition and generally is closed invasive aesthetic procedures and the improved
by the time the maxillary canines erupt.2 In adults, the physical properties of current composite materials has
most common factors in the development of resulted in the extensive utilization of direct bonding
diastemas are tooth-size discrepancies and excessive of composite resin to anterior teeth.10 Contemporary
vertical overlap of the incisors. Other less frequent, composite materials can be handled throughout the
but important, contributing factors are Incisor restorative process to achieve the desired morphology
mesiodistal angulations, generalized spacing, and color of the final restoration. Direct resin build
labiolingual incisor inclination, frenums and up can be a worthy choice to treat diastemas based on
pathological conditions.3 tooth-size discrepancy. However, direct placement of
Maxillary midline diastemas are considered composites for veneering is a laborious process
as esthetic problems by majority of the patients and particularly for multiple teeth. Simpler techniques
thus are an esthetic liability just like crowding or using matrix have been advocated to make the
protrusion of incisors. A study evaluating the procedure less technique sensitive. Use of matrix in
influence of incisal malocclusion on social placing composite simplifies the chair side treatment
attractiveness of young adults in Finland found that procedure. This paper proposes a new simplified
patients with a broad midline diastema were direct composite veneering using a modified matrix
perceived as being less socially successful and of to achieve diastema closure and desirable esthetics in
lower intelligence.4 single visit.
Diastemas can be treated in a multitude of
ways including orthodontic closure, restorative Case Presentation:
therapy, surgical correction or multidisciplinary A 20 year old female patient reported to the
approach depending upon the particular case and the department of conservative dentistry and
etiology of diastema.5,6 6 A carefully developed endodontics, Dr. Z.A Dental College, A.M.U
differential diagnoses allows the practitioner to Aligarh, India with a chief complaint of midline
choose the most effective treatment plan. Diastemas spacing between her upper anterior teeth (fig.1a-b).
based on tooth-size discrepancy are most amenable to The spacing was a social embarrassment to the
restorative solutions.7,8 8 The restorative closure of patient, and was affecting her self-confidence.
diastemas can be achieved by using any of the
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry, Jan-March, 2015;1(1):51-54 51
Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using a Customized…
On examination a space of around 1.5 mm
existed between the maxillary central incisors and
also there was spacing between the right central and
lateral incisor and furthermore all the upper incisors
had relatively less mesiodistal width and improper
contours. After the discussion of the condition with
the patient the following treatment plan was
formulated:
Closure of midline diastema and overall smile build
up using a customized matrix technique.
Fig - 2(a)
Fig – 1(a)
Fig - 2(b)
Fig.2: a) Pre-operative model b) Diagnostic wax up
Fig – 1(b)
Fig.1: Pre-operative view a) intra oral b) frontal
profile
Modified Matrix Fabrication: Fig – 3(a)
Impressions were made and models
prepared. A diagnostic wax up of the models was
performed to modify and finish them to predictable
esthetics for the patient (fig.2a-b). The waxed up
modified models were then duplicated. The
duplicated casts were then placed in a Biostar
machine. The matrix material selected was copyplast
1 mm (Scheu Dental GmbH Am Burgberg 2058642
Iserlohn Germany). Copyplast is a low density
polyethylene (PE-LD) biocompatible material
available in 1mm and 1.5mm round and 0.5mm,
1mm, and 1.5mm square. Copyplast is ideal for
fabricating a temporary matrix. The matrix was
fabricated and trimmed to be used in the patient's Fig – 3(b)
mouth (fig.3a-b). Fig.3: a-b Customized matrix fabrication
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry, Jan-March, 2015;1(1):51-54 52
Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using a Customized…
Restoration:
The teeth were restored with a nano-hybrid
composite, Tetric N Ceram (Ivoclar Vivadent AG
Schaan/Liechtenstein) by a three step etch rinse and
bond technique.
Etching was done for 20 seconds with N-
Etch (Ivoclar Vivadent AG Schaan/Liechtenstein), a
phosphoric acid gel for enamel etching and dentin
conditioning (fig.4a-b).
Bonding was done by Tetric N-Bond
(Ivoclar Vivadent AG Schaan/Liechtenstein), a light-
curing, single-component bonding agent for enamel
and dentin bonding used in combination with the Fig. 5: (a)
total-etch technique.
In the process of resin build up after etching
and bonding, a light-curing, radiopaque nano-hybrid
restorative composite (Tetric N-Ceram, Ivoclar
Vivadent AG Schaan/Liechtenstein) was applied on
the tooth surfaces and then the transparent custom
matrix was placed. The curing was done with a light
emitting diode (LED) curing unit (ART-L3 LED,
Bonart Medical Technology, Inc. CA, USA) through
the transparent matrix for 60 seconds for each tooth
(fig.5a-b). After the curing was complete the matrix
was removed and the extra flash was removed with
fine-grit flame shaped diamonds and finishing Fig. 5: (b)
carbide burs. The final finishing of the restorations Fig.5: (a-b) Composite build up with customized
was done by fine composite finishing discs (Shofu, matrix in place
Inc. Japan). The final restorations resulted in the
diastema closure and as well as overall aesthetic
improvement of the patient, both meeting the
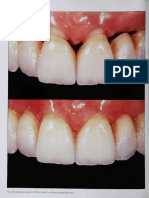
patient’s expectations (fig.6a-b).
Fig. 6: (a)
Fig. 4: (a)
Fig. 6: (b)
Fig.:6(a-b) Final restoration after finishing a) intra
oral view b) frontal profile view
Fig. 4: (b)
Fig.4: (a-b) Etching of the tooth surfaces
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry, Jan-March, 2015;1(1):51-54 53
Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using a Customized…
Discussion: 6. Edwards JG. The diastema, the frenum, the frenectomy: a
With the current trend towards minimally clinical study. Am J Orthod 1977;71(5):489-507.
7. Bolton WA. Clinical application of a tooth-size analysis.
invasive dentistry, direct composite veneering has Am J Orthod 1962;61:504-29
provided clinician with added advantage of achieving 8. Bolton WA. Disharmony in tooth size and its relation to
predictable esthetic results with minimized trauma to the analysis and treatment of malocclusion. Angle Orthod
the teeth.11 1958;28:113-30.
The modern composite restorative materials 9. Bhoyar AG. Esthetic Closure of Diastema by Porcelain
are remarkable with their improved physical and Laminate Veneers: A Case Report. People’s Journal of
Scientific Research 2011;4(1):47-50.
esthetic properties, if manipulated properly they can 10. Dietschi D. Free-hand composite resin restorations: A key
be used to create good quality esthetic restorations to anterior aesthetics. Pract Periodont Aesthet Dent
with sufficient wear resistance providing satisfactory 1995;7(7):15-25.
years of service. They are conservative esthetic 11. Lal SM, Jagadish S. Direct composite veneering
options of restorative dentistry since minimal or no technique producing a smile design with a customised
tooth preparation as compared to ceramics. Direct matrix. J Conserv Dent 2006;9:87-92
12. Shuman IE, Goldstein MB. Anterior aesthetics using
resin veneering can be done by hand sculpting or free direct composite with a custom matrix guide. Dent Today.
hand bonding, but that is a cumbersome process, 2008;27:126-131.
requiring a lot of effort, time and often it is not
possible to veneer multiple teeth in the same
appointment. To simplify composite placement –a
customized matrix for individual patients can be
made which is less technique sensitive and provides
greater opportunity and freedom to deliver optimized
aesthetic goals. The only limitation to the customized
matrix technique can be the need for wax up of the
models and then the accurate fabrication of the
matrix. However, keeping in view the benefits of
using a customized anatomical matrix for direct resin
veneering this extra effort is worth. The advantage of
using a laboratory-fabricated template is, of course,
the freedom from having to sculpt perfect dental
anatomy.12 In the present case report the fabrication
of the customised matrix helped to achieve optimal
aesthetics in a single visit.
Conclusion:
Direct resin veneering can be a valuable
treatment option in treatment of midline diastemas
due to tooth size discrepancies. The utilization of a
customized matrix can greatly improve the control of
the operator over the fine reproduction of anatomic
details and will result in easily achievable aesthetic
restorations. Besides, this can be seen as an economic
treatment option for aesthetic correction of midline
diastemas.
References:
1. Baum AT: The midline diastema. J Oral Med
1966;21:30-39.
2. Broadbent BH: The face of the normal child (diagnosis,
development). Angle Orthod 1937; 7:183-208.
3. Oesterle L.J; Shellhart W.C. Maxillary Midline
Diastemas: a look at the causes. J Am Dent Assoc, 1999;
130:85-94.
4. Kerosuo H, Hausen H, Laine T, Shaw WC. The influence
of incisal malocclusion on the social attractiveness of
young adults in Finland. Eur J Orthod 1995;17:505-12.
5. Dlugokinski MD, Frazier KB, Goldstein RE: Restorative
treatment of Diastema. In: Esthetic in Dentistry
(Vol.2).RE Goldstein, VB Hoywood (Eds.); 2nd Edn.;
BC Decker Inc. London, 2002;703-732.
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry, Jan-March, 2015;1(1):51-54 54
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ortodoncia y ResinaDocument4 paginiOrtodoncia y ResinaJose Salas AdragnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using Putty Index - A CasereportDocument5 paginiClosure of Midline Diastema by Direct Composite Resin Build-Up Using Putty Index - A CasereportIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anterior Esthetic Restorations Using Direct Composite Restoration A Case ReportDocument6 paginiAnterior Esthetic Restorations Using Direct Composite Restoration A Case ReportkinayungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Porcelain Veneers: Techniques and Precautions for Long-Lasting ResultsDocument8 paginiClinical Porcelain Veneers: Techniques and Precautions for Long-Lasting Resultsnobelcyril100% (1)
- Esthetic Conservative Management of Interdental Spaces Using Direct Composite Resin Restorations - A Case ReportDocument4 paginiEsthetic Conservative Management of Interdental Spaces Using Direct Composite Resin Restorations - A Case ReportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Report: Diastema Closure in Anterior Teeth Using A Posterior MatrixDocument7 paginiCase Report: Diastema Closure in Anterior Teeth Using A Posterior MatrixJing XueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restoration of A Large Class IV Fracture Using Direct Composite Resin: A Clinical ReportDocument5 paginiRestoration of A Large Class IV Fracture Using Direct Composite Resin: A Clinical ReportYasmine SalsabilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramic Laminate Veneers: Clinical Procedures With A Multidisciplinary ApproachDocument23 paginiCeramic Laminate Veneers: Clinical Procedures With A Multidisciplinary ApproachBenjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimizing Esthetics With Ceramic Veneers: A Case Report: Jash Mehta, Nimisha Shah, Sankalp Mahajan, Priyanka DesaiDocument5 paginiOptimizing Esthetics With Ceramic Veneers: A Case Report: Jash Mehta, Nimisha Shah, Sankalp Mahajan, Priyanka DesaiBernny GómezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimizing Esthetics With Ceramic Veneers: A Case Report: Jash Mehta, Nimisha Shah, Sankalp Mahajan, Priyanka DesaiDocument5 paginiOptimizing Esthetics With Ceramic Veneers: A Case Report: Jash Mehta, Nimisha Shah, Sankalp Mahajan, Priyanka DesaiBernny GómezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArticleDocument8 paginiArticleMairaMaraviChavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kabbach2018, Diastema ClosuresDocument6 paginiKabbach2018, Diastema ClosurestiberijÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uncut Enamel For Optimizing Bonded Composite Restoration On MultiDocument8 paginiUncut Enamel For Optimizing Bonded Composite Restoration On MultiJack GoldenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restoring Posterior Tooth with Semidirect TechniqueDocument4 paginiRestoring Posterior Tooth with Semidirect Techniquemartariwansyah100% (1)
- E JOD7B PDFDocument3 paginiE JOD7B PDFSaúl HaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Stereolithographic Template For Computer-Assisted Teeth Preparation in Dental Esthetic Ceramic Veneer TreatmentDocument7 paginiA Stereolithographic Template For Computer-Assisted Teeth Preparation in Dental Esthetic Ceramic Veneer TreatmentAndreea CiorneaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screenshot 2023-10-09 at 10.05.37Document7 paginiScreenshot 2023-10-09 at 10.05.37DevanyNataniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recurrent Diastema Closure After Orthodontic Treatment With CeramicDocument4 paginiRecurrent Diastema Closure After Orthodontic Treatment With Ceramicyuana dnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContentServer Asp-6Document9 paginiContentServer Asp-6ValentinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two-Unit Cantilevered Resin-Bonded Fixed Partial Denture As A Substitute For A Prosthodontic-Orthodontic Treatment Plan: A 5-Year Case ReportDocument7 paginiTwo-Unit Cantilevered Resin-Bonded Fixed Partial Denture As A Substitute For A Prosthodontic-Orthodontic Treatment Plan: A 5-Year Case ReportMaika RatriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multidisciplinary Approach for the Closure of Multiple Diastemata With Composite ResinDocument15 paginiMultidisciplinary Approach for the Closure of Multiple Diastemata With Composite ResinCentro Dental IntegralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramic Laminate VeneersDocument23 paginiCeramic Laminate VeneersGerard Andrei Arlovski100% (2)
- Porcelain Laminates Veneers Case ReportDocument6 paginiPorcelain Laminates Veneers Case ReportvodkasaloniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conservative and Esthetic Management of Diastema Closure Using Porcelain Laminate VeneersDocument5 paginiConservative and Esthetic Management of Diastema Closure Using Porcelain Laminate VeneersLuis Alberto Carpio MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resinas Estécticas Inyectables-2216679Document9 paginiResinas Estécticas Inyectables-2216679Roberto PucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qi 52 2 Sampaio p104Document7 paginiQi 52 2 Sampaio p104jcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dentistry: Advanced Research: All Ceramic Bonded Bridge: Clinical Procedure and RequirementsDocument5 paginiDentistry: Advanced Research: All Ceramic Bonded Bridge: Clinical Procedure and RequirementsShintaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caculo Et Al-2013-Journal of Prosthodontics PDFDocument6 paginiCaculo Et Al-2013-Journal of Prosthodontics PDFArchitÎncă nu există evaluări
- RK 1Document5 paginiRK 1dion leonardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramic Laminate Veneers: Clinical Procedures With A Multidisciplinary ApproachDocument24 paginiCeramic Laminate Veneers: Clinical Procedures With A Multidisciplinary ApproachDaniel AtiehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interdisciplinary Approach Using Composite Resin and Ceramic Veneers To Manage An Esthetic ChallengeDocument4 paginiInterdisciplinary Approach Using Composite Resin and Ceramic Veneers To Manage An Esthetic Challengeandres gabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJEDe 2017 - Veneziani - Ceramic Laminate Veneers: Clinical Procedures With A Multidisciplinary ApproachDocument24 paginiIJEDe 2017 - Veneziani - Ceramic Laminate Veneers: Clinical Procedures With A Multidisciplinary ApproachclaudiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roa 2023Document7 paginiRoa 2023victor garciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Easjdom 43 91-96 FTDocument6 paginiEasjdom 43 91-96 FTTuan NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramic Laminate VeneersDocument24 paginiCeramic Laminate Veneershelmuth0207Încă nu există evaluări
- 12 The Changing Face of Aesthetic DentistryDocument8 pagini12 The Changing Face of Aesthetic DentistryOziel Ramirez OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Direct Resilient Relining Material of Denture Base: International Medical Journal (1994) April 2018Document4 paginiNew Direct Resilient Relining Material of Denture Base: International Medical Journal (1994) April 2018lulukzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additive Contour of Porcelain Veneers A Key Element in Enamel PreservationDocument13 paginiAdditive Contour of Porcelain Veneers A Key Element in Enamel PreservationPablo BenitezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 35-2 ZelenDocument5 pagini35-2 Zelenالحب الابديÎncă nu există evaluări
- Researcharticle: Journal of Medical Imaging and Health InformaticsDocument7 paginiResearcharticle: Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informaticskh jhÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Ceramic 5p PDFDocument6 paginiAll Ceramic 5p PDFWiwin Nuril FalahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artigo QDT INGDocument19 paginiArtigo QDT INGJason JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Report Fibre Post & All Ceramic Crown-A Simple Approach To The Perfect SmileDocument3 paginiCase Report Fibre Post & All Ceramic Crown-A Simple Approach To The Perfect SmileAlamMinersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midline Diastema Closure With Partial Laminate Veneers: A Case ReportDocument4 paginiMidline Diastema Closure With Partial Laminate Veneers: A Case ReportAndykaYayanSetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format JurnalDocument14 paginiFormat JurnalAnonymous HtTD0BÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Post-No Core Approach To Restore Severely Damaged Posterior Teeth - An Up To 10-Year Retrospective Study of Documented Endocrown CasesDocument7 paginiNo Post-No Core Approach To Restore Severely Damaged Posterior Teeth - An Up To 10-Year Retrospective Study of Documented Endocrown CasesDiana FreireÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 60 1613455536 1ijdrdjun20211Document8 pagini2 60 1613455536 1ijdrdjun20211TJPRC PublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repairing Worn Dentition: MasterclassDocument5 paginiRepairing Worn Dentition: MasterclassAlfredo RamzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esthetic Rehabilitation of The Smile With No-Prep Porcelain Laminates and Partial Veneers PDFDocument7 paginiEsthetic Rehabilitation of The Smile With No-Prep Porcelain Laminates and Partial Veneers PDFSAMUELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Report: Esthetic Rehabilitation of The Smile With No-Prep Porcelain Laminates and Partial VeneersDocument6 paginiCase Report: Esthetic Rehabilitation of The Smile With No-Prep Porcelain Laminates and Partial VeneersMona CameliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock UpDocument4 paginiMock UpenimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esthetic Restorations-The Putty Matrix TechniqueDocument4 paginiEsthetic Restorations-The Putty Matrix Techniquedentace1Încă nu există evaluări
- Aesthetic Restoration of Anterior Teeth Using The Putty Index Technique - A Case ReportDocument6 paginiAesthetic Restoration of Anterior Teeth Using The Putty Index Technique - A Case ReportUnlikely QuestionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gingival Mask: A Case Report On Enhancing Smiles: ASE EportDocument3 paginiGingival Mask: A Case Report On Enhancing Smiles: ASE EportLouis HutahaeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gingival Mask A Case Report On Enhancing SmilesDocument3 paginiGingival Mask A Case Report On Enhancing SmilesLouis HutahaeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomimetics and Conservative Porcelain Veneer Techniques Guided by The Diagnostic Wax-Up, Diagnostic Matrix, and Diagnostic ProvisionalDocument8 paginiBiomimetics and Conservative Porcelain Veneer Techniques Guided by The Diagnostic Wax-Up, Diagnostic Matrix, and Diagnostic ProvisionalDorobantuMihaiGabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diastema Closure With Direct Composite Architectural Gingival Contouring.20150306122816Document6 paginiDiastema Closure With Direct Composite Architectural Gingival Contouring.20150306122816Rossye MpfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplifed Method For Fabrication of Interim Prosthesis For Maryland Bridge PDFDocument3 paginiSimplifed Method For Fabrication of Interim Prosthesis For Maryland Bridge PDFPanji Adhytama SÎncă nu există evaluări
- TECHNIQUE TO MAKEالصفيحة المعدنية للطقم الكاملDocument7 paginiTECHNIQUE TO MAKEالصفيحة المعدنية للطقم الكاملAbood AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esthetic Oral Rehabilitation with Veneers: A Guide to Treatment Preparation and Clinical ConceptsDe la EverandEsthetic Oral Rehabilitation with Veneers: A Guide to Treatment Preparation and Clinical ConceptsRichard D. TrushkowskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Biomimetic Dental Restoration PDFDocument30 paginiFunctional Biomimetic Dental Restoration PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- GuttaCore - Brochure 2017 Rev2 - ENDocument7 paginiGuttaCore - Brochure 2017 Rev2 - ENMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Resins ReviewDocument6 paginiComposite Resins ReviewDavid ColonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Resins ReviewDocument6 paginiComposite Resins ReviewDavid ColonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neutral Zone Concept and TechniqueDocument6 paginiNeutral Zone Concept and TechniqueJasween KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1143 1412842796 PDFDocument3 pagini1143 1412842796 PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 TelescopicDocument9 pagini1 TelescopicAdmen PasaribuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7491 PDFDocument10 pagini7491 PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schwartz-Carabelli JHE PDFDocument20 paginiSchwartz-Carabelli JHE PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPS Feb14 Utilizing Innovative Matrix Systems WCE 4 0Document5 paginiCPS Feb14 Utilizing Innovative Matrix Systems WCE 4 0Muchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simpleandaethetictreatmentforanteriortoothwear PDFDocument5 paginiSimpleandaethetictreatmentforanteriortoothwear PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- E676 PDFDocument6 paginiE676 PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treze Anos de Acompanhamento Clínico de Restaurações Conservativas de Resina Composta No Fechamento de Diastemas AnterioresDocument5 paginiTreze Anos de Acompanhamento Clínico de Restaurações Conservativas de Resina Composta No Fechamento de Diastemas AnterioresMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1143 1412842796 PDFDocument3 pagini1143 1412842796 PDFMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gendent So16 OwensDocument7 paginiGendent So16 OwensMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Conservative Approach in Restoration With Combination Fixed Partial Denture: Case ReportDocument4 paginiA Conservative Approach in Restoration With Combination Fixed Partial Denture: Case ReportMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gangguan Psychophysiologic Sebagai Salah Satu Penyebab Kelainan Pada Sendi TemporomandibulaDocument44 paginiGangguan Psychophysiologic Sebagai Salah Satu Penyebab Kelainan Pada Sendi TemporomandibulaAnggita Maharani PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.A.,D.D.S.,M.S.D. : Herbert Werdlow, Bethesda, MDDocument7 paginiB.A.,D.D.S.,M.S.D. : Herbert Werdlow, Bethesda, MDMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Print Hitam Putih 1Document15 paginiPrint Hitam Putih 1Muchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 Article 171Document9 pagini2016 Article 171Muchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Louis Hardan Mobile Dental Photography Part I ViaDocument9 paginiLouis Hardan Mobile Dental Photography Part I ViaMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.endo PerioLesionPartIITheTreatmentDocument8 pagini2.endo PerioLesionPartIITheTreatmentMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1111@j 1365-2842 2012 02304 XDocument11 pagini10 1111@j 1365-2842 2012 02304 XMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect Pulp CappingDocument5 paginiIndirect Pulp CappingNaji Z. ArandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- G PulpDocument9 paginiG PulpwindhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological and Clinical Rationale For Vital Pulp TherapyDocument10 paginiBiological and Clinical Rationale For Vital Pulp TherapyMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- z350xt TPPDocument36 paginiz350xt TPPPutri MortezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apd MGZ p3-1-1Document15 paginiApd MGZ p3-1-1Muchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bro TCforSikaCarboDurStructuralStrengtheningSystems UsDocument11 paginiBro TCforSikaCarboDurStructuralStrengtheningSystems UsMuchlis Fauzi EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hess Atechniquetoeliminatesubgingival 2014Document5 paginiHess Atechniquetoeliminatesubgingival 2014wafasahilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amalgams Qs & AsDocument27 paginiAmalgams Qs & Askaran89Încă nu există evaluări
- Dental Implant Failure Diagnosis and ManagementDocument61 paginiDental Implant Failure Diagnosis and ManagementDharshiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toothpaste Consumer SurveyDocument6 paginiToothpaste Consumer SurveyVishakha BhosaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Diagnostic Template ApproachDocument11 paginiThe Diagnostic Template ApproachEugenioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rinchuse 2006Document8 paginiRinchuse 2006jhon HanselÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV DR Shilpa Kalra 2021Document10 paginiCV DR Shilpa Kalra 2021Shilpa Kalra TalujaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articulator - A Literature ReviewDocument7 paginiArticulator - A Literature ReviewAravind KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs Ancorare ScheletalaDocument1 paginăCurs Ancorare Scheletalakevin1678Încă nu există evaluări
- Failure of Amalgam Restoration PDFDocument2 paginiFailure of Amalgam Restoration PDFJaime0% (1)
- Indice de Silness y Loe 1964 PDFDocument15 paginiIndice de Silness y Loe 1964 PDFJossue AriasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atlas of Oral Histology 2nbsped 9788131254844 8131254844Document143 paginiAtlas of Oral Histology 2nbsped 9788131254844 8131254844Dhikra PikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2000 Sandler PJ, Atkinson R, Murray AM. For Four Sixes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop PDFDocument17 pagini2000 Sandler PJ, Atkinson R, Murray AM. For Four Sixes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop PDFplayer osamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partial Veneer Crowns, Inlays and Onlays: DR Shabeel PNDocument32 paginiPartial Veneer Crowns, Inlays and Onlays: DR Shabeel PNPomarida SimboNaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MFD Part 2 Exam Held in JUST, Jordan On 12-2013Document2 paginiMFD Part 2 Exam Held in JUST, Jordan On 12-2013sohaib197Încă nu există evaluări
- All Ceramic Inlay Case ReportDocument7 paginiAll Ceramic Inlay Case ReportAya Ibrahim YassinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asymmetric Deep Bite With A Canted Occlusal Plane - A Case ReportDocument9 paginiAsymmetric Deep Bite With A Canted Occlusal Plane - A Case ReportIacominiGustavoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endo Lecture 1Document17 paginiEndo Lecture 1Nur IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubber DamDocument15 paginiRubber DamSara MahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- KaVo Diagnodent 2095 BrochureDocument2 paginiKaVo Diagnodent 2095 BrochuretopobucciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failures in FPDDocument49 paginiFailures in FPDDhwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Reviews and Abstracts: Begg Orthodontic Theory and TechniqueDocument2 paginiDepartment of Reviews and Abstracts: Begg Orthodontic Theory and TechniqueGokul SivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- James J. Sciubba, DMD, PHD: Dental Implants and The Dry Mouth PatientDocument3 paginiJames J. Sciubba, DMD, PHD: Dental Implants and The Dry Mouth Patientleandrolc01Încă nu există evaluări
- FrasesDocument2 paginiFrasesJhonahan FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BDS Fifth Year & Final Prof. NewDocument4 paginiBDS Fifth Year & Final Prof. NewSumeet SodhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1994 - John Preston - The Golden Proportion RevistedDocument5 pagini1994 - John Preston - The Golden Proportion RevistedJonathan UVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class IV Kennedy Removable Partial DentureDocument23 paginiClass IV Kennedy Removable Partial Denturemarwa100% (1)
- Clinical MCQ Questions Flashcards - Quizlet PDFDocument5 paginiClinical MCQ Questions Flashcards - Quizlet PDFed alkholidyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TX 1 Abs at TX 2 Abs atDocument3 paginiTX 1 Abs at TX 2 Abs atNagita NabilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review in OrthodonticsDocument3 paginiReview in Orthodonticsa3drsabrotÎncă nu există evaluări