Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
A
Încărcat de
Iago GrossDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A
Încărcat de
Iago GrossDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 8 Internal Flow
8-124
Solution A Venturi meter equipped with a water manometer is used to measure to flow rate of air through a duct. For
a specified maximum differential height for the manometer, the maximum mass flow rate of air that can be measured is to
be determined.
Assumptions The flow is steady and incompressible.
Properties The density of air is given to be air = 1.204
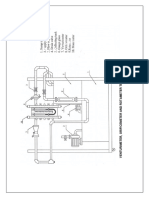
kg/m3. We take the density of water to be w = 1000 kg/m3. 18 cm 6 cm
The discharge coefficient of Venturi meter is given to be Cd
= 0.98.
Analysis The diameter ratio and the throat area of the
meter are h
d / D 6 / 18 0.3333 Water
2 2 2 manometer
A0 d /4 (0.06 m) / 4 0.002827 m
The pressure drop across the Venturi meter can be expressed
as
P P1 P2 ( w f ) gh
Then the flow rate relation for obstruction meters becomes
2( P1 P2 ) 2( w f ) gh 2( w/ air 1) gh
AoCd 4
AoCd 4
AoCd 4
(1 ) f (1 ) 1
Substituting and using h = 0.40 m, the maximum volume flow rate is determined to be
2(1000 / 1.204 1)(9.81 m/s 2 )(0.40 m)
(0.002827 m 2 )( 0.98) 4
0.2250 m 3 / s
1 0.3333
Then the maximum mass flow rate this Venturi meter can measure is
m (1.204 kg/m3 )(0.2250 m 3 /s) 0.2709 kg/s 0.271kg/s
Also, the average flow velocity in the duct is
0.2250 m 3 / s
V 8.84 m/s
Ac D2 / 4 (0.18 m) 2 / 4
Discussion Note that the maximum available differential height limits the flow rates that can be measured with a
manometer.
8-95
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL 13 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and
educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Flowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)Document10 paginiFlowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)meghaparinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venturi MeterDocument4 paginiVenturi Meterprince.patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calibration of Venturimeter: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Document6 paginiCalibration of Venturimeter: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Amisha SharonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Dynamics Student ManualDocument70 paginiFluid Dynamics Student ManualJayachandran SivagurunathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument46 paginiLab ManualAizaz HabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Laboratory: Lab Report SKTG 2741Document20 paginiFluid Mechanics Laboratory: Lab Report SKTG 2741madworldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument4 paginiExperiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice Meterf20221047Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Drip IrrigationDocument5 paginiChapter 3 - Drip IrrigationEng Ahmed abdilahi IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument5 pagini1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterRaghavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex-7 Flow Meter DemonstrationDocument7 paginiEx-7 Flow Meter Demonstrationasefat593Încă nu există evaluări
- Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument6 paginiCalibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterMUTHUKURU VENKATA GOWTHAM REDDYÎncă nu există evaluări
- CABINTOYDocument6 paginiCABINTOYMatt Kristopher DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nittin Bhagat (19ce42)Document4 paginiNittin Bhagat (19ce42)Nittin BhagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate Meters Venturi Meter Nozzle Meter Orifice MeterDocument7 paginiRate Meters Venturi Meter Nozzle Meter Orifice MeterMostafa HamawandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 paginiFalling Head Permeability TestPasindu MalithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction of Pipe 2Document5 paginiFriction of Pipe 2Ranu GamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 12 4 Hydraulics Lab 2Document6 paginiExperiment 12 4 Hydraulics Lab 2Beesam Ramesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Document9 paginiVenturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Somya MaheshwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling Head PermeabilityDocument13 paginiFalling Head PermeabilitySitiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling Head Permeability Lab ReportDocument11 paginiFalling Head Permeability Lab ReportfatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex-7 Flow Meter DemonstrationDocument7 paginiEx-7 Flow Meter Demonstrationasefat593Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer Through Forced Convection Aim:: Dept of MECH, SCCEDocument11 paginiHeat Transfer Through Forced Convection Aim:: Dept of MECH, SCCEAlen SajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam. On Fluid Mechanics - No.2: Tip: You Can Refer To This ExampleDocument1 paginăExam. On Fluid Mechanics - No.2: Tip: You Can Refer To This ExampleNg Lay HoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Measurement Appratus: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 paginiFlow Measurement Appratus: Aim of The ExperimentRavi ParikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- No 2 (A2) - No 3 (2), No 4Document11 paginiNo 2 (A2) - No 3 (2), No 4afi dzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflow Device - ProductionDocument9 paginiInflow Device - Productionmfazaeli40Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mech ManualDocument75 paginiFluid Mech ManualGANESH KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venturi Meter: Experiment No: 1Document4 paginiVenturi Meter: Experiment No: 1anil kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUCLecture 2021 1286891Document13 paginiMUCLecture 2021 1286891khenette.ultrapureÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2Document16 pagini2Zeinab A. ElBhnsawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2Document7 paginiExperiment 2Edyazuan ChannelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportDocument11 paginiFalling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportLee Z QiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of The Coefficient of Discharge of Given Orifice MeterDocument62 paginiDetermination of The Coefficient of Discharge of Given Orifice MeterPandiya RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrugated Plate InterceptorDocument8 paginiCorrugated Plate InterceptorTech Manager100% (1)
- Coulson& Richardson - Cap.10 Gas-Liquid Separation PDFDocument6 paginiCoulson& Richardson - Cap.10 Gas-Liquid Separation PDFHoney TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- H H T T A Al K Ty Permeabili: 3.0 TheoryDocument9 paginiH H T T A Al K Ty Permeabili: 3.0 TheorycrizelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge CoefficientDocument11 paginiDischarge Coefficientsisai12u2420% (2)
- Principle of Working of Grit ChamberDocument11 paginiPrinciple of Working of Grit ChamberAhmed Amedi100% (3)
- Flow MeasurementDocument81 paginiFlow MeasurementmohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venturi MeterDocument4 paginiVenturi MeterSyam RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Venturi ReportDocument8 paginiVenturi Reportstephen kangereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument21 paginiLab Manualhydromec_indiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventury Scrubber Design MethodDocument3 paginiVentury Scrubber Design MethodPukhraj DagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Laminar Case1Document7 paginiFor Laminar Case1Osmanli soonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2: Flowmeter Measurement Apparatus 2.1 THEORY: RotameterDocument6 paginiTopic 2: Flowmeter Measurement Apparatus 2.1 THEORY: Rotameterpelinces_cityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of An Absorption Tower For The Separation of Acrylonitrile in - IndustryDocument9 paginiDesign of An Absorption Tower For The Separation of Acrylonitrile in - IndustryLouell Nikki HipulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fmea ObservationDocument60 paginiFmea Observation20me006Încă nu există evaluări
- Calibration of An Orifice and Venturi Meter PDFDocument20 paginiCalibration of An Orifice and Venturi Meter PDFjamaiiicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas-Liquid SeparatorsDocument27 paginiGas-Liquid Separatorshisoka55Încă nu există evaluări
- LAB MANUAL. EXPERIMENT 2. Calibration of Venturi MeterDocument3 paginiLAB MANUAL. EXPERIMENT 2. Calibration of Venturi Meterjames PrincipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 paginiFalling Head Permeability TestFaeez Zain83% (6)
- FlowLabEOC2e CH02Document3 paginiFlowLabEOC2e CH02tomekzawistowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ffo Lab Prac... 18bt01051Document30 paginiFfo Lab Prac... 18bt01051Sarthak LathiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19bme1137 Thermal Lab Ex 7Document6 pagini19bme1137 Thermal Lab Ex 7Dinesh RéddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Losses in The Pipe Experiment No: 4Document3 paginiFriction Losses in The Pipe Experiment No: 4anil kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fully Report Vs-Group 5Document25 paginiFully Report Vs-Group 5Faradilah Binti Ajma'inÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Manual PDFDocument37 paginiFM Manual PDFSampathkumar MtechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportDe la EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportÎncă nu există evaluări
- X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy XPS, Esca: Photon Inn - Electron OutDocument68 paginiX-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy XPS, Esca: Photon Inn - Electron OutImran KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teran-Virto - Spectra09 - Preliminary Design of Low-Rise Buildings With BRBsDocument27 paginiTeran-Virto - Spectra09 - Preliminary Design of Low-Rise Buildings With BRBsCarlos Ivan Troncoso OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- N30 Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 paginăN30 Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPhO2012 Theoretical ProblemDocument5 paginiIPhO2012 Theoretical ProblemJohnJachersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relatorio ANSYSDocument9 paginiRelatorio ANSYSAnonymous mKxdlpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Power T FTV V2S 200 06-05-5,77m - CornerDocument9 pagini01 Power T FTV V2S 200 06-05-5,77m - CornerPrimož KozlevčarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet Metal RepairDocument72 paginiSheet Metal RepairChirag Dave100% (3)
- The EC Dossier Additives! PDFDocument103 paginiThe EC Dossier Additives! PDFchinmaydabkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection of Electromagnetic Waves From Moving SurfacesDocument2 paginiReflection of Electromagnetic Waves From Moving SurfacesAyien LerioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Lecture HWDocument2 paginiPharmaceutical Manufacturing Lecture HWKimberly Mae MesinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Semiconductor Materials - With NotesDocument57 paginiBasics of Semiconductor Materials - With Notesgourishetty_raveesh100% (1)
- Hot Work Tool Steel: GMTC GMTCDocument2 paginiHot Work Tool Steel: GMTC GMTCpvdangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herts Contact StressDocument4 paginiHerts Contact StressPete SwiftÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diodo MR852Document3 paginiDiodo MR852lorenzobarrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capitulo 6 Moran ShapiroDocument59 paginiCapitulo 6 Moran ShapiroGerman GiraudoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ei 1001 Fibre Optics and Laser Instruments 3 0 0 100Document2 paginiEi 1001 Fibre Optics and Laser Instruments 3 0 0 100Hari KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- #Conclave of Rolling Processes#: Malaviya National Institute of Technology JaipurDocument57 pagini#Conclave of Rolling Processes#: Malaviya National Institute of Technology JaipurAnup MauryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A370-14 Standard Test Methods and Definitions For Mechanical Testing of Steel ProductsDocument7 paginiA370-14 Standard Test Methods and Definitions For Mechanical Testing of Steel ProductsChutha100% (2)
- AUSTROADS List of Test MethodsDocument1 paginăAUSTROADS List of Test Methodsतिप्लोकाची तिरुनचिपल्ली केरकेट्टाÎncă nu există evaluări
- U Value CalculatorDocument1 paginăU Value CalculatorBillieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ragone - Enunciados Problemas (Cap. 1 A 5)Document14 paginiRagone - Enunciados Problemas (Cap. 1 A 5)LucioÎncă nu există evaluări
- AgronomyResearch Vol 13 Number 3Document235 paginiAgronomyResearch Vol 13 Number 3Tetti ManikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.momentum Transfer SummaryDocument5 pagini3.momentum Transfer SummarydoublerainbowatwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glass Colour and Daylight Glare ControlDocument7 paginiGlass Colour and Daylight Glare ControlMaham ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- K12 For Timber Designers' Manuel by MeDocument68 paginiK12 For Timber Designers' Manuel by MesajeeralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clay Water SystemDocument75 paginiClay Water SystemLaxman KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strain Gauge General Information PDFDocument4 paginiStrain Gauge General Information PDFPom tancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Type Quenched and Tempered Steel Steel Grade: 40Cr (YB6-71) Property Entry SummaryDocument5 paginiSteel Type Quenched and Tempered Steel Steel Grade: 40Cr (YB6-71) Property Entry SummarySon NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bimetal ThermometerDocument3 paginiBimetal ThermometerfrenieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Cracks in ConcreteDocument116 pagini4 Cracks in ConcreteJayel Guinto100% (2)