Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Jurnal Kritisi PDF
Încărcat de
Rahmiani MalikTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Jurnal Kritisi PDF
Încărcat de
Rahmiani MalikDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
International Surgery Journal
Edakkepuram U et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3141-3145
http://www.ijsurgery.com pISSN 2349-3305 | eISSN 2349-2902
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173903
Original Research Article
A prospective cohort study of hypoalbuminemia as risk factor of wound
healing in diabetic foot: a study from tertiary hospital in south India
Unnikrishnan Edakkepuram*, Sheeja P. C., Ellikunnel Vithon Gopi
Department of General Surgery, Kozhikode Government Medical College, Kozhikode, Kerala, India
Received: 13 June 2017
Accepted: 08 July 2017
*Correspondence:
Dr. Unnikrishnan Edakkepuram,
E-mail: unniep@yahoo.com
Copyright: © the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under
the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial
use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
Background: Diabetic foot ulcers is a major complication of diabetes mellitus, and precedes >80% of all diabetes
related lower leg amputations. One of the risk factors in non-healing diabetic ulcer is low serum albumin level. The
objectives of this study were to study the effect of low serum albumin level in patients with diabetic foot ulcer and to
study the factors affecting wound healing in diabetic ulcer.
Methods: Prospective cohort study in a tertiary hospital.
Results: The mean age among study was 57.8 out of which 68.3% were males and 31.7% were females. 55% patients
presented with slough over ulcer, 29.2% patients presented with healthy granulation and 15.8% patients presented
with extensive wound infection. Among study group 50% patients had good glycaemic control and 50% patients had
poor glycaemic control.
Conclusions: Low serum albumin level is one of the attributable risk factor of non-healing ulcers in diabetic foot.
Poor glycaemic status is also a risk factor for non-healing ulcer.
Keywords: Diabetic foot ulcer, Factors affecting wound healing, Normal wound healing pattern
INTRODUCTION Many of the risk factors for foot ulcer are also
predisposing factors for amputation, because ulcers are
Foot disorders such as ulceration, infection, and gangrene primary causes leading to amputation.7 An adequate
are the leading causes of hospitalization in patients with description of ulcer characteristics, such as size, depth,
diabetes mellitus.1,2 Approximately 15 to 20 percent of appearance, and location, also provides for the mapping
the estimated 16 million persons in the United States with of progress during treatment.8 Failure to perceive the
diabetes mellitus will be hospitalized with a foot pressure of a 10-g monofilament is a proven indicator of
complication at some time during the course of their peripheral sensory neuropathy and loss of protective
disease.3 sensation.9,10 A positive probe-to-bone finding has a high
predictive value for osteomyelitis.11
The diabetic foot and its sequelae account for billions of
dollars in direct medical expenditures, as well as lengthy Failure to diagnose underlying osteomyelitis often results
hospital stays and periods of disability.3,4 Approximately in failure of wound healing. The existence of odor and
85 percent of all diabetes-related lower-extremity exudate, and the presence and extent of cellulitis must be
amputations are preceded by foot ulcers.5,6 noted.12
International Surgery Journal | September 2017 | Vol 4 | Issue 9 Page 3141
Edakkepuram U et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3141-3145
METHODS evaluated, initial wound status assessed, detected.
Hypoalbuminemia corrected with high protein diet and
The present study was a Prospective cohort study done in supplementations and wound status after 3 months
diabetic foot ulcer patients admitted in General surgery reassessed. During hospitalisation wound managed with
Department, Government Medical College, Calicut from daily cleaning and dressings, slough cutting and extensive
January 2015-June 2016. Study was carried out in 120 debridement.
patients.
Statistical analysis
Inclusion criteria
Data was entered in Excel and the analysis was
All diabetic foot ulcer patients above the age of 35. performed on SPSS software. A P value of <0.05 was
accepted as significant.
Exclusion criteria
RESULTS
Patients with chronic liver diseases, chronic renal
diseases, underlying osteomyelitis, associated peripheral Total no of study group: 120. Total no of male patients:
vascular diseases. 82 (68.3%). Total no of female patients: 38 (31.7%).
Among study group 35.8% presented with ulcer over
Patients admitted, in Government Medical College under dorsal aspect of foot 22.5% patients presented with ulcer
General Surgery Department with diabetic foot ulcers over plantar aspect of foot 21.7% presented with ulcer
were selected, and followed up for a minimum period of over toe. 9.8% presented with ulcer over lateral aspect of
3months. Serum albumin levels and diabetes status foot.
Table 1: Pattern of procedure done.
Frequency Percent Valid percent Cumulative percent
Valid Daily cleaning and dressing 39 32.5 32.5 32.5
Slough cutting 62 51.7 51.7 84.2
Extensive wound debridement 19 15.8 15.8 100.0
Total 120 100.0 100.0
Table 2: Wound status after 3rd month.
Frequency Percent Valid percent Cumulative percent
Healed/healing 61 50.8 50.8 50.8
Not healed 35 29.2 29.2 80
Valid Amputated 17 14.2 14.2 94.2
Lost follow-up 7 5.8 5.8 100
Total 120 100 100
Table 3: Showing correlation between diabetes status and wound status Crosstab.
Wound status after 3 months
Total
1 2 3 4
Count 54 2 1 3 60
% within diabetes status 90.0% 3.3% 1.7% 5.0% 100.0%
Count 7 33 16 4 60
% within diabetes status 11.7% 55.0% 26.7% 6.7% 100.0%
Count 61 35 17 7 120
% within diabetes status 50.8% 29.2% 14.2% 5.8% 100.0%
Among study group 50% presented with controlled admission, after one month and after 3rd month of
diabetes 50% presented with uncontrolled diabetes. follow-up respectively. Among study group 55%
Among study group the mean age was 57.8 and the mean presented with slough over ulcer initially 15.8%
serum albumin level was 2.99, 3.1, 3.17 at the time of presented with extensive infection, 29.2% patients
International Surgery Journal | September 2017 | Vol 4 | Issue 9 Page 3142
Edakkepuram U et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3141-3145
presented with healthy granulation. Among study group
50.8% wound healed after 3 months 29.2% wound not
healed after 3rd month 14.2% patients underwent
amputation 5.8% lost follow up. 90% wound healed in
patients with controlled diabetes, 2% wound not healed in
patients with controlled diabetes. 55% wound not healed
in patients with uncontrolled diabetes. Only 11.7%
wound healed in patients with uncontrolled diabetes. 3%
patients lost follow up. 1.7% patients undergone
amputation. Only 25% wound healed in patients with low
serum albumin level. 47.2% wound not healed in patients
with low serum albumin level. 23.6% patients underwent
amputation among low serum albumin level group.
Figure 4: Initial status of wound.
No amputated patients in group 14.2% lost follow-up in
group 18.3% lost follow-up in group 2. Chi-square value
of 0.000 is significant. So, the study is significant.
It states that hypoalbuminemia is a risk factor of wound
healing in diabetic foot ulcers. Considering the site of
ulcer, ulcer over toes showed better wound healing than
Figure 1: Gender distribution among other sites (61.5%).
study group.
DISCUSSION
During the study period, each patient’s diabetes status
also followed up. Patients above the age of 35 were
included in the study. The mean age among study was
57.8. Out of which 68.3% were males and 31.7% were
females. Among study group 55% patients presented with
slough over ulcer, 29.2% patients presented with healthy
granulation and 15.8% patients presented with extensive
wound infection. Patients were followed up every 2
weeks.
During these times wound managed with daily dressing,
slough cutting, and extensive debridement according to
the wound status. Detected hypoalbuminemia corrected
Figure 2: Distribution of ulcer site. with high protein diet and nutritional supplements. Serum
albumin levels assessed at the end of 1st month and after
3rd month.
Among study group 50% patients had good glycemic
control and 50% patients had poor glycemic control. The
criteria for wound to be considered as healed is that,
complete skin over the initial ulcer. The definition for
healing wound is considered as that, wounds covered
with granulation tissues at the end of 3rd month. coverage
It shows that 50.8% wound healed/healing at the end of
3rd month, 29.2% wound not healed properly, 14.2%
patients underwent amputation and 5.8% patients lose
follow up. Among group one, that is patients with initial
hypoalbuminemia, only 25% wound is healed and 47.2%
wound not healed at the end of 3rd month.
Figure 3: Diabetes status among study group.
International Surgery Journal | September 2017 | Vol 4 | Issue 9 Page 3143
Edakkepuram U et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3141-3145
Whereas 89.6% wound healed in group 2, is patients with underlying osteomyelitis often results in failure of wound
normal albumin levels at the time of admission. 23.6% healing. The existence of odor and exudate, and the
patients underwent amputation in patients with low serum presence and extent of cellulitis must be noted.12
albumin group.
CONCLUSION
This states that hypoalbuminemia is a major contributing
factor in wound healing. If considering the glycemic Diabetic foot ulcer is one of the major complication of
control and wound healing pattern, in well controlled diabetes mellitus, it is a major component of diabetic
diabetic patients 90% of wound healed where as in foot. The major increase in morbidity and mortality
patients with uncontrolled diabetes only 11.7% of wound among diabetic patient is considered to be due to micro
healing observed. 55% wound not healed in uncontrolled and macrovascular complications, that lead to failure of
diabetes. The healing pattern is uniform in both males normal wound healing process. Low serum albumin level
and females. Considering the site of ulcer as shown in is one of the attributable risk factor of non-healing ulcers
61.5% wound healing observed over toe ulcers than other in diabetic foot. Poor glycemic status is also a risk factor
sites. for non-healing ulcer.
The study conducted among hospitalised patients in Funding: No funding sources
Calicut Medical College with diabetic foot ulcers. Conflict of interest: None declared
Analysis done in 120 patients for a period of 3 months Ethical approval: The study was approved by the
prospectively. The total group was further divided into institutional ethics committee
cases and control, with reference to serum albumin level
at the time of admission. Reference serum values ranges REFERENCES
from 3.5-4.5. Patients with normal range of serum
albumin were assigned as group 2 and patients with low 1. Boulton AJ. The diabetic foot: a global view.
serum albumin level were assigned as group 1. Patients Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2000;16:S2-5.
presented with low serum albumin due to non-diabetic 2. Frykberg RG. Diabetic foot ulcers: current concepts.
conditions like chronic liver diseases, chronic kidney J Foot Ankle Surg. 1998;37:440–6.
diseases were excluded from the study group. 3. Reiber GE, Boyko EJ, Smith DG. Lower extremity
foot ulcers and amputations in diabetes. In: National
The ulcers were managed with daily cleaning and Diabetes Data Group (U.S.). Diabetes in America.
dressing, slough cutting and extensive wound 2d ed. Bethesda, Md.: National Institutes of Health,
debridement in patients with healthy granulation, with National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and
slough and extensive infection respectively. Each patient Kidney Diseases. NIH publication. 1995;95-1468.
was followed up for a minimum period of 3 months. 4. Frykberg RG, Armstrong DG, Giurini J, Edwards A,
Serum albumin level monitored at 1st month and 3rd Kravette M, Kravitz S, et al. Diabetic foot disorders:
month. The total duration of study was one and a half a clinical practice guideline. American college of
years from January 2015 to June 2016. Hospitalised cases foot and ankle surgeons. J Foot Ankle Surg.
of diabetic ulcer patients from Government Medical 2000;39(5):S1-60.
College, Calicut, above the age of 35 were included in the 5. Pecoraro RE, Reiber GE, Burgess EM. Pathways to
study. The diabetes status also monitored during the diabetic limb amputation: basis for prevention.
follow- up. The wound status was assessed at the end of Diabetes Care. 1990;13:513-21.
1st month and at 3rd month. 6. American Diabetes Association. Consensus
Development conference on diabetic foot. Wound
For patients presented with initial low serum albumin Care: 7-8 April 1999. Boston, Massachusetts.
levels, high protein diet and nutritional supplementations Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1354-60.
given and further followed up. The study findings were 7. Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Stensel V, Forsberg RC,
tabulated in MS Excel format and analysed using SPSS Davignon DR, Smith DG. A prospective study of
software. After analysis, a significant difference noticed risk factors for diabetic foot ulcer: the Seattle
among the two groups in terms of wound healing, which diabetic foot study. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1036-
is proved by a p value of 0.000 which is significant. This 42.
states that low serum albumin is a risk factor in diabetic 8. Reiber GE, Vileikyte L, Boyko EJ, del Aguila M,
wound healing. Poor glycaemic control is also a risk Smith DG, Lavery LA, et al. Causal pathways for
factor of wound healing in diabetic foot. An adequate incident lower-extremity ulcers in patients with
description of ulcer characteristics, such as size, depth, diabetes from two settings. Diabetes Care.
appearance, and location, also provides for the mapping 1999;22:157-62.
of progress during treatment.8 Failure to perceive the 9. Armstrong DG, Lavery LA. Diabetic foot ulcers:
pressure of a 10-g monofilament is a proven indicator of prevention, diagnosis and classification. Am Fam
peripheral sensory neuropathy and loss of protective Phy. 1998;57:1325-32.
sensation.9,10 A positive probe-to-bone finding has a high 10. McNeely MJ, Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Stensel VL,
predictive value for osteomyelitis.11 Failure to diagnose Reiber GE, Smith DG, et al. The independent
International Surgery Journal | September 2017 | Vol 4 | Issue 9 Page 3144
Edakkepuram U et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3141-3145
contributions of diabetic neuropathy and mellitus. New York: Churchill Livingstone;
vasculopathy in foot ulceration. How great are the 1991:151-95.
risks? Diabetes Care. 1995;18:216-9.
11. Grayson ML, Gibbons GW, Balogh K, Levin E, Cite this article as: Edakkepuram U, Sheeja PC,
Karchmer AW. Probing to bone in infected pedal Gopi EV. A prospective cohort study of
ulcers: a clinical sign of underlying osteomyelitis in hypoalbuminemia as risk factor of wound healing in
diabetic patients. JAMA. 1995;273:721-3. diabetic foot: a study from tertiary hospital in south
12. Frykberg RG. Diabetic foot ulcerations. In: India. Int Surg J 2017;4:3141-5.
Frykberg RG, ed. The high risk foot in diabetes
International Surgery Journal | September 2017 | Vol 4 | Issue 9 Page 3145
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Nur 1210 Maternal Module #2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client (Hemorrhagic)Document21 paginiNur 1210 Maternal Module #2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client (Hemorrhagic)aaaaa100% (1)
- Ketoconazole Cream Clinical ParticularsDocument2 paginiKetoconazole Cream Clinical ParticularsJai MurugeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstrak IsicamDocument22 paginiAbstrak IsicambgusjklÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMC Clinical Recalls 2019 (COMPLETE TILL JUL) - SponsoredDocument46 paginiAMC Clinical Recalls 2019 (COMPLETE TILL JUL) - SponsoredIgor Dias67% (3)
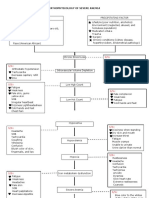
- Pathophysiology of Severe AnemiaDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Severe AnemiaChrizley Shawn DeroniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug PepcidDocument2 paginiDrug PepcidSrkocher0% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing QuestionsDocument7 paginiMedical Surgical Nursing Questionseloisa mae gementizaÎncă nu există evaluări
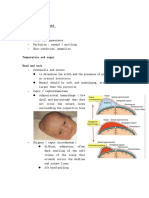
- Newborn AssessmentDocument6 paginiNewborn AssessmentAyuni Salleh100% (1)
- Goactive Brochure PDFDocument2 paginiGoactive Brochure PDFsumitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bariatric SurgeryDocument71 paginiBariatric Surgeryanalourdes87Încă nu există evaluări
- Shin LuluDocument2 paginiShin LuluEka HimawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Burden Disease Death Estimates Sex 2008Document8 paginiGlobal Burden Disease Death Estimates Sex 2008Maria Magdalena DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endometrial Cancer LDocument26 paginiEndometrial Cancer Lapi-19916399Încă nu există evaluări
- Some Imp Oneliner From VolumesDocument16 paginiSome Imp Oneliner From VolumesTejas KaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 - NeoplasiaDocument23 paginiChapter 7 - NeoplasiaAgnieszka WisniewskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wilson Disease - Treatment and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument13 paginiWilson Disease - Treatment and Prognosis - UpToDatericanoy191Încă nu există evaluări
- Short Notes and Short Cases in Ophthalmology PDFDocument108 paginiShort Notes and Short Cases in Ophthalmology PDFInna Bujor100% (1)
- August 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Document6 paginiAugust 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Joanna Carel Lopez100% (3)
- The Amyloid Beta Peptide A Chemist S Perspective. Role in Alzheimer's and FibrillizationDocument46 paginiThe Amyloid Beta Peptide A Chemist S Perspective. Role in Alzheimer's and FibrillizationAdrianEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Oral Pathology 1Document32 paginiIntroduction To Oral Pathology 1Hoor M TahanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver DownloadDocument33 paginiTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver Downloadaliciarodriguezswrtpyjemk100% (24)
- Medical Israeli Syllabus For Internal Medicine For Exam LicenseDocument4 paginiMedical Israeli Syllabus For Internal Medicine For Exam Licensemohammadeid0% (2)
- عبد الرحمن خالد الزميلي Assighment Of Dental Surgery /Principle of routine exodontiaDocument20 paginiعبد الرحمن خالد الزميلي Assighment Of Dental Surgery /Principle of routine exodontiaعبد الرحمن خالد الزميليÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mefenamic AcidDocument5 paginiMefenamic AcidBeeBee SethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Temple 1Document8 paginiStudy Temple 1raunak100% (1)
- Early Diagnosis of NeoplasisDocument25 paginiEarly Diagnosis of NeoplasisDanielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Definitions: PyelonephritisDocument4 paginiUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) Definitions: PyelonephritisSanthosh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ureteroureterostomy For Reflux Duplex SystemsDocument5 paginiUreteroureterostomy For Reflux Duplex Systemsjithin rÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 paginiDrug Study: Far Eastern UniversityChoy DacanayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ananya Deb - 18IUT0290004Document26 paginiAnanya Deb - 18IUT0290004subankar NagÎncă nu există evaluări