Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
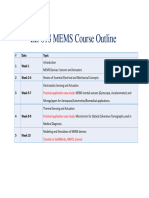
Easwari Engineering College Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering LESSON PLAN (June 2014 - November 2014)
Încărcat de
Divya MohanDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Easwari Engineering College Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering LESSON PLAN (June 2014 - November 2014)
Încărcat de
Divya MohanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Format No.
: LP 01
Issue No. : 01
Issue Date : 05.05.06
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
LESSON PLAN (June 2014– November 2014)
Subject Code : ET 7014 Degree / Branch : M.E / CIE
Subject Name :Application Of MEMS Technology Year/Sem : II / III
Total No. of Hrs given in syllabus : 45
Faculty : Mrs.R.Praveena Tutorial : NIL
Lecture : 45
Practical : NIL
Grand Total : 45
OBJECTIVES:
To give an introductory knowledge about the properties of materials, microstructure and
fabrication methods.
To give basic knowledge about the design and modeling of Electrostatic sensors and actuators.
To give basic knowledge about the design and modeling of Thermal sensors and actuators.
To provide basic knowledge about the fundamentals of piezoelectric sensors and actuators.
To give exposure to MEMS applications and NEMS devices.
Sl. Topic No. of
Text/ Page Nos.
No. Hrs
Ref.
Books
Unit I: MEMS: Micro-Fabrication, materials and Electromechanical concepts
Objective: To give an introductory knowledge about micro fabrication.
To provide basic information about the silicon and other material based
fabrication processes.
To give adequate knowledge about the Electrical and Mechanical concepts.
1. Overview of micro fabrication 1 R1 47-63
Silicon and other material based fabrication
2. 1 R1 63-72
processes
Conductivity of semiconductors – semiconductor
3. materials, charge carrier concentration, conductivity 1 R1 85-92
and resistivity
4. Crystal planes and orientation 1 R1 93-95
Stress and Strain – Definition, Internal force
5. 1 R1 96-105
analysis, stress strain relation
Flexural beam bending analysis – Longitudinal strain
6. 1 R1 107-114
under pure bending, Deflection of beam
7. Torsional deflections 1 R1 118-119
8. Intrinsic stress 1 R1 120-123
Resonant frequency and quality factor
9. 1 R1 125-128
Outcome: Students will be able to understand the basic concepts of MEMS and its
fabrication methods.
Unit II: Electrostatic Sensors And Actuation
Objective: To gain adequate knowledge about electrostatic principle.
To know how to design and fabricate electrostatic sensor and actuator.
To provide more information about the application of sensor and actuators.
Principle and material of electrostatic sensors and
10. actuators 2 R1 141-143
Design and fabrication of parallel plate capacitors as
11. 2 R1 143-145
electrostatic sensors
Design and fabrication of parallel plate capacitors as
12. 1 R1 170-171
electrostatic actuators
Equilibrium position of electrostatic actuator under
13. 1 R1 146-148
bias
14. Pull – In effect of parallel plate actuators 1 R1 149-151
Applications – Inertia sensor – Parallel plate
15. 1 R1 154-158
Capacitance accelerometer
Applications – Pressure sensor – Membrane Parallel
16. 1 R1 160-163
plate pressure sensor
Outcome: Students can practically implement the design and fabrication of
electrostatic sensors and actuators.
Unit III: Thermal Sensing And Actuation
Objective: To give an introductory knowledge about Computer Control Systems.
To provide basic information about the design and fabrication of
thermocouples.
To gain basic knowledge on thermal sensors and actuators.
To provide more information about the application of sensor and actuators.
Principle and material – Thermal sensors and
17. actuators based on thermal transfer and thermal 1 R1 190-198
expansion
18. Design and fabrication of thermal couples 1 R1 207-210
Thermal bimorph sensors – Principle and thermal
19. actuators with a single material 2 R1 198-206
20. Thermal resistor sensors 1 R1 210-212
Applications – Inertia sensor – Accelerometer based
21. on thermal transfer principle 2 R1 213-214
Applications- Infrared sensor- Bimetallic structure
22. 2 R1 228-230
for Infrared sensing
Outcome: Students can practically implement the design and fabrication of Thermal
sensors and actuators.
Unit IV: Piezoelectric Sensing And Actuation
Objective: To give an introductory knowledge about piezoelectric effect.
To provide basic information about the properties of piezoelectric materials.
To give adequate knowledge about modeling of piezoelectric actuator.
To gain knowledge about the applications of piezoelectric sensors and
actuators.
Piezoelectric effect – direct effect and Inverse effect
23. 1 R1 283-287
of piezoelectriciry
24. Cantilever piezo electric actuator model 1 R1 287-288
Properties of piezoelectric materials – Quartz, PZT,
25. 1 R1 290-298
PVDF, ZnO and other materials
Applications – Inertia sensors – Cantilever
26. piezoelectric accelerometer 2 R1 299-300
Applications – Acoustic sensors – PZT piezoelectric
27. 2 R1 303-304
acoustic sensor
Applications – Flow sensor – Piezoelectric flow rate
28. 2 R1 307-309
sensor
Outcome: Students can practically implement the design and fabrication of Thermal
sensors and actuators.
Unit V: Case Studies
Objective: To understand the basic concepts of piezoresistive sensors and magnetic
actuators.
To gain basic information about the microfluidics applications.
To provide adequate knowledge about the medical applications.
To gain knowledge about the optical MEMS and NEMS devices.
Piezoresistive sensors – materials, Application- 248-252
29. 2 R1
Metal piezoresistive flow rate sensor 274-275
Magnetic actuation – magnetization, Magnetic 317-321
30. 1 R1
motor 332-334
Micro fluidics applications – Gas chromatography
31. 1 R1 506-507
channels
Micro fluidics applications – Electrophoresis in
32. microchannels 1 R1 507-509
33. Medical applications – Blood Pressure sensor 1 R1 526-530
Optical MEMS – Interferometric Accelerometer,
34. Cantilever with optical interference position sensing 2 R1 350-355
35. NEMS Devices 1 Notes
Outcome: Students will be able to understand the applications of MEMS in all fields.
Total Hours 45
Content beyond syllabus
S.
TOPIC
No
1. Unit I – Most commonly encountered Materials used in MEMS.
2. Unit II – Tunneling Accelerometer
3. Unit III – Polymer MEMS
4. Unit IV – MAP sensor
5. Unit V – Bio-MEMS
Assignments
S. Date of Date of Return of
TOPIC
No Announcement Submission script
1. Questions from Unit I & Unit II 21.07.2014 28.07.2014 30.07.2014
2. Questions from Unit III & Unit IV 20.08.2014 27.08.2014 01.09.2014
3. Questions from Unit V 22.09.2014 29.09.2014 30.09.2014
REFERENCES:
1. Chang Liu, “Foundations of MEMS”, Pearson International Edition, 2006.
2. Marc Madou , “Fundamentals of microfabrication”,CRC Press, 1997.
3. Boston , “Micromachined Transducers Sourcebook”,WCB McGraw Hill, 1998.
4. M.H.Bao “Micromechanical transducers :Pressure sensors, accelerometers and
gyroscopes”, Elsevier, Newyork, 2000.
5. P. RaiChoudry“ MEMS and MOEMS Technology and Applications”, PHI, 2012.
6. Stephen D. Senturia, “ Microsystem Design”, Springer International Edition, 2011.
Prepared by: Approved by:
(R.Praveena) ( HOD /EIE)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Academic Course DescriptionDocument6 paginiAcademic Course DescriptionRajalearn2 Ramlearn2Încă nu există evaluări
- Ann ADocument3 paginiAnn AHassan RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sir Parshurambhau College, Pune (Autonomous) : Shikshana Prasaraka Mandali'sDocument13 paginiSir Parshurambhau College, Pune (Autonomous) : Shikshana Prasaraka Mandali'sprashantsheetalÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE F111 Electrical Sciences Handout I-Sem - 2023 - 2024Document3 paginiEEE F111 Electrical Sciences Handout I-Sem - 2023 - 2024KAUSHIK KADIUMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Pulses - Lasers - Measuring TechniquesDe la EverandOptical Pulses - Lasers - Measuring TechniquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics Notes For Marine and EeeDocument167 paginiBasic Electronics Notes For Marine and EeeeswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPAs - and - CMOS Readout Techniques For Infrared Imaging Systems PDFDocument12 paginiFPAs - and - CMOS Readout Techniques For Infrared Imaging Systems PDFOmkar KatkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.bee022 Fibre Optics and Laser InstrumentationDocument7 pagini4.bee022 Fibre Optics and Laser InstrumentationSIVAPRAKASH IT2047Încă nu există evaluări
- Eee101and-Its-Applications TH 1.0 47 Eee1018Document2 paginiEee101and-Its-Applications TH 1.0 47 Eee1018Satbir singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOOK Temperature SensingDocument89 paginiBOOK Temperature SensingHugh cab100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: Bachelor of EngineeringDocument3 paginiGujarat Technological University: Bachelor of EngineeringMansi PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bee CopDocument30 paginiBee CopARIVOLI SUNDARAMURTHYÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDC Diploma SyllabusDocument27 paginiEDC Diploma SyllabusParvinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Measurement Systems & Sensors: An Introduction: LectureDocument20 paginiAdvanced Measurement Systems & Sensors: An Introduction: LectureAbdul WaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opto PrintDocument371 paginiOpto Printealleti vikramÎncă nu există evaluări
- First-Stage AvDocument19 paginiFirst-Stage AvAbdullah A. JabberÎncă nu există evaluări
- EIITDocument3 paginiEIITJOSE PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course OutlineDocument2 paginiCourse Outlinesharfudinawan12Încă nu există evaluări
- EC8701-Antennas and Microwave Engineering Department of ECE 2021-2022Document39 paginiEC8701-Antennas and Microwave Engineering Department of ECE 2021-2022rubanraj r (RA1811201010009)Încă nu există evaluări
- Model Curriculum: Assistant Electrician (NSQF Level - 3)Document23 paginiModel Curriculum: Assistant Electrician (NSQF Level - 3)Gourav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC Rev CON-Q0602 Assistant-Electrician 20-07-2017 PDFDocument23 paginiMC Rev CON-Q0602 Assistant-Electrician 20-07-2017 PDFGourav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eee1018 Nanotechnology-Fundamentals-And-Its-Applications TH 1.0 47 Eee1018 PDFDocument2 paginiEee1018 Nanotechnology-Fundamentals-And-Its-Applications TH 1.0 47 Eee1018 PDFNathan ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question BankDocument37 paginiQuestion BankLiu Li100% (1)
- Bmtf183t60 Sensors and Actuators 1Document158 paginiBmtf183t60 Sensors and Actuators 1Ganagadhar CHÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3311101electronic Components & PracticeDocument5 pagini3311101electronic Components & PracticeDarshit KotadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15ecc18 - Sensors and ActuatorsDocument1 pagină15ecc18 - Sensors and Actuatorskamarajme2006Încă nu există evaluări
- FINAL MW LAB Manual 2019Document89 paginiFINAL MW LAB Manual 2019op thakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mems QB 2016Document8 paginiMems QB 2016Manoj Kumar PasupathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani CampusDocument4 paginiBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani CampusAryan JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transient Electromagnetic-Thermal Nondestructive Testing: Pulsed Eddy Current and Transient Eddy Current ThermographyDe la EverandTransient Electromagnetic-Thermal Nondestructive Testing: Pulsed Eddy Current and Transient Eddy Current ThermographyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- MsmeDocument3 paginiMsmeJigneshkumar PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- R18 4-2 B.Tech - OpenElectivesDocument4 paginiR18 4-2 B.Tech - OpenElectives20WH1A0557 KASHETTY DEEKSHITHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Analysis Lab (FEA) 17MEL68: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument52 paginiModelling and Analysis Lab (FEA) 17MEL68: Department of Mechanical EngineeringSarath KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece2034 Flexible-Electronics-And-Sensors TH 1.0 55 Ece2034 PDFDocument2 paginiEce2034 Flexible-Electronics-And-Sensors TH 1.0 55 Ece2034 PDFRithyshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Quantum Electronics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyDe la EverandIntroduction to Quantum Electronics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC I Electronics Syllabus Updated CBCSDocument10 paginiBSC I Electronics Syllabus Updated CBCSchandrakant chaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karim2015-Inicio Tesis1Document10 paginiKarim2015-Inicio Tesis1Maria Alejandra Villanueva LlapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microwave De-embedding: From Theory to ApplicationsDe la EverandMicrowave De-embedding: From Theory to ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece1005 Sensors-And-Instrumentation Eth 2.0 39 Ece1005Document2 paginiEce1005 Sensors-And-Instrumentation Eth 2.0 39 Ece1005vamshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhyDocument8 paginiPhyuser101Încă nu există evaluări
- Department of Collegiate and Technical EducationDocument14 paginiDepartment of Collegiate and Technical EducationHarsha Samagara100% (1)
- Eee f111 Electrical Sciences1Document3 paginiEee f111 Electrical Sciences1aryan mittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22PH101-CE-Unit 1. WAVES AND OSCILLATIONSDocument58 pagini22PH101-CE-Unit 1. WAVES AND OSCILLATIONSajay amuthaprianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syl Lab I ElectricalDocument141 paginiSyl Lab I ElectricalshamikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sem 4Document13 paginiSem 4Prateek SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee: Electronics and Computer EngineeringDocument2 paginiIndian Institute of Technology Roorkee: Electronics and Computer EngineeringTamizh E STÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Out-LineDocument24 paginiCourse Out-LinemandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap-I R-19 SyllabusDocument6 paginiAp-I R-19 SyllabusTejasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectricalElectronics Course Obj N OtcomesDocument6 paginiElectricalElectronics Course Obj N OtcomeskhaleqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 Phy 12Document3 pagini21 Phy 12Siddartha DuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 - Ee231 - Ee 231Document5 pagini45 - Ee231 - Ee 231ahmed kamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics LabDocument50 paginiPhysics Labsplay3159Încă nu există evaluări
- Networks and Simulation LabDocument66 paginiNetworks and Simulation LabLOKENDRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual - EEE18R171Document86 paginiLab Manual - EEE18R171K.V. PrabhasÎncă nu există evaluări
- MWE Syllabus PDFDocument4 paginiMWE Syllabus PDFkhyatichavda100% (1)
- Microwave System Engineering PrinciplesDe la EverandMicrowave System Engineering PrinciplesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Climate ZonesDocument2 paginiClimate Zonesapi-308047560Încă nu există evaluări
- Modern Pulley AnalysisDocument16 paginiModern Pulley AnalysisMariappan ArumugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Gas LawDocument52 paginiChapter 1 - Gas LawLolindah ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV 20.04.2013Document7 paginiCV 20.04.2013kirandas_mullasseryÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.6. Water Diffusion in MeatDocument40 pagini1.6. Water Diffusion in MeatPasha TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems in PhysicsDocument22 paginiSolved Problems in Physicsvasudevan m.vÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To Exercises Reservoir Engineering IIDocument16 paginiSolutions To Exercises Reservoir Engineering IIabdouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 3 - Organic Reactions PDFDocument35 paginiChem 3 - Organic Reactions PDFFeaid Aina OrnedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cold Drawn PDFDocument1 paginăCold Drawn PDFAna Emily PrentissÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Voice Coil (Part 1) : Parts and ProductionDocument5 paginiThe Voice Coil (Part 1) : Parts and ProductionMallickarjuna A.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dorfman & Ogden MullinsEffectReinforcedRubberDocument24 paginiDorfman & Ogden MullinsEffectReinforcedRubberNelson VieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1Document1 paginăLesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1Lloyd Christian PorlajeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Higher National Diploma: National Board For Techncial Education KadunaDocument156 paginiHigher National Diploma: National Board For Techncial Education KadunaLouis FelixÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 - Air Distribution SystemDocument7 pagini10 - Air Distribution SystemZeeshan HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baldwin-Lomax Model - CFD-Wiki, The Free CFD ReferenceDocument5 paginiBaldwin-Lomax Model - CFD-Wiki, The Free CFD Referencepicams_picamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colorado School of Mines CHEN403 Stirred Tank Heater Developing Transfer Functions From Heat & Material BalancesDocument8 paginiColorado School of Mines CHEN403 Stirred Tank Heater Developing Transfer Functions From Heat & Material BalancesSatria WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Speed of Sound WorksheetsDocument1 paginăScience Speed of Sound Worksheetsbart PorcadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP #: 1 Learning Area: SCIENCE - MATTER Grade Level: Grade 8 Quarter: 3 Time Frame: 70 Minutes Teacher: CLAUDINE S. TUL-IDDocument8 paginiDLP #: 1 Learning Area: SCIENCE - MATTER Grade Level: Grade 8 Quarter: 3 Time Frame: 70 Minutes Teacher: CLAUDINE S. TUL-IDElvin VillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prediction and Analysis of Weather Data by Using Doppler Weather Radar For Aircraft NavigationDocument82 paginiPrediction and Analysis of Weather Data by Using Doppler Weather Radar For Aircraft NavigationNandon RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer: March 2019Document9 paginiFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer: March 2019Vinay SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells AbstractDocument3 paginiHydrogen Fuel Cells AbstractAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Refinery Pan BatchDocument5 paginiA Refinery Pan Batchmuhammad alaik nailal HudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emg 2508 Notes Set 3Document27 paginiEmg 2508 Notes Set 3Njuguna FredrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.2 CLIVET Air Cooled Inv-Screw ChillerDocument17 pagini5.2 CLIVET Air Cooled Inv-Screw Chillerremigius yudhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAQ - What Is A 'Fish-Eye' and How Does It Develop - PDFDocument1 paginăFAQ - What Is A 'Fish-Eye' and How Does It Develop - PDFtuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respond Basket Book 2021-CompressedDocument198 paginiRespond Basket Book 2021-CompressedpapujapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blaine Number - Average Particle SizeDocument2 paginiBlaine Number - Average Particle Sizedondo1004Încă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Organic Chemistry Post-Lab 4 Microscale Preparation of Benzyl QuinoxalineDocument4 paginiExperimental Organic Chemistry Post-Lab 4 Microscale Preparation of Benzyl Quinoxalineapi-235187189Încă nu există evaluări
- Pages From Pipenet Transient (Surge)Document2 paginiPages From Pipenet Transient (Surge)absahkahÎncă nu există evaluări