Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter - 2 Review of Coordinate System
Încărcat de
AnandDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter - 2 Review of Coordinate System
Încărcat de
AnandDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter – 2 Review of Coordinate System
Coordinate System
A coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely
determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold. It is designed
to establish position of point with respect to given reference point. The co-ordinate system
consists of one or more reference points, the style of measurement (linear or angular) from
those reference points, and the directions (or axes) in which those measurements will be
taken.
Use of Coordinate System
Coordinate system is used to describe the position of a point in a space from a fixed reference
point called origin. However in real life coordinate system has wide range of application.
Some of them are:
Describing position of any object: coordinate system is used to find the position of
any object from its original place (called origin) to its present location.
Location of Air Transport: We all have seen the aero-planes flying in the sky but
might have not thought of how they actually reach the correct destination. Actually all
these air traffic is managed and regulated by using coordinate geometry.
Map Projections: It is technique to map any 3D curved object on a flat 2D surface.
This is only possible with the help of coordinate system.
The Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS is a space based satellite navigation
system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions. In a
GPS, the longitude and latitude of a place are its coordinates. The distance formula is
used to find the distance between two places in a GPS.
A good understanding of coordinate system can be very useful in solving problems in Applied
Mechanics. A concept of coordinate system is directly applicable to find distances, slopes and
other simple trigonometric calculations in engineering.
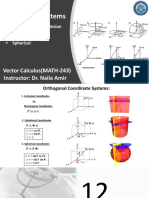
Types of Coordinate System
1. Cartesian or Rectangular Coordinate System
2. Polar Coordinate System
3. Cylindrical Coordinate System
4. Spherical Coordinate System
1. Cartesian or Rectangular coordinate system:
Cartesian coordinate system in two dimensions
A Cartesian coordinate system is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a
plane by a set of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two
fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference line is
called a coordinate axis or just axis (plural axes) of the system and the point where they meet
is its origin, at ordered pair (0, 0). The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the
perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from
the origin.
In 2D Cartesian coordinate system, horizontal axis is called x-axis or Abscissa and the
vertical axis is called the y-axis or Ordinate. The two axes divide the plane into four areas
called as quadrants that are numbered in counterclockwise direction.
Cartesian coordinate system in three dimensions
A Cartesian coordinate system for a three-dimensional space consists of an ordered triplet of
lines (axes) that go through a common point (the origin), and are pair-wise perpendicular
(any two of them being perpendicular); a single unit of length for all three axes; and an
orientation for each axis. As in the two-dimensional case, each axis becomes a number line.
The coordinates of any point P in space are obtained by drawing a line through P
perpendicular to each coordinate axis, and reading the points where these lines meet the axes
as three numbers of these number lines. The reverse construction determines the point P given
its three coordinates.
Chapter – 6 Centroid, Centre of Gravity and Moment of Inertia
Centroid (Centre of Area):
The centroid is defined as the point where the whole area of geometrical figure is assumed to
be concentrated. It is also known as Centre of Area. It is generally denoted by C.
Centre of Gravity (Centre of Mass):
The point through which total weight of the body is assumed to act is called centre of gravity
of that body. It is also known as centre of mass. The centre of gravity of a body or an object is
usually denoted by C.G. or simply G.
For uniform and homogenous body centroid coincides with centre of gravity.
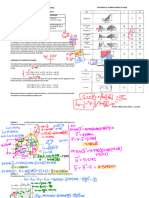
Centroid and Centre of Gravity of Area or 2-Dimensional Body:
Analytical Method Integration Method
Centre of Gravity x́ W =∑ x W x́ W =∫ x́ el d W
ý W =∑ y W ý W =∫ ý el d W
Centroid x́ A=∑ x A x́ A=∫ x́ el d A
ý A=∑ y A ý A=∫ ý el d A
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter - 2 Review of Coordinate SystemDocument2 paginiChapter - 2 Review of Coordinate SystemAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Coordinate System?: Getting StartedDocument4 paginiWhat Is A Coordinate System?: Getting StartedVinothRajagopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4Document59 paginiLecture 4Qateel JuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Three: Reference SystemsDocument19 paginiChapter Three: Reference Systemsmulat abebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3D Dynamics - 0101 - Fundamentals of Kinematics - Coordinate Frames and Position VectorsDocument6 pagini3D Dynamics - 0101 - Fundamentals of Kinematics - Coordinate Frames and Position Vectorssangram6957Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Coordinate System?Document6 paginiWhat Is A Coordinate System?EMINAT PRINCE100% (1)
- Coordinate Systems and ProjectionsDocument18 paginiCoordinate Systems and ProjectionsLluque_19Încă nu există evaluări
- Geomatics For Air Navigation: C02: Coordinate Systems Used in GeodesyDocument39 paginiGeomatics For Air Navigation: C02: Coordinate Systems Used in GeodesyCristiana TemelieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinate Systems in PhysicsDocument7 paginiCoordinate Systems in PhysicsObert MutavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article On Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocument16 paginiArticle On Cartesian Coordinate SystemASHMA MARY ROSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Map ProjectionDocument67 paginiIntro To Map Projectionapi-37882550% (1)
- Coordinate Systems 2Document8 paginiCoordinate Systems 2عمار الشيبانيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths ProjectDocument10 paginiMaths ProjectAnagha JayaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Development DivisionDocument5 paginiCurriculum Development DivisionNajla KhairuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contour:-Shap of Image: Coordinates, Which Are TheDocument2 paginiContour:-Shap of Image: Coordinates, Which Are Theشايك يوسفÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wiki Celestial Reference SystemDocument8 paginiWiki Celestial Reference SystemjoaosevanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CentroidDocument6 paginiCentroidRajendra PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singh KNP Concepts in Coordinate GeometryDocument196 paginiSingh KNP Concepts in Coordinate GeometryStrahinja Donic100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document4 paginiLecture 2Abhay RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinate System - WikipediaDocument11 paginiCoordinate System - WikipediaCarlton Gêê PiruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocument17 paginiCartesian Coordinate SystemertyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths HHW Write UpDocument3 paginiMaths HHW Write UpKratika MauryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centroids and Center of Mass: 3.1 First Moment and Centroid of A Set of PointsDocument34 paginiCentroids and Center of Mass: 3.1 First Moment and Centroid of A Set of PointsMarcelo GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Coordinate SystemsDocument16 pagini2-Coordinate Systemsjunwoo3614Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 03 Coordinate Systems&TransformationsDocument18 paginiWeek 03 Coordinate Systems&TransformationsZeynep AykulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gge 2201 - Geographical Data Projections NotesDocument44 paginiGge 2201 - Geographical Data Projections NotesjonathanondichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generalized CoordinatesDocument8 paginiGeneralized CoordinatesJoshua WoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 3 Geographic Coordinates Systems and Practical Use in Rwanda PDFDocument6 paginiChap 3 Geographic Coordinates Systems and Practical Use in Rwanda PDFBizimenyera Zenza Theoneste100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry ProblemsDocument4 paginiAnalytic Geometry Problemstutorciecle123Încă nu există evaluări
- Center of MassDocument9 paginiCenter of MassChinmaya Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of ElectronicsDocument8 paginiDepartment of ElectronicsAsgher KhattakÎncă nu există evaluări
- IA-How Does GPS WorkDocument15 paginiIA-How Does GPS WorkHuy Bui50% (2)
- Cartograph Y: Map Projections and Coordinate SystemDocument80 paginiCartograph Y: Map Projections and Coordinate SystemArt CaubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spatial Referencing: Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument43 paginiSpatial Referencing: Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning Civil Engineering DepartmentMohammed Al MaqadmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions and Answers For Gis Interview: Que:What Is GIS?Document12 paginiQuestions and Answers For Gis Interview: Que:What Is GIS?shivlakhara144Încă nu există evaluări
- UNIT - I - Electromagnetic Theory - SEEA1202: School of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument111 paginiUNIT - I - Electromagnetic Theory - SEEA1202: School of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringvosecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Center of MassDocument12 paginiCenter of MassK. M. Junayed AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoordDocument1 paginăCoordMehvish MushtaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Position Fixing WK 11Document28 paginiPosition Fixing WK 11Kalel Kasel100% (1)
- Astronomical Coordinate SystemsDocument11 paginiAstronomical Coordinate SystemsObby Dwi Syahputra100% (1)
- Lec - 11 - 12 - Introduction To Photogrammetry and Air SurveyDocument38 paginiLec - 11 - 12 - Introduction To Photogrammetry and Air SurveyGame changerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Coordinate GeometryDocument36 pagini1-Coordinate GeometryTechZenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinate Reference Systems - Bench PartnerDocument3 paginiCoordinate Reference Systems - Bench PartnerSonu BhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Geometry of The EarthDocument96 paginiThe Geometry of The EarthduettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apollo: 'S Coordinate SystemDocument3 paginiApollo: 'S Coordinate SystemiorrusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture # 2 (3D Coordinate Systems)Document40 paginiLecture # 2 (3D Coordinate Systems)Rakhmeen GulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachDocument40 paginiElectromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachdavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- EAS 151 CoG, CoM, Centroid PDFDocument40 paginiEAS 151 CoG, CoM, Centroid PDFNoorhazlindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Center of MassDocument10 paginiCenter of MassVishal Singh ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Sensors Are Instruments That Emit EMDocument12 paginiActive Sensors Are Instruments That Emit EMAbebawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centre of GravityDocument10 paginiCentre of GravityThabang CoolTeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRB Session5 CentroidsMomentofINERTIADocument4 paginiSRB Session5 CentroidsMomentofINERTIAFullo Flores MarviloneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Coordinate GeometryDocument8 paginiApplications of Coordinate GeometryAnshu RsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter1 PDFDocument49 paginiChapter1 PDFchinmay pattnayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alp Bach 2001Document26 paginiAlp Bach 2001Ulasi IfeanyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cylindrical Coordinate System: DefinitionDocument11 paginiCylindrical Coordinate System: DefinitionMujtaba KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Acad Bras Sci 2021 GattassDocument17 paginiAn Acad Bras Sci 2021 GattasstecnicoengenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Graphics Imp1Document35 paginiComputer Graphics Imp1Aswin KVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spacecraft Attitude Determinatio PDFDocument23 paginiSpacecraft Attitude Determinatio PDFAlee K. ObeidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary Positional Astronomy Supported by PC Software ProgramsDe la EverandElementary Positional Astronomy Supported by PC Software ProgramsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Thesis Defense OverviewDocument1 paginăThesis Defense OverviewAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Defense OverviewDocument1 paginăThesis Defense OverviewAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Do A Proper Thesis Defense Using The Right PowerPoint PresentationDocument15 paginiHow To Do A Proper Thesis Defense Using The Right PowerPoint PresentationAnand100% (1)
- Faculty Collaborative Research: Pokhara University Research Center (PURC) Dhungepatan, Pokhara Lekhnath, KaskiDocument8 paginiFaculty Collaborative Research: Pokhara University Research Center (PURC) Dhungepatan, Pokhara Lekhnath, KaskiAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction InstructorDocument7 paginiConstruction InstructorAnjila BhattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Built - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesDocument2 paginiBuilt - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Do A Proper Thesis Defense Using The Right PowerPoint PresentationDocument15 paginiHow To Do A Proper Thesis Defense Using The Right PowerPoint PresentationAnand100% (1)
- Non-Linear AnalysisDocument1 paginăNon-Linear AnalysisAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Linear AnalysisDocument1 paginăNon-Linear AnalysisAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 - Types of AnalysisDocument56 pagini09 - Types of AnalysisAsraf MuidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gorkha DataDocument825 paginiGorkha DataAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Built - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesDocument2 paginiBuilt - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Built - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesDocument2 paginiBuilt - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesAnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tareas de TransferenciaDocument3 paginiTareas de TransferenciaDonaldo CausilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 10 Extended Earthquake Investigation Criteria C and DDocument4 paginiMath 10 Extended Earthquake Investigation Criteria C and DJust a GuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 2 Plane Geometry Quadrilaterals and PolygonsDocument9 paginiMODULE 2 Plane Geometry Quadrilaterals and PolygonsCyndelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap 2Document4 paginiAp 2Muhammad BilalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) and Power BI - Microsoft Power BI CommunityDocument10 paginiMean Time Between Failure (MTBF) and Power BI - Microsoft Power BI CommunityPedro José100% (1)
- DLL-April 25 - 29,2022Document3 paginiDLL-April 25 - 29,2022Jonah Micah Milan MangacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Confusion MatrixDocument14 paginiConfusion MatrixAMIT GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas1 - IDPS6602 - 06398 - ADENTA VALENTHARIQ ASWANDocument6 paginiTugas1 - IDPS6602 - 06398 - ADENTA VALENTHARIQ ASWANValen ThariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions Subject: Research Methodology Paper Code: BBA 206 Unit IDocument15 paginiMultiple Choice Questions Subject: Research Methodology Paper Code: BBA 206 Unit IVicky KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADA Practical 09Document56 paginiADA Practical 09jaytheteacherÎncă nu există evaluări
- On The Computation of The RMSEA and CFI From The Mean-And-Variance Corrected Test Statistic With Nonnormal Data in SEMDocument12 paginiOn The Computation of The RMSEA and CFI From The Mean-And-Variance Corrected Test Statistic With Nonnormal Data in SEMNorberth Ioan OkrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Integration MethodsDocument6 paginiNumerical Integration MethodsOsama HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 4 CH 9 Reteach AkDocument8 paginiGR 4 CH 9 Reteach AkCarlitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Runtime Model Checking of Multithreaded C/C++ Programs: Yu Yang Xiaofang Chen Ganesh Gopalakrishnan Robert M. KirbyDocument11 paginiRuntime Model Checking of Multithreaded C/C++ Programs: Yu Yang Xiaofang Chen Ganesh Gopalakrishnan Robert M. KirbypostscriptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2 Principles of Mathematical InductionDocument7 paginiUnit-2 Principles of Mathematical Inductionritul singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFA Level III - Combined Total Formula Mini TestDocument18 paginiCFA Level III - Combined Total Formula Mini TestcpacfaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bound ChargesDocument17 paginiBound ChargesJorge GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1997 1829 Wake-Body InterferenceDocument10 pagini1997 1829 Wake-Body InterferenceMarcos SoarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Describing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationDocument47 paginiDescribing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationJohn Christian MejiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Power Systems Protection On ETAPDocument41 paginiAnalysis of Power Systems Protection On ETAPRamsha Xehra50% (2)
- Ibps Numerical Ability Sample PaperDocument5 paginiIbps Numerical Ability Sample PaperPriyaJindalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sarmento 2020Document13 paginiSarmento 2020Kylian MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximum & Minimum Problems LagrangeDocument22 paginiMaximum & Minimum Problems LagrangeCarolina Torres Lozano ΨÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alysia Citta Paramitha - Tugas 6 Dan 7Document7 paginiAlysia Citta Paramitha - Tugas 6 Dan 7Moe ChannelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space Vector Modulated Three-Phase To Three-Phase Matrix Converter With Input Power Factor CorrectionDocument13 paginiSpace Vector Modulated Three-Phase To Three-Phase Matrix Converter With Input Power Factor CorrectionkandibanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9Document5 paginiChapter 9lcmehretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Analysis: Lecture - 3Document17 paginiNumerical Analysis: Lecture - 3khizarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BuchblockDocument103 paginiBuchblockRafiqul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcement Learning 2Document13 paginiReinforcement Learning 2Mark RichardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forecasting With Artificial Intelligence: Theory and ApplicationsDocument441 paginiForecasting With Artificial Intelligence: Theory and ApplicationsLong Tran KimÎncă nu există evaluări