Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CHAPTER 3 Chemical Formulae & Equations
Încărcat de
Sarah WongDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CHAPTER 3 Chemical Formulae & Equations
Încărcat de
Sarah WongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
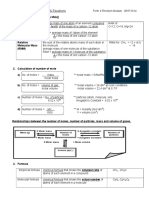
NUMBER OF MOLES b) 1.806 x 1024 hydrogen atoms ii) molecular formulae for the hydrocarbon compound.
c) i) 1.505 x 1023 urene molecules, CO(NH2)2 A hydrocarbon X contains 80% of carbon and 20% of .3
1. How many times two titanium atoms heavier than three
ii) N dlm CO(NH2)2 hydrogen. 1.5 g of the hydrocarbon occupies the volume
oxygen atoms?
iii)peratus N dlm sebatian CO(NH2)2 of 1.12 dm3 at S.T.P. condition. i) Find the
2. P, Q, and R are three elements. Relative atomic mass d) 2.709 x 1022 oxygen molecules .emperical formulae of hydrocarbon X
for R is 210. One R atom is three times heavier than
.ii) Find the relative molecular mass for hydrocarbon X
one Q atom and one Q atom is two times heavier than NUMBER OF MOLES Vs MOLAR VOLUME .iii) Determine the molecular formulae for hydrocarbon X
one P atom. Determine the relative atomic mass for 1. Find out the volume of gas at S.T.P. condition:
element P. a) 0.7 g of nitrogen gas Combustion of X in athe air produces carbon dioxide and
3. Determine the relative molecular mass for the b) 5.4 x 1022 nitrogen dioxide molecules, NO2 .water
compounds below: c) 1.4 g of carbon monoxide, CO .i) write the balance chemical equation
a) methane, CH4 b) ethanol, C2H5OH 2. Calculate the number of molecules of the .ii) calculate the volume of carbon dioxide gas liberated
c) glucose, C6H12O6 d) sodium sulphate, Na2SO4 following subtances at room condition: v) Calculate the mass of water prodiced if 0.6 g of
e) sodium thiosulphate hydrated, Na2S2O3.5H2O a) 120 cm3 of methane gas, CH4 .hydrocarbon X has burnt completely in air
f) cobalt chloride hydrated, CoCl2.6H2O b) 4 dm3 of ammonia gas, NH3
g) ammonium carbonate, (NH4)CO3 c) 36 dm3 of sulfur trioxide, SO3 CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
h) aluminium sulphate, Al2 (SO4)3 i) oxygen gas
3. Determine the mass of gas at S.T.P. condition: 1. Balance the following equation:
a) 3.36 dm3 of ozone gas,O3 a) N2 + (g) H2 (g) NH3 (g)
NUMBER OF MOLES Vs NO. OF PARTICLES
b) 448 cm3 of fluorine gas, F2
1. Calculate the number of particles:
c) 1.12 cm3 of ethane gas, C2H6 b) C2H5OH (ce) + O2 CO2 (g) + H2O (ce)
a) 0.22 mole of nitrogen dioxide, NO2
b) 2.75 mole of zinc ions, Zn2+ c) MnO2 (p) + HCl (ak) MnCl (ak) + Cl2 (g) + H2O (ce)
CHEMICAL FORMULAE
c) 0.5 mole of ammonium chloride, NH4Cl
Combine the ions below to form the compound and
d) 0.2 mole of bromine gas d) Na2CO3 (ak) + HNO3 (ak) NaNO3 (ak) + CO2 (g) +
write their names.
2. Calculate the number of mole for the following 1. Ca2+ + SO42+ H2O (ce)
subtances: e) C4H10 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (ce)
2. Al3+ + NO3-
a) 7.224 x 1022 carbon atoms, C
b) 1.204 x 1024 oxygen gas 3 Na+ + F-
c) 9.632 x 1023 sulfur dioxide, SO2
4. Fe3+ + Cl-
d) 4.515 x 1024 ammonia gas, NH3
5. Mg2+ + O2-
NUMBER OF MOLES Vs MASS (g)
1. Find out the mass of:
6. Cu 2+
+ CO 3
2-
[NA= 6.02 x 1023 zarah]
a) 2/5 moles of zinc, Zn 7. Pb2+ + Cl - .pd. s.t.p [mol gas = 22.4 dm3 1]
b) 0.025 mole of sulfur dioxide, SO2 + 2- pd. suhu / keadaan bilik [mol gas = 24 dm3 1]
8. K + Cr2O4
c) 1.75 moles of oxygen gas
d) 2 moles of chlorine gas 9. K+
+ MnO4 -
; H=1 ; C=12 ; N=14 ; O=16 ; F=19 ; Na=23 ; Al=27 ]
2. Calculate the number of mole of: 10. Zn 2+
+ SO4 2-
S=32 ; Cl=35.5 ; Ti=48 ; Fe=56 ; Co=59 ; Zn=65 ; Br=80]
a) 1.4 g of Iron, Fe
b) 7.2 g of glucose, C6H12O6
c) 2.4 g of hydrogen gas EMPIRICAL FORMULAE
3. Calculate the number of particles of: 1. 6.1 g of metal X combined with m gram of
a) 1.3 g of zinc, Zn oxygen to form an oxide with formulaX2O5.
b) 6.9 g nitrogen dioxide, NO2 Determine the value m.
c) 38.5 g carbon tetrachloride, CCl4 2. 1.5 g of a hydrocarbon compound contains 0.3 g
d) 132 g ozon, O3 of hydrogen. If the relative molecular mass for the
e) 7.1 g chlorine hydrocarbon compound is 30, calculate its:
4. Determine the subtances mass: i) empirical formulae
a) 3.01 x 1023 iron atoms, Fe
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDFDocument53 paginiPecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDFSyarfa FurzanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F5Document7 paginiLIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F5Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Action Word in ProceduresDocument1 paginăAction Word in ProceduresSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry F4 Topic 4 - 5Document16 paginiChemistry F4 Topic 4 - 5Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redox Electrolysis and Chemical Cell PDFDocument2 paginiRedox Electrolysis and Chemical Cell PDFSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3: Chemical Formulas & EquationsDocument10 paginiChapter 3: Chemical Formulas & EquationsSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redox Reaction Quick Notes: No Experiment Diagram Oxidation Half Equation Reduction Half Equation 1Document2 paginiRedox Reaction Quick Notes: No Experiment Diagram Oxidation Half Equation Reduction Half Equation 1Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F4Document7 paginiLIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F4Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Analysis Past Year and Ramalan 2018Document5 paginiChemistry Analysis Past Year and Ramalan 2018Sarah Wong0% (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Chemistry F4 Topic 6Document21 paginiChemistry F4 Topic 6Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry F4 Topic 7Document11 paginiChemistry F4 Topic 7Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- F4 Chapter 1Document10 paginiF4 Chapter 1Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic TableDocument8 paginiPeriodic TableKhairiyah AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of 4 Thermo ExpDocument4 paginiComparison of 4 Thermo ExpSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fats & Oils: Differences Between Fats and OilsDocument5 paginiFats & Oils: Differences Between Fats and OilsSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition Chem SPMDocument6 paginiDefinition Chem SPMSarah Wong100% (1)
- Identify reactants, products and states in chemical equationsDocument2 paginiIdentify reactants, products and states in chemical equationsSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bengkel 1 - Chemical EquationDocument5 paginiBengkel 1 - Chemical EquationSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic StructureDocument3 paginiAtomic StructureSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of PEKA ExperimentsDocument1 paginăList of PEKA ExperimentsSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- f4 - Chapter 7 PDP WorksheetDocument27 paginif4 - Chapter 7 PDP WorksheetSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Command Words in Chemistry Paper 2Document37 paginiCommand Words in Chemistry Paper 2Sarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Number of Mole and EquationsDocument32 paginiChemistry Number of Mole and EquationsSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.experimental TechniquesDocument5 pagini2.experimental TechniquesSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flower PotDocument1 paginăFlower PotSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4s Holiday ModuleDocument1 pagină4s Holiday ModuleSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quote ExamDocument6 paginiQuote ExamSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4s Holiday ModuleDocument1 pagină4s Holiday ModuleSarah WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Physical Science Part 2 ReviewerDocument8 paginiPhysical Science Part 2 Reviewerjerick de veraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoichiometry and Redox Reactions PDFDocument66 paginiStoichiometry and Redox Reactions PDFGopal PenjarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM 015 Chemistry For Engineers Worksheet 4 6Document7 paginiCHEM 015 Chemistry For Engineers Worksheet 4 6Ranah Pauolynne LintanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry, 7-8-6Document25 paginiChemistry, 7-8-6Kissha TayagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculations in Analytical ChemistryDocument23 paginiCalculations in Analytical ChemistryClaire G. MagluyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chm421 Experiment 5Document6 paginiChm421 Experiment 5yaws0% (1)
- Grade 12 Physics NoteDocument35 paginiGrade 12 Physics NoteNebilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resin-Based Daylight Fluorescent PigmentsDocument4 paginiResin-Based Daylight Fluorescent Pigmentsmember2 mtriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document2 pagini1axznpsychoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MolalityDocument10 paginiMolalityClarisse VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of The Relative Atomic Masses of MetalsDocument8 paginiDetermination of The Relative Atomic Masses of Metalshaiyan LIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Chemistry of Soils PDFDocument411 paginiEnvironmental Chemistry of Soils PDFleandro100% (4)
- 07 SolutionDocument72 pagini07 SolutionsyammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Practice Problems (Answers)Document4 paginiUnit 5 Practice Problems (Answers)Ka Siang GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes (AS Level)Document1 paginăChemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes (AS Level)--------100% (1)
- Chapter 11 SolutionsDocument14 paginiChapter 11 SolutionsVinicius CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminum and Copper Chloride LabDocument9 paginiAluminum and Copper Chloride Labwasi ul islamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoichiometry of Formulas and EquationsDocument45 paginiStoichiometry of Formulas and EquationsNitha CwectiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 14 Mass TransferDocument36 paginiLec 14 Mass TransferWaseem abbas100% (1)
- Modul Kimia Potential Daerah Gombak Kertas 2Document26 paginiModul Kimia Potential Daerah Gombak Kertas 2MOHAMAD SYAFIQ BIN MOHD FAROUKE MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstract - Freezing Point Depression Is ADocument5 paginiAbstract - Freezing Point Depression Is AMinahÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Chemistry - Kinetics of A Reaction LabDocument8 paginiAP Chemistry - Kinetics of A Reaction LabJonathan Chen50% (2)
- How temperature affects the mass and volume of an objectDocument4 paginiHow temperature affects the mass and volume of an objectloriah lopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.4 Avogadro's Hypothesis+ Equivalent MassesDocument12 pagini2.4 Avogadro's Hypothesis+ Equivalent MassesSantosh MandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium Analysis EDTA TitrationDocument6 paginiCalcium Analysis EDTA TitrationChun Wing Lai100% (2)
- Practice Exam 4Document7 paginiPractice Exam 4Hasantha PereraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9th Class Chemistry Ch1 McqsDocument2 pagini9th Class Chemistry Ch1 McqsMuhammad FaheemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percent Oxalate DeterminationDocument4 paginiPercent Oxalate DeterminationLeon Jordan100% (2)
- Pauline M. Doran - Bioprocess Engineering Principles 2nd Edition Solutions Manual. 2nd Edition-Elsevier (2013)Document416 paginiPauline M. Doran - Bioprocess Engineering Principles 2nd Edition Solutions Manual. 2nd Edition-Elsevier (2013)Daniele Andrade100% (12)
- Material and Energy BalanceThis document provides a concise title for the given document within 40 characters:TITLE 4. MATERIAL AND ENERGY BALANCE SYLLABUSDocument51 paginiMaterial and Energy BalanceThis document provides a concise title for the given document within 40 characters:TITLE 4. MATERIAL AND ENERGY BALANCE SYLLABUSsmith100% (1)