Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Human Anatomy Reviewer: The Skeletal System
Încărcat de
RhancineClaireTorrenoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Human Anatomy Reviewer: The Skeletal System
Încărcat de
RhancineClaireTorrenoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HUMAN ANATOMY REVIEWER
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
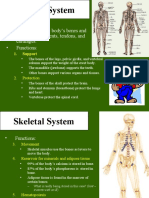
The skeletal system includes:
• Bones
• Cartilages
• Joints
• Ligaments
• Other connective tissues Microscopic Features of Bone
• Periosteum
Functions of the Skeletal System • Outer fibrous layer
• Support against gravity • Inner cellular layer
• Storage • Osteocytes
• Calcium, phosphorous • Within lacunae (holes) in matrix
• Fat • Between lamellae of matrix
• Blood cell production • Branches within canaliculi
• Protection of soft internal organs
• Leverage for muscle action Microscopic Features of Bone
• Osteon—Basic functional unit of
The Structure of Bone compact bone; columnar in shape
Bone (Osseous Tissue) • Strong in long axis of bone
• Specialized cells • Concentric layers of osteocytes
• 2% of bone weight • Concentric layers of matrix (lamellae)
• Strong flexible matrix • Central(Haversian) canal
• Calcium phosphate crystals • Axial tunnel for blood vessels
• Two-thirds of bone weight • Perforating canal
• Collagen fibers • Radial tunnel for blood vessels
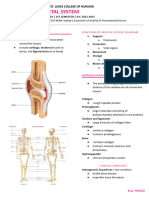
Macroscopic Features of Bone
• General shapes of bones
• Long bones (e.g., humerus)
• Short bones (e.g., carpal bones)
• Flat bones (e.g., parietal bone)
• Irregular bones (e.g., vertebra)
Features in a Long Bone
• Diaphysis (shaft)
• Compact (dense) bone
• Marrow cavity
• Epiphyses (ends)
• Spongy (cancellous) bone
• Articular cartilage Microscopic Features of Spongy Bone
• Periosteum (covering) • No osteons
• Endosteum (lining) • Lamellae as trabeculae
• Arches, rods, plates of bone
• Branching network of bony tissue
• Strong in many directions
• Red marrow (blood forming) spaces
Cells in Bone
• Osteocytes
• Mature bone cells between lamellae
• Osteoclasts
• Source of acid, enzymes for osteolysis
• Calcium homeostasis Requirements for Normal Bone Growth
• Osteoblasts • Minerals
• Responsible for osteogenesis (new bone) • Calcium, phosphate
• Source of collagen, calcium salts • Vitamins
• Vitamin D3
• Vitamin C
Bone Formation and Growth • Vitamin A
Intramembranous Ossification • Hormones
• Ossification—Process of converting other • Growth Hormone
tissues to bone • Sex hormones, thyroid hormone, others
• Forms flat bones of skull, mandible,
clavicle Role of Remodeling in Support
• Stem cells differentiate to osteoblasts • Remodeling—Continuous
• Produces spongy bone, then compact breakdown and reforming of bone
bone tissue
• Shapes reflect applied loads
• Mineral turnover enables adapting
to new stresses
Key Note
What you don’t use, you lose.
The stresses applied to bones
during exercise are essential to
maintaining bone strength and
bone mass
Endochondral Ossification
• Most bones formed this way Homeostasis and Mineral Storage
• Cartilage model replaced by bone • Bones store calcium
• Replacement begins in middle • Contain 99% of body calcium
(diaphysis) • Store up to two kg calcium
• Replacement follows in ends • Hormones control storage/release
(epiphyses) • PTH, calcitriol release bone
calcium
• Calcitonin stores bone calcium
• Blood levels kept constant
Injury and Repair
• Fracture—A crack or break in a bone
• Steps in fracture repair
• Fracture hematoma
• Mitoses in periosteum, endosteum
• Internal callus
• External callus
• Bone remodeling
Aging and the Skeletal System
Osteopenia—Less than normal
ossification (mineral content) in bone
• Osteopenia starts before age 40
• Women lose 8% per decade
• Men lose 3% per decade
• Spongy bone most affected
• Epiphyses
• Vertebrae
• Jaws
An Overview of the Skeleton
Bone Markings (Selected)
• Tuberosity
• Condyle
• Trochlea
• Facet
• Fossa
• Foramen
• Sinus
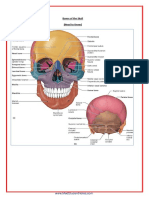
The Axial Division: The Skull
Bones of the Cranium
• Frontal bone
• Forehead, superior surface of orbits
• Parietal bones
• Sides, roof
• Occipital bone
• Foramen magnum
• Temporal bones
• Sides, base
• Sphenoid bone
Skeletal Divisions • Bridge between cranial and facial
• Axial skeleton bones
• Skull • Ethmoid bone
• Thoracic cage and sternum • Cribriform plate
• Vertebral column • Nasal septum
• Appendicular skeleton
• Upper, lower limbs
• Pectoral girdle
• Pelvic girdle
Bones of the Face
• Maxillary bones
• Zygomatic bones
• Zygomatic arch
(with temporal
bones)
• Mandible
• Palatine bones
• The Vomer
• Nasal bones
• Lacrimal bones
• Inferior nasal conchae
• Nasal complex
• Nasal septum
• Paranasal sinuses
• Frontal
• Sphenoidal
• Ethmoidal
• Palatine
• Maxillary
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 paginiThe Skeletal SystemBeah Marie AlisosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY: Chapter 5Document5 paginiANAPHY: Chapter 5Jemimah FVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives: Functions of Bones Classification of BonesDocument7 paginiObjectives: Functions of Bones Classification of BonesIbra TutorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)Document120 paginiSkeletal System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Skeletal SystemDocument8 paginiThe Skeletal SystemMica BernardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 6-Skeletal SystemDocument15 paginiWEEK 6-Skeletal SystemG a i l R i c h w e l lÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP II P3 Skeletal SystemDocument114 paginiHP II P3 Skeletal SystemNazir RabiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY-SKELETAL-Midterm-Reviewer 2Document26 paginiANAPHY-SKELETAL-Midterm-Reviewer 2Lindley PareñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System: Bones and Joints Components of The Skeletal System: Long Bone StructuresDocument8 paginiSkeletal System: Bones and Joints Components of The Skeletal System: Long Bone StructurespangetkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ORTHO-Bone Physiology and Repair (Dr. Gerochi)Document4 paginiORTHO-Bone Physiology and Repair (Dr. Gerochi)Monique BorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Basic NDocument98 paginiBone Basic NSuraj kumar GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Skeletal SystemDocument9 paginiThe Skeletal Systembrfe.devera.upÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compana Le2Document526 paginiCompana Le2bitangyarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System 1: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument57 paginiSkeletal System 1: Dr. Garry NiedermayerWeng Sze TingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 BonesDocument47 pagini6 BonesMarissa GÎncă nu există evaluări
- A&p - All Files in One PDFDocument201 paginiA&p - All Files in One PDFandreeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A&P - 2a. Skeletal System Condensed (13p) PDFDocument13 paginiA&P - 2a. Skeletal System Condensed (13p) PDFandreeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cartlage Bone 2012Document34 paginiCartlage Bone 2012Omar Ali AyoubkhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Skeletal TissueDocument5 paginiChapter 6 Skeletal TissuerenjiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- HISTO - Bone Tissue 22Document39 paginiHISTO - Bone Tissue 22Huda AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch5 Skeletal System 1Document12 paginiCh5 Skeletal System 1Shane PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - 2 Bone Growth and Development - UPDATED NOTE PAGESDocument5 pagini3 - 2 Bone Growth and Development - UPDATED NOTE PAGESdansardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5. Skeletal SystemDocument123 paginiChapter 5. Skeletal SystemAlaine Danica DimaandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Skeletal System 1: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument67 paginiThe Skeletal System 1: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Skeletal and Articular SystemDocument3 pagini2 Skeletal and Articular SystemKimberlee Ced NoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- BONE TissueDocument16 paginiBONE TissuePotini AdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System: - Composed of The Body's Bones and Associated Ligaments, Tendons, and Cartilages. - FunctionsDocument66 paginiSkeletal System: - Composed of The Body's Bones and Associated Ligaments, Tendons, and Cartilages. - FunctionsDenver TanhuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System: Bones and Bone TissueDocument49 paginiSkeletal System: Bones and Bone TissueSumit100% (1)
- Joyce Y. Visitacion NCM 104 Bsn-4Aj SY 2008-2009 Musculoskeletal SystemDocument33 paginiJoyce Y. Visitacion NCM 104 Bsn-4Aj SY 2008-2009 Musculoskeletal Systemyawdle100% (6)
- Major Functions of Skeletal SystemDocument8 paginiMajor Functions of Skeletal SystemDivine Rose TuquibÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument23 paginiUntitledwieka mawieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone & Fracture Healing: Januarsih A.RachmanDocument26 paginiBone & Fracture Healing: Januarsih A.RachmanHafdzi MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Skeletal System 1Document18 paginiChapter 6 Skeletal System 1M GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY SKELETAL SYSTEM MidtermsDocument12 paginiANAPHY SKELETAL SYSTEM MidtermsFraiza BirowaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone & Cartilage - BPTDocument53 paginiBone & Cartilage - BPTVaishnaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Anatomy: The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureDocument71 paginiHuman Anatomy: The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureLeilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistema EsqueletalDocument62 paginiSistema EsqueletalJoel AvalosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone & CartilageDocument31 paginiBone & CartilageKate LionelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2 Rad AnaDocument11 paginiM2 Rad AnaramilccabrigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnatomyDocument105 paginiAnatomyHelena Pascual PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System1 241Document57 paginiSkeletal System1 241bela2011Încă nu există evaluări
- The Skeletal SystemDocument4 paginiThe Skeletal SystemBITE JAY BHIE BENDALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone HistologyDocument22 paginiBone HistologyEniola DaramolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology of Bone 2022Document30 paginiHistology of Bone 2022zahra nabilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic ScienceDocument24 paginiBasic ScienceDioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aaos 2007 Basic Science FinalDocument250 paginiAaos 2007 Basic Science Finalcezarciobotaru.mdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part A: Prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal CollegeDocument41 paginiBones and Skeletal Tissues: Part A: Prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal CollegeRaul ReynosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 BoneDocument22 paginiLecture 2 BoneiamkpvemuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL3307 - Unit1Mod2 - Bone Growth & Repair1Document16 paginiBIOL3307 - Unit1Mod2 - Bone Growth & Repair1Ren StudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 6b Skeletal System 1Document16 pagini2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 6b Skeletal System 1OscarJaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haversian System (Osteon) : Basic Structural UnitDocument7 paginiHaversian System (Osteon) : Basic Structural UnitJulius Matthew MarananÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE Skeletal System: A T E A MDocument27 paginiTHE Skeletal System: A T E A MMiss medÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone TissueDocument61 paginiBone TissueShekeyva SmalleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal SystemDocument35 paginiSkeletal SystemVann Philip RasonableÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Manzanares) Skeletal System Study GuideDocument17 pagini(Manzanares) Skeletal System Study GuideKyla ManzanaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- L1 - BonesDocument50 paginiL1 - BonesJIA YUET NGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDe la EverandSkeletal System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionDe la EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document4 paginiUnit 2Cosmina CorbeanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jan 24 Skeletal Embryology and Limb Growth Stanmore Dr. Riego de Dios CPT TiongsonDocument3 paginiJan 24 Skeletal Embryology and Limb Growth Stanmore Dr. Riego de Dios CPT TiongsonMarlon MejiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bones and Joints of ThoraxDocument57 paginiBones and Joints of ThoraxNunmoy HnialumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy 1.2 Anatomy in MotionDocument4 paginiAnatomy 1.2 Anatomy in Motionlovelots1234Încă nu există evaluări
- The Reverse Planning Method For Lengthening of The Lower LimbDocument13 paginiThe Reverse Planning Method For Lengthening of The Lower LimbAhmed TawfiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO 201 Practical 1 ListDocument9 paginiBIO 201 Practical 1 Listjlette453185Încă nu există evaluări
- Cervifix: Surgical TechniqueDocument32 paginiCervifix: Surgical TechniqueKlemen PečnikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Skeletal SystemDocument7 paginiReviewer For Skeletal SystemRegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Back Ache: Capt PramodDocument67 paginiLow Back Ache: Capt PramodPramod MahenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal StenosisDocument14 paginiSpinal StenosisHONGJYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 The Skeletal SystemDocument47 paginiChapter 5 The Skeletal SystemOlalekan OyekunleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equine Radiographic AnatomyDocument32 paginiEquine Radiographic AnatomySam Bot100% (2)
- Scapula Fracture: DR Jaseem ShamsudeenDocument32 paginiScapula Fracture: DR Jaseem ShamsudeenJaseemshams ThottiyilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 05 Skeletal SystemDocument78 paginiChapter 05 Skeletal SystemLiam MaghanoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- McKenzie LumbarDocument91 paginiMcKenzie LumbarPraneetha100% (1)
- Data Preopfinding FixDocument91 paginiData Preopfinding FixDeniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planeacion Preoperatoria Artroplastia CaderaDocument8 paginiPlaneacion Preoperatoria Artroplastia Caderamontserrat santiago sanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- نماذج باثو نظري هيكليDocument2 paginiنماذج باثو نظري هيكليWael EssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norma Frontalis BY DR SHAZIA FAHMIDocument28 paginiNorma Frontalis BY DR SHAZIA FAHMISyeda AlizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ortho Nursing NotesDocument6 paginiOrtho Nursing NotesRAYANA UBASÎncă nu există evaluări
- FractureDocument4 paginiFractureKaren Garcia AbinsayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bones and LimbsDocument147 paginiBones and LimbsDana IonescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Ana228 - 63Document22 paginiLab Ana228 - 63pachara.p65Încă nu există evaluări
- 8698 - Anatomi PracticalDocument15 pagini8698 - Anatomi PracticalAngely NovianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CastDocument17 paginiCastlemuel_que100% (1)
- Baumann's AngleDocument8 paginiBaumann's Anglejomari dvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fraktur VertebraeDocument41 paginiFraktur VertebraeTomy WiknaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imaging of Spine TraumaDocument19 paginiImaging of Spine TraumaAlejandro ColombanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Vol-I Vishram SinghDocument345 paginiAnatomy Vol-I Vishram Singhleena lost84% (55)
- Lower Extremity Anatomy: Sari Tri Yulianti, S.FT., M.BiomedDocument73 paginiLower Extremity Anatomy: Sari Tri Yulianti, S.FT., M.BiomedDindaÎncă nu există evaluări