Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science 7. Pretest. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer
Încărcat de
Egillen EnamnoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science 7. Pretest. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer
Încărcat de
Egillen EnamnoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SCIENCE 7. PRETEST.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the letter of the correct answer. 14.The kidneys functions are to filter and to remove the waste
1. What do you call a solution when it has a small amount of from the blood which is harmful to the body. What might happen
dissolved solute in comparison to the amount of solvent. to the person if it fails to function?
A. Saturated Solution C. Dilute Solution a. The kidney will be damaged
B. Concentrated Solution D. Unsaturated Solution b. There is no significant effect to the person
c. The cells of the kidney will be affected
2. This is a property of metals which allows it to be drawn into d. The person will suffer and will need to undergo dialysis
wires. treatment
A. Electrical Conductivity C. Luster
B. Ductile D. Malleable 15.What is the basic unit of life?
a. Heart c. Kidney
3. When you lack this element, children will have Rickets and b. Cell d. Organ
other bone diseases.
A. Sulfur C. Calcium 16.What is made up of different organs that help the body
B. Potassium D. Selenium eliminate metabolic wastes and maintain internal balance?
a. Nervous system c. Circulatory system
4. What micromineral is needed to prevent goiter? b. Excretory system d. Reproductive system
A. Sulfur C. Flourine
B. Potassium D. Iodine 17.What organ system is consisting of the heart, blood, and
blood vessels?
5. This is always transparent, light passes through with no c. Nervous system c. Circulatory system
scattering from solute particles which are molecule in size. d. Excretory system d. Reproductive system
A. Colloid C. Solution
B. Mixture D. Solubility 18.Angelo’s father was hospitalized due to chest pain and
difficulty of breathing. Laboratory examination revealed
6. How do you call the light passing through a colloidal increased cholesterol in blood. Which organ system is mostly
dispersion, such as smoky or foggy air. affected?
A. Homogenous C. Tyndall effect a. Nervous system c. Circulatory system
B. Colloid D. Suspension b. Excretory system d. Reproductive system
7. This refers to the physical combination of two or more 19. What is an optical instrument used for viewing very small
substances in which the identities are retained. objects, like plant or animal cells, typically magnified several
A. Solution C. Saturation hundred times?
B. Mixture D. Solubility a. Magnifying glass c. Stage clips
b. Microscope d. Base
8. What do you call a solution that contains the maximum
amount of solute dissolved by a given amount of solvent. 20. What is also known as a simple microscope?
A. Homogenous C. Saturated Solution a. Magnifying glass c. Stage clips
B. Colloid D. Unsaturated Solution b. Microscope d. Base
9. A type of mixture when different parts of the mixture are 21. What holds the specimen on a microscope?
visible to the unaided eye. a. Magnifying glass c. Stage clips
A. Homogenous C. Heterogeneous b. Microscope d. Base
B. Colloid D. Suspension
22. What is the bottom most portion of the microscope that
10. This is always transparent, light passes through with no supports the entire microscope?
scattering from solute particles which are molecule in size. a. Magnifying glass c. Stage clips
A. Colloid C. Solution b. Microscope d. Base
B. Mixture D. Solubility
23. What is a combination of fungus and algae?
11. The heart pumps blood that carries oxygen and nutrients to a. Algae c. Lichen
the different parts of the body. To which organ system does the b. Bacteria d. Fungi
heart belong?
a. Circulatory system c. Excretory System 24. Which of the following is used in making cheese and yogurt?
b. Digestive system d. Reproductive System a. Algae c. Bacteria
b. Lichen d. Mushroom
12.What is the correct sequence from - smallest to biggest - of
the levels of organization in an organism? 25. Which of the following is an example of a fungi?
a. Cell tissue organ organ system organism a. Algae c. Bacteria
b. Cell organ organ system tissue organism b. Lichen d. Mushroom
c. Cell organ system organ tissue organism
d. Cell tissue organism organ organ system 26.What is shown on this diagram?
13.Each part of an organ system plays a specific function. Which
of the following structures DOES NOT match its function? a. Distance c. Initial Position
a. Eyes - sight c. Kidneys - excretion b. Displacement d. Final Position
b. Heart - circulation d. Ears - respiration
27. What does Path 2 show on this diagram? *CLASSIFY THE FOLLOWING*
38.
a. Distance c. Initial Position
b. Displacement d. Final Position
a. Renewable c. Recyclable
28. Based on the diagram above, what does Point B stand for? b. Non-Renewable d. Sustainable
a. Distance c. Initial Position
b. Displacement d. Final Position 39.
29. Based on the diagram above, what does Point A stand for?
a. Distance c. Initial Position
b. Displacement d. Final Position
c. Which of the following statements is NOT true about the a. Renewable c. Recyclable
object moving with constant speed? b. Non-Renewable d. Sustainable
a. The object is not accelerating
b. The speed of the object is equal to zero. 40.
c. The distance travelled by the object increases uniformly
d. The speed of the object remains the same all
throughout the travel
a. Renewable c. Recyclable
31. NATURAL RESOURCES are material or elements from the b. Non-Renewable d. Sustainable
environment that people__________________.
a. did not create. 41. What is the most abundant element in the Earth’s
b. invented for themselves atmosphere?
c. use to meet their needs
d. observe using scientific equipment a. Ar c. N
b. CO2 d. O
32.What do you call the resource that people can use again and
again but its supply can be replaced? 42. What is the correct order of the Earth’s atmosphere layers
a. renewable c. reliable from Bottom to Top?
b. recyclable d. unlimited
a. stratosphere, mesosphere, troposphere, thermosphere,
33. Which pair of resources is renewable? exosphere
a. cotton and leather c. soil and minerals b. stratosphere, troposphere, thermosphere, mesosphere,
b. aluminum and iron d. coal and solar energy exosphere
c. troposphere, stratosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere,
34. How do you call the imaginary line circling the Earth halfway exosphere
between North and South poles? d. troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere,
a. Latitude c. Equator exosphere
b. Longitude d. Prime Meridian
43. Which layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer?
35. How do you call the imaginary lines that
extend horizontally from east to west. a. Mesosphere
a. Latitude c. Equator b. Stratosphere
b. Longitude d. Prime Meridian c. Thermosphere
d. Troposphere
36. How do you call the imaginary lines that extend vertically
from pole to pole on a globe? 44. In which layer do virtually all-weather phenomena take
a. Latitude c. Equator place?
b. Longitude d. Prime Meridian
a. Exosphere
37. How do you call the great circle on the Earth’s surface b. Mesosphere
passing through The North and South Poles, which is c. Stratosphere
considered 0 degrees longitude? d. Troposphere
a. Latitude c. Equator
b. Longitude d. Prime Meridian 45. In which atmospheric layer is most water vapor found?
a. Troposphere
b. Stratosphere
c. Mesosphere
d. Thermosphere
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Summative Science77777Document3 paginiSummative Science77777ParEngJhomArÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Method PowerPointDocument27 paginiScientific Method PowerPointSymon Alonzo VersozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8 School Achievement TestDocument2 paginiScience 8 School Achievement TestMYRNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Quarterly Test: General Biology 2Document10 paginiFirst Quarterly Test: General Biology 2glaiza abucayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissolved Gas Analysis PDFDocument10 paginiDissolved Gas Analysis PDFERIKWTPÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 7Document4 pagini2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 7Noeljaysel AlejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Levels of OrganizationDocument8 paginiLevels of OrganizationQueng ElediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System LaboratoryDocument6 paginiDigestive System LaboratoryValeria ReinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Here are the answers to the evaluation questions:1. c2. b 3. b4. d5. aDocument52 paginiHere are the answers to the evaluation questions:1. c2. b 3. b4. d5. aAiza Manalo Delos ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Test Science 7 - BiologyDocument5 paginiPre-Test Science 7 - BiologyMark Wendel Murillo0% (1)
- Protist and FungiDocument43 paginiProtist and FungiEgillen EnamnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 2nd Quarter, ScienceDocument2 paginiGrade 7 2nd Quarter, ScienceCrisma JahariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herbal Drug Technology (Thakur Publication)Document264 paginiHerbal Drug Technology (Thakur Publication)Munteshwar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUARTER 2 Third-summative-test-2nd-qrtr-M5M6-SCIENCE 7Document2 paginiQUARTER 2 Third-summative-test-2nd-qrtr-M5M6-SCIENCE 7TEOFILA NOLASCO100% (1)
- Science 7 Lesson Exemplar Eccological Interaction MAG Q2Document16 paginiScience 7 Lesson Exemplar Eccological Interaction MAG Q2Marian Anion-Gaurano100% (1)
- Answer Sheet: General Biology 1Document9 paginiAnswer Sheet: General Biology 1HanabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRELIM Exam in Science 9Document5 paginiPRELIM Exam in Science 9Mohammad Javier D. DimaporoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas LawsDocument27 paginiGas LawsChese Ann PepinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 7 Exam BiologyDocument2 paginiScience 7 Exam BiologyJhe SeidelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gear DesignDocument22 paginiGear DesignKhalil Raza100% (4)
- Understanding Biology Through Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 paginiUnderstanding Biology Through Multiple Choice QuestionsSharlyn BalgoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates WorksheetDocument2 paginiCarbohydrates WorksheetPew Collado PlaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Monthly Test Science 7Document4 pagini1st Monthly Test Science 7Seb GanaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport Mechanism Quiz-1Document2 paginiTransport Mechanism Quiz-1KLARK ANDREW MASAQUEL MARQUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Science 7 Quarter 1Document6 paginiDLL Science 7 Quarter 1ANTHONY AQUINO100% (1)
- Summative Test Fungi, Protist, BacteriaDocument2 paginiSummative Test Fungi, Protist, BacteriaMarian Anion-Gaurano0% (1)
- Summative Test On Level of Biological OrganizationDocument2 paginiSummative Test On Level of Biological OrganizationAURORA () CARIAGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Sample Test Living ThingsDocument13 paginiChapter 1 Sample Test Living ThingsyasinalifÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUIZ 1 (Science)Document1 paginăQUIZ 1 (Science)Met XiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretest-Science 7Document2 paginiPretest-Science 7Henry CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 2 Water and Its PropertiesDocument7 paginiActivity 2 Water and Its PropertiesDan Christian BlanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Quarter Test Science 7Document5 paginiSecond Quarter Test Science 7QUEENIE BUTALIDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection of ActuatorDocument6 paginiSelection of ActuatorHarshal KolheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Summative Exam2Document3 paginiScience Summative Exam2Mae CudalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cot G7Document3 paginiCot G7charish catungal100% (1)
- The Bolting BibleDocument82 paginiThe Bolting BibleDan JecanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fungi, - Protists, - Bacteria-1 (1) EditDocument21 paginiFungi, - Protists, - Bacteria-1 (1) EditCel Callao Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directions: Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of Your Answer. I. Multiple ChoiceDocument4 paginiDirections: Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of Your Answer. I. Multiple Choicejam syÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELS Quiz 2: Key Concepts of Life and Unifying Themes in BiologyDocument1 paginăELS Quiz 2: Key Concepts of Life and Unifying Themes in BiologyMichael Paul Sinsuan100% (2)
- Prelims Envi SciDocument5 paginiPrelims Envi SciCyndi SamaniegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System Lab WorksheetDocument3 paginiNervous System Lab WorksheetLMNTerriÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 1 First Periodical Test TosDocument4 paginiGeneral Biology 1 First Periodical Test TosMA. HAZEL TEOLOGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Filter Lab Report RubricDocument1 paginăWater Filter Lab Report Rubricapi-501987746Încă nu există evaluări
- Science 7-Module 1: Virgen Delas Flores High SchoolDocument2 paginiScience 7-Module 1: Virgen Delas Flores High SchoolMon Eric LomedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Ptest in Science 7Document3 paginiFirst Ptest in Science 7Ian Punzalan TenorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 1 - EARTHWORM DISSECTIONDocument4 paginiLABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 1 - EARTHWORM DISSECTIONNazarene Carlo PagaspasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretest: Environmental Science Quarter 2 - Module 3 The Ecological Levels of Organization ObjectivesDocument10 paginiPretest: Environmental Science Quarter 2 - Module 3 The Ecological Levels of Organization ObjectivesPersonalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 7-2ND QUATER EXAMDocument4 paginiScience 7-2ND QUATER EXAMVincent S. RedolosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Exam on Microscope UseDocument3 paginiSummative Exam on Microscope UseMae CudalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Heat End of Unit TestDocument6 paginiGrade 7 Heat End of Unit TestJayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 7 - Performance Task 1 - 3rd Quarter - FinalDocument2 paginiScience 7 - Performance Task 1 - 3rd Quarter - FinalamaezingcielÎncă nu există evaluări
- QTR 2 Module 3 Other Living Things Besides Plants and AnimalDocument9 paginiQTR 2 Module 3 Other Living Things Besides Plants and AnimalNick Bantolo67% (3)
- Module 1: Let's Do The Motion: Lagay National High School Calauag West DistrictDocument2 paginiModule 1: Let's Do The Motion: Lagay National High School Calauag West DistrictJAYNAROSE IBAYANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Date: October 1, 2019 (Day 2) Subject: Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesDocument1 paginăDate: October 1, 2019 (Day 2) Subject: Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesMaricris LacwasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Quiz About Asexual and SexualDocument1 paginăLong Quiz About Asexual and SexualLynne Tuiza EndonÎncă nu există evaluări
- S7Q2 ExamDocument2 paginiS7Q2 ExamCatleah ZamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8 2nd Quiz 2 Understanding TyphoonDocument3 paginiScience 8 2nd Quiz 2 Understanding TyphoonRyan BersaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gayong-Gayong Sur Integrated School Second Periodic Examination in Science 7 Name: - Date: - ScoreDocument3 paginiGayong-Gayong Sur Integrated School Second Periodic Examination in Science 7 Name: - Date: - ScoreLaira Joy Salvador - ViernesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipit National High School Diagnostic Assessment for Science 7Document2 paginiLipit National High School Diagnostic Assessment for Science 7Emma Angelica Valera100% (1)
- Science 7 First Quarter WEEK 1-Components of Scientific Investigation Assessment No. 1 NAME: - GRADE & SECTIONDocument3 paginiScience 7 First Quarter WEEK 1-Components of Scientific Investigation Assessment No. 1 NAME: - GRADE & SECTIONsakunare senpaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACTIVITY 1 MicroscopeDocument2 paginiACTIVITY 1 MicroscopeCastolo Bayucot Jvjc100% (1)
- TOS - Diagnostic Grade 9Document1 paginăTOS - Diagnostic Grade 9berith grace magcalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 1 Course OutlineDocument2 paginiGeneral Biology 1 Course OutlineCedrick GenaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VI - Western Visayas Schools Division of Iloilo Leon, IloiloDocument1 paginăRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VI - Western Visayas Schools Division of Iloilo Leon, IloiloOnin AscuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Test in Science 7Document2 paginiDiagnostic Test in Science 7Nyel MacarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretest in Science 7Document3 paginiPretest in Science 7nh9knshr9xÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Atmosphere Test Answers 11-12Document4 paginiReview Atmosphere Test Answers 11-12Bryan Berino Gonzales100% (1)
- 1 Rutherford Vs BohrDocument4 pagini1 Rutherford Vs BohrEgillen EnamnoÎncă nu există evaluări
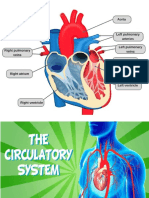
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 paginiCirculatory SystemEgillen EnamnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific InvestigationDocument2 paginiScientific InvestigationEgillen EnamnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carboguard 888 PDSDocument3 paginiCarboguard 888 PDSCane CirpoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mformat Arch PDFDocument11 paginiMformat Arch PDFMary Grace ManiponÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tata Chemicals - WikipediaDocument22 paginiTata Chemicals - WikipediaRavi NayakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kid para Valvula FlowtekDocument1 paginăKid para Valvula FlowtekshenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method 6 Determination of Sulfur Dioxide Emissions From Stationary SourcesDocument13 paginiMethod 6 Determination of Sulfur Dioxide Emissions From Stationary Sourceseliovcr1977Încă nu există evaluări
- TB3 - 117 Engine Maintenance Manual: (EMM Book1 TOC) (Chapter 72 TOC)Document13 paginiTB3 - 117 Engine Maintenance Manual: (EMM Book1 TOC) (Chapter 72 TOC)robinyÎncă nu există evaluări
- India's Vulnerable Borders Fuel Drug TraffickingDocument60 paginiIndia's Vulnerable Borders Fuel Drug TraffickingPrabhanjan GururajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buildings 12 00152 v3 SelfcuringDocument27 paginiBuildings 12 00152 v3 Selfcuringraja sekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro EfbDocument7 paginiHydro EfbFA MonsterÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.0 GPPTEM 2017 NMR Technology For Polymer CharacterizationDocument24 pagini4.0 GPPTEM 2017 NMR Technology For Polymer Characterizationngocanh492Încă nu există evaluări
- CPWD Analysis of Rates 2012Document3.100 paginiCPWD Analysis of Rates 2012bd_gupta_3100% (1)
- The Environmental Health Impacts of Russia's War On Ukraine: Review Open AccessDocument14 paginiThe Environmental Health Impacts of Russia's War On Ukraine: Review Open Accessdk.iitkgp007Încă nu există evaluări
- Personnel Safety Review Checklist: Process Improvement EngineeringDocument3 paginiPersonnel Safety Review Checklist: Process Improvement EngineeringSayed Saad ShehataÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S1878535222006049 MainDocument32 pagini1 s2.0 S1878535222006049 MainAlexandru SavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 Problems 5th EditionDocument2 paginiCH 7 Problems 5th EditionnisannnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cutting SpeedsDocument2 paginiCutting SpeedsefrainneneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dong Zhang Quan 2020Document13 paginiDong Zhang Quan 2020Samanta Sin HacheÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyDocument2 paginiBiologyHesothaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wine Storage Guidelines: Purdue ExtensionDocument4 paginiWine Storage Guidelines: Purdue ExtensionsprabhathÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-strength structural repair mortarDocument4 paginiHigh-strength structural repair mortarBhanuka SamarakoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Proximate Moisture Ash Analysis 2017 EnglishDocument43 pagini02 Proximate Moisture Ash Analysis 2017 EnglishmardhiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uclés2018 Article AnalysisOfThermallyLabilePestiDocument11 paginiUclés2018 Article AnalysisOfThermallyLabilePestimelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLARIANT PRODUCT SHEET Desiccant BagsDocument2 paginiCLARIANT PRODUCT SHEET Desiccant Bagsbango7886Încă nu există evaluări
- Moisture Content of CoalDocument4 paginiMoisture Content of CoalSaad Ahmed100% (1)
- Vacuum Furnace Manufacturers in Bangalore-GLOBALVACUUMPRODUCTSDocument60 paginiVacuum Furnace Manufacturers in Bangalore-GLOBALVACUUMPRODUCTSglobalvacuumproductsÎncă nu există evaluări