Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Case 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary Amenorrhea PDF
Încărcat de
cbac1990Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Case 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary Amenorrhea PDF
Încărcat de
cbac1990Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CASE 03: PRIMARY AMENORRHEA/ CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
AMMENORHEA is the absence of menstruation. The 3 kinds PRIMARY AMENORRHEA
are:
2 GENERAL CAUSES:
1. PRIMARY 1. Congenital Anomalies of the Reproductive System
Absence of MENARCHE (Never had menses in all her life) May be in the form of:
Absence of menses by age 14 years with the absence of Outflow Obstruction
growth or development of secondary sexual o Imperforate hymen
characteristics o Transverse Vaginal Septum
Absence of menses by age 16 years with normal
development of secondary sexual characteristics.
2. SECONDARY
Absence of menstruation who used to menstruate in the
past
Cessation of menstruation for at least 6 months or for at
least 3 of the previous 3 cycle intervals.
For women with IRREGULAR cycle – wait for 6 months
st
Most common cause & 1 thing to r/o: PREGNANCY
The progression of the blockage could eventually lead to
3. PHYSIOLOGIC collection of blood in each part called:
Normal causes
Normally not included in the general classification
Stages:
o Pre-Pubertal
1ST HEMATOCOLPOS: Distensible vagina
o During Pregnancy/ _________
2ND HEMATOMETRA: Uterus
o Post-menopausal 3rd HEMATOSALPINX: Fallopian Tube
4TH HEMOPERITONEUM: Peritoneal cavity
TERMS: 5th ENDOMETRIOSIS: Outside fimbriae
CRYPTOMENORRHEA - Hidden menstruation
PUBARCHE – Development of pubic hair ∴ MENSTRUATION BLOCKAGE FILLING PAIN
THELARCHE – Development of breast
PRECOCIOUS PUBERTY – Menarche BEFORE 8 years old Absence of Uterus, Cervix & Vagina
Absence of Ovaries
Remember the reason why have Breast Examination in GYN? o Ovaries - supply the hormones: E & P
(Case 1: History & Physical Exam) o Progesterone - stimulate endometrial lining
In puberty, the initial change would be BREAST to become: Proliferative phase Secretory
development. It is also the start of OVARIAN function. phase Menstruation Phase
The length of time to anticipate Menarche is 2 years. In
that span, breast development should be in Stage Tanner 2. Genetic Disorders
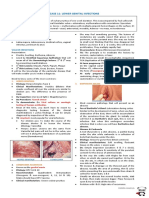
III – IV. Absence of ovaries Turner Syndrome, 45 XO
Hallmark of Puberty: MENARCHE
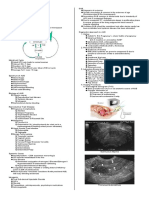
CASE 3
16 yrs. old consulted because she never had menses. She has Breast Budding @ 10 yrs old. By 12 yrs old she started to have Cyclic
Hypogastric Discomfort, , PE: Ht- 4’10 ,Wt- 90 lbs. Breast Tanner IV; Abdomen (+) firm doughy mass @ Hypogastric area, measuring
8x6 cm. No vaginal opening, a membranous structure bulging on the vulvar introitus., Rectal exam (+) fluctuant mass on the
anterior rectal wall & the mass felt abdominally was noted to be superior to this fluctuant mass.
Pathophysiology:
Upon PE, a bulging membrane was noted at the vaginal introitus. This
would mean that there is a blockage of the outflow tract. And since the patient
has an intact endometrium, during her cycle, her uterus contracts to expel blood
with tissue debris from the sloughing of the endometrium, and this would
explain the crampy pain she is experiencing. Furthermore, since the outflow
tract is blocked, the bloody discharge during her menstruation is being filled
from the vagina (hematocolpos) to the uterus (hematometra). This would
present as an abdominal mass on the hypogastric area (Image: hematocolpos) on
palpation and as an enlarged uterus (hematometra) upon rectal examination
noted to be superior to the abdominal mass (hematocolpos) felt.
DX: In conclusion, the probable diagnosis is an IMPERFORATE HYMEN.
ANLAGE OF THE HYMEN:
Anlage: Biology - the initial clustering of embryonic cells from which a part or an organ
develops; primordium.
Incomplete vertical fusion of Sinovaginal bulb & Mullerian Duct
Vagina (2 Anlage):
o Upper 2/3: Mullerian Duct,
o Lower 1/3: Urogenital Sinus (+ Hymen)
TX: CRUCIATE INCISION @ 10, 2 & 6 O’ CLOCK
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES: OVARIAN AGENESIS
Crypto-amenorrhea -B+U
1. Imperforate Hymen TURNERS: short stature, web necked, wide carrying
2. Transverse Vaginal Septum angle, flat chested
3. Vertical Septum Genetic Make-up: 45 XO
Primary Amenorrhea TX: Take what the ovaries supposed to produce
4. Mullerian Agenesis exogenously (hormone therapy) form of E + P hopefully to
5. Ovarian Agenesis make her regularly menstruate
Can she pregnant? Yes, but not babies of her own
TRANSVERSE VAGINAL SEPTUM Laboratory:
Most common location: Junction - Upper 1/3 & Lower 2/3 o Gonadotropins: ↑FSH & LH
COMPLETE septum: Symptomatic Hypergonadotropic
Presentation: Hematocolpos o Endocrine assay: ↓ E + P Hypogonadism
Not felt in the lower part of the vagina as in
Imperforate Hymen Normal: HPO axis:
INCOMPLETE septum (partly patent) Releasing Hormones FSH, LH E + P to affect uterus to
Presentation: Dyspareunia (asymptomatic until menstruate,
evolved in sexual contact) However the absence of ovaries is detected by ↓ E + P that the
TX: Excision Pituitary tries to make more, this is called Positive Feedback
VERTICAL SEPTUM Hormonal profile: HYPERGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
Incomplete to complete septum (all the way from the
cervix down to the vulvar introitus) Image: Turner’s Syndrome
Presentation: Dyspareunia (septum might not be not in
the middle, difficult insertion of the penis)
Remains asymptomatic until detected by annual pelvic
exam
TX: excision
MULLERIAN DUCT ABNORMALITIES
Mullerian Derivatives: Uterus, Tube (which represents the
unfused portion of mullerian duct), Cervix, Upper Third of
Vagina
VAGINAL AGENESIS/ MULLERIAN AGENESIS
Aka Mayer - Rokitansky - Kuster - Hauser Syndrome
Sometimes with concomitant skeletal abnormality
Characterized by congenital absence of vagina & uterus
UTERUS ANOMALIES
Normal Uterus: Pear-shaped
In the PE of a patient with Primary Amenorrhea, there are 2
Waistline - Isthmus dividing body & cervix
organs you have to initially evaluate which are the:
BREAST & UTERUS
Breasts reflects the function of the Ovaries
These 2 organs are needed to be able to menstruate
+B–U
Karyotype: 46 XX (Female)
Transrectal UTZ: 100% Proof - Absence of Uterus
o Not TVS - short length of the Vagina
Cannot bear pregnancy but can donate egg (Surrogacy)
o Phil: Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
TX: Transplant uterus (but not successful)
What other system needed to be reviewed/ ancillary
procedure in patient with Mullerian Duct abnormality?
Urinary tract system/IVP (Intravenous Pyelography) Classification:
NUMBER:
DDX: Androgen Resistance Syndrome (Androgen Insensitivity UNICORNUATE RUDIMENTARY HORN DIDELPHIC
Syndrome)
Karyotype: 46 XY (Male)
Externally, phenotypically female w/ normal female
external genitalia & gonads practically testicles.
Require removal of testicles after about 18 years old SHAPE:
because these gonads maybe at risk for malignant BICORNUATE ARCUATE SEPTATE
degeneration as the patient grows.(Gonadoblastoma)
RUDIMENTARY HORN (RH)
IF RH functioning & communicates to the other cavity , patient may be asymptomatic
IF gets pregnant in the RH may give symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy or similar to endometriosis
Ectopic pregnancy – catastrophic rupture seen in functional non-communicating horn
At times the side of the RH will have absent ureter & kidney Do IVP with Mullerian Duct abnormalities
UNICORNUATE
Least common uterine anomaly
One Uterus
One Mullerian Duct did not develop
DIDELPHY’S
Complete duplication of vagina, uterus & cervix
Anlage – Mullerian Duct developed separately.
Normal: Fusion of Mullerian Duct Body of Uterus
Presentation: Dyspareunia
Not excessive bleeding, the endometrial surface of each endometrial cavity will not be equivalent to the normal.
Remains asymptomatic ‘til detected by prenatal-check up
Can she get pregnant? YES
The clinical implication of Mullerian abnormalities may have bearing on the outcome of pregnancy.
Unicornuate or Didelphy’s - may not expand as normal uterus towards the end of pregnancy, may be candidates of premature
delivery (PPP)
th
Katz 6 : Didelphic Uteri – Do not USUALLY experience repetitive reproductive loss (p. 190)
BICORNUATE - Single-chamber vagina & cervix + completet/ partial septate uterus + 2 uterine bodies)
ARCUATE - Small septate indentation at upper end of the fundus
SEPTATE
Uterus as single organ but has partial/complete septum
Most common Mullerian Duct abnormality that would result to POOR PREGNANCY OUTCOMES
Majority: Abortions in the early trimester
TX: Excision of the septum
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gynecology - Case 14 - Benign Lesions For Ovaries (Gonzalez)Document2 paginiGynecology - Case 14 - Benign Lesions For Ovaries (Gonzalez)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Document2 paginiGynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Document1 paginăGyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 16 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of Cervix (Gonzalez)Document2 paginiGyne - Case 16 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of Cervix (Gonzalez)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFDocument3 paginiGyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 14 Benign Lesions of The OvariesDocument2 paginiGyne - Case 14 Benign Lesions of The Ovariescbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Lec 03 CytologyDocument3 paginiGyne - Lec 03 Cytologycbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Document2 paginiGynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne Notes Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - Dra TrinidadDocument3 paginiGyne Notes Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - Dra Trinidadcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFDocument3 paginiGyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Cervical Cancer and Neoplastic LesionsDocument1 paginăCervical Cancer and Neoplastic Lesionscbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Document1 paginăGyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 12 Upper Genital UTIDocument2 paginiGyne - Case 12 Upper Genital UTIcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & VaginaDocument2 paginiGyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & Vaginacbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 10 MenopauseDocument2 paginiGyne - Case 10 Menopausecbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Lower Genital Infections GuideDocument2 paginiLower Genital Infections Guidecbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 08 Dysmenorrhea & Endometriosis PDFDocument3 paginiGyne - Case 08 Dysmenorrhea & Endometriosis PDFcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Uterine Lesions GuideDocument2 paginiUterine Lesions Guidecbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)Document1 paginăGyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)Document1 paginăGyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Case 4 Anatomic Defect On Pelvic Floor & UrogynecologyDocument1 paginăCase 4 Anatomic Defect On Pelvic Floor & Urogynecologycbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 06 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperandrogenism)Document2 paginiGyne - Case 06 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperandrogenism)cbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Case 2 Pre-Op & Post-Op CareDocument1 paginăCase 2 Pre-Op & Post-Op Carecbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne - Case 05 Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument3 paginiGyne - Case 05 Abnormal Uterine Bleedingcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Case 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary AmenorrheaDocument3 paginiCase 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary Amenorrheacbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- AMC-Residency CV Worksheet-III PDFDocument1 paginăAMC-Residency CV Worksheet-III PDFcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Case 9 Infertility PDFDocument4 paginiCase 9 Infertility PDFcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Case 1 History & PEDocument3 paginiCase 1 History & PEcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- PTAL Residency CaliforniaDocument24 paginiPTAL Residency Californiacbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Menopause and Its Treatment in HomoeopathyDocument5 paginiMenopause and Its Treatment in HomoeopathyIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amenorrhea, Hirsutism, VirilismDocument12 paginiAmenorrhea, Hirsutism, VirilismAly MorganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Women and Exercise Physiology and Sport Medicine PDFDocument349 paginiWomen and Exercise Physiology and Sport Medicine PDFLeandro NascimentoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrics and Gynecology MCQ Practice TestDocument102 paginiObstetrics and Gynecology MCQ Practice TestDev RishabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes of Female InfertilityDocument7 paginiCauses of Female InfertilityNatanael SusantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ob NormalDocument18 paginiOb NormalEspinoza AdrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetric ExamDocument35 paginiObstetric ExamRafi MahandaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Menstrual Irregularities: Causes and Tracking ChangesDocument6 paginiMenstrual Irregularities: Causes and Tracking ChangesLioraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amenorrhea: Student HandoutDocument3 paginiAmenorrhea: Student HandoutJc Mae CuadrilleroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation and Management of Primary Amenorrhea - UpToDateDocument14 paginiEvaluation and Management of Primary Amenorrhea - UpToDateCristinaCaprosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 33 Reproductive and Sexually Transmitted Infection ManagementDocument23 pagini33 Reproductive and Sexually Transmitted Infection ManagementJustine Marie AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marcia Herrin, Maria Larkin - Nutrition Counseling in The Treatment of Eating Disorders-Routledge (2013)Document358 paginiMarcia Herrin, Maria Larkin - Nutrition Counseling in The Treatment of Eating Disorders-Routledge (2013)dhychaz100% (4)
- PLAB 1 MOCK TEST REVIEWDocument34 paginiPLAB 1 MOCK TEST REVIEWDavid YousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmDocument1 paginăSecondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmpolygoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anorexia and bulimia disorders explainedDocument40 paginiAnorexia and bulimia disorders explainedRoxana PoraicuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NoPeriod SecondaryAmenorrheaDocument16 paginiNoPeriod SecondaryAmenorrheaNandhu GangapuramÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCU 2019 Essentials in Gynecology For Undergraduate Medical StudentsDocument414 paginiMCU 2019 Essentials in Gynecology For Undergraduate Medical StudentsHAVIZ YUAD100% (1)
- Obstetrics & Gynecology Key ConceptsDocument23 paginiObstetrics & Gynecology Key Conceptssara khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyperandrogenismDocument3 paginiHyperandrogenismevangelineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anorexia Nervosa (Review) : BMJ (Online) May 2007Document6 paginiAnorexia Nervosa (Review) : BMJ (Online) May 2007Ciprian MocanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR Khaled A-Malek MCDocument63 paginiDR Khaled A-Malek MCﻣﻠﻚ عيسىÎncă nu există evaluări
- For The MRCOG and Beyond: Reproductive EndocrinologyDocument19 paginiFor The MRCOG and Beyond: Reproductive EndocrinologyApurba PailanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrics & Gynecology: Original Review & Revision HyderabadDocument739 paginiObstetrics & Gynecology: Original Review & Revision Hyderabad24k.avinashÎncă nu există evaluări
- MU-MCQs (2020) OBS & GYNDocument330 paginiMU-MCQs (2020) OBS & GYNGhaiidaa khh100% (1)
- Sports Nutrition Final Exam NotesDocument4 paginiSports Nutrition Final Exam NotesTalicia MartineauÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMENORRHEA: AN APPROACH FOR DIAGNOSISDocument41 paginiAMENORRHEA: AN APPROACH FOR DIAGNOSISarfahregarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fmge June 2021 Reacall Questions by Saunil ShahDocument12 paginiFmge June 2021 Reacall Questions by Saunil ShahTamilmani n.mÎncă nu există evaluări
- CalciumDocument7 paginiCalciumMuralidhar K ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falla Ovarica Prematura 2021Document14 paginiFalla Ovarica Prematura 2021Sofía PinzónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clerking Edited by Nada.H.BDocument4 paginiClerking Edited by Nada.H.BAbdulrahman NajiÎncă nu există evaluări