Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Interpreting Categorical Quantitative Data Unit Map
Încărcat de
api-343090158Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Interpreting Categorical Quantitative Data Unit Map
Încărcat de
api-343090158Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Interpreting Categorical & Quantitative Data
Class: Algebra 1 Teachers: Mayarita Castillo, Mi Lin, Margaret Sturtevant
Website: uagreencareersmath.weebly.com Emails: Mcastillo@uagreencareers.org,
Mlin@uagreencareers.org, Msturtevant@uagreencareers.org
Directions
1. Unison Read the Unit Map and Pre-Test in your Responsibility Team (~1 week).
2. Map out what the Standards and Pre-Test want you to learn this unit on the Gist Form.
3. Create a Plan with your Responsibility Team to learn the standards.
4. Take the Post-Test.
5. Submit Evidence of Mastery and Revise.
Standards
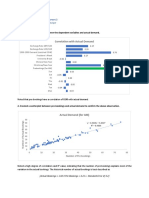
1. HSS-ID.A.1 Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots).
2. HSS-ID.A.2 Use statistics appropriate to the shape of the data distribution to compare center (median,
mean) and spread (interquartile range, standard deviation) of two or more different data sets.
3. HSS-ID.A.3 Interpret differences in shape, center, and spread in the context of the data sets, accounting for
possible effects of extreme data points (outliers).
4. HSS-ID.B.5 Summarize categorical data for two categories in two-way frequency tables. Interpret relative
frequencies in the context of the data (including joint, marginal, and conditional relative frequencies).
Recognize possible associations and trends in the data.
5. HSS-ID.B.6 Represent data on two quantitative variables on a scatter plot, and describe how the variables
are related.
a. Fit a function to the data; use functions fitted to data to solve problems in the context of the data.
Use given functions or choose a function suggested by the context. Emphasize linear, quadratic, and
exponential models.
b. Informally assess the fit of a function by plotting and analyzing residuals.
c. Fit a linear function for a scatter plot that suggests a linear association.
6. HSS-ID.C.7 Interpret the slope (rate of change) and the intercept (constant term) of a linear model in the
context of the data.
7. HSS-ID.C.8 Compute (using technology) and interpret the correlation coefficient of a linear fit.
8. HSS-ID.C.9 Distinguish between correlation and causation.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Reasoning With Equations Inequalities Unit MapDocument2 paginiReasoning With Equations Inequalities Unit Mapapi-343090158Încă nu există evaluări
- Building Functions Unit MapDocument1 paginăBuilding Functions Unit Mapapi-343090158Încă nu există evaluări
- Global 3-4 Nationalism Unit 4 ExamDocument6 paginiGlobal 3-4 Nationalism Unit 4 Examapi-343090158Încă nu există evaluări
- Global 3-4 Science Tech Unit 4 ExamDocument6 paginiGlobal 3-4 Science Tech Unit 4 Examapi-343090158Încă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- CWA Assignment 3Document1 paginăCWA Assignment 3Kartik GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correlation-and-P I GDocument11 paginiCorrelation-and-P I GCamiloArenasBonillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Representation Skills of Students With Different Ability Levels When Learning Using The LCMR ModelDocument16 paginiRepresentation Skills of Students With Different Ability Levels When Learning Using The LCMR ModelSri HaryatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRM Article 2Document9 paginiBRM Article 2Henok AsemahugnÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACTL 2003 Stochastic Models For Actuarial Applications Final ExaminationDocument12 paginiACTL 2003 Stochastic Models For Actuarial Applications Final ExaminationBobÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEP Syllabus 1 - 24082023Document117 paginiNEP Syllabus 1 - 24082023tejasshelke629Încă nu există evaluări
- Heart Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument7 paginiHeart Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Students' Achievement in Normal Labor: Impact of Simulation ModulesDocument6 paginiNursing Students' Achievement in Normal Labor: Impact of Simulation ModulesMd Salah Uddin RajibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4-DMAIC PDFDocument28 paginiChapter 4-DMAIC PDFLayel HamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demand Estimation & Forecasting: Ninth Edition Ninth EditionDocument17 paginiDemand Estimation & Forecasting: Ninth Edition Ninth EditionRogelio VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stats216 hw3 PDFDocument26 paginiStats216 hw3 PDFAlex NutkiewiczÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms Using Diabetes DatasetDocument35 paginiComparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms Using Diabetes DatasetHimangshu Shekhar Baruah100% (1)
- Applied Econometrics: William Greene Department of Economics Stern School of BusinessDocument68 paginiApplied Econometrics: William Greene Department of Economics Stern School of Business郭岱瑋Încă nu există evaluări
- Discussion of Two-Phase Flow Characteristics of Stepped SpillwaysDocument11 paginiDiscussion of Two-Phase Flow Characteristics of Stepped Spillwaysxiaolong zhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- ML ExamDocument5 paginiML ExamAravind Kumar ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maco - Let's Check ULO C - UwuDocument2 paginiMaco - Let's Check ULO C - UwuJessie MacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illiteracy Classification Using K Means-Naïve Bayes AlgorithmDocument6 paginiIlliteracy Classification Using K Means-Naïve Bayes AlgorithmAnwar LudfiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6 - Convolution Neural Network (CNN)Document26 paginiLecture 6 - Convolution Neural Network (CNN)Đặng Anh KhoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OE & HS Subjects For 2020-21 - Ready To PrintDocument122 paginiOE & HS Subjects For 2020-21 - Ready To Printbharath hsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro MatlabDocument6 paginiHydro MatlabRiya KatiyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 31295013211270Document262 pagini31295013211270Qaccee Qaaxalee TaarbiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content Analysis As A Predictive Methodology: Recall, Readership and Evaluations of Business-to-Business Print AdvertisingDocument21 paginiContent Analysis As A Predictive Methodology: Recall, Readership and Evaluations of Business-to-Business Print AdvertisingNupur AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability Distribution On Discrete Random Variables DLPDocument3 paginiProbability Distribution On Discrete Random Variables DLPJoshua OticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 ExosDocument5 paginiChapter 1 ExosRevatee HurilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis: Statistical Tools For Data AnalysisDocument34 paginiHypothesis: Statistical Tools For Data AnalysisApparna BalajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter IIIDocument6 paginiChapter IIIHazel Norberte SurbidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Keperawatan Muhammadiyah: Pelangi Jiwa Aobama, Dedy PurwitoDocument11 paginiJurnal Keperawatan Muhammadiyah: Pelangi Jiwa Aobama, Dedy PurwitoVania Petrina CalistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASA VAM StatementDocument7 paginiASA VAM StatementThe Washington Post100% (1)
- BUSN 2429 Chapter 4 Introduction To Probabilities - SDocument114 paginiBUSN 2429 Chapter 4 Introduction To Probabilities - SAwais SadaqatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2-02 ProbabilityDocument3 paginiChapter 2-02 ProbabilityManilyn Mugatar MayangÎncă nu există evaluări