Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Problem 3.31 PDF
Încărcat de
Kauê BrittoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Problem 3.31 PDF
Încărcat de
Kauê BrittoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
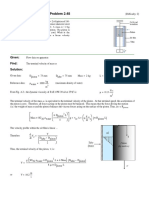
Problem 3.
31 [Difficulty: 2]
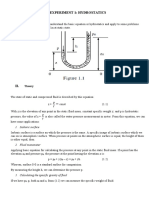
Given: A U-tube manometer is connected to the open tank filled with water as
shown (manometer fluid is mercury). The tank is sealed and pressurized.
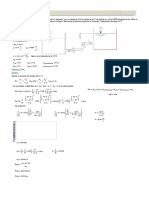
D1 = 2.5⋅ m D2 = 0.7⋅ m d = 0.2⋅ m po = 0.5⋅ atm SGHg = 13.55 (From Table A.1, App. A)
Find: The manometer deflection, l
Solution: We will apply the hydrostatics equations to this system.
Governing Equations: dp
= ρ⋅ g (Hydrostatic Pressure - h is positive downwards)
dh
ρ = SG⋅ ρwater (Definition of Specific Gravity)
Assumptions: (1) Static liquid
(2) Incompressible liquid
Integrating the hydrostatic pressure equation we get:
Δp = ρ⋅ g⋅ Δh
When the tank is filled with water and pressurized, the mercury in the left leg of the D1
manometer is displaced downward by l/2. The mercury in the right leg is displaced d d
upward by the same distance, l/2.
Beginning at the free surface of the tank, and accounting for the changes in pressure with D2 c
elevation:
patm + po + ρwater⋅ g⋅ ⎛⎜ D1 − D2 + d + ⎟ − ρHg⋅ g⋅ l = patm
l⎞
⎝ 2⎠
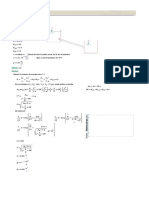
Upon simplification: po
+ D1 − D2 + d
ρwater⋅ g
po + ρwater⋅ g⋅ ⎛⎜ D1 − D2 + d +
l⎞
⎟ = ρHg⋅ g⋅ l l=
⎝ 2⎠
SGHg −
1
2
Substituting values into the expression:
⎛ 5 3 2⎞
⎜ 0.5⋅ atm × 1.013 × 10 ⋅ N × 1 ⋅ m × 1 ⋅ s ⎟ + 2.5⋅ m − 0.7⋅ m + 0.2⋅ m
⎜ 2 1000 kg 9.8 m ⎟
l = ⎝ m ⋅ atm ⎠ l = 0.549 m
1
13.55 −
2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Problem 3.29 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 3.29 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.35 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 3.35 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.37 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 3.37 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.26 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 3.26 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.34 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 3.34 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1Document5 paginiExperiment 1Mạch Vũ Anh KhoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bao Cao Mon Co Luu ChatDocument23 paginiBao Cao Mon Co Luu ChatMạch Vũ Anh KhoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.17Document1 paginăFox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.17Patricia RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions: Solutions Manual For Petroleum and Gas Field Processing 2Nd Edition Abdel AalDocument10 paginiSolutions: Solutions Manual For Petroleum and Gas Field Processing 2Nd Edition Abdel AalFrank Cesar Delgado Montalvo0% (1)
- HTTPS://FR - Scribd.com/document/518094129/2012 Phonetique Progressive Du Francais DebutantDocument7 paginiHTTPS://FR - Scribd.com/document/518094129/2012 Phonetique Progressive Du Francais DebutantkhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepared By: Ahmed A.Maaroof Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering Dept. 2020-2021Document36 paginiPrepared By: Ahmed A.Maaroof Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering Dept. 2020-2021syakoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robert 4Document436 paginiRobert 4로헬Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualDocument25 paginiMechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualJodiAguilareibd100% (49)
- Problem 4.158Document2 paginiProblem 4.158문jmtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solucion Ejercicio 8.163 (Mecanica de Fluidos)Document2 paginiSolucion Ejercicio 8.163 (Mecanica de Fluidos)Jairo RondonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pº 4 Ejer5Document1 paginăPº 4 Ejer5Gustavo Quispe AbascalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.54: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 paginăProblem 3.54: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipes. Flow Rate and Pressure Loss EquationsDocument62 paginiPipes. Flow Rate and Pressure Loss EquationsFrancisco AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1a Preg 3er Parcial SEM 2 - 2013: PlanteamientoDocument3 pagini1a Preg 3er Parcial SEM 2 - 2013: PlanteamientoJHENNY GUISELA VARGAS BRAVOÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEL FormelsamlungDocument2 paginiMEL FormelsamlungLuka VartušekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 paginiFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 paginiFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 paginiFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ploce I LjuskeDocument4 paginiPloce I LjuskeDusan DjordjevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Solutions (Global Edition) : Sketch The Band DiagramDocument8 paginiChapter 10 Solutions (Global Edition) : Sketch The Band Diagram성민김Încă nu există evaluări
- 85 Sample ChapterDocument22 pagini85 Sample ChapterANUJITH V SÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE5107 - Laterally Loaded Piles IIDocument43 paginiCE5107 - Laterally Loaded Piles IIMartin ČudejkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathcad - Análisis Dimensional 2011-0Document1 paginăMathcad - Análisis Dimensional 2011-0Albert CarreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- EGN 3353C Fluid Mechanics: P P P GHDocument7 paginiEGN 3353C Fluid Mechanics: P P P GHSumantri HatmokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipes. Flow Rate and Pressure Loss EquationsDocument62 paginiPipes. Flow Rate and Pressure Loss Equationsrahmat mamuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coursework 2Document2 paginiCoursework 2tanatswaphiri54Încă nu există evaluări
- Solutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7Document14 paginiSolutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7SUNIL KUMAR JANGRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChII PDFDocument30 paginiChII PDFSheryll de GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Losses in Fuel CellsDocument13 paginiLosses in Fuel CellsLjubodrag SamardzicÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1 Solution PDFDocument6 paginiHW1 Solution PDFZuhair AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 paginăProblem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Fluids 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualDocument35 paginiMechanics of Fluids 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manualleroyweavervpgnrf100% (18)
- Problem 3.55: Given: Find: Assumptions: SolutionDocument1 paginăProblem 3.55: Given: Find: Assumptions: SolutionKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathcad - Catenary - Impedance - Single - TrackDocument1 paginăMathcad - Catenary - Impedance - Single - TrackCarlos AlonsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV. Polymer Solutions and Blends: Entropy of MixingDocument30 paginiIV. Polymer Solutions and Blends: Entropy of MixingYan WANGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boundary LayerDocument3 paginiBoundary LayerPatrick Joseph RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.44 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 3.44 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport Phenomena 4Document30 paginiTransport Phenomena 4Kaify PeshmergaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics I Solution 4 Question 1: Problem P2.139: A B B C D DDocument8 paginiFluid Mechanics I Solution 4 Question 1: Problem P2.139: A B B C D Dcartoon_nateÎncă nu există evaluări
- P P P P: ( (P - P) / P) % 0.665 % We Can Neglect The K.E. Term in This ProblemDocument3 paginiP P P P: ( (P - P) / P) % 0.665 % We Can Neglect The K.E. Term in This ProblemAramNawzad100% (1)
- Kumar PDFDocument90 paginiKumar PDFDiego PozoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop - Fluidos II - Tomas Ferrer, Luis LopezDocument8 paginiWorkshop - Fluidos II - Tomas Ferrer, Luis LopezTOMAS JOSE FERRER MONZONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualDocument35 paginiMechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manualleroyweavervpgnrf100% (18)
- Dwnload Full Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 paginiDwnload Full Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual PDFtatting.itacistpjkl100% (10)
- Problem 3.62 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 3.62 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goldstein Solutions Chapter 8Document8 paginiGoldstein Solutions Chapter 8AmnishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap. 03Document165 paginiCap. 03lucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 03 Mecanica Dos Fluidos Fox Mcdonald 8a Edicao SolutionDocument166 paginiCap 03 Mecanica Dos Fluidos Fox Mcdonald 8a Edicao SolutionAlice LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.49: Given: Find: AssumptionsDocument1 paginăProblem 3.49: Given: Find: AssumptionsKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Line Different Types of Transmission Line Transmission Line Per Unit Length Parameters Telegrapher Equation Power FlowDocument15 paginiTransmission Line Different Types of Transmission Line Transmission Line Per Unit Length Parameters Telegrapher Equation Power FlowdiptodevilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fox and Mcdonalds Introduction To Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition Pritchard Solutions Manual 2Document2 paginiFox and Mcdonalds Introduction To Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition Pritchard Solutions Manual 2dextrermachete4amgqgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Δh L= gD: X= dp ds dp ds g'H u g ρ ρ D T= dp/ds g ρDocument13 paginiΔh L= gD: X= dp ds dp ds g'H u g ρ ρ D T= dp/ds g ρabhilash nairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Movimiento de ApoyosDocument7 paginiMovimiento de ApoyosNeverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Fluid FlowDocument5 paginiReal Fluid FlowPatrick Joseph RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99De la EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Încă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.30 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.30 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.28 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 2.28 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.16 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 2.16 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.27: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 paginăProblem 2.27: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.36 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.36 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.25 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.25 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.80: Open-Ended Problem StatementDocument1 paginăProblem 2.80: Open-Ended Problem StatementKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.27 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.27 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.32 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 2.32 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 1 B 1 C 0 2 4 6 X y y y Y: Streamline PlotDocument1 paginăA 1 B 1 C 0 2 4 6 X y y y Y: Streamline PlotKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.49: Given: Find: AssumptionsDocument1 paginăProblem 3.49: Given: Find: AssumptionsKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.27: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 paginăProblem 3.27: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.59 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 3.59 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.11 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 2.11 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.44 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 2.44 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.28 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.28 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.22 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 2.22 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 paginăProblem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.49 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 2.49 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.57 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 3.57 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.49 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.49 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.43 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 3.43 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.42 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 3.42 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.19 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.19 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 3.44 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 3.44 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1.22 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 1.22 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.54 PDFDocument3 paginiProblem 2.54 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.77 PDFDocument1 paginăProblem 2.77 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 2.68 PDFDocument2 paginiProblem 2.68 PDFKauê BrittoÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual: High Pressure Water PumpsDocument64 paginiUser Manual: High Pressure Water PumpsEdwin MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul Ansys Day 3Document28 paginiModul Ansys Day 3GiLang MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress Concentration Analysis For Countersunk Rivet Holes in Orthotropic PlatesDocument10 paginiStress Concentration Analysis For Countersunk Rivet Holes in Orthotropic PlatesMohammad Ahmad GharaibehÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1.2 Storyboard LaunchDocument15 pagini1.1.2 Storyboard Launchshoaib1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Vdocuments - MX - Proportionate and Nonproportionate Shear Walls PDFDocument5 paginiVdocuments - MX - Proportionate and Nonproportionate Shear Walls PDFMalavika G BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsDocument3 paginiStrength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsZoe FallurinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soalan Fi Sem 2 2010Document19 paginiSoalan Fi Sem 2 2010mohamad nizam bin mahbobÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9-Physics-Practice Questions emDocument34 pagini9-Physics-Practice Questions emmahaboob kpÎncă nu există evaluări
- InsulationDocument5 paginiInsulationjaleelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture MechanicsDocument39 paginiFracture MechanicsDEEPAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delhi Metro TEMPERATURE LOADDocument3 paginiDelhi Metro TEMPERATURE LOADHarikrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD TBDocument164 paginiTD TBsampath currentaffaairsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Line SizingDocument12 paginiLiquid Line Sizinglolofm25Încă nu există evaluări
- Broquet Gamme IndustrieDocument8 paginiBroquet Gamme IndustrieJavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bitumen (Discussion)Document2 paginiBitumen (Discussion)tiaramira950% (1)
- Rancang Bangun Alat Praktikum Hukum Bernoulli Pada Fluida IdealDocument4 paginiRancang Bangun Alat Praktikum Hukum Bernoulli Pada Fluida IdealFahmil HusinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Calculators - Steam Turbine Calculator2Document2 paginiSteam Calculators - Steam Turbine Calculator2Adam GordonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElasticityDocument7 paginiElasticityArup palÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIN PLATE - Beam To BeamDocument71 paginiFIN PLATE - Beam To BeamHemant Ramesh Narkar100% (3)
- MSC Nastran Useful Resources - An Overview of SOL 106 - Nonlinear Static AnalysisDocument8 paginiMSC Nastran Useful Resources - An Overview of SOL 106 - Nonlinear Static AnalysisAnonymous MMKF5TRXCÎncă nu există evaluări
- TF-8694 - Therminol - XP - Technical - BulletinDocument8 paginiTF-8694 - Therminol - XP - Technical - BulletingabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conduits ASSIGNMENTDocument12 paginiConduits ASSIGNMENTishaq kazeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vw1004 Control KosoDocument27 paginiVw1004 Control KosolovelycatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ced 506 Hydraulics Assignment TwoDocument6 paginiCed 506 Hydraulics Assignment TwoCula Nauman TamaniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- USS Physics-Pages-491-493Document3 paginiUSS Physics-Pages-491-493Arnav PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 84 Top Strength of Materials Question and AnswersDocument11 pagini84 Top Strength of Materials Question and AnswersM Tatualla0% (1)
- Transition State TheoryDocument10 paginiTransition State TheoryNurshuhada NordinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic AnalysisDocument18 paginiSeismic AnalysisAbdelkader SafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LG Ducted Air Conditioning Catalogue 28incr3229Document1 paginăLG Ducted Air Conditioning Catalogue 28incr3229Mohamed MosaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report 5 DistillationDocument6 paginiLab Report 5 DistillationMyeeka Hammond100% (1)