Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
TOGAF V92 Part1
Încărcat de
rammohan thirupasurTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TOGAF V92 Part1
Încărcat de
rammohan thirupasurDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.
2 Edition
Day 1
Management Overview
TOGAF® standard Version 9.2 Introduction
The TOGAF® standard Version 9.2 Components
Architecture Capability Framework Overview
Architecture Skills Framework
An Introduction to the Architecture Development Method
An Introduction to the ADM Guidelines and Techniques
Architecture Content Framework
Enterprise Continuum
Adapting the ADM: Iterations and Levels
Day 2
Phase P : Preliminary Phase
Architecture Maturity Model
Architecture Partitioning
Other EA Frameworks
EA Tools Landscape
Adapting the ADM: Security & SOA
Phase A : Architecture Vision
Stakeholder Management
Business Scenarios
Architecture Implementation Support Techniques
o Business Transformation Readiness Assessment
o Capability based Planning
o Risk Management
o Building Blocks and Interoperability
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 1
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Day 3
Phase B Business Architecture
Phase B Business Architecture Artifacts
Phase-C-Overview
Phase C Data Architecture
Phase C Data Architecture Artifacts
Integrated Information Infrastructure Reference Model
Phase C Application Architecture
Phase C Application Architecture Artifacts
Foundation Architecture: Technical Reference Model
Phase D Technology Architecture
Phase D Technology Architecture Artifacts
100
Day 4
Phase E Opportunities and Solutions
Migration Planning Techniques
o Implementation Factor Assessment and Deduction matrix
o Consolidated Gaps, Solutions and Dependencies matrix
o Architecture Definition Increments table
o Transition Architecture state evolution table
o Business Value Assessment
Phase F Migration Planning
Phase-G-Implementation-Governance
Phase-H-Architecture-Change-Management
Architecture-Requirements-Management
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 2
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Management
Overview
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
About The Open Group
» The Open Group is a global consortium that enables the
achievement of business objectives through technology
standards
» Its diverse membership of more than 500 organizations
includes customers, systems and solutions suppliers, tool
vendors, integrators, academics, and consultants across
multiple industries.
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 3
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The Open Group Vision
Boundaryless Information Flow™
achieved through global interoperability
in a secure, reliable and timely manner
“Boundaryless does not mean there are no
boundaries – it means that boundaries are
permeable to enable business.”
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The Open Group Mission
The mission of The Open Group is to
drive the creation of Boundaryless
Information Flow™ achieved by:
» Working with customers to capture,
understand and address current and
emerging requirements, establish policies,
and share best practices;
» Working with suppliers, consortia and
standards bodies to develop consensus
and facilitate interoperability, to evolve
and integrate specifications and open
source technologies;
»Developing and operating the industry's
premier certification service and
encouraging the procurement of certified
products.
9
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 4
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Agenda
» The Open Group
» The Architecture Forum
» Why Enterprise Architecture?
» Why a Framework?
» The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2
» The TOGAF Library
» TOGAF 9 Certification
» Summary
10
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture Forum – Mission
» The mission of The Open Group Architecture Forum is to
advance The Open Group vision of Boundaryless
Information Flow, for and between enterprises,
» Through a set of programs that focus on all architectural
aspects, including:
– Providing broad and deep leadership to the EA community
– Validating, publishing, fostering, and maintaining best practices
for EA
– Developing, organizing, researching, and publishing thought
leaders in EA
– Initiating and managing programs and projects to support these
activities
11
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 5
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
What is an Enterprise?
» A collection of organizations that share a common set of
goals
– Government agency
– Part of a corporation
– Corporation
» Large corporations may comprise multiple enterprises
» May be an “extended enterprise” including partners,
suppliers and customers
12
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
What is an Architecture?
» An Architecture is the
fundamental concepts or
properties of a system in its
environment embodied in:
– its elements,
– their relationships to each
other and the environment,
– and the principles governing
its design and evolution.
Adapted from ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010:2011
13
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 6
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
What is Enterprise Architecture?
Enterprise Architecture is:
» The organizing logic for business
processes and IT infrastructure
reflecting the integration and
standardization requirements of
the firm’s operating model.[1]
» A conceptual blueprint that
defines the structure and
operation of an organization.
The intent of an Enterprise
Architecture is to determine how
an organization can most
effectively achieve its current
[1] MIT Center for Information Systems Research
and future objectives. [2]
[2] SearchCIO.com
14
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
ONS
INNOVATI
TYPES OF
Operating Models
Coordinated Unified
High
Integration
Diversified Replicated
Low
Low
High
Standardization
Source: Enterprise Architecture as Strategy
-Jeanne Ross et al
15
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 7
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
16
Broad Strategies
Play to win
Play not to lose
17
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 8
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
18
ONS
INNOVATI
TYPES OF
Types of Innovations
Play not to lose
Semi-Radical Radical
New
Technology
Near to the Incremental Semi-Radical
existing
Near to the
New Play to win
existing
Business Model
19
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 9
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
ONS
INNOVATI
TYPES OF
Experience Innovation
Co-Creating unique value with customers
Co-Creation Building Blocks
D Dialogue
A Access
R Risk Assessment
T Transparency
20
Migrating to Co-creation Experiences
ES
RIENC
EXPE
TION
CREA
C O-
G TO
ATIN
MIGR
Traditional Exchange Co-creation Experience
Goal Of Interaction Extraction of Economic value Co-creation of value through
compelling co-creation
experiences, as well as extraction
of economic value
Locus Of Interaction Once at the end of the value Repeatedly, anywhere, and
chain anytime in the system
Company- Consumer Transaction-based Set of interactions and
relationship transactions focused on a series
of Co-creation experiences
21
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 10
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Migrating to Co-creation Experiences
S
IENCE
EXPER
ION
CREAT
C O-
TO
ATING
MIGR
Traditional Exchange Co-creation Experience
View of Choice Variety of Products and Co-creation experiences
services, features and based on interactions across
functionalities, product multiple channels, options,
performance, and operating transactions and the price-
procedures experience relationship
Pattern Of Interaction Passive, Firm-initiated, Active, initiated by either
between Company and the One-On-One company or consumer , one-
Consumer on-one Or One-to-many
Focus of Quality Quality of Internal processes Quality of Consumer-
and company offerings company interactions and
Co-creation Experiences
22
ONS
INNOVATI
TYPES OF
Experience Innovation
Levers of Experience Innovation
Giving the customer the ability to interact with
Granularity experience environments at any desired level
Exploring how new technologies, channels, or modes of
Extensibility delivery can allow customers to experience in new
ways
Linkage Recognition that events connect in multiple ways from
a consumer point of view
Capturing the learning from co-creation experiences and
Evolvability using it develop experience environments to shape
themselves to customers needs and preferences
23
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 11
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Experience –Centric Information System
Managerial Insight
Line manger focus ; Experiencing the business and
Level-1:
Experience Quality facilitating Co-creation experiences
Increasing complexity of Manager-system
Management
Business analysis:
Level-2: Monitoring, analyzing, and understanding business
Interaction
Business Activity activities
Monitoring
Level-3: Routinized Response :
Business Process Rules based Procedures
Management and Automated reports
24
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
25
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 12
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Definition of “Reengineering”
The fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business
Processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical,
contemporary measures of performance, such as cost, quality,
service, and speed
Source: Reengineering the Corporation by Michael Hammer et al
26
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
Manage complexity
27
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 13
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Seven sins of complexity
Number of different offerings
Number of tasks in the process
Opportunity for errors
Variation in the processing time
Setup time
Processing time
Variability in demand
28
Three rules of complexity
Eliminate complexity that customers will not pay for
Exploit the complexity will pay for
Minimize the costs of the complexity you offer
29
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 14
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Dealing Complexity
Change your existing portfolio of offerings
Improve the profitability of existing offerings
Minimize internal complexity
30
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
Manage complexity
Manage change
31
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 15
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Types of Changes
Business Changes
Technology Changes
32
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
Manage complexity
Manage change
Manage Agility
33
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 16
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
EA?
XT OF
CONTE
THE
Y IN
AGILIT
IS
WHAT
What is Agility?
TOGAF Scrum ITIL
Strategy/Plan Implementation Operations
Develop Governance
Ability to develop a strategy/plan, implement and
operate the business capabilities optimally;
to proactively manage the changes.
34
Attributes of Agility
Flexibility
Cost
Speed of Response
Quality
Reusability
35
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 17
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Factors influencing Agility
• Vision
• Maturity
• Innovation
• Environment
• Complexity
• Coherence
• Governance
36
Vision
o Agility is not about determining what needs to be done as we go along,
but to have a clear Vision and move towards the Vision faster, cheaper and
better even if we encounter many obstacles.
o Define and link different levels of Vision
Long term Vision - 10 - 30 yrs
Near term Vision - 2-5 yrs
Short term Vision - less than 2 yrs
37
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 18
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Maturity
oOrganizations should have enough maturity to be agile
oLarge organizations should have at least Level 3 maturity
None Initial Under Defined Measured Optimized
Development
oSmall organizations should have at least Level 2 maturity
None Initial Under Defined Measured Optimized
Development
38
ARCHITECTURE MATURITY MODELS
Extended EA Maturity Model (E2AMM), Institute for Enterprise Architecture
Developments
A maturity model of implementation of an EA program – Extended
Enterprise Architecture Maturity Model (E2AMM) - Schekkerman, 2007
NASCIO EA Maturity Model - Refer www.NASCIO.org
The US Department of Commerce's ACMM Framework
The goal is to enhance the overall odds for success of IT
Architecture by identifying weak areas
Provides a defined evolutionary path to improving the overall Architecture
process.
39
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 19
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Coherence
Business Perspective
The ability of firms to generate and explore ‘synergies’ of various
types -Teece et al
IT Perspective
Sharing information, managing the number of development environments, and linking
applications within the enterprise
- Wagter et al
40
COHERENCE ATTRIBUTES
◦ Principles: Compliance to the Architecture Principles
◦ EA Framework: The degree to which the an EA Framework is adapted
◦ Quality: The impact on the quality of the Architecture
◦ Time: A measure of the time of processes
◦ Cost: A measure of cost of processes
(Abaas and Steenkamp, 2010)
41
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 20
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Y
AGILIT
AND
ENCE
COHER
EN
BETWE
LATION
CORRE
(Abaas and Steenkamp, 2010)
42
Environment
• Leadership
• High-performance climate
• Commitment
• Connection
• Collaboration
• Freedom of choice
• Openness (Candor)
43
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 21
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
Manage complexity
Manage change
Manage Agility
Reduce time to market
Governance, Risk, Compliance
44
PERFORMANCE
Governance Styles
PROFIT ASSET UTILIZATION GROWTH
Profitability via enterprise wide Efficient operation by Encourage business unit
Strategic Driver integration and focus on core encouraging sharing and reuse innovation with few mandated
Competencies processes
ROI/ROE and business process ROA and unit IT cost Revenue growth
Key Metrics
costs
■ Enterprise wide management ■ Business/IT relationship ■ Budget approval and risk
mechanisms (e.g., executive manager management
committee) ■ Process teams with IT ■ Local accountability
Key IT Governance ■ Architecture process members ■ Portals or other
Mechanisms ■ Capital approval ■ SLA and chargeback information/services sources
■ Tracking of business value of IT ■ IT leadership decision-
making body
Layers of centrally mandated Shared services centrally Local customized capability
IT Infrastructure shared services coordinated with few required shared
services
Low business costs through Low IT unit costs; reuse of Local innovation with
Key IT Principles standardized business processes standard models or services communities of practice;
optional shared services
More centralized Blended More decentralized
Governance E.g., Monarchies and Federal E.g., Federal and Duopoly E.g., Feudal arrangements;
risk management emphasis
45
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 22
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
Manage complexity
Manage change
Manage Agility
Reduce time to market
Governance, Risk, Compliance
Optimize the business processes
46
Optimization Techniques
Lean Methodology
Maximizing the “Customer Value” by Minimizing the
waste in the business
Eg Kaizen – Continuous Improvement
47
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 23
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Optimization Techniques
Six Sigma
Minimizing the number of errors and variation in a
business process
Defects per Million
Sigma Level Opportunities (DPMO)
1 690,000
2 308,537
3 66,807
4 6,210
5 233
6 3.4
48
To Architect the Enterprise
Accelerate the business transformation
Drive “strategic” Innovation
Re-engineer the corporation
Manage complexity
Manage change
Manage Agility
Reduce time to market
Governance, Risk, Compliance
Optimize the business processes
Align IT to Business
49
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 24
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Types
Business
Architecture
Application Data
Architecture Architecture
Technology
Architecture
50
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Why Enterprise Architecture?
» Effective management and exploitation of information
and Digital Transformation are key to business success
» Good information management = competitive advantage
» Current IT systems do not really meet the needs of
business
– Fragmented, duplicated
– Poorly understood
– Not responsive to change
» Investment in Information Technology
– Focussed on system maintenance
– Tactical developments rather than a strategic plan
51
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 25
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Why Enterprise Architecture?
» Two key reasons why you need an Enterprise
Architecture:
– A means to achieve competitive advantage
– Enables managed innovation within the enterprise
52
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Pressure to develop Enterprise Architecture
» Laws and regulations
– Clinger-Cohen Act (US Information Technology
Management Reform Act 1996)
– EU Directives on the Award of Public Contracts
– Sarbanes-Oxley
» More extended enterprises
» More co-operative IT operations
» Greater publicity to failures
» Increase in litigation
» Audit requirements
53
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 26
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Business Benefits of Enterprise Architecture
» It helps an organization achieve its business strategy
» Faster time to market for new innovations and
capabilities
» More consistent business processes and information
across business units
» More reliability and security, less risk
Source: “Why Enterprise Architecture Matters?”, The Open Group White Paper, W076
54
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Business Benefits of Enterprise Architecture
» A more efficient business operation
» A more efficient IT operation
» Better return on existing investment,
» Reduced risk for future investment
» Faster, simpler, and cheaper procurement
See also: “Why Enterprise Architecture Matters?”, The Open Group White Paper, W076
55
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 27
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
What is an Architecture Framework?
» TOGAF Standard Definition: Architecture Framework
– A conceptual structure used to develop, implement, govern, and
sustain an architecture
» It should describe a method for designing target state of
the enterprise in terms of a set of building blocks, and for
showing how the building blocks fit together
» It should contain a set of tools and provide a common
vocabulary
» It should also include a list of recommended standards
and compliant products that can be used to implement
the building blocks
56
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The Value of a Framework
» Provides a practical starting point for an Architecture
Project
– Avoids the initial panic when the scale of the task
becomes apparent
– Systematic – “Codified common sense”
– Captures what others have found to work in real life
– Contains a Baseline set of resources for reuse
57
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 28
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Development Method
A comprehensive general Vendor, tool and technology
method neutral open standard
Complementary to, not
competing with, other Avoids re-inventing the
frameworks wheel
Widely adopted in the
market Business IT alignment
Tailorable to meet an
organization and industry Based in best practices
needs
Possible to participate in
Available under a free the evolution of the
perpetual license framework
58
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
TOGAF Origins
» A customer initiative
» A framework, not an architecture
– A generic framework for developing architectures to
meet different business needs
– Not a “one-size-fits-all” architecture
» Originally based on TAFIM (U.S. DoD)
59
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 29
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Member (End User) Driven
• Customer members demand architecture standards …
• Customer members select TAFIM as preferred starting point…
• DoD Information Systems Agency (DISA) donate TAFIM as base
• TOGAF 1st Edition
• TOGAF 7 Technical Edition
• TOGAF 8.1.1
‘93 ‘94 • TOGAF 9 Enterprise Edition
‘96
‘01
‘02 • TOGAF 9.1
‘03
‘06
‘09
‘11
• The Interoperable Enterprise ‘13
‘15 ‘17
Business Scenario ‘18
first published Certifications >25k TOGAF Standard,
Certifications > 50k Version 9.2
TOGAF 8 Enterprise Edition TOGAF Library
First TOGAF Certification Certifications >70k
Program Launched
60
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
TOGAF Scope
» The TOGAF standard emphasizes business goals as
architecture drivers, and provides a set of best practices,
including:
– TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM)
– ADM Guidelines & Techniques
– TOGAF Architecture Content Framework
– Enterprise Continuum
– TOGAF Capability Framework
» In addition, the TOGAF Library provides a portfolio of
guidance material to support the standard
61
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 30
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
TOGAF Long-term Goals
» An industry standard, generic Enterprise Architecture
method….
» ….usable on its own or in conjunction with frameworks
having products relevant/specific to particular sectors.
– Several frameworks have mind share:
• Zachman, DODAF, MODAF, FEAF, TEAF, …
– Almost all focus on products, not method
– The TOGAF method and…. (not the TOGAF method
or….)
62
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Structure of the Standard
Architecture Content Architecture Capability
ADM Framework Framework
ADM Guidelines
Enterprise Continuum
& Techniques
63
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 31
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2
Table of Contents
Part I - Introduction
Preface, Executive Overview, Core Concepts, Definitions
Part II – Architecture Development Method
Introduction to ADM
ADM Phase Narratives
Part III – ADM Guidelines and Techniques
Guidelines for Adapting the ADM Process
Techniques for Architecture Development
Part IV – Architecture Content Framework
Content Metamodel
Architectural Artifacts
Architecture Deliverables
Building Blocks
Part V – Enterprise Continuum and Tools
Enterprise Continuum
Architecture Partitioning
Architecture Repository
Tools for Architecture Development
Part VI – Architecture Capability Framework
Architecture Board
Architecture Compliance
Architecture Contracts
Architecture Governance
Architecture Maturity Models
Architecture Skills Framework
64
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
TOGAF Components
» Architecture Development Method (ADM)
– An iterative sequence of steps to develop an enterprise-wide
architecture
» ADM Guidelines and Techniques
– Guidelines and techniques to support the application of the ADM
» Architecture Content Framework
– A detailed model of architectural work products, including
deliverables, artifacts within deliverables, and the Architecture
Building Blocks (ABBs) that deliverables represent.
65
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 32
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
TOGAF Components (Cont’d)
» The Enterprise Continuum
– A model for structuring a virtual repository and methods for
classifying architecture and solution artifacts
» The Architecture Capability Framework
– A structured definition of the organizations, skills, roles and
responsibilities to establish and operate an Enterprise Architecture.
» The TOGAF Library
– A supporting element separate to the Standard
– A reference library containing guidelines, templates, patterns, and
other forms of reference material to accelerate the creation of new
Enterprise Architectures.
66
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Modular Structure
Content Framework
Extended Guidance
TOGAF Capability Framework Architectural Styles
Additional ADM detail
Informs the Sets targets, KPIs,
capability Architecture Capability budgets for
Framework (Part VI) architecture roles
Ensures Realization
Drives need for Architecture
of Business Vision Capability maturity
Business needs feed Architecture Development Delivers new
into method Method (Part II) business solutions
ADM Guidelines &
Business Vision Refines Business
Techniques (Part III)
and Drivers Understanding Capabilities
TOGAF ADM &
Architecture Content Content Framework
Framework (Part IV)
Enterprise Continuum &
Tools (Part V)
Informs the Business Operational changes cause
TOGAF Reference Materials updates
of the current state
(TOGAF Library)
TOGAF Enterprise
Continuum & Tools 67
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 33
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Capability Framework
68
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Establishing the Architecture Capability as an
Operational Entity
» The Architecture Capability Framework provides guidance on
establishing an operational enterprise architecture practice
» It recommend they include capabilities such as:
– Financial Management
– Performance Management
– Service Management
– Risk Management
– Resource Management
– Communications and Stakeholder Management
– Quality Management
– Supplier Management
– Configuration Management
– Environment Management
69
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 34
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture
Skills
Framework
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
70
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Roles
Architecture Sponsor CxO
Project
Manager
Architecture
Sponsor
Business
Architecture Board
Member There are many roles involved in an Architect
enterprise architecture practice
Application
Project EA Architect
Manager Manager
Technology Architecture Board
Architect Member
IT Designer
Business Business
Architect Domain
Experts
Data
Architect
QA / Standards Enterprise IT Designer
Groups IT Designer Security
71
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 35
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Purpose
Definitional Rigor
» ‘‘Enterprise Architecture’’ and ‘‘Enterprise Architect’’ are
widely used but poorly defined terms.
» There is a need for clearer definitions.
Basis of an Internal Architecture Practice
» An enterprise architecture practice is a formal program
of development and certification by which an enterprise
recognizes the skills of its architects
» Such a program is essential in order to ensure the
alignment of staff skills and experience with the
architecture tasks that the enterprise wishes to perform
72
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Purpose
» An enterprise architecture practice is both difficult and
costly to set up
» The TOGAF Architecture Skills Framework attempts to
address this need
– By providing definitions of the architecting skills and proficiency
levels required of personnel, internal or external, who are to
perform the various architecting roles defined within the TOGAF
Framework
73
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 36
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Benefits of using the Architecture Skills
Framework
Specific benefits anticipated include:
» Reduced time, cost, and risk in training, hiring, and
managing architecture professionals, both internal and
external.
» Reduced time and cost to set up an internal architecture
practice
» This in turn helps reduce the time, cost and risk of
overall solution development
74
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The structure of the Architecture Skills
Framework
The TOGAF Architecture Skills Framework provides a view
of the competency levels for specific roles within the
enterprise architecture team.
The Framework defines:
» The roles within an enterprise architecture work area
» The skills required by those roles
» The depth of knowledge required to fulfil each role
successfully
75
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 37
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The structure of the Architecture Skills
Framework
A typical architecture team undertaking the development of an
enterprise architecture comprises the following roles:
» Architecture Board Members
» Architecture Sponsor
» Architecture Manager
» Architects for :
– Enterprise Architecture
– Business Architecture
– Data Architecture
– Application Architecture
– Technology Architecture
– Program and/or Project Managers
– IT Designer
– etc . . .
76
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The structure of the Architecture Skills
Framework
Categories of Skills
The TOGAF team skill set will need to include the following main categories of
skills:
» Generic Skills: leadership, team working, inter-personal skills, etc.
» Business Skills & Methods: business cases, business process, strategic
planning, etc.
» Enterprise Architecture Skills: modeling, building block
design,applications and role design, systems integration, etc.
» Program or Project Management Skills: managing business change,
project management methods and tools, etc.
» IT General Knowledge Skills: brokering applications, asset management,
migration planning, SLAs, etc.
» Technical IT Skills: software engineering, security, data interchange, data
management, etc.
» Legal Environment: data protection laws, contract law, procurement law,
fraud, etc.
77
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 38
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The structure of the Architecture Skills
Framework
» Proficiency Levels
78
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The structure of the Architecture Skills
Framework
» Skills Matrices – Example Generic Skills
79
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 39
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
What is the TOGAF ADM?
» The ADM forms the core of the TOGAF framework
» The result of contributions from many architecture practitioners
» A process for developing an enterprise architecture
» Integrates all the elements within the TOGAF standard
» Designed to address enterprise’s business and IT needs by providing:
– A set of architecture views (business, data, application, technology)
– A set of recommended deliverables
– A method for managing requirements
– Guidelines on tools for architecture development
80
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture Development Method – Process
» The ADM is an iterative
process:
– Over the whole process
– Between phases
– Within phases
» For each iteration, re-
consider:
– Scope
– Detail
– Schedules, milestones
81
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 40
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Development Method – Process
» Consider assets from:
– Previous iterations
– Marketplace, according
to availability,
competence, and value:
• Other frameworks
• Systems models
• Vertical Industry models
82
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
ADM Guidelines and Techniques
» A set of guidelines and techniques to support the
application of the ADM
» The guidelines help to adapt the ADM to deal with
different scenarios, including different process styles (e.g.
the use of iteration) and also specific requirements (e.g.
security).
» The techniques support specific tasks within the ADM
(e.g. defining principles, business scenarios, gap
analysis, migration planning, risk management, etc).
83
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 41
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Relationship to other Parts of the TOGAF
Standard
Architecture Capability Framework (Part
VI)
Architecture Development Method (Part II)
ADM Guidelines &
Techniques (Part III)
Architecture Content
Framework (Part IV)
Enterprise Continuum & Tools (Part V)
TOGAF Reference Materials
(TOGAF Library)
84
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Prepare the organization for a successful Set the scope, constraints and expectations
architecture projects for a TOGAF project; create the
Architecture Vision;
ADM Phases
Provide continual monitoring and a change
validate the business context; create the
Statement of Architecture Work
management process to ensure that the
architecture responds to the needs of the Develop Business Architecture
enterprise Develop baseline and target
architectures and
analyze the gaps
Provide architectural oversight for
the implementation; ensure that the
implementation project conforms to
the architecture Develop Information Systems
Architectures
Develop baseline and target
architectures and
Analyze costs, benefits and risks; analyze the gaps
develop detailed Implementation
and Migration Plan
Develop Technology Architecture
Develop baseline and target
architectures and
Ensure that every stage of a TOGAF analyze the gaps
project is based on and validates
business requirements Perform initial implementation 85
planning; identify major
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
implementation projects
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 42
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
ADM – Basic Principles
An iterative method, over the whole
process, between phases and within
phases
Each iteration = new decisions:
Enterprise coverage
Level of detail
Time horizon
Architecture asset re-use:
previous ADM iterations
other frameworks, system models,
industry models,…
Decisions based on:
Competence / resource availability
Value accruing to the enterprise.
86
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
ADM – Basic Principles
Every phase is validated against
and validates the current
requirements of the business
87
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 43
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Preliminary Phase
» This phase includes the
preparation and initiation
activities to create an
Architecture Capability
– Understand business
environment
– High level management
commitment
– Agreement on scope
– Establish principles
– Establish governance
structure
– Customization of the
TOGAF framework
88
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Phase A: Architecture Vision
» Initiates one iteration of the
architecture process
– Sets scope, constraints,
expectations
– Required at the start of
every architecture cycle
» Creates the Architecture
Vision
» Validates business context
» Creates the Statement of
Architecture work
89
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 44
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Phase B: Business Architecture
» The fundamental
organization of a business,
embodied in
– its business processes
and people,
– their relationships
• to each other and the
environment,
and the principles
–
governing its design and
evolution
» Shows how the organization
meets its business goals
90
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Business Architecture - Contents
» Organization structure
» Business goals and
objectives
» Business functions
» Business services
» Business processes
» Business roles
» Business data model
» Correlation of organization
and functions.
91
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 45
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Business Architecture - Steps
1. Select reference models,
viewpoints and tools
2. Define Baseline Architecture
Description
3. Define Target Architecture
Description
4. Perform gap analysis
5. Define candidate roadmap
components
6. Conduct Impact Analysis
7. Conduct formal stakeholder
review
8. Finalize the Architecture
9. Create Architecture
Definition Document
92
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Phase C: Information Systems Architectures
» Documenting the Information
Systems Architecture for a
project including
development of Data and
Application Architectures
addressing:
• The major types of
information and
applications that process
them
• relationships to each
other and the
environment, and the
principles governing its
design and evolution
Continued
93
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 46
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Data or Applications first ?
» It is usually necessary to
address both
• Not always the case,
depending on project scope
and constraints
» May be developed in either
order, or in parallel
• Theory suggests Data
Architecture comes first
• Practical considerations
may mean that starting with
Application Architecture
may be more efficient
» There will need to be some
iteration to ensure consistency
94
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Phase D: Technology Architecture
» The fundamental
organization of an IT system,
embodied in
• its hardware, software
and communications
technology
• their relationships to
each other and the
environment,
• and the principles
governing its design and
evolution
95
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 47
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions
» Perform initial
implementation planning
» Identify the major
implementation projects
» Determine if an incremental
approach is required, if so
define Transition
Architectures
» Decide on approach
• Make v Buy v Re-Use
• Outsource
• COTS
• Open Source
» Assess priorities
» Identify dependencies
96
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Phase F: Migration Planning
» For work packages and
projects identified in Phase E
perform
• Cost/benefit analysis
• Risk assessment
» Finalize a detailed
Implementation and
Migration Plan
97
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 48
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Phase G: Implementation Governance
» Provide architectural
oversight for the
implementation.
» Defines architecture
constraints on
implementation projects
» Govern and manage an
Architecture contract
» Monitors implementation
work for conformance
» Produce a Business Value
Realization.
98
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Phase H: Architecture Change Management
» Provide continual monitoring
and a change management
process
» Ensures that changes to the
architecture are managed in
a cohesive and architected
way
» Establishes and supports the
Enterprise Architecture to
provide flexibility to evolve
rapidly in response to
changes in the technology or
business environment
» Monitors the business and
capacity management.
99
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 49
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Adapting the ADM
» Generic methodology intended for variable:
– Geographies
– Vertical sectors
– Industry types
» Usable with deliverables of other frameworks such
as Zachman, DODAF, …
» It is usual to modify or extend the ADM to suit specific
needs
100
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
ADM Inputs and Outputs
» The TOGAF standard defines a number of input
and output deliverables for each ADM phase
– These are suggestions and need not be followed exactly
– Output of an early phase may be modified in a later phase
– Version numbers are used to manage the output
– A convention is used to illustrate the evolution of deliverables
• 0.1 – a high level outline deliverable
• 1.0 – a formally reviewed detailed deliverable
101
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 50
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Reasons to constrain the Scope of
Architectural Activity
» The organizational authority of the team producing the
architecture
» The objectives and stakeholder concerns to be addressed
within the architecture
» The availability of people, finance, and other resources
102
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Scoping the Architecture Activity
» There are four dimensions in which scope may be
limited:
– Breadth
– Depth
– Time Period
– Architecture Domains
103
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 51
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Integration
104
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The TOGAF® Library
105
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 52
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
TOGAF Library – Overview
» A portfolio of guidance material to support practical
application of the TOGAF standard
» It contains guidelines, templates, patterns and other
forms of reference material
» Over 80 documents (as of April 2018)
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
TOGAF Library – Structure
» Section 1: Foundation Documents
– Broadly applicable information relating to the subject of the TOGAF
framework or Enterprise Architecture
» Section 2: Generic Guidance and Techniques
– Information describing architecture styles and how the TOGAF
framework and Enterprise Architecture can be adapted to exploit the
characteristics of a more specific context
» Section 3: Industry-Specific Guidance and Techniques
– Information describing how the TOGAF framework and Enterprise
Architecture can be applied to meet the specific needs of a vertical
industry segment
» Section 4: Organization-Specific Guidance and Techniques
– Information describing how the TOGAF framework and Enterprise
Architecture have been applied to meet the needs of specific
enterprises
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 53
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
TOGAF Certification
Certification Purpose
Level
TOGAF 9 To provide validation that the candidate has
Foundation gained knowledge of the TOGAF terminology,
structure, and basic concepts, and understands
the core principles of Enterprise Architecture and
the TOGAF standard
TOGAF 9 To provide validation that in addition to knowledge
Certified and comprehension, the candidate is able to
analyze and apply knowledge of the TOGAF
standard
108
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
TOGAF Foundation
Target Audience
» Individuals who require a basic understanding of the
TOGAF 9 standard
» Professionals who are working in roles associated with an
architecture project such as those responsible for
planning, execution, development, delivery and operation
» Architects who are looking for a first introduction to the
TOGAF 9 standard
» Architects who want to achieve Level 2 certification in a
stepwise approach.
109
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 54
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
TOGAF Certified
Target Audience
» Individuals who require a deeper understanding of the
TOGAF 9 standard;
» Professionals who are working in an organization where
TOGAF 9 has been adopted and who need to participate
in architecture projects and initiatives;
» Architects who will be responsible for developing
architecture artifacts;
» Architects who wish to introduce the TOGAF 9 standard
into an architecture practice;
» Architects who want to achieve a recognized qualification
to demonstrate their detailed knowledge of the TOGAF 9
standard.
110
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Summary
The TOGAF® Standard is…
» An effective, industry standard framework and method
for Enterprise Architecture.
» Complementary to, not competing with, other enterprise
frameworks
» A repository of best practice
– It “demystifies” architecture development
» Vendor, tool, and technology neutral
» A framework and method for achieving the
“Boundaryless Information Flow” vision
111
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 55
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture
Content
Framework
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Introduction
» The Architecture Content Framework is a significant part of
the overall TOGAF framework
» It provides a detailed model of architectural work products
» It helps to improve the consistency of the TOGAF outputs
– Presents outputs in a consistent and structured way
– Helps to reference and classify them.
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 56
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Benefits of the Architecture Content Framework
» It provides a comprehensive checklist of architecture outputs
» It promotes better integration of work products if adopted
across an enterprise
» It provides a detailed open standard for how architectures
should be described
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Overview
» The Framework has 3 categories for describing work
products:
– Deliverables
– Artifacts
– Building blocks
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 57
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Deliverables, Artifacts and Building Blocks
» Deliverables » Artifacts
– Formal products – fine grained products that
describe an architecture from
– Contractually specified a specific viewpoint
– Outputs from a project – For example: use-case
– A deliverable can contain specifications, architectural
many artifacts requirements, network
diagrams, etc.
– Classified as:
» Building blocks • Catalogs (lists of things),
– components that can be • matrices (showing
combined with other building relationships between things)
blocks to deliver architectures or
and solutions • diagrams (pictures of things).
– Artifacts make up the content
of the Architecture Repository
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Relationship between Deliverables, Artifacts
and Building blocks
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 58
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Example – Architecture Definition Document
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architectural Artifacts
» Artifacts are products that are created when developing
an architecture.
» An artifact is distinct from a deliverable, which is a
contracted output from a project.
» Usually deliverables contain many artifacts and each
artifact may exist in many deliverables.
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 59
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Content Metamodel
The framework is based on a standard content metamodel
that defines all the types of building blocks in an
architecture.
– Showing how these building blocks can be described
– How they relate to one another
» The content model consists of a core and extensions.
» Catalogs, matrices and diagrams are used to present the
architectural information
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Content Metamodel Overview
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 60
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Mapping the Framework and the ADM
There is a mapping from the Architecture content framework to the
TOGAF ADM phases:
» Architecture Principles, Vision, and Requirements entities
should capture the context of the architecture models, including
general architecture principles, strategic context and requirements.
» Business Architecture entities capture architectural models of
business operations, specifically factors that motivate the enterprise,
how the enterprise is structured and its functional capabilities.
» IS Architecture entities capture architecture models of IT systems,
specifically applications and data.
» Technology Architecture entities capture procured technology
assets used to implement and realize IS solutions.
» Architecture Realization entities capture the transitions between
architecture states and are used to steer and govern the
implementation.
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
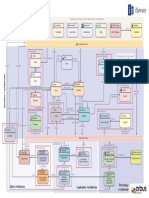
Mapping the Framework and the ADM
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 61
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Content Framework and the TOGAF ADM
» The ADM addresses a business need through a
process of vision, definition, planning and governance.
At each stage the ADM takes information as inputs and
creates outputs.
» The content framework provides a structure for the ADM
that defines inputs and outputs in detail and puts each
deliverable into the context of the architecture.
» So the content framework is a companion to the ADM.
» The ADM describes what needs to be done to create an
architecture and the content framework describes what
it should look like in the end.
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Summary
» The Architecture Content Framework presents outputs in
a consistent and structured way.
– It has 3 categories of work products: deliverables, artifacts and
building blocks.
» The content metamodel consists of a core and some
extensions.
» Catalogs, matrices and diagrams are used to present the
architectural information.
» There is a mapping from the Architecture content
framework to the TOGAF ADM phases
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 62
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Exercise
» What other content frameworks do you know of?
» What are the advantages and disadvantages of opting to
use an external framework in conjunction with the ADM
instead of the TOGAF Architecture Content Framework?
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The Enterprise
Continuum
and Tools
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
127
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 63
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Definition of ‘Continuum’
’
» Noun: a continuous extent of something, no part
of which is different from any other
Source: Wiktionary.org
128
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 Components
Architecture Content Architecture Capability
ADM Framework Framework
ADM Guidelines
Enterprise Continuum
& Techniques
129
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 64
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Overview
» A model for structuring a virtual repository and methods
for classifying architecture and solution artifacts
» Based on architectures and solutions:
– Models, patterns, architecture descriptions
– Deliverables produced in this iteration of the ADM
– Deliverables produced in other iterations of the ADM
– Assets from the industry at large
– Showing how artifacts evolve
» The practical implementation of the Enterprise
Continuum takes the form of an Architecture Repository
Continued…
130
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Overview (Cont’d)
» The Enterprise Continuum is a combination of two
complementary concepts: the Architecture Continuum
and the Solutions Continuum
» It enables effective use of COTS products.
» It improves engineering efficiency
» It aids organization of reusable architecture and solution
assets
» It provides a common language:
– Within enterprises
– Between customer enterprises and vendors
131
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 65
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Reuse
» The Enterprise Continuum consists of all architecture assets:
models, patterns, architecture descriptions, etc.
» External assets include:
– Generic reference models (eg TOGAF’s TRM, Zachmann…)
– IT-specific models (eg a web services architecture)
– Information Processing-specific models (eg e-Commerce, supply
chain management …)
– Vertical-Industry-specific models (eg TMF, ARTS, POSC…)
» The architecture governance function decides which assets
an enterprise considers part of its own Enterprise Continuum
132
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Enterprise Continuum: Constituents
133
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 66
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The Architecture Continuum
Figure 1
134
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Figure 1
» Architectures range from Foundation Architectures through Common
Systems Architectures, and Industry Architectures to an enterprise's
own Organization-Specific architecture
» Arrows represent bi-directional relationship between the different
architectures
– Left to right: meeting enterprise needs and business requirements
– Enterprise needs and business requirements increase in detail from left to
right
– Right to left: leveraging architectural components and building blocks
135
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 67
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Figure 1
» The architectural elements furthest left are the most
reusable
» Requirements for missing elements are passed to the left of
the continuum for inclusion.
» Enterprises can use the same continuum models,
specialized for specific businesses.
» Figure 1 shows the different architectures that may be
developed:
– these are not fixed stages in a process
– different architectures may exist as well.
136
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Figure 1
» Figure 1 does not represent a formal process but
represents a progression occurring at several levels:
– Logical Physical
– Horizontal (IT technology-focused) Vertical (business-focused)
– Generalization Specialization
– Taxonomy Architecture Specification
» At each point, an architecture is designed in terms of the
design concepts and building blocks available.
137
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 68
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The Solutions Continuum
Figure 2
138
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Figure 2
» The most specific architectures are on the right:
– Foundation solutions help to create common systems solutions
– Common systems solutions are used to create industry solutions
– Industry Solutions are used to create organization-specific solutions
» The most generic concepts are on the left.
» The entire spectrum is important when balancing cost and
value.
139
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 69
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The Solutions Continuum:
» Represents the implementations of the architectures at the
corresponding levels of the Architecture Continuum
» Is a population of the architecture with Solution Building
Blocks, either purchased products or built components, that
represent a solution to the enterprise's business need
» Forms a Solutions Inventory or Reuse Library, which adds
significant value to the task of managing and implementing
improvements to the IT environment
140
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Relationships
» The Architecture and Solutions Continuum are related by
guidance, direction, and support.
» E.g. the Foundation Architecture:
– is an architecture of building blocks and corresponding standards
– supports all the Common Systems Architectures and, therefore, the
complete enterprise operating environment
» The Open Group Technical Reference model (TRM) is a
Foundation Architecture
» The Open Group III-RM is a Common Systems Architecture
141
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 70
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The Enterprise Continuum
Figure 3: Best case for leveraging of architecture and solution components
142
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Using the Continuum
» The TOGAF ADM describes the process of
developing an enterprise-specific architecture by
adopting and adapting generic architectures and
solutions
» The Continuum:
– contains complete and work-in-progress solutions
– is a "framework-within-a-framework”
– has few internal assets, at first
– grows by adding reusable building blocks
143
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 71
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Relationships
» The Solutions Continuum assists understanding of
products, systems, services, and solutions
» The Enterprise Continuum improves productivity
through leverage
» The Enterprise Continuum does not represent
strictly chained relationships:
– enterprise architectures may have components from a
Common Systems Architecture
– enterprise solutions may contain a product or service
144
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The need for Tools
» Tools are needed to manage and control the artifacts
within the Enterprise Continuum
– To promote re-use
– To enable sharing of architecture information within an
organization
– To facilitate easier maintenance of the architecture
– To ensure common terminology is used
– To provide stakeholders with relevant models
145
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 72
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Tools can model the Enterprise Architecture
146
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Issues in Tools Standardization
» A single “one size fits all” tool versus multiple tools
» Can a single tool address all needs, all maturity levels?
» The Open Group recognizes the complexity in this area
and is developing a TOGAF 9 Tools Certification
program to assist with the evaluation
147
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 73
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Summary
» The Enterprise Continuum is
– a model for structuring a virtual repository and methods for
classifying architecture and solution artifacts
– It enables the organization of reusable architecture and solution
assets.
– It is also an aid to communication between all architects involved
in building and procuring an architecture by providing a common
language and terminology.
– This in turn enables efficiency in engineering and effective use of
COTS products.
Continued…
148
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Summary
» The Enterprise Continuum
– provides an overall context for architectures and solutions and
classifies assets that apply across the entire scope of the
enterprise.
» The Architecture Continuum
– provides a classification mechanism for assets that collectively
define the architecture at different levels of evolution from
generic to specific.
» The Solutions Continuum
– provides the classification for assets to describe specific
solutions for the organization that can be implemented to
achieve the intent of the architecture.
Continued…
149
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 74
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Summary
» Tools are needed to manage artifacts within the
Enterprise Continuum
» The TOGAF standard provides an introduction to Issues
in Tools Standardization
150
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture
Repository
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
151
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 75
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Purpose
» Effective management and leverage of architectural
output requires a formal taxonomy for different types of
architectural asset
» TOGAF provides a structural framework for an
Architecture Repository
» This is one part of a wider Enterprise Repository
152
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture Repository
153
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 76
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Describes the architecture
framework in use within the
Enterprise
Architecture Repository Shows the state of the operating
enterprise at particular points in
time
Contains re-usable architecture
work products
An architectural representation of
the SBBs supporting the
Architecture Landscape
Defines the compliance criteria
for work governed by architecture
Captures results of the
governance activity
A view of all authorized
architecture requirements
Describes the organisation, roles,
skills and responsibilities of the
154
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
EA practice
Architecture Repository
» The Architecture Repository is a logical information store for outputs of executing the
ADM:
– The Architecture Metamodel describes the architecture framework in use within the
Enterprise
– The Architecture Landscape shows the state of the operating Enterprise at particular
points in time
– The Reference Library contains re-usable architecture work products
– The Standards Information Base defines the compliance criteria for work governed
by architecture
– The Governance Log captures results of governance activity, such as compliance
assessments
– The Architecture Capability describes the organisation, roles, skills and
responsibilities of the Enterprise Architecture practice
– The Architecture Requirements Repository provides a view of all authorized
architecture requirements which have been agreed with the Architecture Board
– The Solutions Landscape presents an architectural representation of the SBBs
supporting the Architecture Landscape which have been planned or deployed by the
enterprise
155
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 77
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Landscape
1. Strategic Architectures:
– show a long-term summary view of the entire enterprise.
– provide an organizing framework for operational and change activity and allow
for direction setting at an executive level.
2. Segment Architectures:
– provide more detailed operating models for areas within an enterprise
– can be used at the program or portfolio level to organize and operationally align
more detailed change activity.
3. Capability Architectures:
– show in a more detail how the enterprise can support a particular capability.
– used to provide an overview of current capability, target capability, and
capability increments and allow for individual work packages and projects to be
grouped within managed portfolios and programs.
156
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Reference Library
» A repository area to hold best practice or template materials that
can be used to construct architectures within an enterprise.
» Reference materials held in the Reference Library are typically
obtained from a variety of sources, including:
– Standards bodies
– Product and service vendors
– Industry communities or forums
– Corporately defined templates
– Best practice resulting from project implementation
157
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 78
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Standards Information Base
» A repository area to hold a set of specifications, to which
architectures must conform.
» Establishment of a Standards Information Base provides an
unambiguous basis for architectural governance since:
– The standards are easily accessible to projects and therefore the
obligations of the project can be understood and planned for
– Standards are stated in a clear and unambiguous manner, so that
compliance can be objectively assessed
158
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Standards Information Base
» Types of Standard » Standards Lifecycle
– Legal and Regulatory – Trial
– Industry – Active
– Deprecated
– Organizational
– Obsolete
159
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 79
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Standards Classification
» Business Standards: » Applications Standards:
– Standard shared business – Standard/shared applications
functions supporting specific business
– Standard role and actor functions
definitions – Standards for application
– Security and governance communication and interoperation
standards for business activity – Standards for access,
» Data Standards: presentation, and style
– Standard coding and values for
» Technology Standards;
data – Standard hardware products
– Standard structures and formats – Standard software products
for data – Standards for software
– Standards for origin and development
ownership of data
– Restrictions on replication and
access
160
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Governance Log
» A repository area to hold shared information relating to
the ongoing governance of projects.
» Maintaining a shared repository of governance
information is important, since:
– Decisions made during projects (such as standards deviations
or the rationale for a particular architectural approach) are
important to retain and access on an ongoing basis.
– Many stakeholders are interested in the outcome of project
governance (e.g., other projects, customers of the project, the
Architecture Board, etc.).
161
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 80
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Governance Log Contents
162
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture Requirements Repository
» A repository area used by all phases of the ADM to
record and manage all information relevant to
Architecture Requirements
» The Architecture Requirements Phase is responsible for
managing the contents of this repository
163
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 81
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Solutions Landscape
» A repository area used to hold architectural
representations of all Solution Building Blocks (SBBs)
supporting Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs)
specified, developed, or deployed
164
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Relationship to other Parts of the TOGAF
Standard
» The TOGAF ADM has reminders when to use assets
from the Architecture Repository
» The Architecture Repository is a model for a physical
instance of the Enterprise Continuum
165
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 82
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Summary
» The TOGAF standard provides a structural framework for a repository
» It is a logical information store for ADM outputs with the following
repository areas defined:
– Architecture Metamodel: describes the architecture framework in use within the
Enterprise
– Architecture Landscape: shows the state of the operating Enterprise at particular
points in time
– Reference Library: contains re-usable architecture work products
– Standards Information Base: defines the compliance criteria for work governed by
architecture
– Governance Log: captures results of governance activity
– Architecture Capability: describes the organisation, roles, skills and responsibilities
of the Enterprise Architecture practice
– Architecture Requirements Repository: provides a view of all authorized
architecture requirements which have been agreed with the Architecture Board
– Solutions Landscape: presents an architectural representation of the SBBs
supporting the Architecture Landscape which have been planned or deployed by the
enterprise
166
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Exercise
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using
Reference Models that are derived from:
a) within the enterprise
b) outside the enterprise?
167
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 83
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Adapting the
ADM:
Iteration and
Levels
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
168
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Module Objectives
The objectives of this module are:
» How to adapt the ADM using iteration and different
levels of architecture engagement
169
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 84
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Iteration and Levels
170
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Iteration and the ADM
» The ADM supports a number of concepts that can be
characterized as Iteration:
• Iteration to describe a comprehensive Architecture Landscape
through multiple ADM cycles based upon individual initiatives
bound to the scope of the Request for Architecture Work
• Iteration to describe the integrated process of developing an
architecture where the activities described in different ADM
phases interact to produce an integrated architecture
• Iteration to describe the process of managing change to the
organization's Architecture Capability
171
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 85
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Iteration to develop a comprehensive
Architecture Landscape
» Projects will exercise through the
entire ADM cycle, commencing with
Phase A.
– Each cycle of the ADM is bounded
by a Request for Architecture Work
– The output populates the
Architecture Landscape, either
extending or changing the landscape
» Separate projects may operate their
own ADM cycles concurrently, with
relationships between them
» One project may trigger the initiation
of another project.
Slide 172
Iteration within an ADM Cycle
» Projects may operate multiple
ADM Phases concurrently
– Typically uses to manage the
inter-relationship between the
Business Architecture,
Information Systems
Architectures and Technology
Architecture
» Projects may cycle between
phases to converge on a Target
Architecture
» Projects may return to previous
phases in order to update work
products with new information
Slide 173
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 86
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Iteration to Manage the Architecture Capability
» Projects may require a new
iteration of the Preliminary
Phase to establish aspects of
the Architecture capability
identified in Phase A to
address a Request for
Architecture work
» Projects may require a new
iteration of the Preliminary
Phase to adjust the
organization’s Architecture
Capability as a result of new
or changed requirements as a
result of a change request in
Phase H
174
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Factors influencing the use of Iteration
» The formality and nature of established checkpoints
within the organization
» The level of stakeholder involvement expected within the
process
» The number of teams involved and the relationships
between different teams
» The maturity of the solution area and expected rework to
arrive at an acceptable solution
» Attitude to risk
175
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 87
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Capability Architecture Development
iterations support creation iterations support creation
and evolution of the and evolution of
Iteration
Architecture Cycles
Capability architecture content by
cycling through Phases B, C,
and D
Architecture Governance
iterations support
governance of change activity
As iterations converge on a
Transition Planning iterations target, extensions into Phases
support the creation of E & F ensure the viability of
formal change roadmaps implementation is considered
176
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Approaches to Architecture Development
» Baseline First
– An assessment of the baseline landscape is used to identify
problem areas and opportunities for improvement
– A suitable approach for when baseline is complex or not clearly
understood
» Target First
– The target solution is elaborated in detail and then mapped back
to the baseline
– A suitable approach for when the target state is agreed at a high
level and where the enterprise wishes to effectively transition to
the target model
177
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 88
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Iteration within the ADM Cycle – Baseline First
178
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Iteration within the ADM Cycle –
Target First
179
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 89
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture Development Iteration “Baseline
”
First”
» Iteration 1
– Define the Baseline Architecture
» Iteration 2
– Define the Target Architecture
and gaps
» Iteration n
– Refine the Baseline Architecture,
Target Architecture, and gaps
180
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture Development Iteration “Target
”
First”
» Iteration 1
– Define the Target Architecture
» Iteration 2
– Define the Baseline Architecture
and gaps
» Iteration n
– Refine the Baseline architecture,
Target Architecture, and gaps.
181
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 90
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Transition Planning
» Iteration 1
– Define and agree a set of
improvement opportunities,
aligned against a provisional
Transition Architecture
» Iteration n
– Agree the Transition
Architecture, refining the
identified improvement
opportunities to fit
182
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Architecture Governance
» Iteration 1
– Mobilize architecture
governance and change
management processes.
» Iteration n
– Carry out architecture
governance and change control
183
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 91
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Classes of Architecture Engagement
» TOGAF defines three typical areas of engagement:
– Identification of Change Required
– Definition of Change
– Implementation of Change
184
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Classes of Architecture Engagement
185
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 92
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Iteration Focus for Classes of Architecture
Engagement (Extract)
Engagement Iteration Focus Scope
Supporting Architecture Capability Broad, shallow consideration given to the
Business Architecture Landscape in order to address a
Strategy Architecture specific strategic question and define terms for
Development (Baseline
First) more detailed architecture efforts to address
strategy realization.
Architectural Architecture Capability Focus on physical assessment of baseline
Portfolio applications and technology infrastructure to
Management of Architecture identify improvement opportunities, typically
the Landscape Development (Baseline
First) within the constraints of maintaining business
as usual.
Architectural Transition Planning Focus on projects, project dependencies, and
Portfolio Architecture landscape impacts to align project sequencing
Governance
Management in a way that is architecturally optimized.
of Projects
186
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Iteration Considerations
» Iteration between ADM Cycles
– Suitable where a higher level architecture guides and constrains
a more detailed architecture
– This approach uses the Migration Planning phase of one ADM
cycle to initiate new projects which will also develop
architectures
– It is a method to develop a complete architecture landscape in
multiple iterations
187
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 93
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
A Hierarchy of ADM Processes
188
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Strategic Architecture provides an
Applying the ADM Across the Architecture
organizing framework for
operational and change activity and
Landscape allows for direction setting at an
executive level
Segment Architecture provides an
organizing framework for
operational and change activity and
allows for direction setting and the
development of effective
architecture roadmaps at a
program or portfolio level
Capability Architecture provides an
organizing framework for change
activity and the development of
effective architecture roadmaps
realizing capability increments
189
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 94
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Applying the ADM Across the Architecture
’d)
Landscape (Cont’
190
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Organizing the Architecture Landscape
» The following characteristics can be used to organize the
Architecture Landscape
– Breadth (subject matter)
– Depth
– Time
– Recency
191
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 95
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Summary
» TOGAF provides guidelines for adapting the ADM for
iteration
» This includes proposed iteration cycles for different
classes of architecture engagement
» Guidance is also provided for the use of levels for
architecture development across the Architecture
Landscape
192
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Exercise
» Describe two examples when applying iteration to the
ADM where the Baseline First is most appropriate.
» Describe two examples when applying iteration to the
ADM where the Target First is most appropriate.
193
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 96
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Architecture
Partitioning
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
194
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Module Objectives
The objectives of this module are to describe:
» How an overall Enterprise Architecture can be
partitioned to meet the specific needs of the
organization
» Key learning outcomes:
– The purpose of Architecture Partitioning
– The classification criteria for solutions and architectures when
considering partitioning
– How Architecture Partitioning can be employed in the
Preliminary Phase of the ADM
195
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 97
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Partitioning
Allows for management of costs and complexity by dividing up the Enterprise and
assigning appropriate roles and responsibilities to each partition
196
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
The Need to Partition
» Managing Complexity
» Managing Conflicts
» Managing Parallel developments
» Managing Re-use
197
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 98
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Applying Classification to Partitioned
Architectures: Solution Partitioning
» Subject Matter (breadth)
– Its content, structure and function
» Time
– All solutions exist for a period of time
» Maturity/Volatility
– The extent to which subject matter and environment of a
solutions are likely to change over time
198
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Applying Classification to Partitioned
Architectures: Architecture Partitioning
» Depth (Level of detail)
– The level of detail has a strong correlation to the stakeholder
groups interested
– Typically, less detailed architectures are of interest to executive
level stakeholders
– As architectures increase in detail, their relevance to
implementation and operational personnel increases
199
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 99
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Applying Partitioning to the ADM
» The Preliminary phase supports the identification of
appropriate architecture partitions and establishment of
governance relationships between related architecture
partitions.
200
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Preliminary Phase
» Determine the organization structure for architecture
within the enterprise
– Identify the teams
» Determine responsibilities for each architecture team
– Subject matter areas
– Level of detail
– Time period
– Stakeholders
» Determine the relationship between architectures
– Where do architectures overlap?
– What are the compliance requirements between architectures?
201
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 100
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Example Teams allocated
202
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Summary
» Architecture Partitioning can be used to manage
complexity, parallel developments, conflicts and re-use
» Classification criteria are defined for architectures and,
solutions
» TOGAF provides guidance on how to use partitioning in
the Preliminary Phase of the ADM cycle
203
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 101
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Adapting the
ADM:
Security
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open
Group in the United States and other countries
204
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Roadmap
205
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 102
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
The Open Group Guide: Integrating Risk and
Security within a TOGAF® Enterprise Architecture
» Provides guidance for security practitioners and
Enterprise Architects who need to work with the TOGAF
standard to develop an Enterprise Architecture.
» Explains how the TOGAF method and framework can be
tailored to make use of an existing Enterprise Security
Architecture in order to address security and risk
properly.
206
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Enterprise Security Architecture
Enterprise Architecture Business Drivers / Business Objectives Enterprise Security Architecture
Security Principles
Risk Appetite
Key Risk Areas / Business Impact
Security Resource Plan
Security Policy Architecture
Security Domain Model
Trust Framework
Risk Assessment
Business Risk Model / Risk Register Identity &
Access Mgt
Applicable Law and Regulation Register
Continuity
Applicable Control Framework Register Management
Security
Intelligence
Security Services Catalogue
Security
Security Classification Monitoring
Data Quality Compliance
Management
Security Standards Etc.
Business Attribute Profile
Control Objectives / Security Objectives Enterprise
Information Risk
Risk Mitigation Plan Security Management
Management
Security Audit 207
Security Training & Awareness
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 103
TOGAF® Standard Courseware V9.2 Edition
Security as a Cross-Cutting Concern
Security
Business
Data
Application
Technology
208
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Adapting the ADM for Security
209
Copyright © The Open Group 2018
Copyright 2009-2018, The Open Group 104
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- TOGAF 9 Summary of Study GuideDocument23 paginiTOGAF 9 Summary of Study GuideJuan K Luna100% (1)
- GoodElearning TOGAF Poster 51 - ToGAF TechniquesDocument1 paginăGoodElearning TOGAF Poster 51 - ToGAF TechniquesFabian HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TogafDocument28 paginiTogafDahlia Gamal0% (1)
- Amnesty - Protest SongsDocument14 paginiAmnesty - Protest Songsimusician2Încă nu există evaluări
- Agile Togaf and Enterprise ArchitectureDocument45 paginiAgile Togaf and Enterprise Architecturedogma28100% (2)
- OG0 093 Exam Dumps 2018 PDFDocument7 paginiOG0 093 Exam Dumps 2018 PDFsaragadamsivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOC002 TOGAF Foundation WorkbookDocument25 paginiDOC002 TOGAF Foundation WorkbookRoySÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentation. Between Science, State and IndustryDocument271 paginiInstrumentation. Between Science, State and IndustryMichel GautamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF 9 Combined Part 1 and Part 2Document84 paginiTOGAF 9 Combined Part 1 and Part 2MbaStudent56100% (1)
- Togaf Foundation Test BankDocument115 paginiTogaf Foundation Test Bankmike83% (6)
- Enterprise Architecture Body Of Knowledge A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDe la EverandEnterprise Architecture Body Of Knowledge A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF9 - CheatSheet - Part II PDFDocument9 paginiTOGAF9 - CheatSheet - Part II PDFMohan KumaresanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hosea - A New Translation With Introduction and Commentary (Anchor Bible 24)Document727 paginiHosea - A New Translation With Introduction and Commentary (Anchor Bible 24)Azoth ImóveisÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF Poster 63 - Capabilities and TOGAFDocument1 paginăTOGAF Poster 63 - Capabilities and TOGAFAchintya Kumar100% (1)
- TOGAF9FCDocument169 paginiTOGAF9FCozkhan786100% (5)
- Togaf EbookDocument8 paginiTogaf Ebookfernandoans100% (4)
- 2 - TOGAF 9 Part 1 Practice Test - Nov2012Document41 pagini2 - TOGAF 9 Part 1 Practice Test - Nov2012swapnil_bankar100% (3)
- TOGAF 9 Enterprise Architecture OverviewDocument55 paginiTOGAF 9 Enterprise Architecture OverviewAhmed Zaheer100% (2)
- Togaf 10 IntroDocument71 paginiTogaf 10 IntroAntwan Bell100% (3)
- Creativity and AestheticDocument17 paginiCreativity and AestheticSyahirah Erahzs100% (1)
- Togaf 9 AdmDocument1 paginăTogaf 9 AdmMustan100% (8)
- Togaf Ebook 2Document8 paginiTogaf Ebook 2Santha KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Own Togaf NotesDocument87 paginiMy Own Togaf NotesEdwin Chan80% (5)
- Togaf 9 Foundation Exam Study GuideDocument3 paginiTogaf 9 Foundation Exam Study Guideswapnil_bankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF 9.1 MetamodelDocument1 paginăTOGAF 9.1 Metamodelcreamz100% (1)
- Togaf 91 in Pictures 2Document13 paginiTogaf 91 in Pictures 2samya222Încă nu există evaluări
- Togaf Short QuestionsDocument24 paginiTogaf Short QuestionssomenathbasakÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF 9 ADM Reference Card Phases N093Document12 paginiTOGAF 9 ADM Reference Card Phases N093kamilprasilÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF® 10 Level 2 Enterprise Arch Part 2 Exam Wonder Guide Volume 2: TOGAF 10 Level 2 Scenario Strategies, #2De la EverandTOGAF® 10 Level 2 Enterprise Arch Part 2 Exam Wonder Guide Volume 2: TOGAF 10 Level 2 Scenario Strategies, #2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Togaf 9 Foundation Part 1 Exam Preparation PDFDocument114 paginiTogaf 9 Foundation Part 1 Exam Preparation PDFRodrigo Maia100% (3)
- RBG - CRM BRD - Marketing - v4.1Document68 paginiRBG - CRM BRD - Marketing - v4.1Manvi Pareek100% (2)
- The Togaf 9.1 Standard: Part I - IntroductionDocument21 paginiThe Togaf 9.1 Standard: Part I - IntroductionGaurav PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togaf by Open GroupDocument26 paginiTogaf by Open GroupPablo Book100% (1)
- TOGAF EA Foundation - Delegate Pack v1.2Document281 paginiTOGAF EA Foundation - Delegate Pack v1.2madhawa30Încă nu există evaluări
- Exam Dumps 2018Document7 paginiExam Dumps 2018mike100% (1)
- Delta Robot KinematicsDocument11 paginiDelta Robot KinematicssekinÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF 9 Part 1 Foundation Level E-Learning WorkbookDocument54 paginiTOGAF 9 Part 1 Foundation Level E-Learning Workbookdennitoz67% (3)
- TogafDocument16 paginiTogafHemant ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCI User GuideDocument2.726 paginiOCI User Guiderammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togaf Overview in One PageDocument1 paginăTogaf Overview in One PageRebeccaLangford100% (3)
- Togaf in PicturesDocument34 paginiTogaf in Picturesnewelljj100% (8)
- Solution ArchitectureDocument20 paginiSolution ArchitectureAjit Kumar SubramanyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling Enterprise Architecture with TOGAF: A Practical Guide Using UML and BPMNDe la EverandModeling Enterprise Architecture with TOGAF: A Practical Guide Using UML and BPMNEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Enterprise ArchitectureDocument318 paginiEnterprise ArchitectureJulian Gonzalez100% (1)
- GoodElearning TOGAF Poster 44 - ToGAF and ArchiMateDocument1 paginăGoodElearning TOGAF Poster 44 - ToGAF and ArchiMateFabian HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togaf QSDocument79 paginiTogaf QSanarki85100% (1)
- Togaf9 TestDocument101 paginiTogaf9 Testbprakash16Încă nu există evaluări
- Fanuc 10t Parameter Manual PDFDocument1 paginăFanuc 10t Parameter Manual PDFadil soukri0% (2)
- ENG TOGAF Quick Start GuideDocument13 paginiENG TOGAF Quick Start GuideAmr SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF V92 Part3Document143 paginiTOGAF V92 Part3rammohan thirupasur100% (1)
- TOGAF V92 Part3Document143 paginiTOGAF V92 Part3rammohan thirupasur100% (1)
- EABOK - Enterprise Architecture Body of Knowledge Guide PresentationDocument42 paginiEABOK - Enterprise Architecture Body of Knowledge Guide Presentationtdloi03vnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togaf QsDocument87 paginiTogaf QsAntwan Bell67% (3)
- TOGAF® 9 Training Course - Level 1 Foundation 3.1.0 ENDocument246 paginiTOGAF® 9 Training Course - Level 1 Foundation 3.1.0 ENsisazara67% (3)
- Togaf CourseDocument64 paginiTogaf Coursecivanus100% (2)
- GoodElearning TOGAF Poster 48 - ToGAF Other Architecture FrameworksDocument1 paginăGoodElearning TOGAF Poster 48 - ToGAF Other Architecture FrameworksFabian HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF V92 Part2Document124 paginiTOGAF V92 Part2rammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togan Coures PDFDocument497 paginiTogan Coures PDFYana HeryanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togaf 9 Scenario QuestionsDocument5 paginiTogaf 9 Scenario QuestionsdineshkaushalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Togaf: The Open Group Architecture FrameworkDocument79 paginiTogaf: The Open Group Architecture FrameworkAbhimanyu BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOGAF® 9.2 Level 1 Wonder Guide Volume 1 – 2023 Enhanced Edition: TOGAF® 9.2 Wonder Guide Series, #1De la EverandTOGAF® 9.2 Level 1 Wonder Guide Volume 1 – 2023 Enhanced Edition: TOGAF® 9.2 Wonder Guide Series, #1Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- TOGAF9 Input OutputDocument1 paginăTOGAF9 Input OutputrupvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Value of Enterprise ArchitectureDocument28 paginiThe Value of Enterprise ArchitecturePeter Evans-GreenwoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical TOGAF 9 Sample Soln 2014Q2Document35 paginiPractical TOGAF 9 Sample Soln 2014Q2HPot PotTechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clearing TOGAF 9 Level 1 and Level 2 Certification ExamDocument4 paginiClearing TOGAF 9 Level 1 and Level 2 Certification ExamfrancoisadtÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArchiMate and TOGAF v3 PDFDocument19 paginiArchiMate and TOGAF v3 PDFhugogoes100% (2)
- A Modern Enterprise Architecture Approach: Enterprise ArchitectureDe la EverandA Modern Enterprise Architecture Approach: Enterprise ArchitectureEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Yantroddharaka Hanumath Stotra Japa 2020 PDFDocument2 paginiYantroddharaka Hanumath Stotra Japa 2020 PDFrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro 3rd PDFDocument68 paginiIntro 3rd PDFrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Chronology of India From Manu To Mah PDFDocument4 paginiThe Chronology of India From Manu To Mah PDFrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studies in Indo-Muslim History (S.H. Hodivala) PDFDocument742 paginiStudies in Indo-Muslim History (S.H. Hodivala) PDFrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. A. A. Semenenko Indo-European Disper PDFDocument1 paginăDr. A. A. Semenenko Indo-European Disper PDFrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Soma Code, Parts I-III: Luminous Visions in The RIG VEDA Soma's Birth & Transmutation Into Indra Visions, Myths & Drugs in The RIG VEDADocument65 paginiThe Soma Code, Parts I-III: Luminous Visions in The RIG VEDA Soma's Birth & Transmutation Into Indra Visions, Myths & Drugs in The RIG VEDArammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tulipmania and Bitcoin. Explain TulipmaniaDocument2 paginiTulipmania and Bitcoin. Explain Tulipmaniarammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who Is Killing India's Nuclear ScientistsDocument5 paginiWho Is Killing India's Nuclear Scientistsrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Indo European Origins PDFDocument6 paginiThe Indo European Origins PDFrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python For BeginnersDocument119 paginiPython For Beginnersrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain: Decentralized Internet Quantum ComputingDocument2 paginiBlockchain: Decentralized Internet Quantum Computingrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astrological Analysis of Nuclear PowerDocument52 paginiAstrological Analysis of Nuclear Powerrammohan thirupasur100% (1)
- VidyamanyarIna Advaita Khandana VyakhyaDocument22 paginiVidyamanyarIna Advaita Khandana Vyakhyarammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Make The Best Use of Live SessionsDocument81 paginiHow To Make The Best Use of Live Sessionsrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excerpt Bouquet of Non Dual TextsDocument10 paginiExcerpt Bouquet of Non Dual Textsrammohan thirupasurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Average and Instantaneous AccelerationDocument35 paginiAverage and Instantaneous AccelerationaraneyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes and Attitude ChangeDocument19 paginiAttitudes and Attitude Changeprajwal-athrey-3069Încă nu există evaluări
- Share Cognitive Notes Doc-1Document15 paginiShare Cognitive Notes Doc-1GinniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Followup Centres May12Document14 paginiFollowup Centres May12Suresh NagpalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 3 MathematicsDocument3 paginiGrade 3 Mathematicsailaine grace alapÎncă nu există evaluări
- YCAP 7 Steps PosterDocument1 paginăYCAP 7 Steps PosterSohila AmrÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Scopes TrialDocument10 paginiThe Scopes Trialapi-607238202Încă nu există evaluări
- Reading Activity - A Lost DogDocument3 paginiReading Activity - A Lost DogGigsFloripaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vip90 2021 Deso10Document6 paginiVip90 2021 Deso10Đỗ KhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Not PrecedentialDocument5 paginiNot PrecedentialScribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adh Dialectical JournalDocument4 paginiAdh Dialectical Journalapi-521174998Încă nu există evaluări
- Revision 5 - OnlineDocument5 paginiRevision 5 - OnlineThu HaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology in EducationDocument3 paginiTechnology in EducationDinesh MadhavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomol LabDocument12 paginiBiomol LabElizabeth BacarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teacher LOA & TermsDocument3 paginiTeacher LOA & TermsMike SchmoronoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIS Tutorial 4 AnswerDocument8 paginiMIS Tutorial 4 AnswerChia Kong Haw0% (1)
- Cranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaDocument3 paginiCranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaSlavica JovanovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- (OCM) Chapter 1 Principles of ManagementDocument23 pagini(OCM) Chapter 1 Principles of ManagementMehfooz PathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The CourtDocument92 paginiThe "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The Courtunknown07blackstarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Q1 PDFDocument29 paginiJurnal Q1 PDFSepti DamayantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIR v. San Roque Power Corp., G.R. No. 187485, February 12, 2013Document8 paginiCIR v. San Roque Power Corp., G.R. No. 187485, February 12, 2013samaral bentesinkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- News StoryDocument1 paginăNews StoryRic Anthony LayasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adv Tariq Writ of Land Survey Tribunal (Alomgir ALo) Final 05.06.2023Document18 paginiAdv Tariq Writ of Land Survey Tribunal (Alomgir ALo) Final 05.06.2023senorislamÎncă nu există evaluări