Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Oslo Poster
Încărcat de
Mihail ButurăTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Oslo Poster
Încărcat de
Mihail ButurăDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
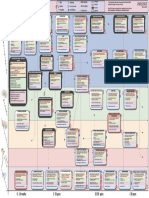
Axl is an essential epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced regulator of breast cancer metastasis and patient survival
Crina Tiron¹, Hallvard Haugen¹, Christine Gjerdrum¹, Torill Høiby¹, Ingunn Stefansson¹ Tone Sandal¹, Karin Collet¹, Emmet McCormack¹, Bjørn Tore Gjertsen¹, David
Micklem¹, Lars Akslen¹, Carlotta Glackin², James Lorens¹. ¹University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway; ²Beckman Center, City of Hope, Duarte, CA
Metastasis underlies the majority of cancer-related deaths. Hence, furthering our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that enable tumor cell dissemination is a vital health issue. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) endow carcinoma cells with enhanced migratory and survival attributes that facilitate malignat progression. We show that the presence of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl in mammography-detected primary breast cancers
independently predicts strongly reduced overall patient survival, and mached patient metastatic lesion show enhanced Axl expression. We demonstrate that Axl is strongly induced by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pre-
malignant mammary epithelial cells that establishes an autocrine signaling loop with its ligant, Gas6. Using epi-allelic RNA interference analysis in metastatic breast cancer cells we deliniated a distinct threshold of Axl expression
for mesenchymal-like in vitro cell invasiveness, and to form tumors in foreign tissue engineered microenvironments in vivo. Importantly, Axl knockdown completely prevented the spread of highly metastatic breast carcinoma cells
from the mammary gland to lymph nodes and several major organs, and increased overall survival, in two diffrent optical imaging-bassed experimental breast cancer models. Thus, Axl represent a novel downstream effector of
tumor cell EMT that is required for breast cancer metastasis. The detection and targeted of Axl-expressing tumors represents an important new therapeutic strategy for breast cancer.
Axl expression is a strong negative prognostic factor for human breast cancer survival
A B Weak AXL expression (90/6) C D
1.0 (A) Axl expression in human breast tumors. (B)
Variable Categories HR P
Probability of survival
Univariate survival analysis (Kaplan-Meier method)
0.8
Histologic grade Grade 1 of breast cancer patients. (C) Multivariate survival
analysis of human breast patients. (D) Axl expres-
0.6
Strong AXL expression (64/11)
Grade 2-3 3.79 0.040 sion in primary breast carcinoma and metastases.
0.4 Lymph node status 0-1
>1 9.16 0.001
0.2
AXL expression
Log Rank test, P=0.035
AXL expression Low(0-4)
0.0 High (6-9) 3.27 0.021
20 40 60 80 100
Months after primary treatment
Axl is required for breast cancer cell invasiveness Axl is upregulated by EMT inducers in breast epithelial cells In vivo epi-allelic analysis reveals a distinct Axl expression thresh-
A B A
MCF10a
B C old required for breast tumor formation
i ii i iii MCF10a
uc x
MDA-MB-231
9 8 0
l27 xl27 xl28 xl2
MDA-MB-231
sh279 shAxl2 o
c T
t
Z S
ol
ntr wis eb2 lug nai
S
l A B
L A hA hA A
sh sh s s sh
Twist
control
Twist
h Axl Gas6
shAxl278
Zeb2 1.8
% of Max
shAxl280
Total Photon/mm²/sec
h Actin Tubulin 1.6
% of Max
% of Max
sh279 shAxl2
lysate IP Slug 1.4 Therapeutic
shLuc Slug 1.8
Std
c xl2 c xl2
shLu shA shLu shA shAxl279 ii MDA-MB-231 shAxl2 Snail Snail
1.2 threshold
shAxl278 1 Ineffective shRNA 1.6 Ineffective
Ineffective
Normalized tumor growth
sh279 shAxl2 Benefit
Snail
Slug
Twist
shAxl280
h Axl
shAxl2 Axl Zeb2 0.8 *
control
Gas6 * control
control 0.6 * * * * 1.4 Benefit
anti-hAxl anti-pAxl 10 10 * *
10¹ 102 103 104 105 E-cadherin 101 10² 10³ 0.4 **
1.2
Tumor growth
Gas6
Axl
EPI
Axl
Axl 0.2
markers
β-catenin 1.0
1.2
C D E
Zeb2
N-cadherin
Tumor Diameter (mm)
0.8
MES
MDA-MB-231 MDA-MB-231 1 Ineffective shRNA
*
shLuc shAxl2 *
1.4 Vimentin Vimentin 0.8 **
** 0.6
shLuc
Actin 0.6 0.4
Relative invasion
1.2
Serum
shAxl279
shLuc
1 shAxl278 0.4 0.2
shAxl280 0.2
0.8
* shAxl2
100x 400x
D 0.0
0 25 50 75 100
0.6
i MCF10a iii 0 1 2 3 4
Axl Knockdown Level
l (A) MCF10a cells transduced with retroviral vectors en-
shAxl2
SDF-1
0.4 * ro Time (weeks)
nt i st ug ail
0.2 co Tw Sl Sn coding Twist, Zeb2, Slug, Snail. (B) Axl surface expres-
100x 400x Gas6 sion in MCF10a cells encoding Twist, Zeb, Slug, Snail.
% of Max
0
Tubulin Slug (C) Mesenchymal morphology at 72 hours post-seeding.
ii (D) Gas6 expression in MCF10a cells (i, total lysate; ii,
(A) Graded Axl surface expression in MDA-MB 231 cells (i, western blots; ii, anti-Axl flow cytometry analysis). (B) Gas6 expres- MCF10a Snail conditioned medium; iii, anti-Gas6 6 flow cytometry (A) Image analysis of tumor growth (total photon) and radial infiltration (signal diameter) by subcutaneous Axl epi-
l allelic MDA-MB-231/GFP-Luc xenografts in NOD/SCID mice comprising shAxl278, shAx280, shAxl2 normalized
sion in MDA-MB-231 cells (i, total lysate; ii, conditioned medium; iii, anti-Gas6 flow cytometry analysis). Invasiveness of ro st ug ail
nt i analysis).
co Tw Sl Sn control to shAxl279 (ineffective shRNA). (B) Tumor growth (normalized 28 day total photon measurements) plotted versus
MDA-MB 231 cells correlates with Axl expresion level (C) serum and (D) SDF-1,*p<0.05. (E) Growth of MDA-MB-231 cells in 10 10 10
Gas6 * Axl knockdown (geometric mean fluorescence). (N = 6mice/group), *p<0.05, **p<0.005.
3D-matrigel. Gas6
Tissue engineered breast tumors require Axl expression Axl is required for human breast carcinoma to metastasize Axl is essential for post-immune response recurrence and
i ii Ai B i metastasis of syngeneic breast carcinoma cells in BALB/c
Weeks post implantation Photon counts Weeks post implantation Photon
counts/mm2/s
mice
0 1 2 3 4 mm²/s 0 2 4 6 8 9 116970 5
control 30
2231 *
MDA-MB 231/D3H2LN GFP-Luc
shAxl2
Total photon (10¹)sec¹¹
1.3 control + EC + SMC
Total photon (10¹)sec¹¹
control
control
A
-
87728 4
shAxl2 + EC + SMC
Tumor diameter (mm)
shAxl2
control + EC + SMC
Primary tumor
***
6
i ii
shAxl2 + EC + SMC 20
3
control
**
1.0 * Weeks postimplantation
MDA-MB 231 GFPLuc
54830 Photon
4
5
2 day1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 counts/mm²/sec
1673 shAxl279
Total Pho ton (x10 5 ) sec-1
10 2590
Ventral scan
0.7 **
shAxl2
32898
sh-mAxl2
4T1-GFP-Luc-shAxl279
1 *
**
0.5 10
0
2 4 6 8 9 0 2 4 6 8 9 1950 3
1045 ii ii Time (weeks) Time (weeks)
** Weeks post implantation
Dorsal scan
Photon
0.2
Metastasis to Lymph node
9
Total photon (10¹)sec¹¹
4 6 8 9 counts/mm2/s
-
24 53 133 526
shAxl2 control
shAxl2
*** 1470 2
4
** 6
627 3
990
Ventral scan
15
4T1-GFP-Luc-shmAxl2
10 10 10 10 1
Tumor diameter (mm)
4 6 8 9
10 Time (weeks)
* *
510
iii ** C Detected metastases D 0
*
Dorsal scan
1.0 shAxl2 (N=5)
** Cell line
10 MDA-MB
In vivo
Organ
Ex vivo
0.8
270 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Time (weeks)
Probability of survival
231/D3H2LN
Control shAxl2 GFP-Luc Lymph node Lungs Kidneys Ovaries Liver 0.6 10
5/6 4/6 3/6 2/6 0/6
5 control
0.4
shAxl2 0/6 0/6 1/6 0/6 0/6
iv N (number of animals/group) = 6 mice/group 0.2
Vector (N=10)
B Detected metastases
0.0 Log Rank, P=0.001
Ex vivo
65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
120 50μm 50μm 0 1 2 3 4 E Number of days alive Cell line Organ
Time (weeks) i Ex vivo imaging ii H/E staining (10x) Lungs Bone Rib cage
Lymph
Ovaries Kidneys Liver Brain Intestine Spleen
MDA-MB 231/D3H2LN GFP Luc MDA-MB 231/D3H2LN GFP Luc nodes
control shAxl2 control shAxl2
shAxl279
Mammary pad
5/7 5/7 5/7 4/7 4/7 3/7 2/7 2/7 2/7 1/7
Mammary pad
1192 1192
v (A) Temporal in vivo bioluminiscence imaging sh-mAxl2 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7 0/7
Microvascular Density
100 20 *
10
117
10
117
of (i) mamary fat pad growth (ii) axillary lymph N (number of animals/group) = 7 mice/group
node metastasis. (B) Biphotonic quantitation of
Vessel Diameter
Lung
Lung
(no.vessels/mm²)
80 16 Axl is required for growth of tricellular tissue im- 10 10 (i) primary mammary tumor (total photon) and
C
Axillary tissue
plants in NOD-SCID mice. (i) Representative in radial infiltration (signal diameter) and (ii) total
Axillary tissue
832 832
60 12
(μm)
vivo bioluminescence images. (ii) Images analysis photon from thoracic lymph node area of
10 10 1
(total photon, upper and tumor diameter, lower). (iii) NOD/SCID mice. (C) Ex vivo detected metas- 1
40 8 Aspect of excised tumor tissue engineering im-
511 511
tasis. (D) Univariate survival analysis (Kaplan-
Ovary
Ovary
plants (28 days). (iv) Anti-human CD31-staining. (v) Meier method) between control and shAxl2 (E)
20 4 Intrascaffold human vessel diameter (left) and mi-
10
1220
10
1220 Ex vivo bioluminiscence images and histologi- 2
6
Kdiney
Kdiney
crovascular density (right) in tissue engineered cal analysis of excised organs showing the
0 0 (tricellular) tumors. (N=7mice/group), *p<0.05, 10 10 presence of metastasis (arrow) in several Anatomical location 7
Control shAxl2 Control shAxl2 **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005. 9 9
organs. (N=6mice/group), *p<0.05,
3 6
1.Brain 3
Liver
Liver
2.Axillary lymph node
0 0
**p<0.005, ***p<0.0005. 7 3.Lungs
4.Ovaries 8
5.Femur and Tibia
4 6.Rib cage 4
8 7.Liver
Conclusions 8.Kidneys
5
shAxl279 5 shmAxl2
● Axl is a strong independent predictor of breast cancer patient overall survival
(A) Temporal in vivo bioluminescence imaging (i) of orthotropic (mammary fat pad) injected synge-
nic 4T1-GFP-Luc cells expressing mouse Axl shRNA (4T1-GFP-Luc-shmAxl2) or negative control
● Autocrine Axl-signaling is induced by EMT human Axl shRNA (4T1-GFP-Luc-shAxl279) into BALB/c mice. (ii) Quantitation of whole-body bio-
luminescence (total photon) injected BALB/c mice. (B) Survey of metastasis sites (8-weeks post-
orthotopic implantation) monitored by ex vivo bioluminescence detection of 4T1-GFP-Luc cells in
● Axl is critical for malignant invasiveness and required tumor formation in foreign microenvironments excised organs. (C) Bioluminescence images from representative female BALB/c mice acquired at
8 weeks post-orthotopic injection. (N=7mice/group), *p<0.05.
● Axl is essential for breast cancer cell metastasis
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Top Down Proteomics Using Online Polymer Reversed Phase (PLRP) Nanocapillary-LC Coupled Fourier Transform Mass SpectrometryDocument1 paginăTop Down Proteomics Using Online Polymer Reversed Phase (PLRP) Nanocapillary-LC Coupled Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometryapi-26001949Încă nu există evaluări
- Pap ADocument9 paginiPap AlandabureÎncă nu există evaluări
- 175P - FCardoso-BYLieve StudyDocument1 pagină175P - FCardoso-BYLieve StudyΒΑΣΙΛΗΣ ΚΟΛΙΝΤΖΙΚΗΣÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ppt. CLL and XMRV Houston 2010Document1 paginăPpt. CLL and XMRV Houston 2010mindykitei_cfscentralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Figure 1. POLARIS Study Design: BackgroundDocument1 paginăFigure 1. POLARIS Study Design: BackgroundAhmed Abd El AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdamOConnell Cov (HealthPromoHEPADocument1 paginăAdamOConnell Cov (HealthPromoHEPAapi-15840052Încă nu există evaluări
- FT MBA Rankings 2010Document1 paginăFT MBA Rankings 2010Shariq ShamimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster Caitlin BrennanDocument1 paginăPoster Caitlin Brennansagun maharjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Va Medica: Treatment Efficacy of Language and Calculation Disorders and Speech Apraxia: A Review of The LiteratureDocument21 paginiVa Medica: Treatment Efficacy of Language and Calculation Disorders and Speech Apraxia: A Review of The LiteraturemohamerrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loïc Caloren - NBS 2021 PosterDocument1 paginăLoïc Caloren - NBS 2021 PosterCBR UBCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beyond Operation ChameleonDocument1 paginăBeyond Operation Chameleonrnk.2k12Încă nu există evaluări
- Blue Belt Level 01 - Fact Sheet - 0 PDFDocument9 paginiBlue Belt Level 01 - Fact Sheet - 0 PDFShayma ShamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIPS2019 TGAN Supplementary PDFDocument7 paginiNIPS2019 TGAN Supplementary PDFAmber SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bulletin 6000ADocument1 paginăBulletin 6000AKala KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zeitschrift Für Mesoamerikaforschung: Vol. Xxxviii Oktober 2016 Nr. 5Document13 paginiZeitschrift Für Mesoamerikaforschung: Vol. Xxxviii Oktober 2016 Nr. 5Sergio CifuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decaydecay Decay Decay Decay: Regurgitation ProblemsDocument1 paginăDecaydecay Decay Decay Decay: Regurgitation Problemsnumber 2Încă nu există evaluări
- SAFC Biosciences Scientific Posters - Optimization of Serum-Free Media For EB14 Cell Growth and Viral ProductionDocument1 paginăSAFC Biosciences Scientific Posters - Optimization of Serum-Free Media For EB14 Cell Growth and Viral ProductionSAFC-GlobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 7 ADocument2 paginiActivity 7 AMemeowwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amino Acid Analysis in Plasma-Serum and Urine Brochure en 4Document6 paginiAmino Acid Analysis in Plasma-Serum and Urine Brochure en 4yousrazeidan1979Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Cartesian GraphsDocument10 paginiBasic Cartesian GraphsJesus David Sierra TaberaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waters 2Document1 paginăWaters 2bram.soenen1Încă nu există evaluări
- Tagore Medical College and Hospital Department of Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument1 paginăTagore Medical College and Hospital Department of Obstetrics and GynaecologyAdharsh SurendhiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmniSure ROM Test Instructions For Use (2019)Document1 paginăAmniSure ROM Test Instructions For Use (2019)Hòa HồÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of An Animal-Component Free Electroporation and Recovery Formulation Using EX-CELL CHO Cloning MediumDocument1 paginăDevelopment of An Animal-Component Free Electroporation and Recovery Formulation Using EX-CELL CHO Cloning MediumSAFC-GlobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 06Document1 paginăGrade 06aloneforever21183Încă nu există evaluări
- Annika Andersson CNS2014Document1 paginăAnnika Andersson CNS2014Coie8tÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis and Treatment (Donna L. White PHD, MPH, Amir Firozi MD (Auth.) EtcDocument752 paginiHepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis and Treatment (Donna L. White PHD, MPH, Amir Firozi MD (Auth.) EtcNurul HidayahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective Viral Clearance in Mab PurificationTOYOPEARL® ResinDocument1 paginăEffective Viral Clearance in Mab PurificationTOYOPEARL® ResinBruno AndreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphene Shear Exfoliation in Liquids - Poster KP PDFDocument1 paginăGraphene Shear Exfoliation in Liquids - Poster KP PDFhijerÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP MathematicsDocument62 paginiDSP Mathematicshameedkhan97Încă nu există evaluări
- Dysplastic Nevi - Do They Exist and What Arethey Actually?Document6 paginiDysplastic Nevi - Do They Exist and What Arethey Actually?Heather Marie MathisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Federal Child Welfare Grant Program Matrix TableDocument2 paginiFederal Child Welfare Grant Program Matrix TableBeverly TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Delhi Undergraduate Admission Arts & Commerce 2nd Cut-Off ListDocument11 paginiUniversity of Delhi Undergraduate Admission Arts & Commerce 2nd Cut-Off ListriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nhs Bronchiolitis Pathway Acute Setting South East Coast SCNDocument2 paginiNhs Bronchiolitis Pathway Acute Setting South East Coast SCNdrgrizahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bbird H NassignmentDocument7 paginiBbird H Nassignmentapi-334644774Încă nu există evaluări
- Karlien Vanhouteghem, Annelies Aerssens, Dirk Ommeslag, Jerina Boelens, Steven Callens, Anne-Marie Van Den AbeeleDocument1 paginăKarlien Vanhouteghem, Annelies Aerssens, Dirk Ommeslag, Jerina Boelens, Steven Callens, Anne-Marie Van Den AbeeleAfien MuktiÎncă nu există evaluări
- QMC A Floor 0219 WebDocument1 paginăQMC A Floor 0219 Webgoogle manÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luzada CholecystitisDocument1 paginăLuzada CholecystitisLEAH LUZADAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mario FERNÁNDEZ-MAZUECOS, Beverley J. GLOVER : BackgroundDocument1 paginăMario FERNÁNDEZ-MAZUECOS, Beverley J. GLOVER : BackgroundMario Fernández-MazuecosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azusa MapDocument1 paginăAzusa MapSouthern California Public RadioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2007 AAPS - Poster - High Throughput Solubility AnalysisDocument1 pagină2007 AAPS - Poster - High Throughput Solubility Analysismr_jpwalsh8941Încă nu există evaluări
- Poster Eunyoung ChunDocument1 paginăPoster Eunyoung Chunsagun maharjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNS Tumor Map 2020 FullDocument1 paginăCNS Tumor Map 2020 FullAlves de MeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fever PrimaryCommunityCare Dec 16 FINAL VSDocument2 paginiFever PrimaryCommunityCare Dec 16 FINAL VSnimraÎncă nu există evaluări
- S Ms Am Xa /e o Co Ioooo Ati Ca Uc: ?BC D CCDocument4 paginiS Ms Am Xa /e o Co Ioooo Ati Ca Uc: ?BC D CC9amar al zamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- S Ms Am Xa /e o Co Ioooo Ati Ca Uc: ?BC D CCDocument4 paginiS Ms Am Xa /e o Co Ioooo Ati Ca Uc: ?BC D CC9amar al zamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 PrevMed PrelimTopicsDocument24 pagini1.1 PrevMed PrelimTopicsLaish Christle CapiendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypesDocument12 paginiThe Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypestigriochelitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- European Seismic Hazard MapDocument1 paginăEuropean Seismic Hazard MapDaiuk.DakÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARTMO Poster Terrabites 2012Document1 paginăARTMO Poster Terrabites 2012oktianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Language Hub Elementary WB U1 2Document12 paginiLanguage Hub Elementary WB U1 2Dana MendeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Practical Guide To Small-Sided & Conditioned Games (SSCG) in Football: Implications For Training DesignDocument1 paginăA Practical Guide To Small-Sided & Conditioned Games (SSCG) in Football: Implications For Training DesignLukas ArenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL121 Study Sheet TemplateDocument5 paginiBIOL121 Study Sheet TemplateRachel LiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- George S Resume-LabDocument1 paginăGeorge S Resume-LabRinku RathoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angiosperm Phylogeny: Flowering Plant SystematicsDocument1 paginăAngiosperm Phylogeny: Flowering Plant SystematicsAulia Absentnomordelapanrasspberryi AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apg IvDocument1 paginăApg IvAngeles Urias VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brighton - Citywide - Map2017Document1 paginăBrighton - Citywide - Map2017LucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathDe la EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: Language ArtsDe la EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: Language ArtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrapment of N-Hydroxyphthalimide Carbon Dots in PDFDocument14 paginiEntrapment of N-Hydroxyphthalimide Carbon Dots in PDFMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrapment of N-Hydroxyphthalimide Carbon Dots in Different Topical Gel Formulations: New Composites With Anticancer ActivityDocument3 paginiEntrapment of N-Hydroxyphthalimide Carbon Dots in Different Topical Gel Formulations: New Composites With Anticancer ActivityMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Models For Muscular DystrophyDocument56 paginiAnimal Models For Muscular DystrophyMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Resolution Oligonucleotide-Based ACGH AnalysisDocument8 paginiHigh Resolution Oligonucleotide-Based ACGH AnalysisMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prezentare Array CancerDocument44 paginiPrezentare Array CancerMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slujba PastiDocument49 paginiSlujba PastiMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agilent Microarrray Overview PDFDocument39 paginiAgilent Microarrray Overview PDFMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slujba PastiDocument49 paginiSlujba PastiMihail ButurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Viator Bilingual International School Academic Planning, Development and Assessment Code Versio DateDocument2 paginiSt. Viator Bilingual International School Academic Planning, Development and Assessment Code Versio DateSamuel PinzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRAC MOA Poster January 6 2022Document1 paginăHRAC MOA Poster January 6 2022Francisco EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 paginiBacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesJerson Aizpuro SuplementoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEET Biology MCQDocument6 paginiNEET Biology MCQIsh MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 Intro of BiotechnologyDocument31 paginiWeek 1 Intro of BiotechnologyMauiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meiosis Study SheetDocument3 paginiMeiosis Study SheetDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 DNA Replication Damage and RepairDocument14 pagini06 DNA Replication Damage and Repairفقوش عبودÎncă nu există evaluări
- Megacolon Aganglionico Congénito (Enfermedad de Hirschsprung)Document32 paginiMegacolon Aganglionico Congénito (Enfermedad de Hirschsprung)Soledad SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Wall of BacteriaDocument7 paginiCell Wall of BacteriaBashir AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 Exemplar-Melc 5Document8 paginiScience 9 Exemplar-Melc 5Thartson Oliveros MagdadaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- CertificateDocument1 paginăCertificateShashankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles Worksheet-PrintDocument2 paginiCell Organelles Worksheet-PrintmuraliMu0% (1)
- Garnier SustainabilityProgressReport 2020 Final HDDocument56 paginiGarnier SustainabilityProgressReport 2020 Final HDK59 Vo Ngoc Yen NhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC 1010C Unit 2 Test - The CellDocument4 paginiBSC 1010C Unit 2 Test - The CellAmalee CarrascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aster Group CoDocument3 paginiAster Group Coeason insightsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coenzyme ListDocument1 paginăCoenzyme ListhvgtachÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCH Portfolio Lipid MetabDocument16 paginiBCH Portfolio Lipid MetabCHLOE IANNAH CALVADORESÎncă nu există evaluări
- HPV PCRDocument34 paginiHPV PCRGuneyden GuneydenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flux Balance AnalysisDocument25 paginiFlux Balance AnalysisRaaisa MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study - BT Talong PDFDocument104 paginiCase Study - BT Talong PDFMicahChooÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIFECODES SSO Typing Products MATCH IT! DNADocument8 paginiLIFECODES SSO Typing Products MATCH IT! DNAObadah QudahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Structure and ChemistryDocument8 paginiDna Structure and ChemistryChristian Bonne MarimlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecules: You Are What You Eat!Document39 paginiBiomolecules: You Are What You Eat!Joanna Ruth SeproÎncă nu există evaluări
- GENETICDocument48 paginiGENETICAngelica CuarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 - Basic Principles of Cell & Cell TheoryDocument4 paginiModule 2 - Basic Principles of Cell & Cell TheoryYsabela Dela PazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Membrane PhysiologyDocument11 paginiChapter 2 - Membrane Physiologytahira UroojÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.10 Competitive Binding AssaysDocument4 pagini1.10 Competitive Binding Assaysmelisa asibalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH2 - ECOLOGY ENGINEERING Rev PDFDocument16 paginiCH2 - ECOLOGY ENGINEERING Rev PDFsyahaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coatings Resins On Bio Based Raw Materials DSMDocument22 paginiCoatings Resins On Bio Based Raw Materials DSMDharmendra B MistryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106Document2 paginiHiv Life Cycle: Fact Sheet Number 106eviÎncă nu există evaluări