Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Conjugação Dos Verbos em Inglês
Încărcat de
Delfino Bernardo ViegasTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Conjugação Dos Verbos em Inglês
Încărcat de
Delfino Bernardo ViegasDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Escola Secundária de Nhangau
Texto de apoio
Conjugação dos verbos em inglês
Verbos são usados para descrever acções ou eventos. Essas acções ou eventos podem ter lugar
em diferentes momentos: No passado, no presente ou no futuro.
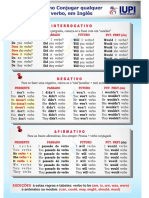
Classes dos verbos
Há duas classes dos verbos em inglês:
Os verbos auxiliares: to be, to have, to do, can, could, may, might, must, ought, shall, should,
will, would, to need, to dare and used.
Verbos principal: to work, to sing, to pray.
Vamos ver como se conjuga os verbos em inglês; tendo como exemplo o verbo to play.
Present Simple Present Continuous
I play – eu jogo I am playing – eu estou jogando
You play – você/tu jogas You are playing – você está jogando
Affirmative
He/she/it plays – ele(a) joga He/she/it is playing – ele(a) está jogando
We play – nós jogamos We are playing – nós estamos jogando
You play – vocês jogam You are playing - vocês estão jogando
They play – eles(as) jogam They are playing - eles(as) estão jogando
NB: I am – I’m. you are – you’re. he is – he’s
I do not play I am not playing
You do not play You are not playing
Negative
He/she/it does not play He/she/It is not playing
We do not play We are not playing
You do not play You are not playing
They do not play They are not playing
NB: do not – don’t e does not - doesn’t NB: are not – aren’t . is not – isn’t
Do I play …? Answer Am I playing? answer
Do you play? Yes, I do/ No I don’t Are you playing? Yes, I am- No, I am not.
Interrogative
Does he play? Yes, he does/ No, he doesn’t Is he playing? Yes, he’s/ No, he isn’t
Do we play? Yes, we do/ No, we don’t Are we playing? Yes, we’re/ No, we aren’t
Do you play? Are you playing?
Do they play? Yes, they do/ No they don’t Are they playing? Yes, they’re/ No, They
aren’t
Observe:
Na Terceira pessoa do singular o verbo leva um –s, podendo variar de acordo com as
situaçoes, ora vejamos: Se o verbo terminar com –s, -sh, -ch acrescenta – se –es.
Pass – passes finish – finishes watch – watches
Nas frases negativas, usa – se o verbo auxiliar do seguido do not, sendo does para
terceira pessoa do singular.
Nas frases interrogativas, também serve – se do verbo auxiliar do/does para formar o
interrogativo.
Author: Francisco Tangawisse Versão 0.0
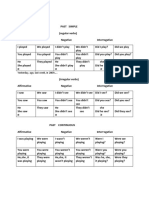
Past simple Past continuous
I played – eu joguei I was playing – eu estava jogando
You played – tu/voce jogaste/jogou You were playing – tu estavas jogando
Affirmative He/she/it played – ele(a) jogou He was playing – ele estava jogando
We played – Nós jogamos We were playing – nós estavamos jogando
You played – vocês jogaram You were playing – vocês estavam jogando
They played eles(as) jogaram They were playing – eles(as) estavam jogando
I did not play I was not playing
You did not play You were not playing
He/she/it did not play He was not playing
Negative
We did not play We were not playing
You did not play You were not playing
We did not play We were not playing
They did not play They were not playing
NB: did not – didn’t NB: was not – wasn’t. were not – weren’t
Did I play? answer Was I playing?
Interrogative
Did you play? Yes, I did/ No, I didn’t Were you playing?
Did he play? Yes, he did/ No, he didn’t Was she playing?
Did we play? Yes, we did/ No, we didn’t Were we playing?
Did you play? Were you playing?
Did they play? Yes, they did/ No, they didn’t Were they playing?
Observe:
A semelhança do present simple, o negative e o interrogative é formado com o verbo
auxiliary do, neste caso o seu passado que é did.
Future simple Future continuous
I shall play – Eu jogarei I shall be playing – eu estarei jogando
You will play – Tu jogarás You will be playing – você estará jogando
Affirmative
He/she/it will play – ele(a) Jogará He will be playing – ele estará jogando
We shall play – nós jogaremos We shall be playing – nós estaremos jogando
You will play – vocês joagarão You will be playing – vocês estarão jogando
They will play – eles(as) jogarão They will be playing - eles(as) estarão jogando
NB: I shall – I’ll/ you will – you’ll
I shall not play I shall not be playing
You will not play You will not be playing
Negative
He/she/it will not play He will not be playing
We shall not play We shall not be playing
You will not play You will not be playing
They will not play They will not be playing
Shall not – shan’t. will not – won’t
Shall I play? Answer Shall I be playing? Answer
Will you play? Yes, I will/ No, I won’t
Will you be playing? Yes, I will/ No, I won’t
Interrogative
Will he play? Yes, he will/ No, he won’t
Will he be playing? Yes, he will/ No, he won’t
Shall we play? Yes, we shall/ No, we shan’t
Shall we be playing? Yes, we shall/ No, we shan’t
Will you play? Will you be playing?
Will they play? Yes, they will/ No, they won’t
Will they be playing? Yes, they will/ No, they
won’t
Observe: Geralmente usamos will para todas pessoas gramaticais, podendo dizer I will ou we
will.
Author: Francisco Tangawisse Versão 0.0
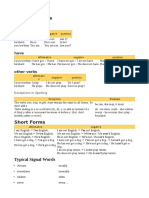
Present perfect simple Present perfect continuous
I have played – eu tenho jogado* I have been playing - eu tenho estado a jogar*
You have played You have been playing
Affirmative
He/she/it has played He has been playing.
We have played We have been playing.
You have played You have been playing
They have been playing They have been playing.
NB: I have – I’ve/ He has – he’s
I have not played I have not been playing
You have not played You have not been playing
Negative
He/she/it has not played He has not been playing
We have not played We have not been playing
You have not played You have not been playing
They have not played They have not been playing
NB: have not – haven’t/ has not – hasn’t
Have I played? answer Have I been playing?
Interrogative
Have you played? Yes, I’ve/ No, I haven’t Have you been playing?
Has she played? Yes, she has/ No, she hasn’t Has she been playing?
Have we played? Yes, we have/ No, we haven’t Have we been playing?
Have you played? Have you been playing?
Have they played? Have they been playing?
* Essa tradução não é muito fiel, é apenas literal. O present perfect tem muita relação com o
past simple.
Como podes observar o present perfect simple é formado com o auxiliar have/has + past
participle e o present perfect continuous com o have/has been + gerund
Past perfect simple Past perfect continuos
I had played – eu tinha jogado I had been playing
You had played You had been playing
Affirmative
He/she/it had played He had been playing
We had played We had been playing
You had played You had been playing
They had played They had been playing
NB: I had – I’d/ he had – he’d
I had not played I had not been playing
You had not played You had not been playing
Negative
He/she/it had not played He had not been playing
We had not played We had not been playing
You had not played You had not been playing
They had not played They had not been playing
NB: had not – hadn’t
Had I played? answer Had I been playing?
Had you played? Yes, I had/ No, I hadn’t Had you been playing?
Interrogative
Had he played? Yes, he had/ No, he hadn’t Had she been playing?
Had we played? Had we been playing?
Had you played? Had you been playing?
Had they played? Had they been playing?
O past perfect simple é formado com o auxiliary had + past participle e o past perfect
continuous é formado com had been + gerund.
Author: Francisco Tangawisse Versão 0.0
Future perfect Future perfect continuous
I will have played – eu terei jogado I will have been playing
You will have played You will have been playing
Affirmative
He will have played He will have been played
We will have played We will have been played
You will have played You will have been played
They will have played They will have been played
I will not have played I will not have been playing
You will not have played You will not have been playing
Negative
He will not have played He will not have been playing
We will not played We will not have been playing
You will not have played You will not have been playing
They will not have played They will not have been +playing
Will I have played? answer Will I have been playing?
Interrogative
Will you have played? Yes, I will Will you have been playing?
Will he have played? No, he won’t Will he have been playing?
Will we have played? Will we have been playing?
Will you have played? Will you have been playing?
Will they have played? Will they have been playing?
Conditional Conditional perfect
I would play - eu jogaria I would have played – eu teria jogado
You would play You would have played
Affirmative
He/she/it would play He would have played
We would play We would have played
You would play You would have played
They would play They would have played
NB: I would- I’d
I would not play I would not have played
You would not play You would not have played
Negative
He would not play He would not have played
We would not play We would not have played
You would not play You would not have played
They would not play They would not have played
NB: would not – wouldn’t
Would I play? answer Would I have played?
Interrogative
Would you play? Yes, I would. Would you have played?
Would he play? No, he wouldn’t Would he have played?
Would we play? Would we have played?
Would you play? Would you have played?
Would they play? Would they have played?
O conditional é formado com o auxiliary would e o conditional perfect é formado com would
have + past perfect
Author: Francisco Tangawisse Versão 0.0
Lista de alguns verbos irregulares
Past Past Past Past
Infinitive significado infinitive significado
simple participle simple participle
Be Was/were been Ser/estar Light lit lit Acender
Beat Beat Beaten Lose lost lost Perder
Become became become Tornar Make made made Fazer
Begin Began begun Começar Mean meant meant Significar
Bite Bit bitten Meet met met Encontrar
Blow Blew blown Soprar Pay paid paid Pagar
Break Broke broken Quebrar Put put put Por
Bring brought brought Trazer Quit quit quit abandonar
Build Built built Construir Read read Read Ler
Buy bought bought Comprar Ride rode ridden Montar(cavalo,
bicicleta)
Catch caught caught Apanhar Ring rang rung Tocar(sino, campaninha)
Choose Chose chosen Escolher Rise rose risen Levantar/nascer do sol
Come Came come Vir Rot rotted Rotted/rotten Apodrecer
Cost Cost cost Custar Run ran run Correr
Cut Cut cut Cortar Saw sawed sawed/sawn Serrar
Do Did done Fazer Say said said Dizer
Draw Drew drawn Desenhar See saw seen Ver
Drink Drank drunk Beber Seek sought sought Procurar
Drive Drove driven Conduzir Sell sold sold Vender
Eat Ate eaten Comer Send sent sent Enviar
Fall Fell fallen Cair Shake shook shaken Agitar
Feel Felt felt Fallen Shave Shaved shaven Barbear/acenar
Fight fought fought Lutar Shine Shone shone Brilhar
Find Found found Encontrar Shoot Shot shot Disparar
Fly Flew flown Voar Show showed showed Mostrar/ exibir
Forget forgot forgotten Esquecer Shut Shut shut Feixar
Get Got got Obter Sing Sang sung Cantar
Go Went gone Ir Sit Sat sat Sentar
Grow Grew grown Crescer Sleep Slept slept Dormir
Give Gave given Dar Smell Smelt smelt Cheirar
Hang Hung hung Pendurar Speak Spoke spoken Falar
Have Had had Ter Spend Spent spent Gastar
Hear Heard heard Ouvir Spell Spelt spelt Soletrar
Hide Hid hidden Esconder Spread Spread spread Espalhar
Hit Hit hit Bater Stand Stood stood Estar de pé
Hold Held held Abraçar Steal Stole stolen Roubar
Hurt Hurt hurt Magoar Swim Swam swum Nadar
Keep Kept kept Guardar Take Took taken Levar
Know Knew known Saber/conhecer teach Taught taught Ensinar
Leave Left left Partir Tear Tore torn Rasgar
Lend Lent lent Emprestar Tell Told told Dizer
Bleed Bled bled Think thought thought Pensar
Learn Learnt learnt apreender Throw Threw thrown Lançar
Slide Slid slid escorregar understand understood understood Entender
Stick Stuck stuck Colar/pregar Wake Woke woken Acordar
Stay stayed stayed Ficar Wear Wore worn Vestir
Let Let let Deixar Win Won won Ganhar
Lie Lay lain Deitar-se Write Wrote written Escrever
Author: Francisco Tangawisse Versão 0.0
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- How to conjugate any English verbDocument1 paginăHow to conjugate any English verbMarisa Amancio100% (4)
- Present Simple: Affirmative InterrogativeDocument2 paginiPresent Simple: Affirmative Interrogativemonica meloÎncă nu există evaluări
- TeachingDocument1 paginăTeachingMirela ChirvăsuțăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Continuous Tense GuideDocument1 paginăPresent Continuous Tense GuideGaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tablas de Conjugación Del Verbo Inglés Play - JugarDocument4 paginiTablas de Conjugación Del Verbo Inglés Play - JugarIvannaRuthMinarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Going To and Present Progressive As FutureDocument2 paginiBe Going To and Present Progressive As FutureJanetteÎncă nu există evaluări
- PinkDocument6 paginiPinkmhanae022Încă nu există evaluări
- SubjectDocument28 paginiSubjectVir BermejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster Present TenseDocument1 paginăPoster Present TenseKatarina Vukičević VeljačaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present, Past and Future - Simple, Continuous and Perfect Verb Tenses PDFDocument1 paginăPresent, Past and Future - Simple, Continuous and Perfect Verb Tenses PDFGlobal Village EnglishÎncă nu există evaluări
- TENSES ChartDocument7 paginiTENSES ChartKostas ValaroutsosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb Tenses PrintableDocument1 paginăVerb Tenses Printablewww.getenglishlessons.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yesterday, Ago, Last Week, in 2009 .Document1 paginăYesterday, Ago, Last Week, in 2009 .Elizabeta KosteskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past ContinuousDocument3 paginiPast ContinuousLida Saavedra PalaciosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material de Soporte Curso de Ingles Basico 2012Document44 paginiMaterial de Soporte Curso de Ingles Basico 2012Yennire SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb Tenses Verb Tenses: Fco Fco. Javier Pérez Vázquez - Javier Pérez VázquezDocument17 paginiVerb Tenses Verb Tenses: Fco Fco. Javier Pérez Vázquez - Javier Pérez VázquezJavier PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The English Tenses: S ED Will ShallDocument9 paginiThe English Tenses: S ED Will ShallAnonymous wIlqpnk7BwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conjugarea Verbelor La Diferite TimpuriDocument5 paginiConjugarea Verbelor La Diferite TimpuriChiosa AdinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab - La Conjugation Englez To - PlayDocument2 paginiBab - La Conjugation Englez To - PlayMirela TomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6: Affirmative NegativeDocument5 paginiUnit 6: Affirmative NegativegmbÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 TensesDocument3 pagini4 TensesZenki-KunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present ContinuousDocument1 paginăPresent ContinuousAlejandra MoraleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument1 paginăPresent Simple Affirmative Negative InterrogativeLiliana NederitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tableau ConjugaisonDocument2 paginiTableau Conjugaisonsimonroux24100Încă nu există evaluări
- Grammaire AnglaiseDocument48 paginiGrammaire AnglaiseMbemba Doumbouya100% (2)
- Present Continuous Tense: Aff.S+To Be+ V1-Ing Neg .S+To Be-Not+ V1-Ing Int. To Be-+s+ V1-Ing?Document3 paginiPresent Continuous Tense: Aff.S+To Be+ V1-Ing Neg .S+To Be-Not+ V1-Ing Int. To Be-+s+ V1-Ing?Clipea Crina StefaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affirmative Interrogative Negative: Present SimpleDocument8 paginiAffirmative Interrogative Negative: Present Simplemit999666Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 - Simple Future S. OulaîchDocument5 paginiLesson 1 - Simple Future S. Oulaîchsabri ugloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activida ° 7 InglesDocument7 paginiActivida ° 7 InglesKercy APÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Simple Present TenseDocument9 paginiGrammar Simple Present TenseIngrid AranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Verb TensesDocument12 paginiContinuous Verb Tensesida rohmaningsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gram MaireDocument19 paginiGram MaireSiham El aouitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present ContinousDocument2 paginiPresent ContinousNurrul LayllaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sesion 4 Present Simple ResumenDocument1 paginăSesion 4 Present Simple ResumenPrins Nuria QuispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- INGLÊS VerbsDocument3 paginiINGLÊS Verbsmartagsf1065Încă nu există evaluări
- INGLÊS VerbsDocument3 paginiINGLÊS Verbsmartagsf1065100% (1)
- Pastsimple PDFDocument2 paginiPastsimple PDFyepes6bÎncă nu există evaluări
- VERBAL TENSES Nuri PDFDocument5 paginiVERBAL TENSES Nuri PDFNereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Continuous_8650f99216df1ae99ea23f8f91f6f1beDocument1 paginăPast Continuous_8650f99216df1ae99ea23f8f91f6f1bemicaelabroithinotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple: Am Not Am Are Are Is Is Don't Do PlayDocument1 paginăPresent Simple: Am Not Am Are Are Is Is Don't Do PlayCarmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument3 paginiAffirmative Negative InterrogativenerepeichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple RulesDocument2 paginiPresent Simple RulesVėželytė-VilkevičienėJuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VerbosDocument4 paginiVerbosAlexandra CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple: Typical Signal WordsDocument3 paginiPresent Simple: Typical Signal WordsAnonymous odpot7KVz0Încă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple PresentationDocument13 paginiPresent Simple PresentationClaudia BalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple - Regular VerbsDocument1 paginăPast Simple - Regular Verbsyepes6bÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Present Simple TenseDocument6 paginiThe Present Simple TenseAdrien NkurikiyumukizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Tense VerbsDocument8 paginiPresent Tense VerbsDELIA GHIȚUNÎncă nu există evaluări
- English - The Present Continuous TenseDocument16 paginiEnglish - The Present Continuous TenseClass100% (12)
- The simple present tense guideDocument2 paginiThe simple present tense guideMaria Monica Murillo RinconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present SimpleDocument8 paginiPresent SimpleSARAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple: Use When WeDocument4 paginiPresent Simple: Use When WeHannaSchool ChaykaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Present Continuous Tense: at The Moment I'm Playing FootballDocument16 paginiThe Present Continuous Tense: at The Moment I'm Playing FootballAndi MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRESENT TENSESDocument27 paginiPRESENT TENSESsloren__Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity 4 OkDocument1 paginăActivity 4 OkVandian Rocha sorrosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb tenses chart in EnglishDocument1 paginăVerb tenses chart in EnglishRaneirosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple and Irregular Verbs LessonDocument9 paginiPast Simple and Irregular Verbs LessonCarito Neyen BelmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conjugaciones Inglés Verbo To PlayDocument8 paginiConjugaciones Inglés Verbo To Playlei TyhÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideDe la EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 SampleRecommendationDocument1 pagină2021 SampleRecommendationMontacer Billah ZemmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- MozambiqueDocument25 paginiMozambiqueDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Scarcity and Climate ChangeDocument60 paginiWater Scarcity and Climate ChangejarameliÎncă nu există evaluări
- DramaDocument53 paginiDramaAbhay Vohra100% (7)
- Tuto Remedio 1Document1 paginăTuto Remedio 1Delfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- MozambiqueDocument25 paginiMozambiqueDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- MozambiqueDocument25 paginiMozambiqueDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inglish CV DBV PDFDocument3 paginiInglish CV DBV PDFDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CISS - Shelter Assistant Job Description - 7 1 14 PDFDocument2 paginiCISS - Shelter Assistant Job Description - 7 1 14 PDFDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- KEY ACCOUNT MANAGER Mozambique - Job Spec To Candidates June 2020 PDFDocument4 paginiKEY ACCOUNT MANAGER Mozambique - Job Spec To Candidates June 2020 PDFDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIRSWIFT. ArturDocument5 paginiAIRSWIFT. ArturDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIRSWIFT. ArturDocument5 paginiAIRSWIFT. ArturDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 SyntaxDocument14 pagini06 SyntaxFatiFlureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consultancy Services For Construction Supervision of The Green Urban Infrastructure in Beira Project - (Gui) RFP N: 01/Wb/Kfw/Pcmc/Aias/2017Document9 paginiConsultancy Services For Construction Supervision of The Green Urban Infrastructure in Beira Project - (Gui) RFP N: 01/Wb/Kfw/Pcmc/Aias/2017Delfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quant. Uni. 1 Area de Limpeza (Marcacao Da Obra)Document4 paginiQuant. Uni. 1 Area de Limpeza (Marcacao Da Obra)Delfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 PDFDocument1 paginăA2 PDFDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- MelhoraDocument1 paginăMelhoraDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICCR (Indian Council For Cultural Relations) : Getting Started GuideDocument17 paginiICCR (Indian Council For Cultural Relations) : Getting Started GuideSesarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curricum Vitae: Work ExperienceDocument2 paginiCurricum Vitae: Work ExperienceDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation LetterDocument1 paginăPresentation LetterDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- DFGHNMDocument6 paginiDFGHNMDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cement Blocks and CGI Roof Rural Building EstimateDocument8 paginiCement Blocks and CGI Roof Rural Building EstimateDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vigas Gerber - Ezquerro, Ana (1045530)Document6 paginiVigas Gerber - Ezquerro, Ana (1045530)Delfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 PDFDocument1 paginăA2 PDFDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoCAD Migration LogDocument3 paginiAutoCAD Migration LogDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ground Floor 1:100Document1 paginăGround Floor 1:100Delfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intituto Beira IndicoDocument1 paginăIntituto Beira IndicoDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoCAD Migration LogDocument3 paginiAutoCAD Migration LogDelfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vigas Gerber - Ezquerro, Ana (1045530)Document6 paginiVigas Gerber - Ezquerro, Ana (1045530)Delfino Bernardo ViegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- T096 - Past Simple or Present Perfect TenseDocument1 paginăT096 - Past Simple or Present Perfect TenseAmelia JugurtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb Tenses Review: TimelineDocument9 paginiVerb Tenses Review: Timelinebatog mariusÎncă nu există evaluări
- English II - UCF 1103 Group Name - Pen Pals Verb Tense: ActivityDocument13 paginiEnglish II - UCF 1103 Group Name - Pen Pals Verb Tense: ActivityHania SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Passive VoiceDocument5 paginiUnderstanding Passive VoicepjNFS 1318Încă nu există evaluări
- Língua Inglesa: Reported SpeechDocument3 paginiLíngua Inglesa: Reported SpeechPatrick AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Voice: Pasos para Pasar de Activa A PasivaDocument3 paginiPassive Voice: Pasos para Pasar de Activa A PasivaEliezer Bueno MartínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Tense - Google SearchDocument1 paginăPresent Tense - Google SearchEnis SopaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses PDFDocument2 paginiTenses PDFSahar Aktham RashedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bahan Ajar English Club SMAN 1 BatujayaDocument30 paginiBahan Ajar English Club SMAN 1 BatujayaPutri AmaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Before E: Hablar Comer VivirDocument12 paginiC Before E: Hablar Comer Vivircbales1984Încă nu există evaluări
- TenseDocument18 paginiTenseRenu JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Most Common French Verbs - FrenchLearnerDocument30 pagini100 Most Common French Verbs - FrenchLearnerAnıl ÇetintoprakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument30 paginiTiempos VerbalesjhadhsgasdasdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses in Nursing Conversation: Ns. Intan Asri NuraniDocument18 paginiTenses in Nursing Conversation: Ns. Intan Asri NuraniNabila Ayu HafifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 SAP 09 KeslingDocument2 pagini4 SAP 09 KeslingJang Ki YongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tense Signal Words Use: Something Things in GDocument5 paginiTense Signal Words Use: Something Things in GEdén Verde Educación Con SaludÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Verb Tenses: Present, Past and FutureDocument18 paginiIntroduction to Verb Tenses: Present, Past and FutureLuciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 1: 1. Adilian Nur Oktasari 2. Lidya Joanda PutriDocument15 paginiGroup 1: 1. Adilian Nur Oktasari 2. Lidya Joanda PutriMuharam sanitarianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect, Past Perfect, Future PerfectDocument21 paginiPresent Perfect, Past Perfect, Future PerfectFISK PROFESSORESÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 Contoh Soal Tenses Beserta JawabannyaDocument22 pagini50 Contoh Soal Tenses Beserta JawabannyaEQ HaryonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Tale of The Two BrothersDocument2 paginiThe Tale of The Two Brothersharvey barrientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Signal of TensesDocument3 paginiTime Signal of TensesAgni Ganesha Al-Karawi100% (1)
- FE AssignmentDocument5 paginiFE AssignmentAce TierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cutting Edge Intermediate Students Book With DVD and MyEnglishLab Pack by Peter Moor, Jonathan Bygrave, Araminta Crace, Sarah Cunningham (Z-Lib - Org) (INGLES3) - RemovedDocument2 paginiCutting Edge Intermediate Students Book With DVD and MyEnglishLab Pack by Peter Moor, Jonathan Bygrave, Araminta Crace, Sarah Cunningham (Z-Lib - Org) (INGLES3) - RemovedLilibeth HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Soal Kalimat Passive (Awpy) - WPS OfficeDocument5 pagini10 Soal Kalimat Passive (Awpy) - WPS OfficeD3TEAgni Wulandara Panggulu YudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4 Category 5 Category 6Document1 paginăCategory 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4 Category 5 Category 6Alandahen AliveiÎncă nu există evaluări
- El Preterito vs. El Imperfecto 2.3Document12 paginiEl Preterito vs. El Imperfecto 2.3Ruth RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas MR YadiDocument3 paginiTugas MR YadiDwi Retno Anom SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contoh Soal Bahasa Inggris Dan JawabanDocument6 paginiContoh Soal Bahasa Inggris Dan JawabanShintaWijaya100% (2)
- Present and Past Perfect TenseDocument12 paginiPresent and Past Perfect TenseBenedictus PrabandanuÎncă nu există evaluări