Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Go 3
Încărcat de
adlinTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Go 3
Încărcat de
adlinDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
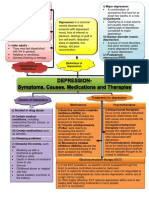
In younger children :
i) Major depression
Sadness
A combination of
Irritability
symptoms that last for at
Hopelessness
least two weeks in a row.
Worry
ii) Dysthymia
Depression is a common Dysthymia is a less severe
In adolescents and teens : mental disorder that but usually more long
Anxiety presents with depressed
lasting type of depression
Anger compared to major
mood, loss of interest or depression.
Avoidance of social
pleasure, feelings of guilt or iii) Bipolar disorder (manic
interaction
low self-worth, disturbed depression)
sleep or appetite, low A group of mood disorders
In older adults : energy, and poor that were formerly called
They may feel dissatisfied concentration. manic-depressive illness
with life in general. or manic depression.
Helpless or worthless. iv) Postpartum
Suicidal thinking or feelings. depression(PPD)
Definition of
Symptoms of depression Types of
depression depression
Treatments for depression
Causes of Depression
Medications Psychotherapies
i) Alcohol or drug abuse i) Selective serotonin reuptake i) Interpersonal therapists
inhibitors (SSRIs) are focus on the patient's disturbed
ii) Certain medical medications that increase the personal relationships that
conditions, including amount of the neurochemical both cause and exacerbate the
underactive thyroid, cancer, or serotonin in the brain. depression.
long-term pain. ii) Tricyclic antidepressants ii) Cognitive/behavioral
(TCAs) work mainly by therapists help patients
iii) Certain medications such increasing the level of change the negative styles of
as steroids. norepinephrine in the brain thinking and behaving that are
synapses, although they also often associated with
iv) Sleeping problems
may affect serotonin levels. depression.
v) Stressful life events, such iii) Monoamine oxidase iii) Psychodynamic therapies
as: inhibitors (MAOIs) elevate the focus on resolving the patient's
levels of neurochemicals in the internal psychological conflicts
Breaking up with a
brain synapses by inhibiting that are typically thought to be
boyfriend or girlfriend
monoamine oxidase. rooted in childhood.
Failing a class
Death or illness of someone Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
close to you
Divorce i) In the ECT procedure, an electric current is passed through the
Childhood abuse or neglect brain to produce controlled convulsions (seizures).
Job loss ii) ECT is useful for those who cannot take or have not responded to
Social isolation (common in a number of antidepressants, have severe depression, and/or are at
the elderly) a high risk for suicide.
iii) Often highly effective, ECT relieves depression within one to two
weeks after beginning treatments in many people.
iv) ECT is not painful.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Combination of Symptoms That Last For at Least Two Weeks in A RowDocument1 paginăA Combination of Symptoms That Last For at Least Two Weeks in A RowadlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cornell Notes Sheet: 1.) What Is Mental Health?Document4 paginiCornell Notes Sheet: 1.) What Is Mental Health?Aleena Mariya SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPCC 133 Guruignou Block-2Document100 paginiBPCC 133 Guruignou Block-2Pulkit HoodaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moood DisorderDocument34 paginiMoood DisorderSraboni BrahmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Go 1Document1 paginăGo 1adlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood Disorders: Presentation By: Jessie NilsonDocument26 paginiMood Disorders: Presentation By: Jessie Nilsonvsvsuresh2099Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document9 paginiChapter 5Ellyza EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- dEPRESSION MEDICAL IN PACIENTSDocument4 paginidEPRESSION MEDICAL IN PACIENTSgjavierperezÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Psychology Module 66+67Document5 paginiAP Psychology Module 66+67kyuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood DisordersDocument25 paginiMood DisordersRence IremedioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood Disorders: A Closer Look at Psychological DisordersDocument25 paginiMood Disorders: A Closer Look at Psychological DisordersManoj Bala100% (1)
- PerDev ReviewerDocument6 paginiPerDev ReviewerChristian CalauadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infografía de La DepresiónDocument1 paginăInfografía de La DepresiónAndreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sychology Actsheets: DepressionDocument4 paginiSychology Actsheets: DepressionLachlan ScholesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood Disorders: Hyacinth C. Manood MD, FPPA - September 2018 - Topic 3Document4 paginiMood Disorders: Hyacinth C. Manood MD, FPPA - September 2018 - Topic 3Justin TayabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEALTH TALK Care of Depression PatientDocument17 paginiHEALTH TALK Care of Depression PatientAmit RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood Disorders (Bautista)Document7 paginiMood Disorders (Bautista)Aljon S. Templo100% (1)
- PSYCHIATRYDocument12 paginiPSYCHIATRYSavanthi Carmaline de SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 3 Mood Disorders RV Rushed 2018Document28 paginiDay 3 Mood Disorders RV Rushed 2018api-433532127Încă nu există evaluări
- Mental HealthDocument8 paginiMental HealthAida SyasyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychia Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 paginiPsychia Multiple Choice QuestionsGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Neurosis and PsychosisDocument4 paginiDifference Between Neurosis and PsychosisShaheen Khan Warsi100% (1)
- Part 3 - Mental Illness - Psychological Health and WellbeingDocument24 paginiPart 3 - Mental Illness - Psychological Health and Wellbeingapi-642709499Încă nu există evaluări
- Block 3Document56 paginiBlock 3aakash atteguppeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Disorder HandoutDocument3 paginiBipolar Disorder Handoutapi-548175940Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Mood DisordersDocument7 pagini1.3 Mood DisordersDomalaon, Princess Sophia B.Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychology Chapter SevenDocument25 paginiPsychology Chapter Sevenmelaku zegeyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depressive DisorderDocument59 paginiDepressive DisorderJoshua RingorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-01 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination Appendix CIC v1Document5 pagini1-01 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination Appendix CIC v1Dane Mikhael CalicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Depression and Mechanisms of TreatmentDocument15 paginiPathophysiology of Depression and Mechanisms of TreatmentWanda HamidahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood DisordersDocument11 paginiMood DisordersPrincessXFaithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiological DisordersDocument38 paginiPhysiological Disordersreview notesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educational Brochure (Abnormal Psychology)Document7 paginiEducational Brochure (Abnormal Psychology)Leonardo YsaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Five or More of These Symptoms:: Bipolar Disorders - Depressive EpisodeDocument2 paginiFive or More of These Symptoms:: Bipolar Disorders - Depressive EpisodeCake ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-03 Management of Anxiety Disorders CIC v1Document5 pagini3-03 Management of Anxiety Disorders CIC v1Dane Mikhael CalicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farmakoterapi Sistem Organ II-DepresiDocument73 paginiFarmakoterapi Sistem Organ II-DepresiDISKA YUNIAROHIMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pshciatry in BriefDocument18 paginiPshciatry in BriefSelim TarekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health High School Curriculum Guide Teacher Knowledge UpdateDocument25 paginiMental Health High School Curriculum Guide Teacher Knowledge Updateapi-356243627Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Mood and Anxiety DisordersDocument14 paginiChapter 3 Mood and Anxiety DisordersDessirie EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry ' Psychiatry ' Section Iii: Psychiatry-Pathology Psychiatry-PathologyDocument20 paginiPsychiatry ' Psychiatry ' Section Iii: Psychiatry-Pathology Psychiatry-PathologyLuis Jose VelazquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- State of The Art: Pathophysiology of Depression and Mechanisms of TreatmentDocument14 paginiState of The Art: Pathophysiology of Depression and Mechanisms of TreatmentChindy AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Disorder: Cretoiu StefanDocument8 paginiMental Disorder: Cretoiu StefanStefanCretoiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood DisordersDocument78 paginiMood Disorderspawan_sharma_55Încă nu există evaluări
- Anxiety Mood Disorders Book NotesDocument1 paginăAnxiety Mood Disorders Book Notesapi-263456844Încă nu există evaluări
- Ab PsychDocument20 paginiAb PsychDDJÎncă nu există evaluări
- GERIATRICS (2nd Sem - ENDTERM NOTES)Document12 paginiGERIATRICS (2nd Sem - ENDTERM NOTES)Meryville JacildoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 5Document5 paginiNCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 5Meryville JacildoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric NursingDocument32 paginiPsychiatric NursingPinky Cuaresma100% (1)
- Mental Health Team 5Document2 paginiMental Health Team 5Antonio Ángeles RoqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood DisordersDocument108 paginiMood DisordersAngellene Firmalino50% (2)
- Neouropsychiatric AssessmentDocument21 paginiNeouropsychiatric AssessmentKopano'Gucci'ModisenyaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschfeld 1994Document8 paginiHirschfeld 1994Dea AnindyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Chapter 7Document8 paginiAbnormal Chapter 7Will BendijoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 8Document6 paginiTask 8Yolan MutiaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DepressionDocument50 paginiDepressionmaha abdallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood DisorderDocument6 paginiMood DisorderDENNROSE DECLAROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood Disorder: - With History of Depression Without Any History of ElationDocument3 paginiMood Disorder: - With History of Depression Without Any History of ElationRyan Gabriel Omengan ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Terms - PsychDocument13 paginiSummary of Terms - Psychapi-642709499Încă nu există evaluări
- Leave the Darkness: Identifying and Managing DepressionDe la EverandLeave the Darkness: Identifying and Managing DepressionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy:: Using CBT to Battle Anxiety, Depression, and Intrusive ThoughtsDe la EverandCognitive Behavioral Therapy:: Using CBT to Battle Anxiety, Depression, and Intrusive ThoughtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- EHV AssignmentDocument2 paginiEHV AssignmentAVINAV GUPTA IPM 2017-22 BatchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brit J of Edu Psychol - 2021 - Snijders - Relationship Quality in Higher Education and The Interplay With StudentDocument22 paginiBrit J of Edu Psychol - 2021 - Snijders - Relationship Quality in Higher Education and The Interplay With Studentcharbel_945Încă nu există evaluări
- Ebook Flowstate PDFDocument16 paginiEbook Flowstate PDFJosh CooperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentiated Planning and Learning For Upper Primary Units 1 3Document134 paginiDifferentiated Planning and Learning For Upper Primary Units 1 3Gabriel MashoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedagogy Module 601 Instructaional Materia Draft Nov. 11, 2016Document151 paginiPedagogy Module 601 Instructaional Materia Draft Nov. 11, 2016Gizachew100% (1)
- Shadow Work Journal PDFDocument80 paginiShadow Work Journal PDFNatalia Gębuś100% (4)
- Walter N. Stone & Roy M. Whitman (1977) Contributions of The Psychology of Process and Group TherapyDocument18 paginiWalter N. Stone & Roy M. Whitman (1977) Contributions of The Psychology of Process and Group TherapyMarta Gil MegíasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument50 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonJaneth Miguel Satrain100% (2)
- Timothy Wlan,: American AnthropologistDocument1 paginăTimothy Wlan,: American Anthropologistmiksi7906Încă nu există evaluări
- 3685 Enmeshed FamiliesDocument11 pagini3685 Enmeshed FamiliesRobert E. WaltonÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeadershipDocument8 paginiLeadershipehm-ar. SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Relationship Between Organizational Trust and Job Satisfaction: An Analysis in The U.S. Federal Work ForceDocument56 paginiThe Relationship Between Organizational Trust and Job Satisfaction: An Analysis in The U.S. Federal Work ForceUniversal-Publishers, Inc.100% (30)
- Worksheet UTSDocument2 paginiWorksheet UTSCheryn VillalonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teori Piaget On PowerpointDocument19 paginiTeori Piaget On PowerpointUthaya Kumar GovindarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organisational ChartDocument2 paginiOrganisational Chartapi-366102737Încă nu există evaluări
- TFN MidtermDocument7 paginiTFN MidtermDimple Lexiry GloriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. A. Akom, Critical Hip Hop PedagogyDocument7 paginiA. A. Akom, Critical Hip Hop PedagogyMilaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lam 2007Document17 paginiLam 2007Michael Joseph DinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polychronic TimeDocument3 paginiPolychronic TimeMegha gohareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enhanced Intervention PosterDocument1 paginăEnhanced Intervention PosterInclusionNorthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2 Module 3Document9 paginiPractical Research 2 Module 3Ericka Marie AlmadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Development: InstructionsDocument6 paginiPersonal Development: InstructionsKinect Nueva EcijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult Learner InterviewDocument5 paginiAdult Learner Interviewapi-279420767Încă nu există evaluări
- An Insiders Guide To Sub-Modalities - Richard BandlerDocument127 paginiAn Insiders Guide To Sub-Modalities - Richard Bandlerjacobpalmer100% (15)
- Unit - 1 Introduction To CommunicationDocument7 paginiUnit - 1 Introduction To CommunicationKriti Dhingra100% (1)
- Integrative Managerial IssuesDocument31 paginiIntegrative Managerial IssuesЗорана МанићÎncă nu există evaluări
- Servant Leadership PDFDocument2 paginiServant Leadership PDFAnonymous bJVS7dÎncă nu există evaluări
- COT Lesson Plan in Health 8Document3 paginiCOT Lesson Plan in Health 8Erwin de Villa80% (5)
- LightHouseLogiThink2 Eng 0601Document17 paginiLightHouseLogiThink2 Eng 0601api-3771376Încă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Introduction To LacanDocument160 paginiClinical Introduction To Lacannallgire100% (1)