Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Thermodynamics Formula Sheet
Încărcat de
poly WannaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Thermodynamics Formula Sheet
Încărcat de
poly WannaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
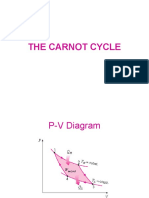
Carnot Cycle Reciprocating Engines
Compression ratio:
Mean effective pressure:
Power:
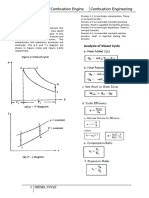
Diesel Cycle 1-2 Isentropic compression
2-3 constant-pressure heat addition
3-4 Isentropic expansion
1-2 Isentropic compression 4-1 Constant-volume heat rejection
Otto Cycle
2-3 Constant-volume heat addition
3-4 Isentropic expansion
4-1 Constant-volume heat rejection Cutoff ratio:
Compression efficiency Expansion efficiency
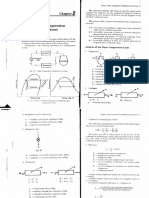
Ericsson Cycle
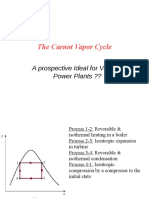
Process 1-2: Reversible isothermal compression.
Process 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition.
Process 3-4: Reversible isothermal expansion.
Process 4-1: Constant pressure heat rejection.
P2=P3, P1=P4, 𝜂𝑆𝑡𝑖𝑟𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑔 = 1 − 𝑇𝑇𝐿
𝐻
Stirling Cycle
1-2 isothermal expansion heat addition
2-3 const. vol. heat removal
3-4 isothermal compression
4-1 const. vol. heat addition
Brayton Cycle 1-2 Isentropic compression (in a compressor)
2-3 Constant-pressure heat addition
3-4 Isentropic expansion (in a turbine)
4-1 Constant-pressure heat rejection
Specific Heats:
Regeneration
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Thermodynamics Formula SheetDocument1 paginăThermodynamics Formula SheetDaniel Ortega100% (3)
- Assignment No. 4 (Problems - Ch. 2) :: Solve The Following ProblemsDocument3 paginiAssignment No. 4 (Problems - Ch. 2) :: Solve The Following ProblemsMohNajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- T 4Document2 paginiT 4Stone WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE21L Experiment 8Document12 paginiEE21L Experiment 8Jian TumaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMT2-hw1 - SolDocument5 paginiEMT2-hw1 - SolSuper Special100% (1)
- Parallel Line Method PDFDocument80 paginiParallel Line Method PDFalbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diode Applications: Chapter ObjectivesDocument23 paginiDiode Applications: Chapter ObjectivesFranco Faza ZamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution:: KVA IpDocument3 paginiSolution:: KVA IpNoor Mohammed100% (1)
- Chemistry in EE Board Exam 1Document2 paginiChemistry in EE Board Exam 1Master Jaguar100% (1)
- Variable Stresses With Stress ConcentrationsDocument16 paginiVariable Stresses With Stress ConcentrationsBryan GounzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric MachineDocument26 paginiElectric MachinealexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical CyclesDocument49 paginiTheoretical CyclesMariaEzzaSyUyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer On Load PDFDocument14 paginiTransformer On Load PDFSnr Berel ShepherdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Powerplant Design Reheat-Regenerative CycleDocument10 paginiSteam Powerplant Design Reheat-Regenerative CycleRouen Jay CorpuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circ 4Document66 paginiCirc 4musa100% (5)
- FormulasDocument7 paginiFormulastthy kÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Carnot CycleDocument9 paginiThe Carnot CyclePatrick Antonio Orge ChingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDocument62 paginiZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions ManualDocument32 paginiEngineering Thermodynamics Solutions ManualMahesh NadarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 5: Heat Engine CyclesDocument36 paginiSection 5: Heat Engine CyclesSams ArefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapor Compression Cycle: Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning by Wilbert F. Stoecker / Jerold W. Jones (Chapter 10)Document16 paginiVapor Compression Cycle: Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning by Wilbert F. Stoecker / Jerold W. Jones (Chapter 10)nauman khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Trick To Remember All Thermodynamic Cycles For Oral ExamsDocument11 paginiImportant Trick To Remember All Thermodynamic Cycles For Oral ExamsParikshit Ugale50% (2)
- Stirling, Ericsson, Atkinson, LenoirDocument32 paginiStirling, Ericsson, Atkinson, LenoirBaranidharan GopiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 - Vapor Compression and Air, Refrigeration CyclesDocument77 paginiTopic 2 - Vapor Compression and Air, Refrigeration CyclesOk SokÎncă nu există evaluări
- MICE I - Topic 1.1.3Document6 paginiMICE I - Topic 1.1.3SivabalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Turbine BasicsDocument25 paginiGas Turbine Basicsdnageshm4n244Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 2. IC - Engine Lecture pdf-1Document58 paginiCH 2. IC - Engine Lecture pdf-1tefe yabatuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamic Cycles For CI Engines: Fuel Injection Starts Fuel Injection StartsDocument5 paginiThermodynamic Cycles For CI Engines: Fuel Injection Starts Fuel Injection StartsCrissa Ann EqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIT - ME336 - 4 - Dual CycleDocument19 paginiCIT - ME336 - 4 - Dual CycleVinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session II VCRSDocument19 paginiSession II VCRSSiddharth PanigrahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Gas TurbinesDocument6 paginiIntroduction To Gas TurbinesHasib IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- GasCycles 2Document10 paginiGasCycles 2BirkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument26 paginiInternal Combustion EngineKhate ÜüÎncă nu există evaluări
- IC EnginesDocument21 paginiIC EnginesChathura KallegodaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Lecture (Carnot and Ideal Rankine Cycle)Document9 pagini2 Lecture (Carnot and Ideal Rankine Cycle)Ali Haider RizviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brayton CycleDocument6 paginiBrayton CycleNavnina Bhatia100% (1)
- 02 Internal Combustion Engine LectureDocument60 pagini02 Internal Combustion Engine LectureLozada JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cycles ReviewerDocument6 paginiCycles ReviewerReinzo GallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elimination of Impracticalities of Carnot CycleDocument16 paginiElimination of Impracticalities of Carnot CycleCalvin GadiweÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4air Refrigeration SystemDocument4 pagini4air Refrigeration Systemtodankarpratham15Încă nu există evaluări
- General Equation For TberkodyDocument98 paginiGeneral Equation For TberkodyEj SalmorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Power Cycle - Internal Combustion EngineDocument5 paginiGas Power Cycle - Internal Combustion EngineHashem Mohamed HashemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sesión 3 Análisis Ciclo Brayton - 2021 - 02Document26 paginiSesión 3 Análisis Ciclo Brayton - 2021 - 0247 RoninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combustion Engine Processes IntroDocument12 paginiCombustion Engine Processes IntroMark Danielle BahintingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Gas TurbineDocument7 paginiChapter 4 - Gas TurbineJay Mark CayonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diesel CycleDocument2 paginiDiesel CycleElison Dave NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamic CyclesDocument14 paginiThermodynamic CyclesBubai111Încă nu există evaluări
- Brayton Cycle Revisi Review PDFDocument23 paginiBrayton Cycle Revisi Review PDFKelly AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GASBRAYTONDocument16 paginiGASBRAYTONJohnCris B. FornilosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Engine Cycles Spring 2024Document50 pagini04 Engine Cycles Spring 2024sajjadf954Încă nu există evaluări
- 5-Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysisDocument28 pagini5-Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysisYashwanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-6 - Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysisDocument40 pagini5-6 - Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysissarvasvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument55 paginiVapor Compression Refrigeration CycleCh. Muhammad UsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 Lecture 3Document29 paginiWeek 7 Lecture 3jimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- TE 1 Notes PDFDocument196 paginiTE 1 Notes PDFfatigue puttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration Chapter 2Document24 paginiRefrigeration Chapter 2predmarkjÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Air Standard Dual Combustion Cycle: (Ideal Cycle For Most IC Engines)Document31 paginiThe Air Standard Dual Combustion Cycle: (Ideal Cycle For Most IC Engines)jchummunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Power CyclesDocument17 paginiGas Power Cycleskimosave99Încă nu există evaluări
- Diesel Power PlantDocument23 paginiDiesel Power PlantMa. Mikhaela ApuradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Machines: Mechanical PE Thermal & Fluids Systems Exam Prep CourseDocument35 paginiHydraulic Machines: Mechanical PE Thermal & Fluids Systems Exam Prep Coursepoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe Mechanical Thermal & Fluids Systems Prep Course HomeworkDocument1 paginăPe Mechanical Thermal & Fluids Systems Prep Course Homeworkpoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo Cheat SheetDocument1 paginăThermo Cheat Sheetpoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics: MTX 220 DefinitionsDocument8 paginiThermodynamics: MTX 220 Definitionspoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo Cheat SheetDocument1 paginăThermo Cheat Sheetpoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamic FormulasDocument17 paginiThermodynamic Formulasdaniebenade86% (28)
- Thermodynamics 1Document84 paginiThermodynamics 1Nick Decillo90% (145)
- Mer331 Fluid Mechanics Final Exam Equation Sheet: Some Mass Moments of InertiaDocument4 paginiMer331 Fluid Mechanics Final Exam Equation Sheet: Some Mass Moments of Inertiapoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressible Flow: Mechanical PE Thermal & Fluids Systems Exam Prep CourseDocument27 paginiCompressible Flow: Mechanical PE Thermal & Fluids Systems Exam Prep Coursepoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExamineeGuide May 2019Document36 paginiExamineeGuide May 2019Hemanth UsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Laws Ws PDFDocument6 paginiGas Laws Ws PDFJulia Franchesca BorromeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PoliticsDocument1 paginăPoliticspoly WannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- QSK60 G6Document2 paginiQSK60 G6Jhan Carlos HuamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation On The Heat Transfer Correlations and Simulation Verification For Typical LNG Open Rack VaporizerDocument6 paginiCalculation On The Heat Transfer Correlations and Simulation Verification For Typical LNG Open Rack VaporizerabdoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DokwegII - Auxiliary - Maintenance Oil SystemDocument51 paginiDokwegII - Auxiliary - Maintenance Oil SystemCarlin BabuchasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fig. 900 Fig. 940: Safety ValveDocument36 paginiFig. 900 Fig. 940: Safety ValveJesús Santiago QuijadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studies On GS Road Pavement Structures PDFDocument12 paginiStudies On GS Road Pavement Structures PDFVgkBharadwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Fluids in MotionDocument3 paginiIntroduction To Fluids in MotionEditor IJRITCCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vicat Test: Report1Document5 paginiVicat Test: Report1Khalid MohammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asiatech Development & Builders (Adb) Corporation: Concrete Pouring ChecklistDocument1 paginăAsiatech Development & Builders (Adb) Corporation: Concrete Pouring ChecklistGenevieve GayosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Mist PresentationDocument26 paginiWater Mist PresentationAmar BayasgalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RR320306 HeattransferDocument8 paginiRR320306 HeattransferAnil Frivolous AbstemiousÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Experimental Study On The Effect of MIG Welding Parameters On The Weld-Bead Shape CharacteristicsDocument5 paginiAn Experimental Study On The Effect of MIG Welding Parameters On The Weld-Bead Shape Characteristicstejap314Încă nu există evaluări
- Convected Co OrdinatesDocument1 paginăConvected Co Ordinatesrd_mechÎncă nu există evaluări
- CARRARO Axle Repair Ca130070Document104 paginiCARRARO Axle Repair Ca130070Sunthron Somchai100% (3)
- PHD Thesis Optimization of Bow Shape For Large, Slow Ships by NordåsDocument84 paginiPHD Thesis Optimization of Bow Shape For Large, Slow Ships by NordåsPrasad PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- JC Gasket CranfoilDocument2 paginiJC Gasket CranfoilMachineryengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series 4300 Vertical In-Line: SubmittalDocument2 paginiSeries 4300 Vertical In-Line: SubmittalBrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lemken Spare Parts Catalogue enDocument116 paginiLemken Spare Parts Catalogue enVlad Ptashnichenko100% (2)
- Manufacturing Process DiagramDocument3 paginiManufacturing Process DiagramCris Diane G. DatingginooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1400SRM0046 (06 2017) Uk en PDFDocument46 pagini1400SRM0046 (06 2017) Uk en PDFCosmin GîrleanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC100 Training Manual Ver 2 0 PDFDocument382 paginiAC100 Training Manual Ver 2 0 PDFما ضاقت الا لتفرج80% (5)
- Pressure Test Procedure FOR Portable Methanol Injection Package (GBWP-A-4200)Document13 paginiPressure Test Procedure FOR Portable Methanol Injection Package (GBWP-A-4200)dharwin apÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spong, Block - The PendubotDocument2 paginiSpong, Block - The Pendubotaleong1Încă nu există evaluări
- Uav Introduction 4Document10 paginiUav Introduction 4Vijayanandh RÎncă nu există evaluări
- TKC40升降机维修说明书TKC Man Lift Maintenance ManualDocument36 paginiTKC40升降机维修说明书TKC Man Lift Maintenance Manualkiên phạm trungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Motor EE ST and L - EEA Comment Attended 22 July 2015Document193 paginiElectric Motor EE ST and L - EEA Comment Attended 22 July 2015gomeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPBR Flush Bottom Ball ValveDocument2 paginiIPBR Flush Bottom Ball Valvedevang asherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoichiometry Questions & AnswersDocument2 paginiStoichiometry Questions & Answersnosirat aladeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDocument9 paginiProblem Set 2.projectile MotionChristian OconÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On A Control Method With A Ventilation Requirement of A VAV System in Multi-ZoneDocument3 paginiA Study On A Control Method With A Ventilation Requirement of A VAV System in Multi-Zonepsn_kylmÎncă nu există evaluări