Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bicycle Parking and Storage Solutions: Give Cycling A Push
Încărcat de
Alvaro IgnacioTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Bicycle Parking and Storage Solutions: Give Cycling A Push
Încărcat de
Alvaro IgnacioDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Give Cycling a Push
Infrastructure
Implementation Fact Sheet
INFRASTRUCTURE/ PARKING
BICYCLE PARKING AND STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Overview
Dispersed, small bicycle parking systems, such as inverted U-stands, allow cyclists to park and
attach their bicycle for short periods and near their destination. More elaborate secured storage
facilities, such as lockers or supervised storage, allow cyclists to store their bicycle safely for
longer periods, at slightly larger distances to their destination. Available products range from
inexpensive small parking devices to automated systems and supervision.
Background and Objectives
Function
Bicycle parking systems (racks, stands) and storage facilities (lockers, cycle centers) are a range
of facilities allowing cyclists to park their bicycles safely, conveniently and in an orderly way. As
such they contribute to a well-organized public space and increase the attractiveness of cycling.
Scope
Bicycles can be parked anywhere, leaning against a wall or attached to a post or a railing.
However, with large numbers of bicycles, the situation becomes messy and confused. This is
no longer practical and safe for cyclists, and it turns into a physical and visual nuisance in public
space. This in turn may discourage bicycle use and turn opinion against cyclists.
Wherever a concentration of parked bicycles is present, expected or desired, these need to be
accommodated with well-organized, convenient and safe public bicycle parking facilities.
This in itself will encourage the use of cycling.
□ For short-term bicycle parking, reserved on-street spaces should be provided, dispersed
over streets and squares. These should be equipped with appropriate parking systems to
support the bicycle and secure it.
□ For longer-term parking and increased protection against theft, protected storage
facilities should be provided, such as lockers and supervised cycle centers. These can
range from small individual lockers to vast cycle stations.
For more information on neighbourhood storage facilities, reserved to local residents, see the fact
sheet on BICYCLE PARKING IN RESIDENTIAL AREAS.
For more information on planning quantity, type and location of parking facilities, see the fact
sheet on BICYCLE PARKING IN THE CITY CENTRE.
For more information on bicycle parking at public transport stops and stations, see the fact sheet
on CYCLING FACILITIES AT INTERCHANGES.
Implementation
Definition
Public bicycle parking facilities includes two types of provision.
□ Bicycle parking systems are structures that support a standing bicycle. These include
various types of racks and stands, for a single bicycle or for several, with an integrated
bolt locking system or not. They allow cyclists to park a bicycle.
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 1 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
□ Bicycle storage facilities are protected spaces for storing a bicycle. These include
individual and collective lockers, as well as cycle centers. They may be supervised or not,
automated or not, free or paying. In the larger ones, bicycles will be stored in parking
systems. They allow cyclists to store a bicycle.
Short-term parking systems
Cyclists first and foremost need to able to park bicycles. Parking means leaving the bicycle
behind for a short time, 2 h or less. They will want to park as near as possible to their
destination, typically less than 50 m. Research in major UK city centres illustrates this: asked
why they parked in a particular location, 86% of cyclists said because it was close to destination
(only 16% security); it also showed that 75% of cyclists park for less than two hours within 50 m
of their destination1. This demand needs to be met with a dispersed offer of small parking
facilities, at short distance intervals.
The simplest way is to allocate reserved bicycle parking space, without installing a parking
system. This can be done by simple marking, by different surface materials or using street
furniture. This in itself will already incite cyclists to park there. The advantage is that space is left
free for other uses, for instance in town squares. However, it is only suitable for bicycles that have
their own kickstand and fitted lock. Even then, the bicycle is not attached to a fixed object and
risks falling over or being stolen or vandalized.
Reserved bicycle parking space, with only markings, and the clutter it avoids (Amsterdam, NL)
It is recommended to provide a fixed structure that supports the bicycle and to which it can
be attached. This can take the form of a stand, for a single bike or one on each side, or of a rack,
for multiple bicycles in a row.
A wide range of products is available on the market, but not all are equally good value. The
following criteria should be considered in assessing product quality.
□ Does it provide stability? A bicycle with 10 kg of luggage in a side bag should be able to
stand up without damage to the bicycle.
□ Does it protect against theft? It should be possible to secure both the frame and the
front wheel. If only a wheel can be attached, thieves may detach the wheel. If the bicycle
only has a fitted lock, not attached to the parking system, thieves may just lift the bike
and break the lock later.
□ Is it compatible with many types of different bikes? Many preformed systems to
accommodate the fork or the front wheel may not fit children’s bicycles, racing bicycles or
the increasingly popular folding bicycles. Suspension systems are not suitable for longer
bicycles. Specific solutions may be considered in some situations, such as special provision
for children’s bicycles at schools.
1
DfT, 1997: Traffic Advisory Leaflet 7/97 – Supply and demand for cycle parking (results of surveys and field
observation in Leicester, Nottingham and Southampton).
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 2 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
□ Is it practical? The system should be easy to use, self-explanatory and require minimum
effort. Sophisticated anti-theft devices may be confusingly difficult to operate. Any system
that requires lifting the bike will be less used.
□ Is it robust? The system should be solidly fixed to the ground or wall, weather proof and
vandal-resistant. Small parts often provide leverage for destruction. Systems with built-in
locks, risk malfunctioning or being damaged by vandals.
□ Is it easy to maintain? The system should not attract litter and be easy to clean, even
when fully occupied.
In view of these requirements, it is not surprising that the inverted U-shaped bar is widely
recommended. The height is between 0.7 m and 0.8 m. The bicycle frame leans against it and
the frame and a wheel can be attached with a single lock. It is easy to use and suitable for all
types of bicycle. It’s a simple, low-tech and robust design that makes it easy to install and difficult
to vandalize. It is inexpensive and requires minimal maintenance. An extra horizontal bar is useful
to support smaller bicycles. Moreover, any number of them can be simply aligned and provided
with a roof for covering. It also allows for design variations to fit in with street furniture.
Inverted U-shaped bar stands, with design variations (UK – image source: Cycling England)
For the same reasons, low front-wheel grips should be avoided. These can be slots in
concrete, or wheel grips attached to a wall or incorporated in racks. They do not give enough
stability, so that bicycles may fall over and be damaged, also on purpose by vandals. They also do
not allow the frame to be secured. Finally, racks attract leaves and litter and need more
maintenance. However, in Denmark, front-wheel wedge-shaped grips are widely used and
recommended, on condition that the grips are sufficiently wide and mounted at the same height as
the wheel. But they still have the disadvantage that the frame cannot be secured, so they are not
recommended where theft is a major concern.
Horizontal front-wheel grips are TO BE AVOIDED (image source: T. Asperges)
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 3 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
Vertical front-wheel grips, common in Denmark (image source: P. Celis – 2008, Bicycle Parking Manua, DK)
Bicycle systems allow for innovative and arty design. They may become striking objects in
public space. The basic quality criteria should, however, always be respected.
A creative example is the bicycle key developed in Odense. This is an elegant locking device than
is sunk into the ground when not used. The cyclist pulls up an eyelet that can be attached to the
bicycle’s lock. The eyelet is attaché to a wire and a weight that pulls it down when released. The
advantage is that it takes up no space and can be used with all kinds of bikes. The disadvantage is
that it does not support the bicycle: in Odense it complements a front-wheel bicycle rack.
The Odense bicycle key
Bicycle stands as design objects, but still solid, robust and secure (David Byrne, New York)
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 4 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
Long-term storage facilities
Cyclists also need to store their bicycles. Storing means leaving your bicycle inside an access-
restricted and covered facility. Cyclists will feel this need for longer-term parking, which may be
from an hour upwards, to a whole day, all night or several days. The UK research already
mentioned notes that 77% people on commuting, business or education trips who were not
prepared to leave their bicycle behind for more than two hours were concerned about theft or
vandalism, but only 55% of people on shorter shopping or leisure trips2.
This demand can be served by a range of secure storage facilities: individual lockers, collective
lockers and supervised cycle storage centres.
Individual bicycle lockers
Individual bicycle lockers are used in situations calling for protection against bicycle theft and
vandalism, but where the demand is too low to create a supervised storage facility (e.g. small
railway stations, park & bikes near city centers).
□ Lockers in public places are usually privately rented for periods from a day to a year. The
user is identified and receives a unique key. Users pay a premium price for the added
value of security and a reserved space. Lockers also allow users to store accessories
safely, such as helmet, pumps, special clothing etc. Locking options vary, from keys,
padlocks, smart-cards and number key-pads. The disadvantage is that storage space is not
efficiently used, since they remain empty for part of the time.
□ Lockers can also be used more flexibly on a first-come-first-served basis. They can be
free: users bring their own lock or insert a coin they retrieve afterwards. This easily leads
to abuse: lockers are used to store other things or monopolized. Alternatively, users pay
short term rent and receive a key or an access code. Recently, electronic lockers have
made their appearance, in which users have a smart card and book a locker in advance.
□ Individual lockers are mostly mobile and can be moved to other locations. On the other
hand, they are bulky and consume much more space than parking outside lockers. This
means they are also more difficult to integrate physically and aesthetically into public
space. They may also require some form of supervision and maintenance, possible
control by CCTV.
□ Lockers can be managed by public authorities, a public transport company, a parking
agency or a private provider.
□ The price of a basic individual locker lies around 1000 €.
Individual lockers at Brugge (BE) Individual lockers at Dutch railway stations – NS Fiets
2
DfT, 1997: Traffic Advisory Leaflet 7/97 – Supply and demand for cycle parking (results of surveys and field
observation in Leicester, Nottingham and Southampton).
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 5 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
Commercial e-locker provider in the San Francisco Bay Area.
Users buy a smart card, which allows them to open lockers and use them at an hourly rate.
Collective bicycle lockers
A collective bicycle locker can contain a number of bicycles. Each user pays rent and has a key.
□ The most important advantage of the collective locker is that it takes up considerably less
space for the same number of bicycles than individual lockers.
□ Users need to know and trust each other. Neighbourhood bicycle storage is mostly
organized this way, as an indoor storage space shared by a number of local residents.
□ One user can be designated as supervisor and contact person for the managing
organization, for instance in exchange for a reduced rent.
□ Collective lockers can also be installed on the street. One example is the ‘bicycle drum’
which is often used in urban neighborhoods (in The Netherlands) where there is not
enough space to park bicycles off-street. The cost of a bicycle drum parking 10 bicycles is
around 5.000 €.
Carousel cycle locker: bicycles are on hand-rotated platform that
moves your bicycle in front of the single-door entrance
A bicycle drum (Sweden, see clip on www.plug.se)
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 6 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
Supervised bicycle storage facilities
A supervised bicycle storage facility can be considered in almost any city centre and main
station. The following conditions should be met.
□ The destination attracts large number of cyclists.
□ A considerable share of the cyclists wants to park their bicycle for a period of more than
one hour.
□ The risk of theft in the area is relatively high.
Some further recommendations.
□ Locate the facility max. 500 m from the destination it is meant to serve.
□ Use available location opportunities. A large-scale cycle centre can be a prestigious new
construction. But it can also be set up outdoors in public space, preferably covered: this is
often more visible, more easily accessible and less expensive. Mobile supervised storage
can be set up at events, with bicycle systems cordoned off with temporary fences.
□ Consider making it free. This has the strongest impact on cycle theft reduction and overall
bicycle use.
□ Choose a familiar location. A cycle in or near a town centre or a landmark building will
more easily be absorbed in cyclists’ minds.
□ Make it easily accessible. Ground level is to be preferred. Underground storage should be
accessible via inclines and carefully designed: wide entrances, lighting.
□ Assure social safety. Make sure the entrances are visible and at places with sufficient
social control.
Supervision and automation
Access management and supervision can be organized by staff personnel or partly or fully
automated.
□ Supervision by personnel is generally appreciated by users. They have someone to turn
to in case of problems and perceived safety increases. However, staffing is costly and
normally only feasible for limited periods, typically from 8:00 h to 18:00 h. This restricts
usage of the facility outside peak times.
□ Staff is often supported by partially automated supervision. Camera supervision (CCTV)
and electronic access systems allow reducing the number of personnel and exploitation
costs.
□ This technology now allows access and supervision to be unmanned and fully
automated, doing away with all need for staffing. This allows 24-hour operation. In those
cases special care should be taken to assure social safety: play music at all times, let in
daylight and provide views to the streets outside, integrate 24-hour functions nearby, such
as a snack bar. If the facility is perceived as unsafe, it will not be used.
Unmanned and fully automated storage facilities at Dutch railway stations – NS Fiets
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 7 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
A recent development is the appearance of fully automated on-street storage systems.
□ The principle is that bicycles are delivered – against payment – to a facility which then
automatically parks the bicycle underground.
□ The benefit is that they operate on a 24h basis and are safe for the bicycle and for the
cyclist. In principle, this type of parking facility safeguards 100% against theft and
vandalism. Often there is also room for your helmet and jacket. At the same time, these
systems are accessed at street level, and can be established in highly visible locations with
good lighting at night.
□ The disadvantage is the time needed to get your bicycle back at ground level. It doesn’t
take more than 35 seconds for any system to retrieve your bicycle, but at rush hours or
train arrivals you may have to stand in line. Therefore, the number of bicycles should be
limited, from 50 to 100.
Bike Tree: 12 bicycles Biceberg: fully automated
are hanged on their underground bicycle
front wheel. 30% of parking in the form of a
space is saved. horizontal giant mill. It
can be delivered in
modules from 23, 46, 69
or 92 bicycles. In Spain
different types are
working. www.biceberg.es
Bicycle mill in Nieuw- Velominck and Velowspace
Vennep in The system. www.Velominck.nl
Netherlands:
underground parking for
200 bicycles, in the form
of a giant mill, 3m
above ground, 9 m
below.
www.fietsmolen.nl
Basic dimensions for bicycle parking
Design recommendations for parking spaces for standard adult bicycles.
□ Provide a depth of 2 m, with a minimum of 1.8 m. The standard length of bicycles varies
from 1.8 m to 2 m.
□ Provide a width of 0.65 m. This is the centre-to-centre distance between bicycles needed
to accommodate the standard width of handlebars, between 50 to 65 cm. Cyclists can then
park easily, without getting handlebars entangled with the next bicycle. Below this
distance, most probably only one in two spaces will be used. At a distance of more than 70
cm, an additional bicycle may park in between when supply is short.
□ Provide a free access path of 1.8 m, for easy maneuvering. In large storage facilities,
people need to be able to walk past each other wheeling their bicycles: the access path
should 3 m to 3.5 m.
□ Provide wider space for specific needs. At supermarkets or in shopping districts, the
width must be increased to allow customers to load their bags easily. The same goes for
facilities outside day-care centres and kindergartens, to allow parents to lift children easily
in an out of the baby seat. If space is lacking, shoppers and parents will be forced to load
or lift children in the access space, blocking other cyclists.
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 8 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
□ Consider compact high-low systems. In these, bicycles are alternatively stacked on a
slightly different level. This way, handlebars cannot get entangled, and the centre-to-
centre width can be reduced to 4 m (min. 0.375 m). The level difference should be at least
0.25 m and the lifting height should not be more than 0.35 m.
□ Consider compact angled parking. When bicycles are parked at a 45° angle, handlebars
are less likely to become entangled. In addition, this reduces the depth and maneuvering
space needed. The centre-to-centre distance can be reduced to 0.5 m (or even 0.4 m) and
the depth to 1.4 m. The inconvenience is that parking space can only be accessed from
one direction.
□ Allow a standard space consumption of 1.8 m2 per bicycle. This includes the parking
space itself (1.3 m2) and a shared access path for two rows (0.5 m2 per bicycle). This can
vary from around 1 m2 for compact solutions up to 3 m2 with a more comfortable width of
0.8 m.
□ Only use two-tier parking as a last resort. Parking on two-tiers, one bike above
another, significantly reduces space consumption, up to 50%. In very large parking
facilities, this may be unavoidable to reduce the distance to be walked. However, lifting
bikes requires a serious effort that many cyclists will try to avoid. The effort may be
reduced by sinking the bottom tier slightly below ground level and by providing ramps for
the upper tier, or by providing lifting mechanisms.
Space gained by a angled parking
Danish guidance on bicycle parking dimensions (slightly larger dimensions are recommended)
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 9 of 10
Give Cycling a Push
Implementation Fact Sheet
The sole responsibility for the content of this fact sheet lies with the authors. It does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the European
…with sunken … or extractable wheel High-low rack
Communities. The European Commission is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information contained therein.
Two-tier parking
system lower tier gutters
Considerations
Strengths
Good-quality parking systems and storage facilities
□ make parking and storing bicycles safer, more convenient and more orderly;
□ include very cost-effective and little space-consuming products, such as the inverted U-
shape stand
□ include automated solutions, highly secure and reducing personnel costs
Weaknesses
Good-quality parking systems and storage facilities
□ can take up considerable space, especially individual lockers
□ can be quite expensive to install, or maintain or both, especially when personnel
supervision is involved
Alternative options
With large numbers of bicycles, there is no alternative: no bicycle provision will result in cluttered
space and most likely reduced bicycle use.
Bicycle parking and storage solutions page 10 of 10
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nebraska Pond ManagementDocument96 paginiNebraska Pond ManagementNEGameandParksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bike Lane Design Guidelines 09-22-2014Document17 paginiBike Lane Design Guidelines 09-22-2014civilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Nutrient Functions and Deficiency and Toxicity Symptoms MSU 2013Document16 paginiPlant Nutrient Functions and Deficiency and Toxicity Symptoms MSU 2013RaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitance-Resistance Model - Larry Lake PDFDocument99 paginiCapacitance-Resistance Model - Larry Lake PDFsotorkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working with Dynamic Crop Models: Methods, Tools and Examples for Agriculture and EnvironmentDe la EverandWorking with Dynamic Crop Models: Methods, Tools and Examples for Agriculture and EnvironmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Los Angeles IB P ZC2002 001 - Parking Design GuideDocument22 paginiLos Angeles IB P ZC2002 001 - Parking Design GuidebradideaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAES Master Catalog 39th Edition Digital PDFDocument452 paginiPAES Master Catalog 39th Edition Digital PDFalam zanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature Based Solutions Highways PDFDocument232 paginiNature Based Solutions Highways PDFRaffaele MarinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standards For Parking DesignDocument21 paginiStandards For Parking DesignPoorvi SarepakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reddy 2016Document451 paginiReddy 2016Sarai Olmedo CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquaponics p676Document49 paginiAquaponics p676Brandon JacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community-Scale Composting Systems - Table of ContentsDocument2 paginiCommunity-Scale Composting Systems - Table of ContentsChelsea Green Publishing0% (1)
- Center Pivot IrrigationDocument23 paginiCenter Pivot IrrigationZIGAME100% (2)
- Bicycle Parking HandbookDocument40 paginiBicycle Parking HandbookMário PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantifying Water and Energy Linkages in Irrigation: Experiences from Viet NamDe la EverandQuantifying Water and Energy Linkages in Irrigation: Experiences from Viet NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bicycle Parking GuidelinesDocument8 paginiBicycle Parking GuidelinesTutorEdgarMadridÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pond Water Aeration SystemsDocument32 paginiPond Water Aeration Systemsmuratout3447Încă nu există evaluări
- Aquaponics DatasetDocument3.696 paginiAquaponics Datasetsimple electric gadgets and thingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top Elevation Left Side Elevation: Scale 1:25 Meters Scale 1:25 MetersDocument1 paginăTop Elevation Left Side Elevation: Scale 1:25 Meters Scale 1:25 MetersDye ArÎncă nu există evaluări
- Winnipeg Parking Strategy: A Conceptual FrameworkDocument55 paginiWinnipeg Parking Strategy: A Conceptual FrameworkElishaDaceyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Libro Planificacion en Recursos Hidricoscompleto PDFDocument690 paginiLibro Planificacion en Recursos Hidricoscompleto PDFSamuelson CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Crop Growth Simulation ModellingDocument44 paginiPrinciples of Crop Growth Simulation ModellingManuel P. Marcaida IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parking RequirementsDocument6 paginiParking RequirementsRufina TiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ODMP Hydrology and Water Resources Inception ReportDocument68 paginiODMP Hydrology and Water Resources Inception ReportAse JohannessenÎncă nu există evaluări
- TFL - Traffic Modelling Guidelines PDFDocument184 paginiTFL - Traffic Modelling Guidelines PDFThiago Tavares100% (1)
- Soil Mapping and Process Modeling for Sustainable Land Use ManagementDe la EverandSoil Mapping and Process Modeling for Sustainable Land Use ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microirrigation Management PDFDocument423 paginiMicroirrigation Management PDFthjmacedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gambia: Banjul Urban ProfileDocument48 paginiGambia: Banjul Urban ProfileUnited Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT)Încă nu există evaluări
- AquacultureDocument21 paginiAquaculturesunny0908Încă nu există evaluări
- Bicycle Safety ReportDocument19 paginiBicycle Safety ReportwtopwebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope of Work: September 2015Document13 paginiScope of Work: September 2015M-NCPPCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sumo ModelDocument88 paginiSumo Model1419Încă nu există evaluări
- Testing Aqua Ponic WaterDocument20 paginiTesting Aqua Ponic Waterpelopas3Încă nu există evaluări
- Draft Bike Plan - RevisedDocument64 paginiDraft Bike Plan - RevisedScott Glenn100% (2)
- Aquaponics System, Plants. Volume 2: Sistemas de acuaponíaDe la EverandAquaponics System, Plants. Volume 2: Sistemas de acuaponíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RG CubeVoyagerDocument1.000 paginiRG CubeVoyagerChong Wah Lih100% (1)
- OKRA Standards For UKDocument8 paginiOKRA Standards For UKabc111007100% (2)
- International Guidebook of Environmental Finance ToolsDocument13 paginiInternational Guidebook of Environmental Finance ToolsUNDP_EnvironmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safeguarding The Plastics Recycling Value ChainDocument17 paginiSafeguarding The Plastics Recycling Value ChainKarina CadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To CubeBase and CubeVoyager - Delhi - 2009 PDFDocument193 paginiIntroduction To CubeBase and CubeVoyager - Delhi - 2009 PDFkumarnramÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st International Roadside Safety ConferenceDocument15 pagini1st International Roadside Safety Conferencegreat_triskelionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical FarmingDocument8 paginiVertical Farmingfelo345Încă nu există evaluări
- Inefficiences in Agriculture Supply Chain IT Opportunities PDFDocument60 paginiInefficiences in Agriculture Supply Chain IT Opportunities PDFavijeetboparaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greater Hobart Urban Travel Demand ModelDocument84 paginiGreater Hobart Urban Travel Demand ModelcitilabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A Recirculating Hydroponics System For A Tomato Greenhouse (A Case Study of HM Clause Farm in Nanyuki, Kenya)Document124 paginiDesign of A Recirculating Hydroponics System For A Tomato Greenhouse (A Case Study of HM Clause Farm in Nanyuki, Kenya)EL AFOUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Towards Transformational Change: UNDP's Work in Environment and Sustainable Development 2008-2012Document64 paginiTowards Transformational Change: UNDP's Work in Environment and Sustainable Development 2008-2012UNDP_Environment100% (1)
- Sydney Water Best Practice Guidelines For Turf Open SpaceDocument108 paginiSydney Water Best Practice Guidelines For Turf Open Spacedsl64Încă nu există evaluări
- Shigeharu Shimamura LED FarmDocument24 paginiShigeharu Shimamura LED FarmJustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greenhouse Automation System PDFDocument6 paginiGreenhouse Automation System PDFpabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems An Overview of Critical ConsiderationsDocument38 paginiRecirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems An Overview of Critical ConsiderationsSteveTillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pumptrack ProposalDocument23 paginiPumptrack Proposalapi-301806909100% (1)
- Lms Imagine - Lab Amesim Solutions GuideDocument20 paginiLms Imagine - Lab Amesim Solutions Guidejlee_296737Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 - Cube Land in CaliforniaDocument16 pagini2.1 - Cube Land in Californiacitilabs100% (1)
- How Can I Become A Data Scientist - QuoraDocument16 paginiHow Can I Become A Data Scientist - QuoraPallav Anand100% (1)
- Contents of ThesisDocument75 paginiContents of ThesisOlyadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquaculture 12Document16 paginiAquaculture 12fdlabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Traffic Assignment and ApplicationsDocument38 paginiDynamic Traffic Assignment and ApplicationsaldojudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 119 1 PDFDocument8 pagini119 1 PDFJulius OgowewoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Land Use Changes PDFDocument20 paginiLand Use Changes PDFMarilena BrastaviceanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC - of Work Shop PresentationDocument29 paginiCC - of Work Shop PresentationSEEPSocialÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAO-idp26 1Document374 paginiFAO-idp26 1CIO-CIO100% (2)
- An Open System For Farming Black Soldier Fly Larvae As A Source of Proteins For Smallscale Poultry and Fish ProductionDocument7 paginiAn Open System For Farming Black Soldier Fly Larvae As A Source of Proteins For Smallscale Poultry and Fish ProductionAndres Alejandro CamargoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NuevoDocumento 2018-08-17Document6 paginiNuevoDocumento 2018-08-17Alvaro IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKF PDFDocument112 paginiSKF PDFAlvaro IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios ElectrotecniaDocument98 paginiEjercicios ElectrotecniaAlvaro IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard DVS 2207-1 For Butt Fusion Welding PDFDocument12 paginiStandard DVS 2207-1 For Butt Fusion Welding PDFAlvaro Ignacio100% (1)
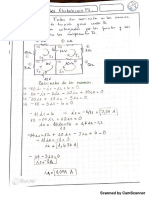
- Ejercicios de Series. Analizar La Convergencia de Las Siguientes Series, Calcular Cuando Sea Posible 1) (Converge)Document1 paginăEjercicios de Series. Analizar La Convergencia de Las Siguientes Series, Calcular Cuando Sea Posible 1) (Converge)Alvaro IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cop On Vehicle Parking Provision in Development Proposals 2019 Edition PDFDocument97 paginiCop On Vehicle Parking Provision in Development Proposals 2019 Edition PDFShumei ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Motorized PlanDocument201 paginiNon Motorized PlanRanjith ParvathapuramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine House Bill 5240Document5 paginiPhilippine House Bill 5240Tiklop Society PH100% (1)
- Bicycle Parking ManualDocument100 paginiBicycle Parking ManualActiveUrbesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site Appurtenances GuidelinesDocument6 paginiSite Appurtenances GuidelinesAthirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bicycle Parking and Storage Solutions: Give Cycling A PushDocument10 paginiBicycle Parking and Storage Solutions: Give Cycling A PushAlvaro IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- TASK 9 Kajang Local PlanDocument30 paginiTASK 9 Kajang Local PlanKhairussaadah MisnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Term Bicycle Parking StrategyDocument86 paginiLong Term Bicycle Parking StrategySan Francisco ExaminerÎncă nu există evaluări