Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Care of Patients With Asthma: Peak Flow Monitoring
Încărcat de
Belle Makinano0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
10 vizualizări2 paginiasthma
Titlu original
Final Handout Asthma
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentasthma
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
10 vizualizări2 paginiCare of Patients With Asthma: Peak Flow Monitoring
Încărcat de
Belle Makinanoasthma
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Care of Patients with Asthma Leukotriene modifiers.
Anti Leukotrienes are
By: Mari, Lean & Ruiz, Lord Ian potent bronchoconstrictors that also dilate blood
Definition vessels and alter permeability.
What is Asthma? Immunomodulators. Prevent binding of IgE to
the high affinity receptors of basophils and mast
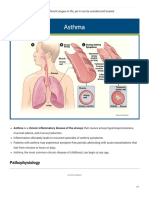
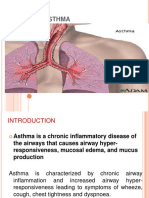
- Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the cells.
airways that causes increased responsiveness of the
trachea and bronchi to various stimuli, results in Peak flow Monitoring
widespread narrowing of the airways that improves
either spontaneously or with therapy.
Peak flow meters. Peak flow meters measure
the highest airflow during a forced expiration.
- An intense, unrelenting bronchospasm that does not
respond to the usual modes of therapy may result to
status asthmaticus (severe, prolonged asthma) Daily peak flow monitoring. This is
recommended for patients who meet one or more
2 types of asthma of the following criteria: have moderate or severe
persistent asthma, have poor perception of
changes in airflow or worsening symptoms, have
- Extrinsic asthma is caused by external agents such as
unexplained response to environmental or
dust, lint, insecticides, mold spores, foods, pollen,
occupational exposures, or at the discretion of
danders, or feathers. This type is best understood as an
the clinician or patient.
allergic reaction to specific allergens. Exposure to an
allergen can cause an attack.
Function. If peak flow monitoring is used, it
- Intrinsic asthma indicates that the specific causes helps measure asthma severity and, when added
cannot be identified. It may be precipitated by many to symptom monitoring, indicates the current
situations, such as a common cold, upper respiratory degree of asthma control.
infection, or even exercise. This type usually begins in
humans over 35 years of age and develops into a CAUSES OF ASTHMA
lifelong condition.
▹ Family History
Pathophysiology ( see chart B1) ▹ Environment and Occupation
▹ Other Medical Conditions
a. Assessment and Diagnostic tests ▹ Race and Ethnicity
Bronchiectasis is not readily diagnosed because ▹ Sex
the symptoms can be mistaken for those of
simple chronic bronchitis. A definite sign is Environment and Occupation
offered by the prolonged history of productive
cough, with sputum consistently negative for - Exposure to cigarette smoke during pregnancy or in a
tubercle bacilli. The diagnosis is established by a child’s first few years
compound tomography (CT) scan, which - Exposure to different microbes in the environment
demonstrates either the presence or absence of - Exposures that occur in the workplace, such as
bronchial dilation. chemical irritants or industrial dusts
- Poor air quality from pollution or allergens
b. Complications and Prevention - Exercise
Complications of asthma may include status - Stress/ Emotional Upset
asthmaticus, respiratory failure, pneumonia, and
atelectasis. Airway obstruction, particularly Other Medical Conditions
during acute asthmatic episodes, often results in
hypoxemia, requiring the administration of
▹ Allergies.
oxygen and the monitoring of pulse oximetry
▹ Obesity. Although the reasons are unclear, some
and arterial blood gases. Fluids are administered
experts point to low-grade inflammation in the body
because people with asthma are frequently
that occurs with extra weight.
dehydrated from diaphoresis and insensible fluid
▹ Respiratory infections and wheezing. Young
loss with hyperventilation.
children who often have respiratory infections caused
by viruses.
c. Medical Management
Pharmacologic Therapy
Short-acting beta2 –adrenergic agonists. These Race and Ethnicity
are the medications of choice for relief of acute
symptoms and prevention of exercise-induced African Americans and Puerto Ricans are at higher risk of
asthma. asthma than people of other races or ethnicities.
Anticholinergics. Anticholinergics inhibit Sex
muscarinic cholinergic receptors and reduce
intrinsic vagal tone of the airway. Among children, more boys than girls have asthma. Among
teens and adults, asthma is more common among women than
Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are most men.
effective in alleviating symptoms, improving
airway function, and decreasing peak flow CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
variability.
cough (with or without mucus production), dyspnea,
and wheezing
attacks often occur at night or early in the morning allergen contacts such as dust, animal dander, feathers,
Generalized chest tightness and dyspnea and pollen.
Expiration requires effort and becomes prolonged 4. Teach the patient adaptive breathing techniques and
diaphoresis, tachycardia, and a widened pulse breathing exercises such as pursed-lip breathing and
pressure may occur along with hypoxemia and positioning.
central cyanosis 5. Teach the patient and family effective coughing
techniques.
II. Nursing Management 6. Teach the importance of consuming large quantities of
fluid to liquefy secretions.
7. Teach relaxation techniques.
NURSING PROCESS: ASSESSMENT
8. Provide the patient and family with information regarding
the care, cleaning, and maintenance of inhalation
▹ Assess the patient’s respiratory status by monitoring equipment being used in the hospital or to be used at
the severity of the symptoms. home.
▹ Assess the level of oxygen saturation through the 9. Provide the patient and family with respiratory related
pulse oximeter health information such as pollution indexes, secondary
▹ Monitor the patient’s vital signs. infection exposure, and community support groups.
▹ Assess history. 10. Teach the patient to obtain vaccine for influenza and
▹ Assess respiratory status. pneumococcal pneumonia.
▹ Assess medications 11. Teach the patient the signs and symptoms to report to the
physician, e.g., changes in sputum characteristics,
NURSING PROCESS: DIAGNOSIS excessive fatigue, increased cough, increased SOB, fever,
chills, chest discomfort, and wheezing.
▹ Ineffective airway clearance related to increased 12. Teach the patient to avoid contact with people who have
production of mucus and bronchospasm. respiratory infections.
▹ Impaired gas exchange related to altered delivery of
inspired O2.
▹ Anxiety related to perceived threat of death.
PS. Some parts of the discussion are not found in the
powerpoint and handout. Please just take notes
NURSING PROCESS: PLANNING
Notes:
▹ Maintenance of airway patency.
▹ Expectoration of secretions.
▹ Demonstration of absence/reduction of congestion
with breath sounds clear, respirations noiseless,
improved oxygen exchange.
▹ Verbalization of understanding of causes and
therapeutic management regimen.
▹ Demonstration of behaviors to improve or maintain
clear airway.
▹ Identification of potential complications and how to
initiate appropriate preventive or corrective actions.
NURSING PROCESS: IMPLEMENTATION AND
EVALUATION
- Would depend on situation
DISCHARGE AND HOME CARE GUIDELINES
▹ Collaboration
▹ Health Education
▹ METERED DOSE INHALERS (WITH
SPACER
▹ NEBULIZER
▹ Compliance to therapy
▹ Home Visits/ Continuing Care
Health Education: Patient Teaching
1. Teach about prescribed medications such as
bronchodilators and corticosteroids: name, dosage,
purpose, time of administration, and side effects.
2. Provide the patient and family with information about
asthma as a disease, how to assess an asthmatic response,
what to do during the process of care, and criteria for
requesting professional assistance and acute emergency
care.
3. Assist the patient and family to examine secondary factors
that may precipitate asthmatic episodes, such as emotional
stress, fatigue, or environmental changes or specific
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Fast Facts: Respiratory Allergies: Understand aeroallergens, improve treatment responseDe la EverandFast Facts: Respiratory Allergies: Understand aeroallergens, improve treatment responseÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesDe la EverandA Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Asthma: Exercise-Induced Asthma Occurs Within 5Document4 paginiAsthma: Exercise-Induced Asthma Occurs Within 5April PunzalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsthmaDocument10 paginiAsthmaAbirajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition & Pathogenesis (Ngân) : Asthma - Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2015Document4 paginiDefinition & Pathogenesis (Ngân) : Asthma - Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2015everydayisagift9999Încă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument7 paginiConcept Map Asthmashehada bondad100% (2)
- Asthma: Vanessa T. Ucat, RN MSN 302 December 2015Document39 paginiAsthma: Vanessa T. Ucat, RN MSN 302 December 2015Vane UcatÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTHMADocument9 paginiASTHMAmildred alidonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma: Prepared By: DR - Habab AbdelrhmanDocument43 paginiAsthma: Prepared By: DR - Habab AbdelrhmanJdjshsbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Nursing Care Management and Study GuideDocument7 paginiAsthma Nursing Care Management and Study GuideRamakrishna BadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument20 paginiBronchial AsthmaJuliet De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma: Prepared by Fatima Hirzallah RN, MSN, CNS, PHDDocument21 paginiAsthma: Prepared by Fatima Hirzallah RN, MSN, CNS, PHDناصر دويكاتÎncă nu există evaluări
- RespiDocument27 paginiRespierisha.cadagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Copd Asthma 2022Document65 paginiPresentation Copd Asthma 2022Pwani aquaponicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case PresentationDocument68 paginiCase Presentationslimescared01Încă nu există evaluări
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 11 AsthmaDocument2 paginiNCM 112 LEC Topic 11 AsthmaViviene Faye FombuenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asma BronkialDocument18 paginiAsma BronkialLala SamosirÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Should One Investigate A Chronic CoughDocument3 paginiHow Should One Investigate A Chronic Coughtsiko111Încă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument5 paginiUntitledTruptilata SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsthmaDocument15 paginiAsthmaLuisa GrassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation - FinalDocument17 paginiBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation - Finalmary_sulit_150% (2)
- Classification of AsthmaDocument4 paginiClassification of AsthmaAlejandro LugoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-Obstractihe Pulmonary Diseases (Asthma) PDFDocument50 pagini01-Obstractihe Pulmonary Diseases (Asthma) PDFsima.koye2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Asthma: Dr. Raed ShudifatDocument36 paginiAsthma: Dr. Raed ShudifatRema WaleedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Respiratory DisordersDocument37 paginiUpper Respiratory DisordersClaire Maurice JuaneroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma: EpidemiologyDocument22 paginiAsthma: EpidemiologyananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zhu 18 05Document8 paginiZhu 18 05ABÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Cough - N Engl J Med 2000Document7 paginiDiagnosis and Treatment of Cough - N Engl J Med 2000ErnestoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute ExaerbationDocument4 paginiAcute ExaerbationEden RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- File 18585Document15 paginiFile 18585Mohammed MuthanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma OpdDocument59 paginiAsthma OpdJb TlntinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsthmaDocument22 paginiAsthmaAnna EmÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTMA NisreenDocument19 paginiASTMA NisreenMuhd ShafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Davidson + Osmosis + Step Up MedicineDocument2 paginiAsthma Davidson + Osmosis + Step Up MedicineElyas MehdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTHMADocument4 paginiASTHMAKhasim AgwilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Year of Universalization of Health": I.S.T.P: Course: Especiality: Cycle: Topic: Teacher: StudentDocument8 pagini"Year of Universalization of Health": I.S.T.P: Course: Especiality: Cycle: Topic: Teacher: StudentKarina DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- LECTURE NOTE ON ASTHMA-WPS OfficeDocument7 paginiLECTURE NOTE ON ASTHMA-WPS OfficeNaija Nurses TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma: by Ajagidi O. Joy B.S. NursingDocument33 paginiAsthma: by Ajagidi O. Joy B.S. NursingMatt Joseph CabantingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphylactic Shock ReaderDocument3 paginiAnaphylactic Shock ReaderzipheleleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Used in AsthmaDocument135 paginiDrugs Used in AsthmaDR. MUSICÎncă nu există evaluări
- T. Pulmonary DisordersDocument5 paginiT. Pulmonary DisordersJyl Yan SelasorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Guide AsthmaDocument20 paginiLecture Guide Asthmalady birdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult Nursing - The Final PresentationDocument70 paginiAdult Nursing - The Final Presentationក្មេងប្រុស ល្ងីល្ងើÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document16 paginiChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Kimberly Abella CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Study of Pulmonary DiseaseDocument66 paginiClinical Study of Pulmonary DiseaseNajamAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vestil - Case Study On AsthmaDocument7 paginiVestil - Case Study On Asthmaninachristenevestil25Încă nu există evaluări
- Farmasi Klinis 2 - Asma Akut (Eksaserbasi Asma) - From: Gina 2017 - By: Amelia Lorensia - 2017Document52 paginiFarmasi Klinis 2 - Asma Akut (Eksaserbasi Asma) - From: Gina 2017 - By: Amelia Lorensia - 2017Alifah SyarafinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Respiratory Disease: BY: Niña Alessandra ValerianoDocument20 paginiCommon Respiratory Disease: BY: Niña Alessandra ValerianokarenbescaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Lecture 2022Document32 paginiAsthma Lecture 2022grim reaperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of AsthmaDocument29 paginiManagement of AsthmaAbdullah Al ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsthmaDocument8 paginiAsthmahusainozelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Childhood Asthma: DR - Rodman Tarigan, Spa.,MkesDocument35 paginiChildhood Asthma: DR - Rodman Tarigan, Spa.,MkesBambang IrwansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTHMADocument5 paginiASTHMAabdulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma 160424141552Document54 paginiAsthma 160424141552almukhtabir100% (1)
- Bronchial Asthma in Children FdneDocument36 paginiBronchial Asthma in Children FdneRonit ChandÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Bronchial AsthmaDocument9 pagini4 Bronchial Asthmashanfiza_92Încă nu există evaluări
- CHD AsthmaDocument20 paginiCHD AsthmaRj MagpayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moleno April Mariebsn Ii F Case Scenario 1 Pediatric-Community Acquired Pneumonia Pcap-C IDocument11 paginiMoleno April Mariebsn Ii F Case Scenario 1 Pediatric-Community Acquired Pneumonia Pcap-C IyounggirldavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochial Asthma EditedDocument40 paginiBrochial Asthma EditedMituran IshwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Complete Asthma Guide: An Asthma book for adults and children, that teaches how to be asthma free naturally with the right therapeutic diets, medications & alternative herbal therapiesDe la EverandThe Complete Asthma Guide: An Asthma book for adults and children, that teaches how to be asthma free naturally with the right therapeutic diets, medications & alternative herbal therapiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginnings of GriefDocument3 paginiBeginnings of GriefBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulmonary TB DrugsDocument6 paginiPulmonary TB DrugsBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belle, Health Care Ethics 1.Document2 paginiBelle, Health Care Ethics 1.Belle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Juliena DraftDocument3 paginiJuliena DraftBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study AmbroxolDocument2 paginiDrug Study AmbroxolBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example of A BrochureDocument3 paginiExample of A BrochureBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemoglobinopathies OutlineDocument1 paginăHemoglobinopathies OutlineBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCOVgroup 2Document1 paginăNCOVgroup 2Belle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tele OlogyDocument7 paginiTele OlogyBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Women and Families During PostpartumDocument3 paginiCare of Women and Families During PostpartumBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument3 paginiPregnancy ComplicationsBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MU2010Document1 paginăMU2010Belle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemoglobinopathies OutlineDocument1 paginăHemoglobinopathies OutlineBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homeostatic Imbalances in The SkinDocument1 paginăHomeostatic Imbalances in The SkinBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of Family & Family Nursing ProcessDocument3 paginiConcept of Family & Family Nursing ProcessBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEALTHCAREDocument1 paginăHEALTHCAREBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Drugs: D. Hormone DeliveryDocument8 paginiCardiovascular Drugs: D. Hormone DeliveryBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Drugs: D. Hormone DeliveryDocument8 paginiCardiovascular Drugs: D. Hormone DeliveryBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ha NotesDocument1 paginăHa NotesBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles For All MedicationDocument6 paginiPrinciples For All MedicationBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homeostatic Imbalances in The SkinDocument1 paginăHomeostatic Imbalances in The SkinBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sources: Karch, Pharmacology Pilliteri, Maternal Kozier: Delivery?Ismobileset FalseDocument1 paginăSources: Karch, Pharmacology Pilliteri, Maternal Kozier: Delivery?Ismobileset FalseBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Osteoarthritis: UnderstandingDocument4 paginiA. Osteoarthritis: UnderstandingBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles For All MedicationDocument6 paginiPrinciples For All MedicationBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of Family & Family Nursing ProcessDocument3 paginiConcept of Family & Family Nursing ProcessBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuation Sa PregnancyDocument3 paginiContinuation Sa PregnancyBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Drugs in The Labor Room and Delivery RoomDocument4 paginiCommon Drugs in The Labor Room and Delivery RoomBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Microbes in The EnvironmentDocument7 paginiControl of Microbes in The EnvironmentBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument2 paginiReproductive System ReviewerBelle MakinanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low-Cost Breath AnalyzerDocument20 paginiLow-Cost Breath AnalyzeradnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip Class Reflection 1Document3 paginiFlip Class Reflection 1api-301784889Încă nu există evaluări
- Schedule of Charges-Holy Family - Sep 08Document64 paginiSchedule of Charges-Holy Family - Sep 08Quirinevv100% (1)
- Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument32 paginiMonoclonal AntibodieskhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Calculi: Ahmednagar Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital AhmednagarDocument15 paginiRenal Calculi: Ahmednagar Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital AhmednagarSuhas IngaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation - UpToDateDocument37 paginiPulmonary Rehabilitation - UpToDateAlejandro CadarsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Types of Nurses in HospitalDocument6 paginiReading Types of Nurses in HospitalAlfa HamiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pain SheetDocument4 paginiPain SheetMohammad Al GhroryÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effect of The Pandemic On The Mental Health of The Senior High School Students of Saint Anthony College of Roxas CityDocument3 paginiThe Effect of The Pandemic On The Mental Health of The Senior High School Students of Saint Anthony College of Roxas CityKANT JAMES D. MAHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prosta LacDocument16 paginiProsta LacantoniofacmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyper Calc Emi ADocument31 paginiHyper Calc Emi AFatima SajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Trip To The Hospital - A Coloring BookDocument0 paginiMy Trip To The Hospital - A Coloring Bookili_thÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Isi FormulariumDocument9 paginiDaftar Isi FormulariumNilam atika sariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lbbbi18 Long Exam 1Document71 paginiLbbbi18 Long Exam 1namkimseoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Tests of Renal FunctionDocument5 paginiLaboratory Tests of Renal Functiongiselle155204Încă nu există evaluări
- Part 2 Lecture 2Document53 paginiPart 2 Lecture 2Shella SilvestreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parafin Sept 2011Document28 paginiParafin Sept 2011Sarin AvniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Peter McCullough - COVID Vaccines Have Already Killed 50,000 Americans.Document7 paginiDr. Peter McCullough - COVID Vaccines Have Already Killed 50,000 Americans.chingatchgook80% (5)
- Monetization Letter VillonesDocument2 paginiMonetization Letter Villonesleslia salundagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arabic Clerking Etc-3Document26 paginiArabic Clerking Etc-3walefamousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wurzel 2016Document8 paginiWurzel 2016prolanis pkmmulyoharjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giraffe Blood CirculationDocument9 paginiGiraffe Blood Circulationthalita asriandinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis and Management of COPD: A Case Study: RespiratoryDocument4 paginiDiagnosis and Management of COPD: A Case Study: RespiratoryUssy TsnnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial Resistance Trends in Bacterial Keratitis Over 5 Years in Sydney, AustraliaDocument9 paginiAntimicrobial Resistance Trends in Bacterial Keratitis Over 5 Years in Sydney, AustraliaBima RizkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To SplenomegalyDocument37 paginiApproach To SplenomegalySarath Menon R100% (1)
- Booklet Bcu Revisi 5Document8 paginiBooklet Bcu Revisi 5irza nasutionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complications in Dentoalveolar Surgery PDFDocument37 paginiComplications in Dentoalveolar Surgery PDFmirfanulhaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacological Management of Agitation in Emergency SettingsDocument8 paginiPharmacological Management of Agitation in Emergency SettingsnurulnadyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Floppy InfantDocument44 paginiApproach To Floppy InfantNavya Hegde100% (2)
- Cholinergic System Model Questions & AnswersDocument45 paginiCholinergic System Model Questions & AnswersDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (5)