Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pid Tuning PDF
Încărcat de
simbamikeTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pid Tuning PDF
Încărcat de
simbamikeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Page 8 -- PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2
INTUNE Version 5
PID Loop Tuning
Process Performance Monitoring, Reporting,
Tuning, & Diagnostic Tool
INTUNE V5 is a plant management and engineering tool that
Pocket Guide
Version 2.0
combines process control monitoring functions with powerful
diagnostic and tuning tools. The software monitors all plant/
process loops without intruding on the process, and can
automatically generate reports that identify poorly performing
loops. In its diagnostic capability, INTUNE V5 generates reports
that will notify managers, engineers, or operators via e-mail,
phone call, or alarm, if process performance violates certain pre-
set conditions. INTUNE V5 then provides a tool to resolve process
issues quickly and easily.
Contents
2 Description of Processes
2 Description of PID Units
MANTRA
Advanced Process Control System 3 Closed Loop Tuning Procedure
MANTRA is a state-of-the-art advanced control system. It is a full-
blown, configurable control system with more than 90 function 4-5 Open Loop Tuning Procedure
blocks, configurable faceplates, and very easy to use, intuitive,
drag-and-drop type of function block programming. The
advanced control functions in MANTRA include our patented
6-7 Reference List of
model-based control suite—IMC (Internal Model Control), CC Common Controllers
(Coordinated Control), and MMC (Modular Multivariable Control).
MANTRA allows users to build all necessary logic on top of the
multivariable predictive control functions to take care of any 8 INTUNE v5 & MANTRA Descriptions
operation or control needs. It also allows users to switch the
control back and forth between MANTRA and their existing
8 ControlSoft Contact Information
control system.
E-MAIL info@controlsoftinc.com
WEB www.controlsoftinc.com
PHONE 440-443-3900; FAX 440-443-0249
5387 Avion Park Drive, Highland Heights OH 44143
DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com
Page 2 -- PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2 PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2 -- Page 7
DESCRIPTION OF PROCESSES
Fast Loops (flow, pressure) Integrating (level & insulated temp)
P - Little [Too much will cause P - More
cycling] I - Little [Will cause cycling]
I - More D- Must [If D is not used, the loop will continued from page 6
D - Not needed cycle.]
GE PID BLOCKS OMRON PID BLOCKS
Slow Loops (temperature) Noisy Loops (any PID loop where the
Series 90/30/70 PID Block ISA PID Block
P - More measurement is constantly changing) P Gain (Gain * 100) P Gain (Gain * 1)
I - Some [Too much will cause P - Low [Will cause cycling] I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1000) I Time Constant (Sec * 10)
cycling] I - Most [Accumulated error] D Time Constant (Sec * 100) D Time Constant (Sec * 10)
D - Some D - Off [Will cause cycling]
Series 90/30/70 PID Block Independent
P Gain (Gain * 100) SIEMENS TI PID BLOCKS
I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1000) PID Block
DESCRIPTION OF PID UNITS D Gain (Gain * 100) P Gain (Gain * 1)
Proportional Term is the amount added to the output based on the I Time Constant (Min * 1)
D Time Constant (Min * 1)
current error.
Proportional Gain is a Multiplier. MANTRA PID BLOCKS
If the error is 10 and the Gain is .8, then the output will move 8%. PID Block Series
SQUARE D PID BLOCKS
Proportional Band is a Divider as a percentage. P Gain (Gain * 1)
PID Block
If the error is 10 and the Band is 125%, then output is (10*(100/125))=8%. I Time Constant (Sec * 1)
P Gain (Gain * 100)
Conversion between P-Gain and P-Band: D Time Constant (Sec * 1)
I Reset Rate (Repeats/min * 100)
P-Band = 100/P-Gain D Time Constant (Min * 6000)
PID Block Parallel
P Gain (Gain * 1)
Integral Term is the amount added to the output based on the sum of the I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1)
error. D Gain (Gain * 1) WESTINGHOUSE
Time Constant is the time for one full repeat of P-Term. WFDP PID Block
If the P-Term is 8% and the Time Constant is 10 seconds, then the output PID Block Non-Interacting P Gain (Gain * 100)
P Gain (Gain * 1) I Time Constant (Sec * 1)
will ramp up 8% every 10 seconds.
I Time Constant (Sec * 1) D Gain (Gain * 1)
Reset Rate is amount the output will move in one second.
If the P-Term is 8% and the Reset Rate is .1 repeat/sec, then the output D Time Constant (Sec * 1)
Ovation PID Block
will move .1*8 every second and take 10 seconds for the full repeat of P Gain (Gain *1)
the P-Term of 8%. MODICON PID BLOCKS I Time Constant (Sec *1)
Integral Gain is the same as the Reset Rate multiplied by the P-Gain. KPID Block D Gain (Gain *1)
Conversion between Time and Reset Rate: P Gain (Gain * 1)
Reset Rate = 1/ Time Constant I Time Constant (Sec * 1)
I-Gain = (1/Time Constant)*P-Gain D Time Constant (Sec * 1)
PID Block
Derivative Term is the amount subtracted from the output based on the P Gain (Gain * 1)
rate of change of the error. I Time Constant (Sec * 1)
Time Constant is the amount of time the controller will look forward. D Time Constant (Sec * 1)
Derivative Gain is the amount of time the controller looks forward
multiplied by the P-Gain. PID2 Block
P Band (Gain * 1)
I Reset Rate (Repeats/min * 100)
D Time Constant (Min * 100)
DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com
Page 6 -- PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2 PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2 -- Page 3
REFERENCE CLOSED LOOP TUNING PROCEDURE
Following is a summary of many of the more common controllers available
on the market. For units of other controllers, please contact ControlSoft CLOSED LOOP STEP 1: KNOW THE PROCESS
(see page 8 for contact information). Identify the loop you intend to tune and determine the speed of the loop. A rough
categorization is as follows:
Fast loop has response time from less than one second to about 10 seconds,
ControlLogix PID Block Dependent such as a flow loop. Use of PI controller is sufficient.
AB PID BLOCKS
P Gain (Gain * 100) Medium loop has response time of several seconds up to about 30 seconds, such
PLC5 Integer Block ISA
I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1) as flow, temperature, and pressure. Use either PI or PID controller
P Gain (Gain * 100)
D Gain (Gain * 1) Slow loop has response time of more than 30 seconds, such as many
I Time Constant (Min * 100)
temperature loops and level loops. Use of PID controller is recommended.
D Time Constant (Min * 100)
ControlLogix PIDE Block Independent
PLC5 Integer Block Independent Gains P Gain (Gain * 1)
P Gain (Gain * 100) I Time Constant (Min * 1) CLOSED LOOP STEP 2: KNOW THE CONTROLLER
I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1000) D Time Constant (Min * 1)
Identify the units of your PID controller,
D Gain (Gain * 100)
ControlLogix PIDE Block Dependent Proportional term (P-Term) is either a Proportional Gain (P-Gain) or Proportional
P Gain (Gain * 100) Band (P-Band).
PLC5 PD Block ISA
I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1) Integral term (I-Term) can be a Time Constant (in minutes or seconds), Reset Rate
P (Gain *1)
D Gain (Gain * 1) (1/second or 1/minute), or I-Gain (Reset rate * Proportional gain).
I Time Constant (Min * 1)
Derivative term (D-Term) can be Time Constant (in seconds or minutes) or
D Time Constant (Min * 1)
Derivative Gain (derivative time constant * proportional gain).
In this document, Proportional Gain, Integral Reset Rate, and Derivative Gain are
PLC5 PD Block Independent Gains BAILEY INFI90 PID BLOCKS assumed.
P Gain (Gain * 1) 156,0 PID Block Convert back to your controller units if necessary.
I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1) P Gain (Gain *1) The Reference section is a summary of many of the more common controllers
D Gain (Gain * 1) I Reset Rate (Repeats/min * 1) available on the market.
D Time Constant (Min * 1) For units of other controllers, please contact ControlSoft.
PLC5 PCO Block Dependent Gains
P Gain (Gain * 1) 156,1 PID Block
I Time Constant (Min * 1) P Gain (Gain * 1)
D Time Constant (Min * 1) I Reset Rate (Repeats/min * 1) CLOSED LOOP STEP 3: WATCH THE RESPONSE
PLC5 PCO Block Independent Gains D Time Constant (Min * 1) Make a small change of setpoint (say 5%) or wait for a disturbance in the
P Gain (Gain * 1) process. Then watch for process variable (PV) and control output (CO)
I Reset Rate (Repeats/sec * 1) 156,2 PID Block responses.
D Gain (Gain * 1) P Gain (Gain * 1) — If no visible instantaneous change of CO upon the change of setpoint or no
I Reset Rate (Repeats/min * 1) apparent overshoot (over damped), increase your proportional gain by 50%.
SLC PID Block with RG bit on D Time Constant (Min * 1) — If the PV is unstable or has sustained oscillation, with overshoot greater than
P Gain (Gain *100) 25%, reduce Proportional Gain by 50% and reduce Integral Reset Rate by
I Time Constant (Min * 100) 156,3 PID Block 50%.
D Time Constant (Min * 100) P Gain (Gain * 1) — If PV oscillation persists with tolerable overshoot, reduce Proportional Gain by
I Time Constant (Min * 1) 20% and reduce Integral Reset Rate by 50%.
SLC PID Block with RG bit off D Time Constant (Min * 1) — If 3 or more consecutive peaks occur upon the change of setpoint, reduce
P Gain (Gain *10) Integral Reset Rate by 30% and increase Derivative Gain by 50%.
I Time Constant (Min * 10) — If PV stays fairly flat and below (or above) the setpoint for a long time, after
D Time Constant (Min * 10) change of setpoint or beginning of disturbance (long tail scenario), increase
Integral Reset Rate by 100%.
ControlLogix PID Block Independent Repeat step 3 until the closed-loop response is satisfactory to you.
P Gain (Gain * 1)
I Time Constant (Min * 1)
D Time Constant (Min * 1) continued on page 7
DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com
Page 4 -- PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2 PID Loop Tuning Pocket Guide, Version 2 -- Page 5
OPEN LOOP TUNING PROCEDURE
OPEN LOOP STEP 1: OPEN LOOP STEP 3:
KNOW THE PROCESS OPEN LOOP TEST FOR NON-INTEGRATING LOOPS
Identify the loop you intend to tune and determine the speed a. Put loop in manual control mode, keep control output
of the loop. A rough categorization is as follows: constant, and wait for process to stabilize. d. Select initial PID values such that
Fast loop has response time from less than one second to P = 2* (Deadtime + Time constant)/Model gain
about 10 seconds, such as a flow loop. Use of PI b. Make a small step change on control output (say 5 or I = (Deadtime + Time constant)
controller is sufficient. 10%), and watch the response. D = (Deadtime / 3) or (Time constant / 6)
Medium loop has response time of several seconds up to
about 30 seconds, such as flow, temperature, and c. Estimate process model according to Figure 1: For slow loop, select whichever is greater.
pressure. Use either PI or PID controller Model gain = PV change / CO change. For fast loop, select smaller value.
Slow loop has response time of more than 30 seconds, Deadtime: time lapse between change of CO and
such as many temperature loops and level loops. Use observable changes on PV. e. These initial PID values should give you a reasonable
of PID controller is recommended. Time constant: The time it takes for PV to reach about closed-loop response. Fine-tune the controller by
63% of total changes. using the closed-loop tuning method (see Step 3 on
page 3) to get your desired response.
OPEN LOOP STEP 2:
KNOW THE CONTROLLER
Identify the units of your PID controller,
Proportional term (P-Term) is either a Proportional Gain (P- Controller Output (CO)
Gain) or Proportional Band (P-Band). Process Input
Integral term (I-Term) can be a Time Constant (in minutes
or seconds), Reset Rate (1/second or 1/minute), or I-
Gain (Reset rate * Proportional gain). CO Change
Derivative term (D-Term) can be Time Constant (in
seconds or minutes) or Derivative Gain (derivative
time constant * proportional gain). Time
In this document, Proportional Gain, Integral Time Constant
(in seconds), and Derivative Time Constant (in Figure 1.
seconds) are assumed. First Order
Convert back to your controller units if necessary. Non-Integrating Deadtime Time Constant
The Reference section (starting on page 6) is a summary Model
of many of the more common controllers available on Calculation Process Value (PV)
the market. Process Output
For units of other controllers, please contact ControlSoft. 63% of PV Change
PV Change
Noise Band
Time
Gain = PV_Change / CO_Change
DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com DS405-12/04 -- www.controlsoftinc.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Advanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlDe la EverandAdvanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneDe la EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneÎncă nu există evaluări
- PID Loop Tuning Guide Control Soft DS405v21 020405Document4 paginiPID Loop Tuning Guide Control Soft DS405v21 020405NAPZ69Încă nu există evaluări
- Pid ControllersDocument132 paginiPid Controllers14071988Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is PID - TutorialDocument5 paginiWhat Is PID - Tutorialsocrates19582405Încă nu există evaluări
- Smith Predictor Desc enDocument8 paginiSmith Predictor Desc entalljatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hitachi Inverter PID Control Users' GuideDocument16 paginiHitachi Inverter PID Control Users' GuideMirinhaeThiago RosárioÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Manually Tune A Three-Mode PID ControllerDocument5 paginiHow To Manually Tune A Three-Mode PID ControllerlorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PID Control Manual 6540Document26 paginiPID Control Manual 6540Lizandro ZapataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantage and Disadvantage of PIDDocument6 paginiAdvantage and Disadvantage of PIDNathaniel PascuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acfrogdgl836ldvbuspou Eyl6uhjugculhmtzdojwbgtlkkup E7yn7z3wkk04xjugsulhx0ouzu9rws3smog3t9o06r7-Cs1zavkubqcfvimg43ogdym21jddxoevtgcy ZznougjhwjcxkhnDocument40 paginiAcfrogdgl836ldvbuspou Eyl6uhjugculhmtzdojwbgtlkkup E7yn7z3wkk04xjugsulhx0ouzu9rws3smog3t9o06r7-Cs1zavkubqcfvimg43ogdym21jddxoevtgcy ZznougjhwjcxkhnMOHAMED THARIKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mesb333 Pid ControlDocument13 paginiMesb333 Pid ControlMohd KhairiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PID Control PID Control: Session Outlines & Objectives Session Outlines & ObjectivesDocument24 paginiPID Control PID Control: Session Outlines & Objectives Session Outlines & ObjectivesOwais100% (2)
- Tuning Workshop PID Controllers: Shell Global SolutionsDocument33 paginiTuning Workshop PID Controllers: Shell Global SolutionsP Pablo CardenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 8Document81 paginiCH 8kfaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- XC9572 In-System Programmable CPLD: Features DescriptionDocument9 paginiXC9572 In-System Programmable CPLD: Features DescriptionManish PushkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Key Terms Associated With PID Temperature ControlDocument8 paginiIntroduction To The Key Terms Associated With PID Temperature ControlBộ Môn DieuKhienhoc100% (1)
- APPLICATION GUIDE - PID FunctionDocument43 paginiAPPLICATION GUIDE - PID FunctioniedmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- UAV Tech - PID Tuning PrinciplesDocument8 paginiUAV Tech - PID Tuning PrinciplesJavier Alonso MadridÎncă nu există evaluări
- User's Manual: FDC 4100 / 7100 / 8100 / 9100 Auto-Tune Fuzzy / PID Process / Temperature ControllerDocument60 paginiUser's Manual: FDC 4100 / 7100 / 8100 / 9100 Auto-Tune Fuzzy / PID Process / Temperature ControllerkmpoulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Strategy, Selective Control SystemDocument10 paginiControl Strategy, Selective Control SystemHutama Putra WibawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual For IA Controlers V6Document60 paginiManual For IA Controlers V6Bharadwaj SubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pid Tuning OperatorDocument18 paginiPid Tuning OperatorkarmoweldingÎncă nu există evaluări
- LG Surucu Ig5Document16 paginiLG Surucu Ig5uyung_mustofaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sitrain s7-1200 PWM - PidDocument46 paginiSitrain s7-1200 PWM - Pidleningfe100% (3)
- PracticalDocument10 paginiPracticalSec ArcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bayer CLINITEC 500 Urine Chemistry Analyzer Service ManualDocument322 paginiBayer CLINITEC 500 Urine Chemistry Analyzer Service Manualtunet1106Încă nu există evaluări
- App PIDDocument12 paginiApp PIDP Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeDocument11 paginiName: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeMayukh BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is PID-Tutorial Overview: Proportional Band Integral DerivativeDocument5 paginiWhat Is PID-Tutorial Overview: Proportional Band Integral Derivativethenu.chandru1042Încă nu există evaluări
- LG VFD Drive ManualDocument16 paginiLG VFD Drive ManualrnkmipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline: DGU3073 Process Instrumentation & ControlDocument66 paginiCourse Outline: DGU3073 Process Instrumentation & ControlAaron ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruction Manual: Pid Based Pressure Loop TrainerDocument28 paginiInstruction Manual: Pid Based Pressure Loop TrainerKiran BennyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Control and Common TermsDocument210 paginiProcess Control and Common TermsGeorge Markas100% (1)
- Ls Inverter Ic5Document20 paginiLs Inverter Ic5lamonahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ge - TC100Document4 paginiGe - TC100cbmanausÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ziegler-Nichols Closed-Loop Tuning Method - Control Notes PDFDocument5 paginiZiegler-Nichols Closed-Loop Tuning Method - Control Notes PDFDraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yokogawa Centum VP Standard OperationDocument16 paginiYokogawa Centum VP Standard OperationAnonymous zMWvcT100% (2)
- Macom@cnt 35 96Document3 paginiMacom@cnt 35 96Cesar GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementing A PID Controller Using A PICDocument15 paginiImplementing A PID Controller Using A PICJavier CharrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operator 2011Document68 paginiOperator 2011romulooliveiraaraujo100% (1)
- Working or Operation of PID ControllerDocument7 paginiWorking or Operation of PID Controllerjohn glenn magnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuzzy Controller X: Instruction ManualDocument98 paginiFuzzy Controller X: Instruction ManualOla SkeikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Release NotesDocument6 paginiRelease Notesikhtiyar ali khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Specifications: GS 33K05D10-50EDocument16 paginiGeneral Specifications: GS 33K05D10-50Esarfaraz055Încă nu există evaluări
- Lambda Tuning TAPPIDocument12 paginiLambda Tuning TAPPIMariana Alejandra Quioy Woods100% (1)
- Closed-Loop Control Toolbox APP-RTT-E-GBDocument11 paginiClosed-Loop Control Toolbox APP-RTT-E-GBLuis Enrique PariapazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DX-610 626 (Eum-L)Document12 paginiDX-610 626 (Eum-L)escuela_danza_2Încă nu există evaluări
- Anti Pid WindupDocument14 paginiAnti Pid WindupgirijashankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process ControlDocument24 paginiProcess ControlEr Shubham RaksheÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Paper PID Control in Vacuum Systems - Final 2020Document4 paginiWhite Paper PID Control in Vacuum Systems - Final 2020giselleÎncă nu există evaluări
- En00w4 2011Document45 paginiEn00w4 2011knightfelix12Încă nu există evaluări
- Features of Practical PID ControllersDocument8 paginiFeatures of Practical PID ControllersGeorge MarkasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsDe la EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosDe la EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGDe la EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesDe la EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibtphem Course Flyer and Application 2020Document3 paginiIbtphem Course Flyer and Application 2020Kj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- E1 NLPDocument2 paginiE1 NLPKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic System Models ShortDocument19 paginiDynamic System Models ShortKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire Safety Basic Series Flyer TB1Document1 paginăFire Safety Basic Series Flyer TB1Kj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- 802Document29 pagini802Kj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Note 2: Configuration Space: ECE5463: Introduction To RoboticsDocument19 paginiLecture Note 2: Configuration Space: ECE5463: Introduction To RoboticsKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Geographical Information System (GIS) Technology in The Control of Buruli Ulcer in GhanaDocument9 paginiApplication of Geographical Information System (GIS) Technology in The Control of Buruli Ulcer in GhanaKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens Overview For Factory Mounted Ps2'SDocument1 paginăSiemens Overview For Factory Mounted Ps2'SKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positioner Set Up & Calibration: Dyna-Flo Control Valve Services LTDDocument1 paginăPositioner Set Up & Calibration: Dyna-Flo Control Valve Services LTDKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positioner Set Up & Calibration: Dyna-Flo Control Valve Services LTDDocument1 paginăPositioner Set Up & Calibration: Dyna-Flo Control Valve Services LTDKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens PS2: Installation and F.A.Q.'SDocument1 paginăSiemens PS2: Installation and F.A.Q.'SKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Upgrade: SiemensDocument1 paginăFunctional Upgrade: SiemensKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens PS2: Installation and F.A.Q.'SDocument1 paginăSiemens PS2: Installation and F.A.Q.'SKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens Overview For Factory Mounted Ps2'S: Figure 7 Display WindowDocument1 paginăSiemens Overview For Factory Mounted Ps2'S: Figure 7 Display WindowKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
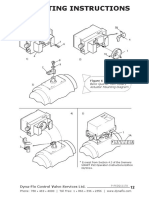
- Mounting Instructions: Basic Quarter Turn Rotary Actuator Mounting DiagramDocument1 paginăMounting Instructions: Basic Quarter Turn Rotary Actuator Mounting DiagramKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9758-Article Text-17770-2-10-20190313Document15 pagini9758-Article Text-17770-2-10-20190313Kj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
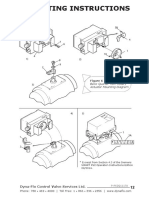
- Mounting Instructions: Basic Quarter Turn Rotary Actuator Mounting DiagramDocument1 paginăMounting Instructions: Basic Quarter Turn Rotary Actuator Mounting DiagramKj_bdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Tyre TechnologyDocument4 paginiGreen Tyre TechnologyAnuj SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rhea Huddleston For Supervisor - 17467 - DR2Document1 paginăRhea Huddleston For Supervisor - 17467 - DR2Zach EdwardsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Schedule World BankDocument249 paginiTechnical Schedule World BankPramod ShastryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bitmicro Case Complainants PositionDocument19 paginiBitmicro Case Complainants PositionNoy SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MetasploitDocument9 paginiMetasploitDhamlo KheralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Land Surveying Chapter 2 Leveling p1Document66 paginiLand Surveying Chapter 2 Leveling p1Azrul ZulwaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Highway EngineeringDocument4 paginiWhat Is Highway EngineeringNagesh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIVPRO - Case Compilation No. 2Document95 paginiCIVPRO - Case Compilation No. 2Darla GreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Semester Question Paper Programming in CDocument8 paginiMid Semester Question Paper Programming in CbakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF of Proposed Museum ProjectDocument145 paginiPDF of Proposed Museum ProjectHarshita ParnamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp.1 (Screening) Group1Document16 paginiExp.1 (Screening) Group1itokki otoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrugated Horn AntennasDocument4 paginiCorrugated Horn AntennasmiusayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unilift de DGDDocument36 paginiUnilift de DGDLove SemsemÎncă nu există evaluări
- National School Building Inventory (NSBI) Encoding For SY 2021-2022Document31 paginiNational School Building Inventory (NSBI) Encoding For SY 2021-2022Renato Rivera100% (1)
- GROZ Tools & Equipment 2018Document3 paginiGROZ Tools & Equipment 2018ayush bansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tween 80 CoADocument1 paginăTween 80 CoATấn Huy HồÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chennai CMDA Master Plan 2026 Volume 3 Sectorial BackgroundDocument270 paginiChennai CMDA Master Plan 2026 Volume 3 Sectorial BackgroundMalathi Kathirvel100% (1)
- Ten Rules of NetiquetteDocument11 paginiTen Rules of NetiquetteAriel CancinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture6 - RPGT Class Exercise QDocument4 paginiLecture6 - RPGT Class Exercise QpremsuwaatiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- School MemoDocument1 paginăSchool MemoBellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corality ModelOff Sample Answer Hard TimesDocument81 paginiCorality ModelOff Sample Answer Hard TimesserpepeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonus 6 - Mastering ASP - NET Core SecurityDocument147 paginiBonus 6 - Mastering ASP - NET Core SecurityDark Shadow100% (1)
- 2011 Hyundai Service FiltersDocument18 pagini2011 Hyundai Service FiltersTan JaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColgateDocument32 paginiColgategargatworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procter & Gamble Global Geothermal Screening Study FINAL 9 Feb 2023Document56 paginiProcter & Gamble Global Geothermal Screening Study FINAL 9 Feb 2023Mohammad Syahir JamaluddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 SpecificationDocument20 pagini2 Specificationprithvi614710Încă nu există evaluări
- PCIB Vs Escolin DigestDocument3 paginiPCIB Vs Escolin DigestsamontedianneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Art. 128 and 129 of The Labor CodeDocument3 paginiDifference Between Art. 128 and 129 of The Labor CodeKarl0% (1)
- BeechDocument1 paginăBeechperovojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco SPARDocument3 paginiEco SPARMohammad LabinÎncă nu există evaluări