Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Eecb351-Exp 9 BPSK
Încărcat de
zawirTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Eecb351-Exp 9 BPSK
Încărcat de
zawirDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LABORATORY
EXPERIMENT 9: BINARY PHASE SHIFT KEYING (BPSK)
A. OBJECTIVE OF EXPERIMENT
1. Investigates the generation and reception of binary phase shift keying (BPSK) waveforms
2. Investigate the effect of noise in BPSK signal
B. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
1. Emona Telecoms –Trainer 101
2. Oscilloscope and Patch leads
3. Dual Channel Oscilloscope
C. SUMMARY OF THEORY
Recalls that ASK uses the digital data’s 1s and 0s to switch a carrier between two amplitudes, while
FSK uses them to switch a carrier between two frequencies. An alternative to these two methods is to
use the data stream’s 1s and 0s to switch the carrier between two phases. This method is called Binary
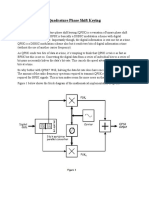
Phase Shift Keying (BPSK). Figure 1 below shows what a BPSK signal looks like time-coincident
with the digital signal that has been used to generate it.
Figure 1
Notice that when the change in logic level causes the BPSK’s signal’s phase to change, it does so by
180O. For example, where the signal is travelling towards a positive peak, the change in logic level
causes it to reverse direction and head back toward the negative peak (and vice versa). BPSK is actually
almost similar like Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSBSC) modulation, but the input message
is digital data stream. That being the case, BPSK generation and the recovery of the data can be handled
by conventional DSBSC modulation and demodulation techniques.
D. PROCEDURE
Part A. – Generating a BPSK signal
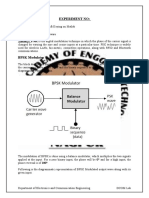
1. Connect the setup as in figure 2 below.
2. Use the oscilloscope to monitor the digital data stream and the BPSK signal’s envelopes.
3. Save the digital signal and the BPSK signal. Determine the output phase for bit 0 and bit 1.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LABORATORY
Figure 2: Block diagram for BPSK generation
Part B. – Demodulating a BPSK signal using product detector
1. Modify the setup according to the block diagram shown in figure 3 below:
Figure 3: Block diagram of BPSK modulation and demodulation
2. Save the digital signal and demodulated BPSK signal waveforms. Compare these two signals
and write your observations.
Part C. – Restoring the recovered data using a comparator
1. Modify the setup in Part B according to the block diagram shown in figure 4.
2. Monitor the digital input signal and the restored digital signal. Do necessary adjustment to obtain
the correct waveforms.
3. Save the Digital signal and the restored digital signal waveforms.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LABORATORY
IN
Tunable
LPF REF
Figure 4: Block diagram of BPSK system
E. RESULTS AND CALCULATION
1. Digital signal and the BPSK signal waveforms.
2. Digital signal and demodulated BPSK signal waveforms.
3. Digital signal and the restored digital signal waveforms.
F. DISCUSSION
1. Explain the function of each block diagram of BPSK system shown in Figure 4.
2. Explain the steps taken to obtained the restored digital signal
3. What type of PSK does not require a carrier recovery circuit for the demodulation?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Commsys Lab EXPERIMENT 8 Full ReportDocument8 paginiCommsys Lab EXPERIMENT 8 Full ReportShaarveen RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 - Binary Phase Shift Keying: NameDocument11 pagini19 - Binary Phase Shift Keying: NameLeux GuillenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hardware and Software Co-Simulation of BPSK Modulation and DemodulationDocument7 paginiHardware and Software Co-Simulation of BPSK Modulation and DemodulationseventhsensegroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPSK DemodDocument3 paginiBPSK DemodNOORÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPSK Modulation Technique FOR Digital Communication: 2 International E-Conference On Emerging Trends in TechnologyDocument3 paginiBPSK Modulation Technique FOR Digital Communication: 2 International E-Conference On Emerging Trends in TechnologyJubin JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 8 and 9Document10 paginiLab 8 and 9zawir gulamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 5 BPSK - Binary Phase Shift KeyingDocument5 paginiLab 5 BPSK - Binary Phase Shift KeyingNo_pidas_CCH_ni_prepa_unamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implement BPSK Modulator and Demodulator Using VHDLDocument9 paginiImplement BPSK Modulator and Demodulator Using VHDLDeekshitha KgÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPSK - Generating and Demodulating Binary Phase Shift Keyed SignalsDocument10 paginiBPSK - Generating and Demodulating Binary Phase Shift Keyed SignalsHayatun NufusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MATLABDocument5 paginiImplementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MATLABseventhsensegroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of Digital Modulation Techniques in Matlab: Virendrakumar V. RautDocument9 paginiImplementation of Digital Modulation Techniques in Matlab: Virendrakumar V. Rautazmi0% (1)
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsDocument28 pagini15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conduct and Analyse BPSK Modulation and Demodulation ExperimentDocument7 paginiConduct and Analyse BPSK Modulation and Demodulation ExperimentSubhashree DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETI 2413 Digital Communication Principles - 2Document20 paginiETI 2413 Digital Communication Principles - 2Kevin NdemoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MatlabDocument5 paginiImplementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MatlabHayatun NufusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 3Document7 paginiExp 3Tejaswini AÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM 8Document11 paginiCM 8Danielle SanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPSK 2012Document6 paginiBPSK 2012Raffi SkÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Manual Final PDFDocument25 paginiDC Manual Final PDFAsma FirdouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadrature Phase Shift Keying - 1Document15 paginiQuadrature Phase Shift Keying - 1RANA RAMEEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASK - Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument15 paginiASK - Amplitude Shift KeyingAbhijith C SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijett V4i9p160Document5 paginiIjett V4i9p160kuzhaloliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comsim Lab FileDocument25 paginiComsim Lab Fileshubham.scribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSK Lab ManualDocument4 paginiPSK Lab ManualSakshi DewadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Analog and Digital CommunicationsDocument93 paginiIntroduction To Analog and Digital CommunicationsK R Shenthil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digtal Modulation TechniquesDocument32 paginiDigtal Modulation TechniquesIka Dwi CahyantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eecb351-Exp 6 PCMDocument5 paginiEecb351-Exp 6 PCMzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Lab 2018 HandoutsDocument22 paginiDC Lab 2018 HandoutssruthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication Systems (ELE 3151) RCSDocument2 paginiCommunication Systems (ELE 3151) RCSAkshat PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trans Lab TemplateDocument8 paginiTrans Lab TemplateEdith CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 467 Experiment3Document10 pagini467 Experiment3mid_cyclone100% (1)
- A Novel Approach For High Speed Multimedia Compression Using 64 Bit Quadrature Amplitude Modulator/DemodulatorDocument7 paginiA Novel Approach For High Speed Multimedia Compression Using 64 Bit Quadrature Amplitude Modulator/DemodulatoreditorinchiefijcsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Communications LaboratoryDocument25 paginiDigital Communications Laboratorysunny756Încă nu există evaluări
- CEE 312 Experiment 5: Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK)Document4 paginiCEE 312 Experiment 5: Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK)Hayatun NufusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phase Shift Keying - PSK: Unit-3 (Digital Modulation and Transmission)Document15 paginiPhase Shift Keying - PSK: Unit-3 (Digital Modulation and Transmission)FyhhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Shift Keying: ObjectivesDocument3 paginiFrequency Shift Keying: ObjectivesSyam SundarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document4 paginiWelcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bai 4 Phu Luc PSK Generator and DemondulatorDocument4 paginiBai 4 Phu Luc PSK Generator and DemondulatorNguyễn Thanh BằngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Part 1Document16 paginiMatlab Part 1rajaranjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sy, Francis Oliver F.-402a-Com01lab-Experiment No. 5Document18 paginiSy, Francis Oliver F.-402a-Com01lab-Experiment No. 5SY, FRANCIS OLIVER F.Încă nu există evaluări
- Exp 6Document9 paginiExp 6Mei Qii100% (1)
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument14 paginiDigital Modulation Techniquesafroz_khan100% (5)
- SIMULATION AND IMPLEMENTATION OF BPSK MODULATORDocument5 paginiSIMULATION AND IMPLEMENTATION OF BPSK MODULATORRiad Al JuboriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Binary Phase Shift KeyingDocument5 paginiStudy of Binary Phase Shift KeyingShivachandran NadarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Document74 paginiPhase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Sumit PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation on System GeneratorDocument3 paginiSimulation of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation on System GeneratorAbhishek SinghaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Material (Question Bank)Document4 paginiCourse Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 ౼ Communication Systems Simulation Using MATLAB: 1. Before the StartDocument5 paginiLab 3 ౼ Communication Systems Simulation Using MATLAB: 1. Before the StartKishore KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 ౼ Communication Systems Simulation Using MATLABDocument5 paginiLab 3 ౼ Communication Systems Simulation Using MATLABmaenfadelÎncă nu există evaluări
- PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY PHASE SHIFT KEYINGDocument46 paginiPONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY PHASE SHIFT KEYINGjovan avery dalluayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manual Autonomous Pvp-12Document57 paginiDepartment of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manual Autonomous Pvp-12Ravi JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter III: BPSK and QPSK Modulation and Demodulation With SimulinkDocument10 paginiChapter III: BPSK and QPSK Modulation and Demodulation With SimulinkMilo SalloumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anupam Term PaperDocument8 paginiAnupam Term PaperAbhishek MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDe la EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4De la EverandDigital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4Evaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignDe la EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3Document8 paginiExperiment 3Nazifi AfanddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test1 SolutionDocument8 paginiTest1 SolutionzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eecb351-Exp 6 PCMDocument5 paginiEecb351-Exp 6 PCMzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 PDFDocument5 paginiExperiment 2 PDFNazifi AfanddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution To Question 1 Test 1 Sem1 2011-2012Document3 paginiSolution To Question 1 Test 1 Sem1 2011-2012zawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 11 LectureDocument13 paginiWeek 11 LecturezawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1 Electrical Power System II Solution UpdatedDocument4 paginiTest 1 Electrical Power System II Solution UpdatedzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals and Systems: University Tenaga NasionalDocument30 paginiSignals and Systems: University Tenaga NasionalzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1: Introduction To Emona 101 Trainer: Communication System LaboratoryDocument6 paginiExperiment 1: Introduction To Emona 101 Trainer: Communication System LaboratoryzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 9 LectureDocument21 paginiWeek 9 LecturezawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communicating Lab FundamentalsDocument7 paginiCommunicating Lab FundamentalsEdward YaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 12 LectureDocument19 paginiWeek 12 LecturezawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systems: Mathematical Model of A Physical ProcessDocument15 paginiSystems: Mathematical Model of A Physical ProcesszawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 8 LectureDocument11 paginiWeek 8 LecturezawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 13 Lecture PDFDocument16 paginiWeek 13 Lecture PDFzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 6 LectureDocument10 paginiWeek 6 LecturezawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Theater February 2010Document91 paginiHome Theater February 2010zawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stereophile January 2010Document147 paginiStereophile January 2010zawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Quick GuideDocument39 paginiElectrical Quick GuideMelvin EsguerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condition Based MaintenanceDocument2 paginiCondition Based MaintenancezawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Campus Design Concept for High-Tech Campus in Gua MusangDocument17 paginiCampus Design Concept for High-Tech Campus in Gua MusangzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP AsgmentDocument6 paginiDSP AsgmentzawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euclidean Vector SpacesDocument48 paginiEuclidean Vector SpaceszawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wide Band LTSA Design and Performance EvaluationDocument83 paginiWide Band LTSA Design and Performance EvaluationKhaqan TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5G Elevator Dedicated Analog Wireless Video Transmission System Model: ST5832DTDocument5 pagini5G Elevator Dedicated Analog Wireless Video Transmission System Model: ST5832DTMark ArandiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4) Ofdma and ScfdmaDocument49 pagini4) Ofdma and Scfdmaavishek2005Încă nu există evaluări
- LTE Features LicensesDocument4 paginiLTE Features LicensesNino BongoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet+HBXX 6516DS VTMDocument3 paginiDatasheet+HBXX 6516DS VTMArturo CadenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless CW NIHAN 21038437Document44 paginiWireless CW NIHAN 21038437Swtzz AmjadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Efficiency and Antenna GainDocument3 paginiAntenna Efficiency and Antenna GainBiswajit MohantyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AG SOHO 60 - 65 Specification SheetDocument2 paginiAG SOHO 60 - 65 Specification SheetClaudia TabaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microstrip feed annular ring slot antenna design and analysisDocument3 paginiMicrostrip feed annular ring slot antenna design and analysisN Abid Ali KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey Paper On Metaterial AntennaDocument17 paginiSurvey Paper On Metaterial AntennasxascÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Lect 10 11Document25 paginiAntenna Lect 10 11dilawar sumraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huawei Parameters Dictionary - Rev2Document43 paginiHuawei Parameters Dictionary - Rev2Iqbal HamdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RW-5510-0A50 Subscriber Unit - Data Sheet: Radwin 5000 HPMPDocument3 paginiRW-5510-0A50 Subscriber Unit - Data Sheet: Radwin 5000 HPMPPatricio Alexandro Calderón ArriagadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noise / Interference Reduction Unit: Instruction ManualDocument40 paginiNoise / Interference Reduction Unit: Instruction ManualJosias CamargoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Point-to-Point Radio - Data Sheet (RW2000/ODU/Alpha/F35/UNI/INT/500M)Document3 paginiPoint-to-Point Radio - Data Sheet (RW2000/ODU/Alpha/F35/UNI/INT/500M)Dave BlackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Private Mobile Radio: Elevated AntennaDocument2 paginiPrivate Mobile Radio: Elevated AntennaJon-Pierre BooysenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kathrein AntennaDocument202 paginiKathrein Antennarezwan2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCX2 190BB PDFDocument2 paginiSCX2 190BB PDFIvan José Campos MadridÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Signal Amplifier CircuitDocument3 paginiGSM Signal Amplifier CircuitK_Hussan0% (2)
- Lecture Notes in Transmission Media and Antenna Systems: Mapua Institute of Technology School of EeceDocument115 paginiLecture Notes in Transmission Media and Antenna Systems: Mapua Institute of Technology School of EecejobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Introduction To Digital Communications - Line Coding, Bandpass Modulation PDFDocument29 pagini3 Introduction To Digital Communications - Line Coding, Bandpass Modulation PDFdragoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22 - Storm H 1Document2 pagini22 - Storm H 1Semih Atalay100% (1)
- Eye Diagram With Raised Cosine FilteringDocument7 paginiEye Diagram With Raised Cosine Filteringpanga_radhakrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: MR918 MR918Document2 paginiProduct Specifications Product Specifications: MR918 MR918TC Cemal GüntürkünÎncă nu există evaluări
- 65° Dualband Directional Antenna: General SpecificationsDocument2 pagini65° Dualband Directional Antenna: General SpecificationsCAMILO SEBASTIAN DAROCH PAQUIENÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC6402 Communication Theory PDFDocument166 paginiEC6402 Communication Theory PDFparantn0% (1)
- PW 2004 08Document80 paginiPW 2004 08alexanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAY 53 DSC VHF RaymarineDocument45 paginiRAY 53 DSC VHF RaymarineOkan TaktakoğluÎncă nu există evaluări
- IC-R100 SSB ModificationDocument13 paginiIC-R100 SSB ModificationSergheyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selex Model - 1118A - 1119A - DME - Datasheet ANSDocument2 paginiSelex Model - 1118A - 1119A - DME - Datasheet ANSLê Khắc HưngÎncă nu există evaluări