Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technologies: Science, Technology Assessment, and Analytics
Încărcat de
joel enciso enekeDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technologies: Science, Technology Assessment, and Analytics
Încărcat de
joel enciso enekeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science, Technology Assessment,
SEPTEMBER 2019
and Analytics
WHY THIS MATTERS
Distributed ledger technology (e.g. blockchain) allows
users to carry out digital transactions without the need
SCIENCE & TECH SPOTLIGHT: for a centralized authority. It could fundamentally
BLOCKCHAIN & DISTRIBUTED
change the way government and industry conduct
business, but questions remain about how to mitigate
fraud, money laundering, and excessive energy use.
LEDGER TECHNOLOGIES
/// THE TECHNOLOGY
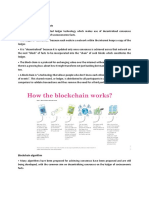
What is it? Distributed ledger technologies (DLT) like blockchain are a
secure way of conducting and recording transfers of digital assets without
the need for a central authority. DLT is “distributed” because multiple
participants in a computer network (individuals, businesses, etc.), share
and synchronize copies of the ledger. New transactions are added in a
manner that is cryptographically secured, permanent, and visible to all
participants in near real time.
Figure 2. How blockchain, a form of distributed ledger technology, acts as a means of
payment for cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are a digital representation of value and
represent the best-known use case for DLT. The regulatory and legal
frameworks surrounding cryptocurrencies remain fragmented across
Figure 1. Difference between centralized and distributed ledgers. countries, with some implicitly or explicitly banning them, and others
allowing them.
How does it work? Distributed ledgers do not need a central, trusted
authority because as transactions are added, they are verified using what In addition to cryptocurrencies, there are a number of other efforts
is known as a consensus protocol. Blockchain, for example, ensures the underway to make use of DLT. For example, Hyperledger Fabric is
ledger is valid because each “block” of transactions is cryptographically a permissioned and private blockchain framework created by the
linked to the previous block so that any change would alert all other Hyperledger consortium to help develop DLT for a variety of business
users. With an agreement on that history, users may then conduct a new applications. The consortium is made up of companies such as Airbus,
transaction with a shared understanding of who has which resource. Cisco, American Express, IBM, and Intel.
Distributed ledgers can be either “permissioned” or “unpermissioned.” /// OPPORTUNITIES
With unpermissioned ledgers, which are generally public, any participant
can conduct a transaction. Permissioned ledgers may or may not be ■■ Transparency. Because any user can view the ledger, DLT may
public, but only trusted users can conduct transactions. result in benefits such as reduced corruption.
How mature is it? Businesses have been using ledgers to record ■■ Reduced labor costs. DLT reduces or eliminates the need for
transactions for thousands of years, and a defining characteristic of such human workers to track data.
ledgers was their reliance on central management. Furthermore, DLT is ■■ Data quality and reliability. Transaction information is automatically
not a new technology, but an innovative way of using existing, mature generated by a computer, which may reduce errors.
technologies. In October 2008, an unknown author using the name
Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper called “Bitcoin – A Peer-to- ■■ Wide applicability. DLT is being explored for use across many
Peer Electronic Cash System”, which is credited as the first theoretical sectors, including supply chain and logistics, news, energy,
framework of a DLT. In January 2009 the service the paper described was healthcare, and government. For example, Target built a system now
launched. known as ConsenSource to verify products are sourced sustainably.
GAO-19-704SP Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technologies
Science, Technology Assessment,
and Analytics
The New York Times created the News Provenance Project to ■ Lack of regulation. Businesses may express concern about making
explore a blockchain-based system for recording and sharing investments in DLT because of uncertainties surrounding how such
information published by news organizations. technologies might be regulated. While there have been initial efforts
to regulate cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, much less has been
/// CHALLENGES
done around other DLT use cases.
■ Excessive energy usage. Some uses of DLT can be costly to /// POLICY CONTEXT AND QUESTIONS
operate. For example, cryptocurrencies using “proof-of-work”
consensus protocols (also known as “mining”) require large amounts DLT use across many sectors is increasing, but challenges remain to
of computing power and energy to generate new units of currency. widespread adoption. Some key questions for consideration include:
■ Collusion. Security of the network relies on the consensus protocol ■ In what situations is DLT useful, and when should it be avoided or
that maintains the ledger, and research has shown that users who used with caution?
collude could gain enough influence to manipulate the ledger to their
benefit and gradually disrupt the protocol. ■ To what extent can DLT be used to facilitate illegal activities, and
how might policymakers mitigate such use?
■ Security. Entities using DLT will need to ensure data stored on a
permissioned distributed ledger is not accessible to outside actors. ■ How are federal agencies evaluating and using DLT.
Additionally, holders of cryptocurrency can have their digital wallets /// SELECTED GAO WORK
hacked and their currency stolen.
■ Financial Technology: Additional Steps by Regulators Could Better
■ Permanence. While the permanence of transactions may be a core
Protect Consumers and Aid Regulatory Oversight, GAO-18-254
strength of DLT, it can also be a weakness should an entity find that
it needs to regularly correct errors in its ledger, as it would be unable ■ Trends Affecting Government and Society: United States
to easily do so with DLT. Government Accountability Office Strategic Plan 2018-2023, GAO-
18-396SP
■ Lack of transparency. Because DLT can be used without a
central authority, governments may feel uncomfortable allowing ■ Financial Technology: Information on Subsectors and Regulatory
cryptocurrencies (or other DLT) to be used as a method of exchange Oversight, GAO-17-361
or contracting, since they cannot easily be tracked and could be ■ Virtual Currencies: Emerging Regulatory, Law Enforcement, and
used to facilitate illicit activity (such as tax evasion and money Consumer Protection Challenges, GAO-14-496
laundering).
/// REFERENCES
Bank for International Settlements, “BIS Quarterly Review September 2017: International
banking and financial market developments.” (2017), 58-71.
Congressional Research Service, “Blockchain: Background and Policy Issues.” (2018).
Olnes, Svein. “Blockchain in government: Benefits and implications of distributed ledger
technology for information sharing.” Government Information Quarterly 34: 355-364 (2017).
United Kingdom Government Office of Science “Distributed ledger technology: beyond
blockchain.” (2019).
Figure 3. Permanence and lack of transparency and regulation raise concerns about
adoptability.
GAO SUPPORT:
GAO meets congressional information needs in several ways, including by
providing oversight, insight, and foresight on science and technology issues.
GAO staff are available to brief on completed bodies of work or specific reports This document is not an audit product and is subject to revision based on continued
and answer follow-up questions. GAO also provides targeted assistance on advances in science and technology. It contains information prepared by GAO
specific science and technology topics to support congressional oversight activities to provide technical insight to legislative bodies or other external organizations.
and provide advice on legislative proposals. This document has been reviewed by the Chief Scientist of the U.S. Government
Accountability Office.
Timothy M. Persons, Ph.D., Chief Scientist, personst@gao.gov
Staff Acknowledgments: William Carrigg (Assistant Director), Jon Menaster
(Analyst-in-Charge), Anika McMillon, Ben Shouse, and Jessica Smith.
GAO-19-704SP Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technologies
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Covered California Grants: For Outreach To IndividualsDocument2 paginiCovered California Grants: For Outreach To IndividualsKelli RobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain in LogisticsDocument28 paginiBlockchain in Logisticsrami.sweidane125100% (4)
- Block Chain FinalDocument15 paginiBlock Chain FinalRomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ( (Sig1 Es :signer1:signature) )Document8 pagini( (Sig1 Es :signer1:signature) )SUNNY SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- JPM - Decrypting CryptocurrenciesDocument31 paginiJPM - Decrypting CryptocurrenciesEduardo Luis Dourado100% (2)
- SECTOR 19 001 Blockchain LowresDocument28 paginiSECTOR 19 001 Blockchain LowreshishamuddinohariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformation Strategy Update: UBS Sydney Investor Session Presentation 18 March 2021Document34 paginiTransformation Strategy Update: UBS Sydney Investor Session Presentation 18 March 2021joel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Blockchain Technology On Financial Technology in NigeriaDocument7 paginiImpact of Blockchain Technology On Financial Technology in NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Assets - Tokenized Revolution in Financial ServicesDocument18 paginiDigital Assets - Tokenized Revolution in Financial ServicesSoluciones en BlockchainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whitepaper CardanoDocument15 paginiWhitepaper CardanoSicoe Denisa- IoanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- @poli@ $hack Instagram Account$ #2020# # (Hack Insta Using Our Website #EASY) (NO Verification Instant Access) # (HACK INSTAGRAM)Document3 pagini@poli@ $hack Instagram Account$ #2020# # (Hack Insta Using Our Website #EASY) (NO Verification Instant Access) # (HACK INSTAGRAM)joel enciso eneke0% (1)
- Innovation Blockchain RevolutionDocument39 paginiInnovation Blockchain RevolutionSengupta SuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aristotle PDFDocument6 paginiAristotle PDFAnonymous p5jZCn100% (1)
- Applications of Blockchain Technology in Banking FinanceDocument18 paginiApplications of Blockchain Technology in Banking FinancemonuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q2 2017 ColliersQuarterly JakartaDocument46 paginiQ2 2017 ColliersQuarterly JakartadetrutamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deutsche Bank CaseDocument3 paginiDeutsche Bank CaseVamsee Krishna Reddy Bheri67% (3)
- SECTOR 19 001 Blockchain LowresDocument21 paginiSECTOR 19 001 Blockchain LowresM Tariqul Islam MishuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distributed Ledger Technology Blockchains and Identity 20180907iiDocument34 paginiDistributed Ledger Technology Blockchains and Identity 20180907iipriya reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roland Berger Blockchain A Promising Technology For The Belgian Public AdministrDocument16 paginiRoland Berger Blockchain A Promising Technology For The Belgian Public AdministrKamal TabajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain RevolutionDocument36 paginiBlockchain RevolutionLucky GalvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- V15-028 Blockchain: Saved by The EnterpriseDocument17 paginiV15-028 Blockchain: Saved by The EnterprisetabbforumÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMF (FinTech Notes) Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms - A Primer For SupervisorsDocument18 paginiIMF (FinTech Notes) Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms - A Primer For SupervisorsMuning AnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain and FintechDocument10 paginiBlockchain and FintechThilakPathirageÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP Sas 165 11Document14 paginiMP Sas 165 11Box VoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- GNAT 10849001 Written Question AnsDocument7 paginiGNAT 10849001 Written Question Anshamid116422Încă nu există evaluări
- Sfig Blockchain Report PDFDocument40 paginiSfig Blockchain Report PDFbablu boroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain in USADocument34 paginiBlockchain in USASubhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain NFTA Information Sheet - Standards - Org.au OurOrganisation Events DocumentsDocument4 paginiBlockchain NFTA Information Sheet - Standards - Org.au OurOrganisation Events DocumentsyezdiarwÎncă nu există evaluări
- ePIQ WhitepaperDocument4 paginiePIQ Whitepaperابوالحروف العربي ابوالحروفÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ey Industrializing Blockchain in AseanDocument17 paginiEy Industrializing Blockchain in AseanVarun MittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distributed Ledger Technology For Securities Clearing and Settlement: Benefits, Risks, and Regulatory ImplicationsDocument25 paginiDistributed Ledger Technology For Securities Clearing and Settlement: Benefits, Risks, and Regulatory ImplicationsIsaac GoldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain Beyond BitcoinDocument3 paginiBlockchain Beyond BitcoinVladimir Guimarães Farias SodréÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating How Blockchain Can Transform The Pharmaceutical and Healthcare IndustriesDocument9 paginiEvaluating How Blockchain Can Transform The Pharmaceutical and Healthcare IndustriesBeate IgemannÎncă nu există evaluări
- DAG NiceDocument20 paginiDAG NiceِAbbas Fadhil WahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procurement in The Philippine Government Through A Proposed Smart Contract Framework With I.T. PolicyDocument5 paginiProcurement in The Philippine Government Through A Proposed Smart Contract Framework With I.T. PolicyOA-6, Mary Anne Retulin, Civ HRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchains Uncut:: Risks, Rewards & RegulationDocument21 paginiBlockchains Uncut:: Risks, Rewards & RegulationHelielton MainardesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dex: A Dapp For The Decentralized Marketplace: Chris DaiDocument12 paginiDex: A Dapp For The Decentralized Marketplace: Chris Daigamers305Încă nu există evaluări
- Materials Today: Proceedings: T. Murugajothi, R. RajakumariDocument7 paginiMaterials Today: Proceedings: T. Murugajothi, R. RajakumariKarthick NpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Chain in Banking SectorDocument6 paginiBlock Chain in Banking SectoraanilarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Blockchain Technologies and Their Uses PDFDocument3 paginiTypes of Blockchain Technologies and Their Uses PDFmigdonÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of The Cumberlands Final Paper ITS 832 - Info Tech in A Global EconomyDocument10 paginiUniversity of The Cumberlands Final Paper ITS 832 - Info Tech in A Global EconomySrinivas AdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain Implementation in Todays Security Settlement Process 2Document26 paginiBlockchain Implementation in Todays Security Settlement Process 2isasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 Securities Settlement Paper SUBMISSION...Document32 pagini20 Securities Settlement Paper SUBMISSION...GANESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Transformation-Block ChainDocument12 paginiDigital Transformation-Block ChaintemozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document8 paginiUnit 3TarynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 6Document46 paginiLec 6Samuel RomanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feasibility StudyDocument29 paginiFeasibility StudyKhairun NatsirunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applicability of Blockchain in OrganizationDocument12 paginiApplicability of Blockchain in Organizationronaldweasley6Încă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain For Fragile States, The Good, The Bad and The UglyDocument8 paginiBlockchain For Fragile States, The Good, The Bad and The UglyCristhian J Mendoza VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 112.blockchaintechnologgy OverviewDocument13 pagini112.blockchaintechnologgy OverviewManthan JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Blockchain Technology in Banking & Finance: February 2018Document18 paginiApplications of Blockchain Technology in Banking & Finance: February 2018MallikarjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Bad and The Ugly BlockchainDocument8 paginiThe Bad and The Ugly BlockchainSam TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain Business ModelsDocument19 paginiBlockchain Business ModelssarmascribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Answer What A 773015 ndx-1Document4 paginiQuick Answer What A 773015 ndx-1Radeea AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain in The Cyber World: What Is A BlockchainDocument4 paginiBlockchain in The Cyber World: What Is A BlockchainSumit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain Technology: Student NameDocument12 paginiBlockchain Technology: Student Namerabia basriÎncă nu există evaluări
- EY Building Blocks of The FutureDocument5 paginiEY Building Blocks of The FutureManuel VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain For Construction WhitepaperDocument12 paginiBlockchain For Construction WhitepaperMaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impacts of Blockchain On Accounting Profession.: Name 1Document9 paginiImpacts of Blockchain On Accounting Profession.: Name 1fredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Blockchain Technology in Banking & Finance: February 2018Document18 paginiApplications of Blockchain Technology in Banking & Finance: February 2018AnishRanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLT Legal Challenges - Short EssayDocument1 paginăDLT Legal Challenges - Short Essaya.drapataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecbop172 enDocument35 paginiEcbop172 enTBP_Think_TankÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC Unit I, Ii, IiiDocument22 paginiBC Unit I, Ii, Iiiss9933575Încă nu există evaluări
- It Audit Fundamentals What To Audit? Format Journal 1. Abstract Past Tense, Short Summary of The Whole Paper 2. Intro General ObjectiveDocument8 paginiIt Audit Fundamentals What To Audit? Format Journal 1. Abstract Past Tense, Short Summary of The Whole Paper 2. Intro General ObjectiveMaan RetulinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic, Qualitative Scoring of The Clock Drawing Test (CDT) Based On U Net, CNN and Mobile Sensor DataDocument33 paginiAutomatic, Qualitative Scoring of The Clock Drawing Test (CDT) Based On U Net, CNN and Mobile Sensor Datajoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithms For Drawing Planar Graphs: Algoritmen Voor Het Tekenen Van Planaire GrafenDocument237 paginiAlgorithms For Drawing Planar Graphs: Algoritmen Voor Het Tekenen Van Planaire Grafenjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- External Scholarship OpportunitiesDocument5 paginiExternal Scholarship Opportunitiesjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customs External Policy Refunds and Drawbacks: Effective 30 July 2021Document20 paginiCustoms External Policy Refunds and Drawbacks: Effective 30 July 2021joel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Children: The Physical Education Class Perceived by Schoolchildren From 6 To 8 Years Old Expressed Through DrawingsDocument15 paginiChildren: The Physical Education Class Perceived by Schoolchildren From 6 To 8 Years Old Expressed Through Drawingsjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide Line To Follow During Preparation of Autocad Drawing For Online Building Plan Sanction Under Eodb U/S 393ADocument11 paginiGuide Line To Follow During Preparation of Autocad Drawing For Online Building Plan Sanction Under Eodb U/S 393Ajoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Arts: Drawing & Painting: Recommended Four-Year Plan (Fall 2021)Document2 paginiVisual Arts: Drawing & Painting: Recommended Four-Year Plan (Fall 2021)joel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forticlient: 7.0 Visibility and Controls For Zero Trust Network Access (Ztna) and Secure Access Service Edge (Sase)Document6 paginiForticlient: 7.0 Visibility and Controls For Zero Trust Network Access (Ztna) and Secure Access Service Edge (Sase)joel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- This How-To Guide Highlights Specific DAS Construction Services PDF Formatting RequirementsDocument31 paginiThis How-To Guide Highlights Specific DAS Construction Services PDF Formatting Requirementsjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Prize Drawings: Weekly, One Student Will Win The Choice of One of The Following PrizesDocument1 paginăWeekly Prize Drawings: Weekly, One Student Will Win The Choice of One of The Following Prizesjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warranty Information: MODEL 12816Document8 paginiWarranty Information: MODEL 12816joel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT 92 - 7KE Cargo/Pole Trailer Brooks Brothers Trailers: CapacityDocument2 paginiPT 92 - 7KE Cargo/Pole Trailer Brooks Brothers Trailers: Capacityjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Conditions: Accredited Mass Management Scheme (AMMS) Prime Mover, Trailer CombinationsDocument17 paginiOperating Conditions: Accredited Mass Management Scheme (AMMS) Prime Mover, Trailer Combinationsjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oracle Linux 7: Security GuideDocument74 paginiOracle Linux 7: Security Guidejoel enciso eneke100% (1)
- SAP Cloud Platform Integration Security GuideDocument42 paginiSAP Cloud Platform Integration Security Guidejoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Command Center Evaluation GuideDocument7 paginiSecurity Command Center Evaluation Guidejoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Container Runtime Security: User GuideDocument44 paginiContainer Runtime Security: User Guidejoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covid-19 Update: Age 65+ Phase 1ADocument3 paginiCovid-19 Update: Age 65+ Phase 1Ajoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplify and Strengthen Your Strategy With Intrinsic SecurityDocument9 paginiSimplify and Strengthen Your Strategy With Intrinsic Securityjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep LearningDocument1 paginăTowards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learningjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Detail Interpretation of Ethical HackingDocument8 paginiThe Detail Interpretation of Ethical Hackingjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Game Notes: Kyle AndersonDocument23 paginiGame Notes: Kyle Andersonjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly Instructions: Important, Retain For Future Reference. Read CarefullyDocument15 paginiAssembly Instructions: Important, Retain For Future Reference. Read Carefullyjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Club Chairs: Important, Retain For Future Reference. Read CarefullyDocument15 paginiClub Chairs: Important, Retain For Future Reference. Read Carefullyjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22 SssDocument675 pagini22 Sssjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- As at 31 August 2020 Subject To Change at The Discretion of Commsec Margin Lending LVR Changes Changes Since The Last Approved Securities List Was Published Are Outlined in The Below TableDocument4 paginiAs at 31 August 2020 Subject To Change at The Discretion of Commsec Margin Lending LVR Changes Changes Since The Last Approved Securities List Was Published Are Outlined in The Below Tablejoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing Cyber Risk in M&A: Unearth Hidden Costs Before You Pay ThemDocument12 paginiAssessing Cyber Risk in M&A: Unearth Hidden Costs Before You Pay Themjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuxictr: An Open Benchmark For Click-Through Rate PredictionDocument9 paginiFuxictr: An Open Benchmark For Click-Through Rate Predictionjoel enciso enekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NRDA NOC Received For A FileDocument2 paginiNRDA NOC Received For A FileMuktesh SwamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inc 2Document19 paginiInc 2MathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study On Capital GainDocument2 paginiCase Study On Capital GainMeghna PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karnataka Act No. 26 of 2020 The Karnataka Epidemic Diseases Act, 2020Document9 paginiKarnataka Act No. 26 of 2020 The Karnataka Epidemic Diseases Act, 2020Rajendra PÎncă nu există evaluări
- January Philippine Historical EventsDocument5 paginiJanuary Philippine Historical Eventsjeric mayugbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Data Sheet: Magnafloc LT25Document9 paginiSafety Data Sheet: Magnafloc LT25alang_businessÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIChE Code of Ethics and Code of Good Governance Alignment MatrixDocument10 paginiPIChE Code of Ethics and Code of Good Governance Alignment MatrixBabeejay2Încă nu există evaluări
- Rutherford County BallotsDocument8 paginiRutherford County BallotsUSA TODAY NetworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDS Salisbury Rub Out TowellettesDocument8 paginiSDS Salisbury Rub Out TowellettesMarco Bonilla MartínezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Wall Street Journal - 19.09.2019Document42 paginiThe Wall Street Journal - 19.09.2019Nadia BustosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CGRF Greater NOIDA Finds Builders Overcharging For ElectricityDocument12 paginiCGRF Greater NOIDA Finds Builders Overcharging For ElectricitydeegaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rosales Balm105 1Document4 paginiRosales Balm105 1Allyssa Melan RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civrev1 CasesDocument264 paginiCivrev1 Casessamjuan1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Penn Exemption Rev-1220Document2 paginiPenn Exemption Rev-1220jpesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramiro, Lorren - Money MarketsDocument4 paginiRamiro, Lorren - Money Marketslorren ramiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deposits: CA. Pramod JainDocument23 paginiDeposits: CA. Pramod JainNishant RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equatorial Realty v. MayfairDocument33 paginiEquatorial Realty v. Mayfairfjl_302711Încă nu există evaluări
- Teachers Service Commission: Tender Document For Procurement of ServicesDocument56 paginiTeachers Service Commission: Tender Document For Procurement of ServicesinyasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiffusionDocument15 paginiDiffusionRochie DiezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contract Act 4 PDFDocument18 paginiContract Act 4 PDFyisjoxaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STHBDocument4 paginiSTHBketanrana2Încă nu există evaluări
- National Law University Odisha: Labour Law Project On A Critical Note On Banglore Water Supply CaseDocument19 paginiNational Law University Odisha: Labour Law Project On A Critical Note On Banglore Water Supply CaseSarthak AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- GOOD MORAL CertDocument19 paginiGOOD MORAL CertUno Gime PorcallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diploma in Business MPU2422: Teamwork Cohesion Development Group 1: The Perspective of Diploma in Business Students Towards Racism in America Youtube LinkDocument6 paginiDiploma in Business MPU2422: Teamwork Cohesion Development Group 1: The Perspective of Diploma in Business Students Towards Racism in America Youtube LinkJiunHongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legislative IssuesDocument323 paginiLegislative IssuesOur CompassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartolomeo Vanzetti The Story of A Proletarian Life A4Document36 paginiBartolomeo Vanzetti The Story of A Proletarian Life A4James SlaughterÎncă nu există evaluări