Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Anatomy-The Study of Biological Form Physiology - Study of Bio Functions
Încărcat de
izabelle dolores0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări4 paginiThis document discusses the levels of organization in living organisms from the simplest protoplasmic level to the complex organ system level. It also summarizes the main tissue types found in animals including epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. Each tissue type has multiple subtypes and contains different cell types that allow organisms to have structure and carry out specialized functions.
Descriere originală:
lecture notes
Titlu original
animal cells
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document discusses the levels of organization in living organisms from the simplest protoplasmic level to the complex organ system level. It also summarizes the main tissue types found in animals including epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. Each tissue type has multiple subtypes and contains different cell types that allow organisms to have structure and carry out specialized functions.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări4 paginiAnatomy-The Study of Biological Form Physiology - Study of Bio Functions
Încărcat de
izabelle doloresThis document discusses the levels of organization in living organisms from the simplest protoplasmic level to the complex organ system level. It also summarizes the main tissue types found in animals including epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. Each tissue type has multiple subtypes and contains different cell types that allow organisms to have structure and carry out specialized functions.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
Anatomy- the study of biological form planes through the
Physiology- study of bio functions longitudinal axis
Life is characterized by hierarchal levels of 3. Biradial
organization, each with emergent properties Only to planes through
longitudinal axis
4. Bilateral
Can be divided along
sagittal plane (right and left
halves)
5. Segmentation
Metamerism (metamere-
segments)
Serial repetition of body
segments
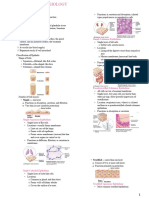
Levels of organization in organismal Types of tissue
complexity REPRODUCTIVE
1. Protoplasmic 1. Sperm
Unicellular organisms 2. Egg/oocyte
All life functions are
confined within the SOMATIC TISSUE
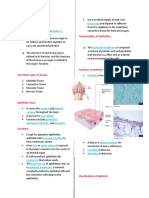
boundaries of a single cell Epithelial
Protoplasm is Covers the outside of the body and
differentiated lines organs and cavities within the
Ex paramecium body
2. Cellular Compact; occurs in sheets of tightly
Aggregation of cells that packed cells
are functionally Little intercellular substance
differentiated Polarized (apical, basal)
A division of labor is o Apical- exposed to air or
evident fluid lumen, structures:
3. Cell tissue microvilli, cilia, flagella
Aggregation of similar cells o Basal
into definite patterns of Have 3 main types of intercellular
layers, thus becoming a links
tissue o Tight junctions- prevents
4. Tissue-organ leakage of ecf
An aggregation of tissues o Desmosomes- anchoring
into organs junction, fasten cells into
5. Organ-system rivets, reinforced by keratin
Organs work together to o Gap junctions-
perform some function communicating junction
Systems are associated Types according to layering
with basic body functions o Simple - single layer cells
Animal Body Plains o Stratified- many layers
Symmetry o Pseudostratified- appear as
- Refers to balanced proportions multi layered but made up
1. Spherical of a single layer only
any plane
2. Radial
body can be div into similar
halves by more than two
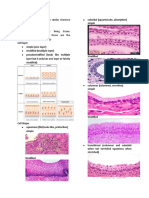
Type according to shape o Endothelium- lining of
o Cuboidal blood and lymph vessels
o Squamous Connective
o Columnar Mechanical support
Types: Exchange of metabolites between
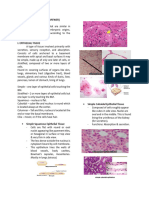
o Simple squamous- form a blood and tissues
continuous delicate lining Storage of energy reserve
of blood capillaries, lungs Protection against infection; repair
etc; permits passive Ecm is embedded in liquid or jelly
diffusion like substance
o Stratified squamous- 2 to Types of cells
many layers, adapted to Fixed
mech abrasion, basal Fibroblast/ fibrocyte
undergo continuous mitotic Mesenchymal
div Adipose
o Simple columnar- found on Fixed microphage
highly absorptive surfaces Wandering (from blood)
o Stratified columnar- at least White blood cells
two layers, in anorectal Amorphous ground substance
region & salivary duct o Glycosaminoglycans- ex
o Simple cuboidal- lines small chondroitin sulphate
ducts and tubules, o Permit diffusion of gases,
secretory and absorptive water substances,
functions nutrients, wastes
o Pseudostratified- single o Important for places with
layer, in vertebrates: forms absence of small blood
a mucous membrane vessels
o Transitional- accommodate Types of connective fibers
great stretching, found in o Collagenous fibers
urinary tract and bladder Made up of
o Glandular- absorb or collagen
secrete chemical solutions, Flexible, non-
can be exocrine, endocrine elastic, does not
or mixed tear easily when
pulled lengthwise
o Elastic
Elastin
Rubbery
o Reticular
Very thin and
branched
Collagen
Joins connective
tissue to adjacent
tissues
Special terms
o Mesothelium- squamous Major types of connective tissue
cells lining serous cavities Fibrous/dense
such as peritoneal and - Dense due to its large number of
pleural activities and lining collagenous fibers
visceral organs
- Fibers are organized into parallel - Plasma
bundles Proteins: fibrinogen, albumin,
- Forms tendons and ligaments globulin
Loose Supplies for cells: glucose, fats,
- Binds epithelia to underlying tissue amino acids, salts
- Functions as packing materials Cell products: enzyme,
holding organs in place hormones, antibodies
- Has all three fiber types Wastes: urea, uric acid
- Two cell types predominantly: - Formed elements- produced by
fibroblasts and macrophages bone marrow
Types of white blood cells
Adipose Granulocyte
- Specialized form of loose tissue that Neutrophil- phagocytic
stores fat in adipose cells Eosinophil
- Pads and insulates body and stores Basophil- inflammatory
fuel as fat molecules
Cartilage Agranulocyte
- Has abundance of collagenous fibers Lymphocyte- antibody prod
embedded in a rubbery matrix made monocyte
of chrondroitin sulphate
- Chondrocytes secrete collagen and Muscular
chondroitin sulphate composed of muscle fibers that are
capable of contracting when
Types: stimulated by nerve impulses
Hyaline- sig proportion of collagenous fibers, most abundant tissue in most
nose larynx trachea, support and animals
reinforcement muscle contraction accounts for
most of the energy consuming
Elastic- contains fine collagenous fibers and cellular work in active animals
many elastic fibers, external ears epiglottis Types
Skeletal
Fibrocartilage- many large collagenous fibers, - Cylindrical and striated cells with
absorbs compression shock multiple nuclei (syncytial)
- Occurs in muscles attached to
Bone skeleton
- Mineralized connective tissue - Single innervation attached to
- Osteoblasts are cells that deposit a skeleton
matrix of collagen - Voluntary movement
- Calcium, magnesium and phosphate Smooth muscle
ions combine and harden within the - Spindle-shaped cells, single nucleus
matrix into the mineral - Have no striations
hydroxyapatite - Double innervation by para
- Hard mineral + collagen = harder sympathetic nervous system;
than cartilage involuntary
- Blood vessel and digestive tract
Blood walls
- Composition: - For movement of substances in
55% plasma (water, salts dissolved lumens of body
proteins)
45% formed elements (erythrocytes,
leukocytes, platelets)
Cardiac muscle
- Cylindrical but branching striated
cells, with single nucleus
- Double innervation by para and
sympa ns; involuntary
- Occurs in wall of heart
- For pumping of blood
Nervous Tissue
Irritability and conductivity
Senses stimuli and transmits signals
Neurons= functional unit; consists
of cell body, dendrites and axons
o Dendrite- transmits nerve
impulses from their tips
toward the rest of the
neuron; receive stimuli
o Axon- transmits impulses
toward another neuron or
effector (muscle cell)
Types of neurons:
o Sensory (afferent)
o Motor (efferent)
o Interneuron
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Human Machine by RL Bijlani, SK ManchandaDocument176 paginiThe Human Machine by RL Bijlani, SK ManchandaMUSKANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Tissues: Lesson 02Document33 paginiTypes of Tissues: Lesson 02DASH100% (2)
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 paginiTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Biochemistry IntroductionDocument72 paginiBiochemistry IntroductionNatasha Jean100% (1)
- Biology 1: Learning Activity SheetDocument184 paginiBiology 1: Learning Activity SheetJohn joseph Ursulum100% (1)
- Ex 5Document7 paginiEx 5leanicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biospect 21 Manual - EngDocument47 paginiBiospect 21 Manual - EngOBERON-INTROSPECT-BIOSPECT100% (1)
- Transes Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Document6 paginiTranses Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Reign Saplaco100% (1)
- Human TissueDocument47 paginiHuman TissueAngelo Cadenas75% (4)
- 0893 Lower Secondary Science Stage 7 Scheme of Work - tcm143-595695Document103 pagini0893 Lower Secondary Science Stage 7 Scheme of Work - tcm143-595695manoj0% (1)
- LO 1 (Week 2) Cell Structure and Organisation (Cheng)Document4 paginiLO 1 (Week 2) Cell Structure and Organisation (Cheng)nit33vÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Document5 paginiMc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Karl Devin CorderoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY Tissue W AnnotationsDocument6 paginiANAPHY Tissue W AnnotationssamanthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConnectiveDocument12 paginiConnectiveGwyneth NovesterasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 paginiShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 2Document18 paginiGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell TypesDocument8 paginiCell TypesMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.Încă nu există evaluări
- Tissue Gen Bio ReviewerDocument9 paginiTissue Gen Bio ReviewerAlfred CariñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- E1.3 Body TissuesDocument5 paginiE1.3 Body TissueshzntrpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDocument6 paginiEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY Lec Session #3 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document13 paginiANAPHY Lec Session #3 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Tissues: Microscopic Human Structural BiologyDocument2 paginiIntroduction To Tissues: Microscopic Human Structural BiologyKeith Arleigh JosonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forms and Characteristics of Epithelial Cells: Basement MembranesDocument5 paginiForms and Characteristics of Epithelial Cells: Basement MembranesA18- Jessa Mae DayagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology Notes 2Document13 paginiHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epithelium: DR - Iman NabilDocument6 paginiEpithelium: DR - Iman Nabilsiti aisyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesDocument10 paginiThe Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesgilissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues & Membranes: The Relationship Between Structure and Function of Epithelial TissuesDocument3 paginiTissues & Membranes: The Relationship Between Structure and Function of Epithelial Tissueskyla columnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumDocument3 paginiEpithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumVanyVillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- MICRO - 1S07 Epithelial CellsDocument4 paginiMICRO - 1S07 Epithelial CellsKeith Arleigh JosonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY Lec Session #3 - SASDocument12 paginiANAPHY Lec Session #3 - SASFherry Mae UsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP03-TissuesDocument12 paginiAP03-TissuesLyn YmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal TissuesDocument2 paginiAnimal TissuesMami AmihanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RIVERA - WEEK 4 LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues & Integumentary SystemDocument9 paginiRIVERA - WEEK 4 LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues & Integumentary SystemMichelle MunozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Connective Tissues 2Document71 paginiConnective Tissues 2Asma Aijaz100% (1)
- Botany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Document12 paginiBotany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Patricia GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionDocument7 paginiEpithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- epiTHITE TissueDocument10 paginiepiTHITE TissueDandel G. GollosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues: ClassDocument4 paginiTissues: ClassShail KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZooLab ActDocument9 paginiZooLab ActdatoysybilrussmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Connective Tissue ReviewerDocument4 paginiThe Connective Tissue ReviewerSasukeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphy Mia Rev3Document5 paginiAnaphy Mia Rev3antonettevegamia3Încă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide Tissues and MembraneDocument19 paginiStudy Guide Tissues and MembraneSheam MarcosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology of Cell and Tissue: Chapter 7: TissuesDocument53 paginiHistology of Cell and Tissue: Chapter 7: TissuesAmirah AdlinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionDocument9 paginiAct05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionPaula Nicole AlanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HistologyDocument13 paginiHistologyangelo davidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes-Structural Organisation in Animals NewDocument35 paginiNotes-Structural Organisation in Animals NewKisna guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument9 paginiChapter 4 TissuesBaylon, MarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 TissuesDocument3 paginiModule 2 TissuesRaphael SevillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewr Tissue CompleteDocument4 paginiReviewr Tissue CompleteJomar ManalangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument4 paginiChapter 3 Cells and TissuesClarisse Anne QuinonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsDocument16 paginiCH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsREENA GULERIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Tissues: 1. Epithelial TissueDocument18 paginiBody Tissues: 1. Epithelial TissueHi SseulgiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Document2 paginiHISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Edzeal Bruan JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Scan 09 Feb 2024Document8 paginiAdobe Scan 09 Feb 2024shradhasharma2101Încă nu există evaluări
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 paginiEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumDocument22 paginiEpithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumMahmoud IdlbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 paginiAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue: Simple Epithelia Stratified EpitheliumDocument2 paginiEpithelial Tissue: Simple Epithelia Stratified EpitheliumVarenLagartoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A P Topic 5 SummaryDocument9 paginiA P Topic 5 SummaryMax Delvalle100% (1)
- BIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesDocument13 paginiBIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesdonnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Connective TissuesDocument6 paginiConnective TissuesPenelopeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaDocument3 paginiTissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology ReviewerDocument11 paginiHistology ReviewerMaryell Denize LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 649539f145572900183c11f2 ## Structural Organisation in Animals ShortDocument4 pagini649539f145572900183c11f2 ## Structural Organisation in Animals Shorts.yagyan prasad acharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pagini8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANIMAL-CELL Group 2Document35 paginiANIMAL-CELL Group 2mjecbjÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONTENT FOR BRIDGE COURSE STD 9thDocument5 paginiCONTENT FOR BRIDGE COURSE STD 9thGoo GleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 Plant Structure and Function - 032212Document45 pagini21 Plant Structure and Function - 032212Nudiya SappalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Support and Transport Systems in PlantsDocument50 pagini10 Support and Transport Systems in Plantsapi-202349222Încă nu există evaluări
- HistologyDocument116 paginiHistologyAshwani KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- модуль варіант №3 контрольDocument8 paginiмодуль варіант №3 контрольShambhu AshokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ReportDocument2 paginiLab ReportKiro Zero100% (1)
- Act 17 - RootsDocument15 paginiAct 17 - RootsRyan OdioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Plant Morphology and Anatomy BBDocument23 pagini14 Plant Morphology and Anatomy BBmka8208650% (2)
- Plant StructureDocument28 paginiPlant StructurepencintaAllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyDocument70 paginiBiologyImran Hunzai25% (4)
- To Study The Natural Phenomenon of InheritanceDocument1 paginăTo Study The Natural Phenomenon of InheritanceDhruv AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant TransportDocument23 paginiPlant TransportBalakrishnan MarappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alexix Carol Mysticism of Cell CultureDocument20 paginiAlexix Carol Mysticism of Cell CultureARGHA MANNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides HistoDocument7 paginiSlides HistoMirriam MallariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Report: Techniques and Management of Science Laboratory Preparation Technique of Plant TissueDocument13 paginiPractical Report: Techniques and Management of Science Laboratory Preparation Technique of Plant TissueyennyarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 07 Science 2nd Term Test Paper 2019 English Medium - North Western ProvinceDocument8 paginiGrade 07 Science 2nd Term Test Paper 2019 English Medium - North Western ProvinceRithaj HarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Human Physiology 3rd Canadian Edition by SherwoodDocument36 paginiTest Bank For Human Physiology 3rd Canadian Edition by Sherwoodbombacesurclewjh59100% (44)
- 9 Cbse - Term-1 - ScienceDocument13 pagini9 Cbse - Term-1 - ScienceSHUAIN PARAMBIL (EMP324)Încă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHY Lec Session #3 - SASDocument12 paginiANAPHY Lec Session #3 - SASFherry Mae UsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Chapter 40 Animal Structure and FunctionDocument3 paginiAP Chapter 40 Animal Structure and FunctionKayleigh SullivanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology 2 HistologyDocument2 paginiPhysiology 2 HistologyFahim Khan100% (2)
- Dps Exam PaperDocument6 paginiDps Exam Papermeenusaini312Încă nu există evaluări
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 1Document2 paginiHes 029 Lab Sas 1Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanÎncă nu există evaluări