Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
2 Research PDF
Încărcat de
Lynssey Danielle0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
14 vizualizări1 paginăQuantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data using computational, statistical, and mathematical tools. It uses sampling techniques like simple random sampling or stratified sampling to gather data from participants. Common statistical analysis tools include t-tests, Pearson's R, multiple regression, and ANOVA, which are used to describe phenomena, correlate variables, predict outcomes, and analyze differences between groups. Surveys like questionnaires and interviews are typical methods for collecting quantitative data.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
2-RESEARCH.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentQuantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data using computational, statistical, and mathematical tools. It uses sampling techniques like simple random sampling or stratified sampling to gather data from participants. Common statistical analysis tools include t-tests, Pearson's R, multiple regression, and ANOVA, which are used to describe phenomena, correlate variables, predict outcomes, and analyze differences between groups. Surveys like questionnaires and interviews are typical methods for collecting quantitative data.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
14 vizualizări1 pagină2 Research PDF
Încărcat de
Lynssey DanielleQuantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data using computational, statistical, and mathematical tools. It uses sampling techniques like simple random sampling or stratified sampling to gather data from participants. Common statistical analysis tools include t-tests, Pearson's R, multiple regression, and ANOVA, which are used to describe phenomena, correlate variables, predict outcomes, and analyze differences between groups. Surveys like questionnaires and interviews are typical methods for collecting quantitative data.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
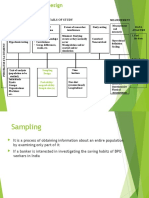
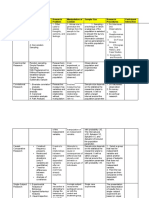
Quantitative Research
A way of collecting and analyzing data obtained from different sources.
It involves the use of computational, statistical and mathematical tools to derive results .
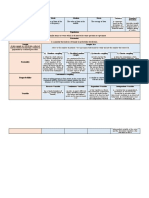
Research Design Sampling Technique Common statistical tool Survey Types
Descriptive Probability Non-Probability Pearson’s R Questionnaire
- To observe and report - Measure of the strength of - Paper and pencil
phenomenon. linear association between instrument that is
Simple Random Purposive two variables. administered to the
- Has an equal respondents.
Correlational opportunity Sampling T – Test
- Most judgemental
- To determine the nature
of relationship between
sampling. - The t-distribution and Interview
variables. Stratified degrees of freedom to
determine the probability of
- More personal and
probing.
- With regards to
characteristic.
Convenience difference between
Ex Post Facto Sampling
populations.
- To infer the causes of Observation
- Availability of the
phenomenon which has Cluster - Observing and
already occurred. - With characteristics
participant.
Multiple Regression measuring the world
- powerful technique used for around you.
of grouping in
number. predicting the unknown value
Quasi Experimental of a variable
- Not highly randomized;
with characteristic of Systematic
intact group. - With patterns; can Spearman's Rho
start anywhere. - non-parametric test used to
measure the strength of
Experimental association between two
- Highly randomized; variables.
without characteristic of Anova
intact group. - Used to analyze the differences
among group means in a sample.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Practical Research Lesson 1Document2 paginiPractical Research Lesson 1Reinn DionisioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative MatrixDocument3 paginiComparative MatrixKristel RoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 12: Selecting A SampleDocument2 paginiCHAPTER 12: Selecting A Samplealia.delareineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expounding The Terms in ResearchDocument49 paginiExpounding The Terms in ResearchElon MuskÎncă nu există evaluări
- C GEMTH MidtermsDocument4 paginiC GEMTH MidtermsKarl LintanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ana ChemDocument1 paginăAna ChemElizer Robles Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Sampling & EstimationDocument3 paginiSampling & EstimationCratos_PoseidonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research 9 Q3Document17 paginiResearch 9 Q3MMALTEZ, RALPH CHRISTIAN, R.Încă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Scie Process SkillsDocument4 paginiIntegrated Scie Process SkillsJonsen Keon GayosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR Module 1Document18 paginiPR Module 1Aprilyn Martelino ObregonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Quantitative: Random VariableDocument4 paginiQualitative Quantitative: Random VariablejenduekieÎncă nu există evaluări
- APP006 REVIEWER HotdogDocument6 paginiAPP006 REVIEWER HotdoglopezorateangelitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cidam StatDocument4 paginiCidam StatJanisah Abdulsamad60% (5)
- Reviewer PRDocument4 paginiReviewer PRLaisan SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary TemplateDocument2 paginiApprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary Templateapi-393590941Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 03Document3 paginiChapt 03SAIVAGEÎncă nu există evaluări
- SASA ReviewerDocument4 paginiSASA ReviewerMia FayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- wuolah-free-STATISTICS-1Document12 paginiwuolah-free-STATISTICS-1pabloenriquerh28Încă nu există evaluări
- Which Statistical Tests To UseDocument1 paginăWhich Statistical Tests To UsePam FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regression Analysis and Statistical Learning in Social Science ResearchDocument59 paginiRegression Analysis and Statistical Learning in Social Science ResearchA Y I E SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handouts 1Document4 paginiHandouts 1Ken DumpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Methods Table - CAIE 9990 Psychology AS LevelDocument12 paginiResearch Methods Table - CAIE 9990 Psychology AS Levelkhushi.mehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 - Quantitative Research - HANDOUTSDocument2 pagini02 - Quantitative Research - HANDOUTSJOSEPH EARNEST TIEMPOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agents: Definition and Formal Architectures: Lecturer: S Luz Luzs@cs - Tcd.ie September 23, 2014Document11 paginiAgents: Definition and Formal Architectures: Lecturer: S Luz Luzs@cs - Tcd.ie September 23, 2014ShAh NawaZzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Details of Study: Sampling DesignDocument29 paginiDetails of Study: Sampling DesignharsimranÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Sampling Procedure and The Sample": Population 1. HeuristicsDocument2 pagini"Sampling Procedure and The Sample": Population 1. HeuristicsAngelica DelfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics and Probability FIDPDocument31 paginiStatistics and Probability FIDP123 456Încă nu există evaluări
- Shafiq Sir All GFBDocument110 paginiShafiq Sir All GFBAbir WahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2: Sampling Size and Sampling TechniquesDocument7 paginiPractical Research 2: Sampling Size and Sampling TechniquesJohnJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistical techniques and tests classified by variables and scalesDocument5 paginiStatistical techniques and tests classified by variables and scalesethachappunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 1 - Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFDocument36 paginiLESSON 1 - Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFKent SalmorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistic and Probability ReviewerDocument1 paginăStatistic and Probability ReviewerABORDO, JANE ELEONORÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMS3033Document4 paginiSMS3033HaooonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPSTONEDocument3 paginiCAPSTONEAlen Joy CamachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Q2 NotesDocument8 paginiResearch Q2 NotesaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stat PPT 1Document11 paginiStat PPT 1CHRISTIAN INFANTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inquiries, Investigation, and ImmersionDocument6 paginiInquiries, Investigation, and ImmersioniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1901.11365 PDFDocument16 pagini1901.11365 PDFMohammed KharbatliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mba 102 ReviewerDocument4 paginiMba 102 ReviewerFrancheska LarozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR1 Lesson 3 Types of Research PDFDocument3 paginiPR1 Lesson 3 Types of Research PDFYiel Ruidera PeñamanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument4 paginiPractical Research 2 ReviewerAJ Lorenz MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Participant (29.7 × 21 CM)Document2 paginiResearch Participant (29.7 × 21 CM)Lutfia Arum PambudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADMS 2320 Test 1 SheetDocument1 paginăADMS 2320 Test 1 SheetJustin St Louis WoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ib Psych NotesDocument114 paginiIb Psych NotesLucy Han100% (2)
- Quantitative vs Qualitative ResearchDocument5 paginiQuantitative vs Qualitative ResearchEissa SamanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative Research Approaches and Types of Data CollectedDocument2 paginiQuantitative Research Approaches and Types of Data CollectedJoseph Mark BaldomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set Features For ADDocument15 paginiSet Features For ADJorge CasajusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics (Mid-Terms!) : Steps in Data GatheringDocument5 paginiStatistics (Mid-Terms!) : Steps in Data GatheringLaila Joshbeth SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Northeastern Philippines School of Graduate Studies Iriga CityDocument4 paginiUniversity of Northeastern Philippines School of Graduate Studies Iriga CityKim NoblezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect Data: Lesson 4Document32 paginiUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect Data: Lesson 4Sam IntongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR Notes Unit 1Document4 paginiPR Notes Unit 1Alyssa MacamayÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEA1000 Final CSDocument3 paginiGEA1000 Final CSSherman LiamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Five Statistical Models For Likert-Type Experimental Data On Acceptability JudgmentsDocument46 paginiFive Statistical Models For Likert-Type Experimental Data On Acceptability JudgmentsmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Quantitative Research NCM111 Lec 2PDocument9 paginiIntroduction To Quantitative Research NCM111 Lec 2PMary Queenie TulinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2 Reading 1Document5 paginiPractical Research 2 Reading 1maennehsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro to Biostatistics - performing estimations and hypothesis testsDocument2 paginiIntro to Biostatistics - performing estimations and hypothesis testsAlyssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Research MethodsDocument6 paginiBasic Research MethodsRashi kothariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Research Chapter 4. Research at Paradigm LevelDocument26 paginiMethods of Research Chapter 4. Research at Paradigm LevellornfateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistical and Neural Classifiers: An Integrated Approach to DesignDe la EverandStatistical and Neural Classifiers: An Integrated Approach to DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Techniques in Wildlife Investigations: Design and Analysis of Capture DataDe la EverandTechniques in Wildlife Investigations: Design and Analysis of Capture DataEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Angeles, Angelica Mae - Avcomm2101 - Midterm ProjectDocument5 paginiAngeles, Angelica Mae - Avcomm2101 - Midterm ProjectLynssey DanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaklsyshbx Saisn AjsbDocument1 paginăAnaklsyshbx Saisn AjsbLynssey DanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science and Technology in The Philippines Past and PresentDocument4 paginiScience and Technology in The Philippines Past and PresentMichael John B BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendices SummaryDocument32 paginiAppendices SummaryLynssey DanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Experimental Analysis: The Effectiveness of Team Size On Managing Complex TaskDocument21 paginiAn Experimental Analysis: The Effectiveness of Team Size On Managing Complex TaskLynssey DanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team Size Effectiveness on Complex TasksDocument41 paginiTeam Size Effectiveness on Complex TasksLynssey DanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Experimental Analysis: The Effectiveness of Team Size On Managing Complex TaskDocument21 paginiAn Experimental Analysis: The Effectiveness of Team Size On Managing Complex TaskLynssey DanielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCGDocument36 paginiBCGdadaisgreat100% (1)
- Public Art, Private PlacesDocument20 paginiPublic Art, Private PlacesLisa Temple-CoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Munsat, S. - ProcessDocument6 paginiMunsat, S. - ProcessBen FortisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accelerating research insightsDocument13 paginiAccelerating research insightsViệt Dũng NgôÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Hawley) - The Practice of Silviculture (1946)Document380 pagini(Hawley) - The Practice of Silviculture (1946)Karpincho30% (1)
- 9-Nietzsche and Super LaughterDocument18 pagini9-Nietzsche and Super Laughtergannoa02Încă nu există evaluări
- USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/4/18Document3 paginiUSA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/4/18สฮาบูดีน สาและÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psycho Yoga 12Document25 paginiPsycho Yoga 12merlin7magikÎncă nu există evaluări
- BT 203 Basic Mechanical Engineering May 2019 PDFDocument2 paginiBT 203 Basic Mechanical Engineering May 2019 PDFKunta PatleÎncă nu există evaluări
- GMP SIMATIC WinCC V15 en en-US PDFDocument216 paginiGMP SIMATIC WinCC V15 en en-US PDFsybaritzÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExportDocument361 paginiExportStefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bec Guide For Students PDFDocument2 paginiBec Guide For Students PDFPritam KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Payment For Building PermitDocument1 paginăPayment For Building PermitSterben ShouchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- David Ticknor Resume 2018 1Document1 paginăDavid Ticknor Resume 2018 1api-430534745Încă nu există evaluări
- Data Encryption DecryptionDocument60 paginiData Encryption DecryptionMohit Sharma100% (2)
- FTT - en 45545 EU Railway Industry 2015 - CompressedDocument24 paginiFTT - en 45545 EU Railway Industry 2015 - Compresseddody andiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Đề 1Document9 paginiĐề 1trung anÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spitler McQuiston Lindsey 93 2Document11 paginiSpitler McQuiston Lindsey 93 2Shafawati ShahneelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer NetworksDocument4 paginiComputer NetworksMainul HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trends in Linguistics - Studies and MonographsDocument550 paginiTrends in Linguistics - Studies and MonographsNelly PaniaguaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endcarriage - KZL-S 315Document116 paginiEndcarriage - KZL-S 315Josip Nuno CoricÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11-1203 Syed Hussain HaiderDocument16 pagini11-1203 Syed Hussain HaiderSalman Nisar BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pork Carcass ChillingDocument6 paginiPork Carcass ChillingDumitru PodgorneakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tolerances of A Polystyrene Film: 2.2.25. ABSORPTION Spectrophotometry, Ultraviolet and VisibleDocument3 paginiTolerances of A Polystyrene Film: 2.2.25. ABSORPTION Spectrophotometry, Ultraviolet and Visibleivan cuadradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10Document30 paginiChapter 10Fernando Alcala Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCD DLP PDP ComparisonDocument27 paginiLCD DLP PDP Comparisonahmad_wazierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution Transformer Manufacturing Process ManualDocument29 paginiDistribution Transformer Manufacturing Process ManualAnonymous Jf6X8nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Ink Identification: Standard Guide ForDocument5 paginiWriting Ink Identification: Standard Guide ForEric GozzerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centre For Political Studies: End-Semester Examination Time-Table Monsoon Semester 2019 ExaminationDocument2 paginiCentre For Political Studies: End-Semester Examination Time-Table Monsoon Semester 2019 ExaminationAbhijeet JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ifw Process GimDocument24 paginiIfw Process Gimmyownhminbox485Încă nu există evaluări