Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dynamometer
Încărcat de
Mohammad Zia Nasir BhuttaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dynamometer
Încărcat de
Mohammad Zia Nasir BhuttaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TYPES OF DYNAMOMETER
By: M. ZIA NASIR BHUTTA
OCTOBER 14, 2019
Dynamometer
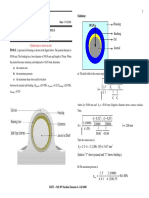
Dynamometer is a device which is used to measure the frictional resistance. By knowing the
frictional resistance we can determine torque transmitted and hence power of the engine.
Dynamometer can be used to measure either torque, force or power.
Types of Dynamometer:
Dynamometer is further classified into two major type:
Absorption Dynamometer
Transmission Dynamometer
Absorption Dynamometer:
This dynamometer measure and absorb the power output of the engine to which they are
coupled. The power is usually dissipated as heat by some means.
Following are the types of absorption dynamometer:
Prony brake dynamometer
Rope brake dynamometer.
Prony Brake Dynamometer:
It works on the principle of converting power into heat by dry friction. In this method of
measuring horsepower is to attempt to stop the engine by means of a brake on the flywheel and
measure the weight which an arm attached to the brake will support, as it tries to rotate with
the flywheel. In Prony brake dynamometer, when brakes is to be put in operation, the long end
of the lever is loaded with suitable weight W and the nuts are tightened until engine shaft runs
at a constant speed and the lever is in horizontal position. Under these conditions, the moment
due to weight must balance the moment of the frictional resistance between the block and the
pulley.
Rope Brake Dynamometer:
It consist of a number of turns of rope wound around the rotating drum attached to the output
shaft. One side of rope is connected to a spring balance and the other to a loading device. The
power is absorbed in friction between the rope and thee drum. The drum therefore require
cooling. Rope brake is cheap and easily constructed. It is not very accurate because of changes
in the friction coefficient of the rope with temperature. The upper rope is attached to a spring
balance while the lower end is kept in position by applying a dead weight. In order to prevent
the slipping of the ropes over the flywheel, wooden blocks are placed at intervals around the
circumference of the flywheel. During operation of the brake, the prime mover is made to run
at constant speed.
Transmission Dynamometer:
In this dynamometer, the energy is used for doing work. The power developed by the prime
mover is transmitted by the dynamometers to some machine which the power is suitably
measured.
Following are the type of transmission dynamometer:
Belt transmission dynamometer
Epicyclic train dynamometer
Torsion dynamometer.
Belt transmission dynamometer:
A belt transmission Dynamometer consist of driving pulley, rigidly fixed to the shaft of the
prime mover. There is another driven pulley mounted on another shaft, to which the power
from pulley is transmitted. The pulley are connected by means of a continuous belt passing
through the two loose pulleys, which are mounted on the lever. The lever carries a dead weight
at the one end, and a balancing weight is attached at the other end.
Epicyclic train dynamometer:
ETD is a dynamometer which measures power while it is being transmitted from driving to the
driven shaft. It consist of simple Epicyclic fear train. The pinion is free to rotate on a pin fixed
to the liver arm. The lever is pivoted about the common axis of the driving and driven shaft.
When the dynamometer is in operation, two tangential forces acts at the end of pinion.
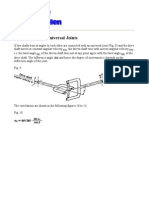
Torsion Dynamometer:
A torsion dynamometer is used to measure large power developed by a turbine or marine
engines. A large number of torsion dynamometers are used to measure the angle of twist.
Therefore, a torsion dynamometer works on the principle of angle of twist. When power is
transmitted along a shaft, the driving end twists through a small angle relative to the driven
end. Torque transmitted is directly proportional to the angle of twist.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shaft Misalignment and Vibration - A ModelDocument13 paginiShaft Misalignment and Vibration - A ModelPeak NeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLG418 Operation &maintainance ManualDocument66 paginiCLG418 Operation &maintainance ManualLYCANTROPOFAGO89% (9)
- Seleccion y Diseño GerotorDocument28 paginiSeleccion y Diseño GerotoremersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contactless Hall Effect Torque Sensor For EPASDocument8 paginiContactless Hall Effect Torque Sensor For EPASJessica OwensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotordynamic Capabilities in ANSYS Mechanical PDFDocument3 paginiRotordynamic Capabilities in ANSYS Mechanical PDFFarzad SadrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wheelhub Integration of Electric Motor in FSEDocument35 paginiWheelhub Integration of Electric Motor in FSEShivam WankhedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Literature Review On Exhaust Manifold DesignDocument4 paginiA Literature Review On Exhaust Manifold DesignijsretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationDe la EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Massenza Mi4 Manual PDFDocument44 paginiMassenza Mi4 Manual PDFsean100% (1)
- MEC322 Chapter 7 - TORQUE & POWER MEASUREMENTDocument19 paginiMEC322 Chapter 7 - TORQUE & POWER MEASUREMENTAiman ArhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cogging Torque MeasurementDocument3 paginiCogging Torque MeasurementIon TrifuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torque Measuremen T: MQC SeminarDocument17 paginiTorque Measuremen T: MQC SeminarVaibhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brake CalculationDocument10 paginiBrake CalculationKarthick DavoothÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training, Class I, Testing, IIb, 1-10Document12 paginiTraining, Class I, Testing, IIb, 1-10luis_hernandez_qÎncă nu există evaluări
- DynamometerDocument7 paginiDynamometerGaurav S PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Disc Brake and Caliper of Four WheelerDocument5 paginiDesign and Analysis of Disc Brake and Caliper of Four WheelerIJSTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hexply 8552 DatasheetDocument6 paginiHexply 8552 DatasheetMuhammad KhyzerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cam Experimental Lab: ObjectiveDocument8 paginiCam Experimental Lab: ObjectiveMuhammad Changez Khan100% (2)
- 08 CH-6, Fluid Motion Within Combustion ChamberDocument24 pagini08 CH-6, Fluid Motion Within Combustion ChamberAhsan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry of Screw Compressor Rotors and Their ToolsDocument17 paginiGeometry of Screw Compressor Rotors and Their ToolsPhox IndiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 4Document3 paginiTutorial 4snoozermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brake Force CalculationDocument25 paginiBrake Force CalculationVicky TjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Brushless DC Motor in MilitaryDocument10 paginiApplication of Brushless DC Motor in Militarymighty_heart100% (1)
- A Review of Structural and Thermal Analysis of Traction MotorsDocument11 paginiA Review of Structural and Thermal Analysis of Traction MotorsGari PastranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Analysis of Three Stage Coupled Planetary Gear Train and Determination of EfficiencyDocument3 paginiStructural Analysis of Three Stage Coupled Planetary Gear Train and Determination of EfficiencyInnovative Research PublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Bearings PDFDocument50 paginiChapter 4 Bearings PDFAnonymous 7aN0oYUm7vÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report 3C2Document41 paginiSeminar Report 3C2Pritish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Machine Fault Simulator (MFS) For Fault DiagnosisDocument8 paginiDesign and Development of Machine Fault Simulator (MFS) For Fault DiagnosisAnonymous pKuPK3zUÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB - General Purpose Motors Cast Iron - GB 092003Document49 paginiABB - General Purpose Motors Cast Iron - GB 092003ivanjaviergutierrezoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To R.T.P.P: 1.1 GeneralDocument12 paginiIntroduction To R.T.P.P: 1.1 GeneralSairam Kumar ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Banshee Scythe InfoDocument1 paginăBanshee Scythe InfobuilttorideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted byDocument34 paginiSeminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted bySouraj PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Chemistry - Fundamentals of ThermodynamicsDocument64 paginiPrinciples of Chemistry - Fundamentals of Thermodynamicsred velvetÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOMAS UsersManualDocument94 paginiTOMAS UsersManualrodruren01Încă nu există evaluări
- Turbulent Flow in An Intake-Manifold PDFDocument6 paginiTurbulent Flow in An Intake-Manifold PDFzoragiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - Engine Performance ParametersDocument20 pagini4 - Engine Performance ParametersWHO IS ITÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gears and TransmissionsDocument27 paginiGears and TransmissionsAshish ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- GearboxDocument6 paginiGearboxedhy_03Încă nu există evaluări
- Model For Prediction of Churning LossesDocument6 paginiModel For Prediction of Churning LossesSaipriya BalakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torque and Power Measurement SecondDocument11 paginiTorque and Power Measurement SecondShukor Az100% (1)
- Metrology in MicromachiningDocument34 paginiMetrology in MicromachiningDeepakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damping of Torsional Vibrations of Ship Engine Crankshafts - General Selection Methods of Viscous Vibration DamperDocument5 paginiDamping of Torsional Vibrations of Ship Engine Crankshafts - General Selection Methods of Viscous Vibration Dampersuhas110Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Mounts and Powertrain Mounting SystemsDocument22 paginiEngine Mounts and Powertrain Mounting SystemsErdiner ParmaksızÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cam MechDocument24 paginiCam MechmarcglebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural and Thermal Analysis of An Exhaust Manifold of A Multi Cylinder Engine IJERTCONV3IS10016 PDFDocument4 paginiStructural and Thermal Analysis of An Exhaust Manifold of A Multi Cylinder Engine IJERTCONV3IS10016 PDFKarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material ReportDocument13 paginiMaterial ReportSrivathsan R. Sharma100% (3)
- End Winding Vibration Hydro GeneratorDocument5 paginiEnd Winding Vibration Hydro Generatorpatel chandramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsDocument12 paginiUnderstanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsArni 2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Dm200 CatalogDocument6 paginiDm200 CatalogAS_865025438Încă nu există evaluări
- Klein Technical GuidelineDocument21 paginiKlein Technical GuidelinePeter100% (2)
- Fabrication of Turbocharger For Two Wheeler PDFDocument2 paginiFabrication of Turbocharger For Two Wheeler PDFWesleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Vibrations Sample QuestionsDocument3 paginiMechanical Vibrations Sample QuestionsTotoGoatsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viva Questions - Internal Combustion Engine - Liquefied Petroleum GasDocument4 paginiViva Questions - Internal Combustion Engine - Liquefied Petroleum Gasmailsk123Încă nu există evaluări
- CEP VFD ManualDocument234 paginiCEP VFD ManualUsama ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gearboxes ClassDocument35 paginiGearboxes ClassNaveen Vachipalli100% (1)
- GT Power Product DescriptionDocument4 paginiGT Power Product Descriptionrudey18Încă nu există evaluări
- Influence of Anti Dive and Anti Squat Geometry in Combined Vehicle Bounce and Pitch DynamicsDocument12 paginiInfluence of Anti Dive and Anti Squat Geometry in Combined Vehicle Bounce and Pitch Dynamicslakshmanakumarr@gmail.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic of GearsDocument35 paginiBasic of Gearskcshieh100% (1)
- Structural Health MonitoringDe la EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationDe la EverandDesign Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Order Large Eddy Simulation for Shock-Boundary Layer Interaction Control by a Micro-ramp Vortex GeneratorDe la EverandHigh Order Large Eddy Simulation for Shock-Boundary Layer Interaction Control by a Micro-ramp Vortex GeneratorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyundai Motor Company Company ProfileDocument11 paginiHyundai Motor Company Company Profileishwar singh0% (1)
- VE Pump TrainingDocument36 paginiVE Pump TrainingNarendra FirmansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Ford Flex 3.5L Eng VIN 8 SE c200bDocument6 pagini2014 Ford Flex 3.5L Eng VIN 8 SE c200bMemo VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 SpoolDocument8 pagini3 SpoolTufha NiwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Combustion Engines PresentationDocument23 paginiInternal Combustion Engines PresentationNitesh BirlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nstruction Manua: Model Year: Model Name: PurposeDocument15 paginiNstruction Manua: Model Year: Model Name: PurposeOrestis AgathokleousÎncă nu există evaluări
- B4 100 Propeller ArrangementDocument1 paginăB4 100 Propeller Arrangementrisky antoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trailer 40 PiesDocument2 paginiTrailer 40 Piesmaomischo3992Încă nu există evaluări
- Suspension PartsDocument410 paginiSuspension Partskontejner93Încă nu există evaluări
- TRITON Spec-SheetDocument2 paginiTRITON Spec-SheetJet acostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal Smith MiniplaneDocument4 paginiMetal Smith Miniplanetdfsks50% (2)
- Craftsman Model 143.666382 Parts ListDocument8 paginiCraftsman Model 143.666382 Parts ListscttygÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module1 - EV TechnologyDocument40 paginiModule1 - EV TechnologyThiruvenkadam SrinivasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equipment RentalDocument1 paginăEquipment RentalKate Perez100% (1)
- TWJ 5000 Litres - New FormaDocument3 paginiTWJ 5000 Litres - New Formamuhammad iqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2004 Corolla Electrical Diagram - Part NumbersDocument4 pagini2004 Corolla Electrical Diagram - Part NumbersNick BaptisteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Leasing TOTAL LOSSDocument5 paginiUnit Leasing TOTAL LOSSRoniIrpannsyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 - Beta RSC24, C45PRODocument12 pagini2021 - Beta RSC24, C45PROTan Xin YiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meritor School Bus Replacement Parts PDFDocument274 paginiMeritor School Bus Replacement Parts PDFмакс игнатовÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engine BrakeDocument8 paginiEngine BrakeIzz Bahar100% (1)
- Qy70v533 Technical SpecificationDocument28 paginiQy70v533 Technical SpecificationMallikarjun DevarapalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pollution Under Control Certificate: Form 59Document1 paginăPollution Under Control Certificate: Form 59rahul raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torque Specification: Service SpecificationsDocument1 paginăTorque Specification: Service SpecificationsClodoaldo BiassioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 53 Mitsubishi 1B F4A41 F4A4B EtcDocument18 pagini53 Mitsubishi 1B F4A41 F4A4B EtcEduardo Alvarez Huiza0% (1)
- Hankook Pattern Digest 2013-2014 (Iso 29mb)Document187 paginiHankook Pattern Digest 2013-2014 (Iso 29mb)Nguyễn Hoài NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard HeadlampsDocument2 paginiStandard HeadlampsHichem BenmohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mercedes Benz VitoDocument366 paginiMercedes Benz Vitobmwscribd33% (3)