Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science 8
Încărcat de
Amor Ramirez0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6 vizualizări1 paginăScience
Titlu original
SCIENCE 8
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentScience
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6 vizualizări1 paginăScience 8
Încărcat de
Amor RamirezScience
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
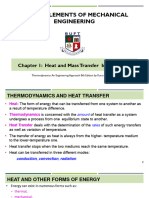
SCIENCE 8 ( MONTHLY 2ND QUARTER)
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE OHM’ s LAW
- Explains the relationship between voltage,
A hot object will have more kinetic energy current and resistance.
which means faster moving particles. - Used by electricians, automotive, technicians
A cold object will have less kinetic energy which stereo installers.
means slower moving particles. VOLTAGE - push or pressure behind current flow
HEAT – the thermal energy being transferred from one through a circuit and is measured in volts (V).
object to another due to the temperature difference. CURRENT – quantity or volume of electrical flow.
- Travels from the object with higher Measured in Amps (A)
temperature to the object with lower RESISTANCE – flow of the current. Measured by ohms.
temperature.
- Commonly referred to as internal energy. ALESSANDRO VOLTA – developed the first electric cell
INTERNAL ENERGY – grand total of all the energies in an - Introduced the unit of volt
object. ANDRE MARIE AMPERE – discovered electromagnetism
- Introduced the unit of ampere.
Once heat energy touches the object, it is GEORG SIMON OHM – invented electrochemical
converted into internal energy. - Discovered the relationship of Ohm’s law
Internal energy is directly proportional to the
temperature. ELECTRICITY- form of energy. It is the flow of electrons.
The higher the temperature, the greater the - basic part of nature and it is one of our most widely
internal energy used form of energy.
HEAT – measured by calorimeter Electric circuit- provides a complete closed path for
Units of heat: calorie and joule electricity.
Symbol : Q
TEMPERATURE- measure of the degree of hotness and TYPES OF CIRCUIT
coldness of abody. CLOSED CIRCUIT- has a complete path and good
- Average kinetic energy of the molecules in the continuity of current flow.
body. OPEN CIRCUIT- one where the continuity of the current
- Measured by a thermometer flow has been broken by an interruption.
- Units: °C (degree Celsius or centigrade) SERIES CIRCUIT- circuit in which the same current flows
°F ( degree farenheit) through all component.
K ( kelvin) PARALLEL CIRCUIT- circuit in which the components are
- Symbol: T arranged so that the current must break up before
a. Clinical – body temperature meeting anf combining again
b. Wall – air temperature SHORT CIRCUIT- low resistance connection between
c. Laboratory- temperature of hot or cold water two conductors supplying power to any circuit.
and soil
HEAT CAPACITY ( Q ) – is the amount of heat needed
raise the temperature of a body by 1°C or 1 kelvin.
Q = MC∆T
Where: m = mass in g or kg.
𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑗𝑜𝑢𝑙𝑒
C = specific heat of a substance in 𝑔.°𝐶 or 𝑔.°𝐶
∆T = change in temperature
∆T = Tf – Ti
𝑸 = heat capacity or amount of heat absorbed
or lost in calorie or joule.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Thermoelectric Refrigeration: Comparision With Conventional Cooling SystemDocument15 paginiThermoelectric Refrigeration: Comparision With Conventional Cooling SystemKirandeep GandhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 - Heat ThermodynamicsDocument47 paginiChapter 9 - Heat ThermodynamicsMuhammad Aminnur Hasmin B. HasminÎncă nu există evaluări
- BME Unit V ThermodynamicsDocument22 paginiBME Unit V ThermodynamicsArvind Bhosale100% (3)
- Thermoelectric Energy ConversionDocument4 paginiThermoelectric Energy ConversionMenchie LabadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Energy and Earthquakes ReviewDocument20 paginiHeat Energy and Earthquakes ReviewSheena PagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 3 Energy Applications - Key TermsDocument2 paginiLesson 1 3 Energy Applications - Key Termsapi-26094890550% (2)
- Geas Reviewer 2Document2 paginiGeas Reviewer 2Francis DrakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 3 KeytermsDocument2 pagini1 3 Keytermsapi-291530288Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch-1 (HMT)Document32 paginiCh-1 (HMT)Hamza ShahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1 Unit2Document56 paginiPaper 1 Unit2sagar narkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 2101-Heat Transfer and ThermodynamicsDocument58 paginiME 2101-Heat Transfer and ThermodynamicsSaul GoodmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bicycle Pedal Powered RefrigeratorDocument27 paginiBicycle Pedal Powered RefrigeratorAanya SethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics: PressureDocument7 paginiPhysics: PressureJason TehÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECT ENERGY CONVERSION GUIDEDocument69 paginiDIRECT ENERGY CONVERSION GUIDERavichandran SekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThermodynamicsDocument28 paginiThermodynamicsShlok MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ثرمو محاضرة 1 مرحلة 3Document35 paginiثرمو محاضرة 1 مرحلة 3Al-Hassan NeimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TE19 Thermal Conductivity ExperimentDocument11 paginiTE19 Thermal Conductivity ExperimentbassamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectrics - Unit - VIIDocument8 paginiThermoelectrics - Unit - VIIAbdulbar kelilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectric ConvertersDocument111 paginiThermoelectric ConvertersKamal Vijay Ram R SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 8 TempDocument18 paginiChapter - 8 TempdigamberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Fundamentals ExplainedDocument23 paginiThermodynamics Fundamentals ExplainedAmit ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- File 68248Document29 paginiFile 68248Abeera MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro to Thermodynamics LawsDocument33 paginiIntro to Thermodynamics LawsJanicz Balderama0% (1)
- Chapter Ten Thermodynamics: ConductionDocument3 paginiChapter Ten Thermodynamics: ConductionTony AtefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric HeatingDocument19 paginiElectric HeatingksrmuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Thermodynamics ConceptsDocument27 paginiBasic Thermodynamics ConceptsLorielle OlivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Peltier Devices For Temperature Control: MSL Technical Guide 41Document5 paginiUsing Peltier Devices For Temperature Control: MSL Technical Guide 41Aldrin HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Heat Transfer Modes of Heat Transfer: ConductionDocument21 paginiChapter 1 - Heat Transfer Modes of Heat Transfer: Conductionalbin thomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectric Materials: A Review of Fundamental Principles and Modern ApplicationsDocument29 paginiThermoelectric Materials: A Review of Fundamental Principles and Modern ApplicationsRahul YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectric Refrigerators - Docx FinalDocument12 paginiThermoelectric Refrigerators - Docx FinalShivam GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC For Course2Document251 paginiHVAC For Course2Anwar Pariyarath0% (1)
- 1-Chapter Four Chemical Dynamics-2016-First PartDocument42 pagini1-Chapter Four Chemical Dynamics-2016-First PartMOHAMMAD NAZMUL ISLAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 002general Energy Analysis of THERMODYNAMICSDocument30 pagini002general Energy Analysis of THERMODYNAMICSm7sen mohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPICE Model of Thermoelectric Elements Including Thermal EffectsDocument5 paginiSPICE Model of Thermoelectric Elements Including Thermal EffectsLucas CarvalhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Direct Thermoelectric Conversion - Heat Input EquationDocument15 paginiPrinciples of Direct Thermoelectric Conversion - Heat Input EquationhportezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Electricity and Thermal PhysicsDocument3 paginiUnit 2 Electricity and Thermal PhysicsRaisa Binte HudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 2021Document51 paginiChapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 2021BT20MEC058AdeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Science Part1Document12 paginiGeneral Science Part1Adrian OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latest Physics Project 2023 Class 12 2.0Document19 paginiLatest Physics Project 2023 Class 12 2.0Tusharr sgrÎncă nu există evaluări
- KedarIndian Conference PDFDocument5 paginiKedarIndian Conference PDFKedar A. MalusareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat and Mass Transfer Lecture on Conduction, Thermal Properties and Energy BalanceDocument17 paginiHeat and Mass Transfer Lecture on Conduction, Thermal Properties and Energy BalanceAbdullah RiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHE333_Shell Energy Transfer 2023_2024Document36 paginiCHE333_Shell Energy Transfer 2023_2024tomini.korodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics ReviewerDocument118 paginiThermodynamics ReviewerAngelo Luigi Yasay100% (2)
- UPCAT Physics Review Part 2Document37 paginiUPCAT Physics Review Part 2Clarise VicenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5 Conduction - Fourier Law of Heat ConductionDocument24 paginiLesson 5 Conduction - Fourier Law of Heat Conductionsurya kiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 131.8 Introduction To Heat TransferDocument41 pagini131.8 Introduction To Heat TransferJelor GallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Properties of Materials GuideDocument27 paginiThermal Properties of Materials GuideLouise UmaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUCLecture 2021 112940914Document26 paginiMUCLecture 2021 112940914Noor FarhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem 8 - General Chemistry 2Document5 paginiStem 8 - General Chemistry 2lorencegalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Exchanger Types and Peltier Cooling PrinciplesDocument31 paginiHeat Exchanger Types and Peltier Cooling PrinciplesArryan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature and The Ideal Gas LawDocument18 paginiTemperature and The Ideal Gas LawAKISÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument4 paginiPhysicsAakrish AryalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Energy LawsDocument24 paginiThermal Energy LawsPengintaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoelectric Refrigeration ExplainedDocument58 paginiThermoelectric Refrigeration ExplainedMaruthappan SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Manual: Heat Transfer ME-316-EDocument27 paginiLaboratory Manual: Heat Transfer ME-316-EMark KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study ChemDocument13 paginiStudy ChemJanthina Rose AusteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utilities 1 ReviewerDocument11 paginiUtilities 1 ReviewerESCARO, JOSHUA G.Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 3-1Document32 paginiModule 3-1MechVfx ProgrammeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peltier Module and Its RefrigerationDocument7 paginiPeltier Module and Its RefrigerationAniket DusaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6ra 2620 6d v57 1a Z Simoreg d38035 Siemens Manual 02Document18 pagini6ra 2620 6d v57 1a Z Simoreg d38035 Siemens Manual 02Stefan IstratescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genie GTH 4013Document202 paginiGenie GTH 4013Sam Manutenção100% (2)
- Damper mechanism details for Atlas Copco rock drills under 40 charactersDocument27 paginiDamper mechanism details for Atlas Copco rock drills under 40 characterssalvador341100% (2)
- Transport Phenomena: Instructor: Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering, BUET, Dhaka-1000Document21 paginiTransport Phenomena: Instructor: Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering, BUET, Dhaka-1000touhidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fallout 1 ManualDocument124 paginiFallout 1 ManualDave100% (1)
- Universal Gen Controller Manual - Digital Display, 8 Inputs, 4 RelaysDocument21 paginiUniversal Gen Controller Manual - Digital Display, 8 Inputs, 4 RelaysBrianHazeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrographic SurveyDocument24 paginiHydrographic SurveyKamal Veer100% (1)
- 262 Controlled Switching of HVAC Circuit Breaker PDFDocument34 pagini262 Controlled Switching of HVAC Circuit Breaker PDFepriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microstructural Characterization, Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms of A Quenched and Tempered Steel Effect of Heat Treatment ParametersDocument22 paginiMicrostructural Characterization, Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms of A Quenched and Tempered Steel Effect of Heat Treatment ParametersAlmerindo JuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zseise 40 ADocument23 paginiZseise 40 ANini FarribasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection, Test, Marking and RecordsDocument10 paginiInspection, Test, Marking and RecordssuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Biasing in TransisterDocument61 paginiAC Biasing in TransisterHariom RavatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nikunj Sir FinalDocument32 paginiNikunj Sir FinalSakthi MuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principle Design Solenoid ValvesDocument28 paginiPrinciple Design Solenoid Valveshassan alrokabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zaman of Chapter 1 - Introduction of HydraulicsDocument35 paginiZaman of Chapter 1 - Introduction of HydraulicsFatin HazwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPU 2201 Online HGNotes - 1 ACADEMIC ESSAYDocument19 paginiMPU 2201 Online HGNotes - 1 ACADEMIC ESSAYtharaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operator's Manual-TT55-TT65-TT75-English PDFDocument129 paginiOperator's Manual-TT55-TT65-TT75-English PDFvalgorunescu@hotmail.com88% (16)
- Ufc 3 430 09Document106 paginiUfc 3 430 09carlcrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume Dr. R.N.MukerjeeDocument13 paginiResume Dr. R.N.MukerjeeRahul Mukerjee100% (1)
- EXPANSION VALVES SERIES DOCUMENT (THERMOSTATIC & CONSTANT PRESSUREDocument44 paginiEXPANSION VALVES SERIES DOCUMENT (THERMOSTATIC & CONSTANT PRESSURESite EngineeringtiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lumidor Minimax XTDocument4 paginiLumidor Minimax XTPaky PakicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adelino Horizontal Multistage PumpDocument13 paginiAdelino Horizontal Multistage PumpJaved HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- More power in less space with SMA SUNNY CENTRAL UPDocument4 paginiMore power in less space with SMA SUNNY CENTRAL UPBrahadeesh Perinkolam MuraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wa500-6 Sen00236-04d PDFDocument1.705 paginiWa500-6 Sen00236-04d PDFanggie100% (4)
- SGP Chapter-1Document81 paginiSGP Chapter-1Shashank ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medium Power Substation Instruction ManualDocument24 paginiMedium Power Substation Instruction ManualOmar GraterolÎncă nu există evaluări
- OMM 00023 Maintenance Guide JDocument49 paginiOMM 00023 Maintenance Guide Jkenedi74100% (2)
- Pneumatic Slotting MachineDocument3 paginiPneumatic Slotting MachineSwami NathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apocalyptic Rhetoric KritikDocument31 paginiApocalyptic Rhetoric KritikMilkdelishÎncă nu există evaluări