Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Parts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 Foundation
Încărcat de
John Thiery FedericoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Parts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 Foundation
Încărcat de
John Thiery FedericoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
(
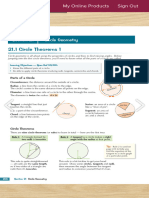
Parts of Circles
Components, circumference, and area of circles.
Parts of Circles
Circles
A circle is the set of all points in the
plane that are the same distance away
from a specific point, called the center.
The center of the circle below is point A .
We call this circle “circle A ,” and it is
A.
⨀
labeled
Important Circle Parts
Radius: The distance from the center of
the circle to its outer rim.
Chord: A line segment whose endpoints
are on a circle.
Diameter: A chord that passes through
the center of the circle. The length of a
diameter is two times the length of a
radius.
Secant: A line that intersects a circle in
two points.
Tangent: A line that intersects a circle in
exactly one point.
Point of Tangency: The point where a
tangent line touches the circle.
The tangent ray −→
T P and tangent
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
segment T P are also called tangents.
Tangent Circles: Two or more circles
that intersect at one point.
Concentric Circles: Two or more circles
that have the same center, but different
radii.
Congruent Circles: Two or more circles
with the same radius, but different
centers.
What if you drew a line through a circle
from one side to the other that does not
pass through the center? What if you
drew a line outside a circle that touched
the circle at one point? What would you
call these lines you drew?
Parts of Circles: Lesso…
Examples
Example 1
A that best fit each
⨀
Find the parts of
description.
a. A radius
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
HA or AF
b. A chord
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
CD , HF , or DG
c. A tangent line
←→
BJ
d. A point of tangency
Point H
e. A diameter
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
HF
f. A secant
←→
BD
Example 2
Draw an example of how two circles can
intersect with no, one and two points of
intersection. You will make three
separate drawings.
Example 3
Determine if any of the following circles
are congruent.
From each center, count the units to the
outer rim of the circle. It is easiest to
count vertically or horizontally. Doing
this, we have:
Radius of A = 3 units
⨀
Radius of B = 4 units
⨀
Radius of C = 3 units
⨀
From these measurements, we see that
A≅ C.
⨀ ⨀
Notice the circles are congruent. The
lengths of the radii are equal.
Example 4
Is it possible to have a line that intersects
a circle three times? If so, draw one. If
not, explain.
It is not possible. By definition, all lines
are straight. The maximum number of
times a line can intersect a circle is twice.
Example 5
Are all circles similar?
Yes. All circles are the same shape, but
not necessarily the same size, so they
are similar.
Review
Determine which term best describes
⨀
each of the following parts of P.
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
1. KG
2. ←→
FH
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
3. KH
4. E
←→
5. BK
←
6. CF
→
7. A
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
8. JG
9. What is the longest chord in any
circle?
Use the graph below to answer the
following questions.
10. Find the radius of each circle.
11. Are any circles congruent? How
do you know?
12. Find all the common tangents for
B and C.
⨀ ⨀
C and E are externally
⨀ ⨀
13.
tangent. What is CE ?
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
14. Find the equation of CE .
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this
PDF file and look for section 9.1.
Resources
Introduction to Circles
Found a content error?
Tell us
Notes/Highlights
Color Highlighted Text Notes
Please Sign In to create your own
Highlights / Notes
Vocabulary Language: English ▼
Term Definition
A line segment whose
chord
endpoints are on a circle.
A circle is the set of all points at
Circle a specific distance from a given
point in two dimensions.
Two or more circles that have
concentric
the same center, but different
circles
radii.
Two or more circles with the
congruent
same radius, but different
circles
centers.
Diameter is the measure of the
distance across the center of a
Diameter
circle. The diameter is equal to
twice the measure of the radius.
point of The point where the tangent
tangency line touches the circle.
The radius of a circle is the
Radius distance from the center of the
circle to the edge of the circle.
The circumference of a circle is
the measure of the distance
Circumference
around the outside edge of a
circle.
The secant of an angle in a
right triangle is the value found
by dividing length of the
Secant hypotenuse by the length of the
side adjacent the given angle.
The secant ratio is the
reciprocal of the cosine ratio.
The tangent of an angle in a
right triangle is a value found by
dividing the length of the side
Tangent
opposite the given angle by the
length of the side adjacent to
the given angle.
Tangent Circles are two or
Tangent
more circles that intersect at
Circles
one point.
Image Attributions
Show Details
Reviews
Was this helpful? ! Yes " No
Back to the top of the page ↑
ABOUT SUPPORT
Our Mission Certified Educator Program
Meet the Team Webinars
Partners CK-12 Resources
Press Pilot Program
Careers Help
Security Contact Us
Community BY CK-12
Success Stories Common Core Math
Blog K-12 FlexBooks®
Overview College FlexBooks®
CK-12 Usage Map Tools and Apps
Testimonials BRAINGENIE™
Select Language ▼
# $ % & '
Terms of Use | Privacy | Attribution Guide |
v2.8.13.20191015113115 | © CK-12 Foundation 2019
FlexBook® Platform
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 5 - Q2 MathDocument19 pagini5 - Q2 MathmtchqnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 Math 7Document7 paginiWeek 7 Math 7Girlie Mae FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Term Lap 2015 16 Unit On CirclesDocument32 pagini2nd Term Lap 2015 16 Unit On CirclesJoshua Tirao100% (1)
- CO1 CircleDocument57 paginiCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CO Math10 Q2 Module3Document18 paginiCO Math10 Q2 Module3Teacher ApolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of A Circle PresentationDocument14 paginiParts of A Circle Presentationromar.allen73Încă nu există evaluări
- Topik-2 Bulatan CircleDocument36 paginiTopik-2 Bulatan Circle许如楠Încă nu există evaluări
- CirclesDocument78 paginiCirclesR Nov100% (1)
- CIRCLES - Angles, ChordsDocument158 paginiCIRCLES - Angles, ChordsMika Pelagio100% (2)
- Circles TheoryDocument4 paginiCircles TheoryJamal AliyevÎncă nu există evaluări
- MELVINDocument16 paginiMELVINRosito BaragoÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 Math Q2 - Week 2 - 3 Angles-and-Arcs-of-Circles-PowerPointDocument64 paginiG10 Math Q2 - Week 2 - 3 Angles-and-Arcs-of-Circles-PowerPointOlive BotiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance TaskDocument3 paginiPerformance TasksaisumichoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angles and Arcs of Circles PowerPointDocument63 paginiAngles and Arcs of Circles PowerPointJP Gorospe50% (2)
- CircumferenceDocument10 paginiCircumferenceyetriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geom Chapter 12 NotesDocument10 paginiGeom Chapter 12 NotesnanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CO1 CircleDocument50 paginiCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil Marquez100% (1)
- Relationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocument12 paginiRelationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesMobile legends gamer100% (2)
- Maths Project For Class 10Document18 paginiMaths Project For Class 10John Nguyen57% (42)
- Use Properties of TangentsDocument13 paginiUse Properties of Tangentssunny2110Încă nu există evaluări
- Polygons, Congruent, Circle and Its PartsDocument9 paginiPolygons, Congruent, Circle and Its PartsVine AlparitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles, Secants & TangentsDocument39 paginiCircles, Secants & TangentsKimmy Airam Ramos100% (1)
- Grade 10 Session 4 CircleDocument57 paginiGrade 10 Session 4 CirclemarlonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 10 CirclesDocument48 paginiNcert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 10 CirclesShubham VishwakaramaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 10 Q2W2Document69 paginiMath 10 Q2W2Leander Kelly Transporte MarianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- COLLEGE PREP Section 10.1/10.2: Distance & Midpoint Formulas, and Circ LesDocument3 paginiCOLLEGE PREP Section 10.1/10.2: Distance & Midpoint Formulas, and Circ LesAml AmlÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP CircleDocument7 paginiLP CircleJoan Grimpola SisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesDocument25 paginiMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesAndreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CirclesDocument23 paginiCirclesDanna Marie OlioÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRE CALCULUS Q2 Angle Measures in A Unit Circle Standard Position of Angles and Its Coterminal AnglesDocument16 paginiPRE CALCULUS Q2 Angle Measures in A Unit Circle Standard Position of Angles and Its Coterminal AnglesekloymontecalvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles Pythagoras and Trigonometry The Secondary VersionDocument91 paginiCircles Pythagoras and Trigonometry The Secondary VersionTonluck Kaimak100% (1)
- Worksheet Q3 Week 6Document2 paginiWorksheet Q3 Week 6Jaybie Tejada100% (1)
- Math 7 Q3W6 Circle and Its PartsDocument52 paginiMath 7 Q3W6 Circle and Its PartsCarlo De Jesus Luna100% (2)
- 2Q-S6 Chords Arcs and Central Angles-1of2Document22 pagini2Q-S6 Chords Arcs and Central Angles-1of2Alice KrodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathamatics Project Inroduction: Name: Ansh Walia Class: 8-F Personal No.: 18469 Topic: CircleDocument5 paginiMathamatics Project Inroduction: Name: Ansh Walia Class: 8-F Personal No.: 18469 Topic: CircleGeta GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet06dated16072021 PDFDocument1 paginăWorksheet06dated16072021 PDFPushpendra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles and Circumference: Lesson 9-5Document10 paginiCircles and Circumference: Lesson 9-5Irene LebrillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolygonsDocument23 paginiPolygonsPietrelle Liana PuruggananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 10 CirclesDocument36 paginiChapter - 10 CirclesYash GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle (Parts, Circumference, and Area)Document12 paginiCircle (Parts, Circumference, and Area)Jerry Mae RanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Week 5&6Document17 paginiOnline Week 5&6Rondex PabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeaP Math G5 Week 8 Q3Document4 paginiLeaP Math G5 Week 8 Q3archie monreal100% (3)
- GEOM Chapter 10ADocument177 paginiGEOM Chapter 10ARaj BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles IntroductionDocument1 paginăCircles IntroductionNelda OabelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles and Other Related TermsDocument36 paginiCircles and Other Related TermsPatricia CadacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demo FinalDocument22 paginiDemo Finalellorinmymae17Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Essential of GeometryDocument14 paginiChapter 1 Essential of GeometryNina HÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Edition - Digital AccessDocument1 paginăOnline Edition - Digital AccessAmreen TiwanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles PPT 1Document14 paginiCircles PPT 1johnzky aquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test AllDocument141 paginiSummative Test AllLairepmi EmjaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 Math Q2 Arcs Angles Segments of A Circle PDFDocument66 paginiG10 Math Q2 Arcs Angles Segments of A Circle PDFshinzhi95Încă nu există evaluări
- Junior78 Feb17Document11 paginiJunior78 Feb17Sawhlan HtetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 19: The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesDocument26 paginiMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 19: The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesSean the sheep60% (5)
- Math ScrapbookDocument13 paginiMath ScrapbookMark Danielle GeolagioÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIRCLESDocument12 paginiCIRCLESripraikouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle and It's PartsDocument20 paginiCircle and It's Partsricel jean panganÎncă nu există evaluări
- CircleDocument45 paginiCircleRoselle G. FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP 2 (Day 2)Document10 paginiDLP 2 (Day 2)Krizia LagmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Elements of Euclid for the Use of Schools and Colleges (Illustrated)De la EverandThe Elements of Euclid for the Use of Schools and Colleges (Illustrated)Încă nu există evaluări
- Dodong G-12Document2 paginiDodong G-12John Thiery FedericoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIL - Q1 - M2 - Introduction To Media and Information Literacy: Imekj Jde Kdbgrijtkgd Lktmrj'yDocument1 paginăMIL - Q1 - M2 - Introduction To Media and Information Literacy: Imekj Jde Kdbgrijtkgd Lktmrj'yJohn Thiery FedericoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.2.4.8 Worksheet - Research FirewallsDocument2 pagini10.2.4.8 Worksheet - Research FirewallsJohn Thiery Federico63% (8)
- Mapeh 10Document31 paginiMapeh 10John Thiery FedericoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A.1 Iterative MethodsDocument20 paginiA.1 Iterative MethodsSaad ManzurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cuet MathDocument8 paginiCuet MathLaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series CompletionDocument7 paginiSeries CompletionKhushi RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 2.: Basic Concepts of Binary Relations and Composition of Binary RelationsDocument2 paginiProblem Set 2.: Basic Concepts of Binary Relations and Composition of Binary RelationsLaith SandoukaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Proof of The Trace Theorem of Sobolev Spaces On Lipschitz DomainsDocument10 paginiA Proof of The Trace Theorem of Sobolev Spaces On Lipschitz DomainsIlyes FerrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ad ReferDocument53 paginiAd ReferHoàng Duy ĐỗÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spcg6e PPT 6 2Document45 paginiSpcg6e PPT 6 2api-334707195Încă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic Equations #BB2.0Document117 paginiQuadratic Equations #BB2.0B MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntegralDocument213 paginiIntegralanantadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LaberportDocument9 paginiLaberportMark GadgetsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2Document10 paginiPaper 2api-210359472Încă nu există evaluări
- Acmna122 - Types of Numbers - Square Triangle Cubed Prime Composite Negative Postive Decimals - UnitDocument67 paginiAcmna122 - Types of Numbers - Square Triangle Cubed Prime Composite Negative Postive Decimals - Unitpoojadogra678Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 14 - Rayleigh and Rician RVDocument6 paginiLecture 14 - Rayleigh and Rician RVSumit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IAL Edexcel Pure Math 1 January 2020Document28 paginiIAL Edexcel Pure Math 1 January 2020Mohamed Said Daw100% (4)
- Four Expressions For Electromagnetic Field Momentum: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Document8 paginiFour Expressions For Electromagnetic Field Momentum: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Abha SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anisiu ValeriuDocument2 paginiAnisiu ValeriuGeorge ProtopapasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlgebraDocument4 paginiAlgebravarchasva SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4: Indices and Logarithms: Jacques Text Book (Edition 4) : Section 2.3 & 2.4Document22 paginiTopic 4: Indices and Logarithms: Jacques Text Book (Edition 4) : Section 2.3 & 2.4Teena_wonder100% (1)
- Intermediate Value Theorem: ContinuousDocument16 paginiIntermediate Value Theorem: ContinuousmasyatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Algebraic ExpressionDocument32 paginiUnit 7 Algebraic Expressionvidyamane23Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 (Derivatives)Document10 paginiChapter 2 (Derivatives)XXUnknownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Trigonometry inDocument11 paginiGrade 10 Trigonometry inDev MaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Einstein 1937Document12 paginiEinstein 1937JonathanHdzÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Ranking Method of Single Valued Neutrosophic Numbers and Its Applications To Multi-Attribute Decision Making ProblemsDocument14 paginiA Ranking Method of Single Valued Neutrosophic Numbers and Its Applications To Multi-Attribute Decision Making ProblemsMia AmaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 The Error in Polynomial InterpolationDocument13 pagini1 The Error in Polynomial InterpolationLovinf FlorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Week 1Document7 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Week 1Paul John TasicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Analysis and Reliability Assessment of Spherical LPG ...Document6 paginiFinite Element Analysis and Reliability Assessment of Spherical LPG ...Suleyman HaliciogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMAE 517: Illinois Institute of TechnologyDocument227 paginiMMAE 517: Illinois Institute of TechnologypadaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics Problems & SolutionsDocument39 paginiStatics Problems & SolutionsYanli Baltero Cruz100% (1)