Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM
Încărcat de
anandkusDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM
Încărcat de
anandkusDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
Critical Alarm
Trouble-
shooting Guide
Document Type: MOP
Document Number: Huawei-GSM-17022010-0001
Prepared By Reviewed By Authorized By
Manish Singh
& Santosh M Jagtap Hiren Joshi
Umesh Jagtap
Release On :- 17-Feb 2010
Validity: Till Further Notification
Page 1 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 1
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
****************************INDEX****************************
Sr.No. Alarm Name Pg
No.
1. 340-Cell PS Service Fault. 3
2. 140-BSC Unable to Read License File. 5
3. 21501-MTP3 DSP Unreachable. 7
4. 21204-Unavailable Sub-Rack. 8
5. 21205-Board Fault. 10
6. 21026-License check Fail Alarm. 14
7. 20233-Service Unequipped On The High-Order Path Of The 16
Optical Port(HPUNEQ).
8. 20238-Remote Defect Indication on the High-Order Path of the 17
Optical Port(HPRDI).
9. 20240-Tributary Unit Alarm Indication Signal. 18
10. 20323-GGCU Failure-Abnormal Frequency Doubler. 19
11. 21210-CPU Overload. 20
12. 20422-Abnormal Voltage. 21
13. 20421-Abnormal Temperature. 22
14. 155-All Ater LAPD Link Faulty. 23
15. 20431-FAN Block Alarm. 24
16. 293-GB BC Faulty. 25
17. 20042-High Board Temperature. 26
18. 331-NSVC Faulty. 27
19. 7508-Optical receive Channel Alarm. 29
20. 7510-Optical Transmit Channel Alarm. 31
21. 21525-SCCP DSP Unreachable. 33
22. 21526-SCCP Subsystem Prohibited. 36
Page 2 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 2
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 340-Cell PS Service Fault.
DESCRIPTION:: This alarm is generated when the Um interface is blocked, or the
Gb interface is blocked.
IMPACT: The CS services and PS services of the out-of-service are disrupted.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check the value of the parameter "Possible cause" in the information used
for locating the fault.
a. "Possible cause" is 0. Add the GDPUP to increase the number of
packet DSPs available.
b. "Possible cause" is 1. Need to apply for a license that supports this
feature.
c. "Possible cause" is 2. Go to 2.
d. "Possible cause" is 3. Go to 3.
2. Run the MML command DSP PSCELL to check whether the cell Um
administration state is blocked.
Y => Adjust the BTS to unblock the Um interface. For example, unblock
the blocked cell.
N => The alarm is cleared.
3. Run the MML command DSP PSCELL to check whether the cell Gb
administration state is blocked.
Y => Go to 4.
N => The alarm is cleared.
4. If the Gb interface board is the GFGUG, check whether the following
types of parent alarms exist.
a. Log in to the LMT. Choose Alarm Maintenance > Browse Alarm to
check whether any of the following parent alarms is reported.
331 NSVC Faulty
332 NSVL Faulty
Page 3 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 3
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
333 NSE Faulty
342 PTP BVC Faulty
Y => Go to b.
b. If any of these alarms is reported, rectify the fault according to the
alarm . Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Page 4 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 4
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 140 BSC Unable to Read License File .
DESCRIPTION: This alarm is generated when the BSC fails to read the license file.
IMPACT: The functions and resources of the BSC system are restricted. If the alarm
persists for seven days, all the services are prohibited.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check the parent alarms.
a. Log in to the LMT. Choose Alarm Maintenance > Browse Alarm to check
whether the following parent alarm is reported.
157 License Inferior Limit
b. If the alarm is reported, rectify the fault according to the alarm. Then,
check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to 2.
2. Check whether the license file exists.
Y => Go to 3.
N => Go to 5.
3. On the MML client, run the MML command LST LICENSE to check whether
the license file is activated.
Y => If the value of "Whether Current License" is "Yes" in the returned
messages, go to [6].
N => Go to 4.
4. On the MML client, run the MML command ACT LICENSE to activate the
specified license file.
Y => If the activation is successful, go to [6].
5. Apply for a valid license file and activate the file.
a. Apply for a valid license file and copy the file to
"\bsc6000\Common\SWM\LICENSE" in the LMT installation directory.
Page 5 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 5
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
On the MML client, run the DLD LICENSE to download the specified
license files on the FTP server to the OMU server.
b. On the MML client, run the MML command ACT LICENSE to activate
the specified license file. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
6. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
Page 6 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 6
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 21501 MTP3 DSP UNREACHABLE.
DESCRIPTION: The alarm is reported when:
(1) There is no response to the MSC or the message cannot be returned.
(2) There is no available route to the DSP.
IMPACT: The signaling unit cannot be sent by the local signaling point to the DSP. The
service is disrupted.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check whether a correlated parent alarm is reported.
Y => Clear the parent alarm according to the corresponding handling suggestions.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
N => Go to 2.
Correlated parent alarm
21503 MTP3 Link Unavailable
This alarm is reported when the parent alarm occurs on the ports for all the
internal signaling links. The parent alarm leads to the child alarm, and they are
reported simultaneously without fixed sequence.
2. Check whether the signaling links to the DSP is configured.
Y => Configure the signaling links.The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to 3.
For details about how to configure the signaling links, refer to the HUAWEI
BSC6000 Base Station Controller Data Config
3. Check the status of the MTP2 link.
Y => If the status of the MTP2 link is in service, Please contact to TEC.
N => check whether the MTP2 Link Service Disrupted alarm is reported.Handle
the alarms according to the suggestions. The alarm handling is complete.
Page 7 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 7
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM : 21204 UNAVAILABLE SUBRACK .
DESCRIPTION: Both active SCU and standby SCU are unavailable. Services related to
the subrack are unavailable.
IMPACT: Both active SCU and standby SCU are unavailable. Services related to the
subrack are unavailable.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check the location information of the alarm. If the extension sub rack reports the
alarm, Go to [2].If remote sub rack reports the alarm, Go to [4].
2. Insert the Ethernet cable securely between the main sub rack and extension sub
rack. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Go to 3.
3. Replace the Ethernet cable between the main subrack and extension subrack.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Go to 6.
4. Check the connectivity/Transmission between the local subrack and remote
subrack. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Go to 5.
5. Replace the E1 cable between the local subrack and remote subrack. Check
whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Go to 6.
6. Request the maintenance personnel to check whether the status of the GSCU
board in the subrack is available.
Page 8 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 8
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
Y => The status of the GSCU is available. Contact to TEC .
N => The status of the GSCU is unavailable. Identify the cause for unavailability
and reset the GSCU. The alarm handling is complete.
Page 9 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 9
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 21205 BOARD FAULT.
DESCRIPTION: This alarm is generated on the SCU in the GMPS when the
communication between the board and the SCU in the GMPS is interrupted.
IMPACT: GOMU:
• The board cannot be maintained.
• If the alarm is generated because the OMU software is stopped, the external IP
address is released. In such a case, if no physical IP address is configured,
operations cannot be performed to the BSC through the network remotely.
• If the alarm is generated because the backup channel is faulty, then the function of
GOMU backup does not take effect, the function of GOMU switchover does not
take effect, and the system performance deteriorates.
Boards other than GOMU:
• The board cannot be maintained.
• The board for which the alarm is generated does not provide services. If the board
works in active/standby mode, the active board takes over the services on the
standby board. If the board does not work in active/standby mode, services on the
board are interrupted.
• If the alarm is generated because the Ethernet cable between subracks is
disconnected, the services may be interrupted.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
If the faulty board is….GOMU:
1. On the LMT, check whether a pair of GOMUs is configured for the BSC.
Y => Go to 2.
N => Contact to TEC.
2. Check whether the standby GOMU is powered on and started.
Y => Go to 3.
N => Insert the standby GOMU. Then, wait until the startup of the GOMU is
complete. Go to 4.
Page 10 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 10
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
3. Check whether the standby GOMU is in the resetting process.
Y => Wait until the startup of the GOMU is complete. Go to 6.
N => Go to 4.
4. Check whether the OMU software on the standby GOMU is started.
Y => Contact to TEC.
N => Start the OMU software on the standby GOMU. Then, check whether the
alarm is cleared.
5. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Contact to TEC.
Boards other than the GOMU:
1. If the remote TC subrack is configured, check whether the OML on the Ater
interface is disconnected.
a. On the LMT, check whether the remote configuration is adopted and
whether all boards in the TC subrack are unavailable.
Y => Go to b.
N => Go to 2.
b. Log in to the LMT. Choose Alarm Maintenance > Browse Alarm to check
whether the following parent alarm is reported.
21551 Ater OML Broken Alarm
Y => Go to c.
N => Go to 2.
c. If the alarm is reported, rectify the fault according to the alarm . Then,
check whether the alarm is cleared.
Page 11 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 11
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to 2.
2. Check whether the Ethernet cable between SCUs of the GMPS and another
subrack is disconnected.
a. On the LMT, check whether all boards in the subrack are unavailable.
Y => Go to b.
N => Go to 3.
b. Check whether the port on panel of the SCU in the GMPS is enabled.
Y => Go to d.
N => Enable the port on the panel. Go to c.
c. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to d.
d. Check whether the Ethernet cable between the SCUs on the GMPS and the
problematic subrack is normal and whether the Ethernet port LED is
normal.
Y => Contact to TEC.
N => Replace the Ethernet cable. Go to 4.
3. Check whether the board is faulty.
a. On the LMT, check whether the board is being loaded. After the board is
successfully loaded, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to b.
b. Check whether the board is removed. Insert the board and wait until the
loading of the board is complete. Then, check whether the alarm is
cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
Page 12 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 12
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
N =>Go to c.
c. Remove and then reinsert the board when the traffic volume is low. Then,
check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to d.
d. Replace the board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Contact to TEC.
4. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Contact to TEC.
Page 13 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 13
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 21026 LICENSE CHECK FAIL ALARM
DESCRIPTION: This alarm is generated when the parsing of the license file fails because
the license file is not available, the license file will expire in 30 days, or the license file
already expires.
IMPACT: 60 days after the license file is invalid, the functions and resources controlled
by the license will be restricted and the control items of products are reduced to the
minimum configuration. This may affect the services.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check the value of the parameter Reason of check failure in the information used
for locating the fault.
a. The value is "0 = Parsing license error". Go to 2.
b. The value is "1 = License expired". Go to 6.
c. The value is "2 = No activated license". Go to 3.
d. The value is "3 = License will expire". Go to 6.
2. Reload the specified license file and reactivate it.
a. Run the MML command DLD LICENSE on the MML client to
download the specified license file on the FTP server to the GOMU server
through FTP.
b. Run the MML command ACT LICENSE on the MML client to activate
the specified license file.
Y => Go to 7.
N => Go to c.
c. Check whether the license file matches the configured signaling point.
Y => Contact to TEC.
N => Go to d.
d. Apply for a new license according to the configured signaling point and
activate it. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
Page 14 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 14
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
N => Contact to TEC.
3. Check whether the license file exists.
Y => Go to 4.
N => Go to 5.
4. Run the MML command LST LICENSE on the MML client to check whether
the license file is activated.
Y => Go to 7.
N => Go to 5.
5. Run the MML command ACT LICENSE on the MML client to activate the
specified license file.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Contact to TEC.
6. Apply for a valid license file and activate it.
a. Apply for a valid license file and copy it to
\bsc6000\Common\SWM\LICENSE in the LMT installation directory.
Run the MML command DLD LICENSE on the MML client to
download the specified license file on the FTP server to the GOMU or
GBAM server through FTP.
b. Run the MML command ACT LICENSE on the MML client to activate
the specified license file. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Contact to TEC.
7. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Contact to TEC.
Page 15 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 15
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 20233 SERVICE UNEQUIPPED ON THE HIGH-
ORDER PATH OF THE OPTICALPORT (HPUNEQ).
DESCRIPTION: Higher order path is unequipped with service.
IMPACT: The services on this optical faulty are interrupted.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check the connection between BSC board and peer board.
2. Check the configuration of peer board…
Set the RX C2 byte on the peer board to 0x02, and then check whether the alarm is
cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Please contact to TEC.
Page 16 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 16
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 20238 REMOTE DEFECT INDICATION ON THE
HIGH-ORDER PATH OF THE OPTICAL PORT (HPRDI).
DESCRIPTION: Higher order path remote defect indication at the receiver side of optical
interface.
IMPACT: The service carried on the faulty optical fiber is interrupted.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check whether any of the following alarms exist on the peer equipment: 20232
Loss of Administration Unit Pointer (AULOP),20231 Administration Unit
Alarm Indication Signal (AUAIS), 20235 High-Order Path Signal Label Byte
Mismatch (HPSLM), or 20234 Trace Flag Mismatch on the High-Order Path
of the Optical Port (HPTIM).
Y => Go to 2.
N => Please contact to TEC.
2. Ask the maintenance personnel at the peer end to clear the alarms there, and then
check whether the alarm on the local equipment is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Please contact to TEC.
Page 17 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 17
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM : 20240 TRIBUTARY UNIT ALARM INDICATION
SIGNAL.
DESCRIPTION: Tributary unit alarm indication signal. No signal is detected between the
peer equipment (BTS or BSC) and the transmission equipment, whereas the transmission
equipment is normally connected with the local equipment.
IMPACT: Services carried on the affected tributary unit stop.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check the connection at peer board.
2. Check the status of Transmission availability.
3 Check the status of peer board availability.
Page 18 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 18
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM : 20323 GGCU FAILURE-ABNORMAL
FREQUENCY DOUBLER.
DESCRIPTION: Clock frequency doubler of GGCU board abnormal alarm.
IMPACT: System performance may degrade.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
Reset the board.
1. Wait until the board is successfully loaded and restarted. Check whether the alarm
is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Go to 2.
2. Replace the board and wait until the board is successfully restarted. Check
whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Please contact to TEC.
Page 19 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 19
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM: 21210 CPU OVERLOAD.
DESCRIPTION: This alarm is generated when the CPU usage exceeds 85% and this
situation lasts for more than one minute. When the CPU usage is over high, the flow
control occurs. As a result, the capability of processing services reduces and even the
board is reset.
IMPACT: When the CPU usage is overhigh, the flow control occurs. As a result, the
capability of processing services reduces and even the board is reset.
ALARM RESTORATION PROCEDURE:
1. Check whether the current traffic is increasing.
Y => The alarm is cleared after the traffic reduces. The alarm handling is
complete.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Go to 2.
2. Check whether any hardware or software fault of the board occurs.
a. If the boards work in active/standby mode, log in to the LMT to perform
the board switchover. If the boards do not work in active/standby mode,
reset the board (the services will be interrupted). Then, check whether the
alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to b.
b. Remove and then reinsert the board when the traffic volume is low. Then,
check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Go to c.
c. Replace the board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N=> Contact to TEC.
Page 20 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 20
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:20422-Abnormal Voltage
Alarm Description
This alarm is reported when one supply voltage of the input power in the power
distribution box or one supply voltage of the environment monitoring device exceeds the
upper or lower voltage limitation
Impact on System
The power distribution box supplies power abnormally. This may has an impact on
normal running of the system. If the voltage exceeds the upper or lower limitation, the
power module on the board might stop supplying power and the service is interrupted.
Step to Resolve the Alarm
1. Check the duration of the alarm. If the duration is less than 10 seconds, the alarm
is reported because of the voltage pulsation and is unnecessary to be handled.
2. If the duration is long, Check whether the power supply is normal.
Y=> This indicates that the board is faulty. Go to 3.
N=> The power supply is over voltage or under voltage. Inform the network
operator to take certain measures, such as power transfer or battery maintenance.
The alarm handling is complete.
NOTE:
The evaluation standard of 48 V power supply system: Undervoltage alarm ranges
from -40 V to -42 V; overvoltage alarm ranges from -57 V to 60 V.
The evaluation standard of 60 V power supply system: Undervoltage alarm ranges
from -71 V to -75 V;
overvoltage alarm ranges from -42 V to -50 V.
3. Reset the power distribution box on the LMT. After the power distribution box is
registered successfully, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y =>The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N =>The alarm persists. Please contact TEC.
Page 21 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 21
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:20421-Abnormal Temperature.
Description
An over temperature alarm is reported when the fan box or independent fan
box detects that the temperature exceeds the upper temperature threshold.
An under temperature alarm is reported when the temperature of the power
distribution box or the environment monitor device exceeds the lower
temperature threshold. In reverse, an over temperature alarm is reported.
Impact on System
The over temperature or the under temperature of the cabinet has an impact
on normal running of the system.
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. According to the alarm information, you can make sure that the alarm
is caused by over temperature or under temperature.
Y=> An over temperature alarm is reported. Go to 2.
N=> An under temperature alarm is reported. Go to 3.
2. If an over temperature alarm is reported, you can power on the air
conditioner or the ventilating fan to lower the environment
temperature.
Y =>The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N =>The alarm persists. Please contact TEC.
3. If an under temperature alarm is reported, you can power on the air
conditioner to increase the environment temperature.
Y =>The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N =>The alarm persists. Please contact TEC.
Page 22 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 22
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:155All Ater LAPD Link Faulty
Alarm Description
This alarm is reported when all of the Ater Lapd links are disrupted.
Impact on System
The BSC can not apply the resource for the services.
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check the E1/T1 links on the Ater interface are faulty
Y = Check the Ater interface GOIUT card in BSC.
N = Go to 2.
2. Chek at any LOSS on all ater E1
Y = Check at Transport end.
N = Please contact TEC.
Page 23 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 23
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:20431-FAN Block Alarm.
Alarm Description
The alarm is reported in case of fan block
Impact on System
Fan block affects system running environment, such as temperature and humidity.
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check whether the air filter is functional.
Y => Go to 3.
N => Clean the air filter and then install it. For the method of installing the air
filter, refer to the BSC6000 Parts Replacement Guide. Go to 2.
2. Check whether the fan rev is nomal. The full rev is 4000 RPM.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Go to 3.
3. Replace the fan subrack and check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => Please contact TEC.
Page 24 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 24
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:293-GB BC Faulty
Alarm Description
BC is a binding of E1's some slots for transferring service data and signaling data. This
alarm is reported when the Gb interface is broken, the configuration of Gb interface is
faulty, or the BC is blocked.
Impact on System
The services of the SCCP subsystem are stopped
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check whether the E1 cable between the BSC and the SGSN is correct;
Y => Go to 2;
N => Connect BSC and SGSN again.
2. On the local maintenance terminal of BSC and SGSN, separately run the MML
command LST BC. Check whether the configurations include sub rack No., slot
No., port No., BC ID, Times lot Mask of BSC and SGSN are the same;
Y => Same, Go to 3;
N => Different, Go to 4;
3. On the local maintenance terminal of BSC, run the MML command DSP BC.
Check whether the BC is blocked;
Y => Blocked, run the UBL BC to unblock the BC;
N => Unblocked, contact TEC
Page 25 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 25
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:20042-High Board Temperature
Alarm Description
The temperature of the test point of the board is over the critical high threshold
Impact on System
The board will be damaged soon
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check whether the fan box is faulty .
Y => The fan box is faulty. Replace the fan box. Go to 2.
N => The fan box is normal. Go to 2.
2. Check whether there are empty slots which have not installed dummy panels.
Y => There are empty slots which have not installed dummy panels. Go to 3.
N => All the slots have installed boards or dummy panels. Go to 3.
3. Check whether the temperature exceeds the normal operation range for the
equipment.
Y => The temperature exceeds the normal operation range for the equipment.
Adjust the temperature to the normal operation range. Go to 4.
N => The temperature does not exceed the normal operation range. Please contact
TEC.
4. Wait for 30 minutes and check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Please contact TEC.
Page 26 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 26
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:331-NSVC Faulty
Alarms Description
The NSVC refers to the virtual connection at the NS layer of the Gb interface. This alarm
is generated when the GEPUG is faulty, the NSVC is blocked, the bearer channel is
inaccessible, or the configuration of the BSC and SGSN is faulty.
Impact on System
• If the backup NSVL is not configured, the data services in the relevant cells
cannot be performed;
• If a backup NSVL is configured, the data services in the relevant cells can be
performed, but the service capacity decreases.
Steps to resolve the alarm
1. Run the MML command DSP NSVC to check whether the NSVC is blocked.
Y => Run the MML command UBL NSVC to unblock the NSVC.
N => Go to 2.
2. Run the MML command DSP BC to check whether the BC is available.
Y => Go to 3
N => Configure the BC until the service is available.
3. On the LMT of the BSC and the SGSN, separately run the MML command LST
NSVC. Check whether the configuration of the NSE and NSVC on the BSC and
that on the SGSN are consistent.
Y => Go to 4.
N => Configure the NSE and Configure the NSVC of the BSC to ensure that they
are consistent with those of the SGSN
4. On the LMT, check whether the GEPUG runs normally.
Y => Go to 5.
N => Remove and reinsert the GEPUG until the board works normally.
Page 27 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 27
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
5. Run the MML commands DSP BC and DSP PVC. Check whether the statistical
data of the BC and PVC is normal.
Y => The alarm handling is complete.
N => TEC
Page 28 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 28
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:7508-Optical receive Channel Alarm
Alarm Description
This alarm is triggered when the RLOS (signal loss at receiving end) alarm, or the RLOF
(frame loss at receiving end) alarm, or the HPLOM (multi-frame loss at high-phase
channel) alarm occurs to the TEU.
Impact on System
Services borne by the faulty optical interface are interrupted. If the optical interface
connecting to the lower level devices fails, services supported by the lower level devices
will be interrupted. If the optical interface connecting to the upper level devices fails,
services supported by the devices of the lower level or the local level will be interrupted.
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check configuration for optical fiber
On optical transmission network management system, select the TEU, click
"Configuration/Upload/Download Configurations" to upload the board data. Click
the "Payload" button in the toolbar to display an interface, where the
configuration for "Westward", "Eastward" and "TU" are listed. If "Eastward" has
been configured but the corresponding fiber has not been connected, then remove
the configuration of Eastward service. View whether the alarm is cleared.
Y=> The alarm handling ends.
N=> Go to Step 2.
2. Check optical transmission network
Check to ensure the power supply for other network elements (NE) in the optical
transmission network is normal, and the cable connecting to the local BTS has
been connected properly, and the transmission devices of the upper layer are in
normal operation. Clear the faults of other NEs if any. View whether the alarm is
cleared.
Y=> The alarm handling ends.
N=> Go to Step 3.
3. Check the fiber connector and flange
Page 29 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 29
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
Check whether the tail fiber is neat, and whether the flange is properly connected.
Clean the tail fiber if dirty and reconnect the flange properly. View whether the
alarm is cleared.
Y=> The alarm handling ends.
N=>Go to Step 4.
4. Measure power of optical signals from the peer end
Measure the power of optical signals from the peer end to see whether the result is
smaller than -28dBm.
Y=>The optical path is normal. Go to Step 5.
N=>Since the attenuation of optical signals is overmuch or the components of the
optical path are in poor contact, the BTS cannot receive optical signals. Clear the
fault of the peer end. The alarm handling ends.
5. Perform self-loop for western optical fiber and eastern optical fiber
Perform self-loop for western optical fiber and eastern optical fiber. View whether
the alarm is cleared.
Y=> The alarm handling ends.
N=> TEC. The alarm may be caused by TEU hardware failure.
Page 30 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 30
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:7510-Optical transmit Channel Alarm
Alarms description
This alarm is triggered when the optical transmitter in the IASU detects transmit loss of
signal (TLOS) or transmit loss of clock (TLOC) or the optical receiver detects multiplex
section remote defect indication (MSRDI) from the peer site.
Impact on System
Services borne by the faulty optical interface are interrupted. If the optical interface
connecting to the lower level devices fails, services supported by the lower level devices
will be interrupted. If the optical interface connecting to the upper level devices fails,
services supported by the devices of the lower level or the local level will be interrupted.
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check the fiber connector and pigtail fiber
Check whether the fiber connector is loose or blurred. If yes, clear it with alcohol
and securely connect it to the port.
Check whether the pigtail fiber connected with the local or peer site is severely
bent or broken. If yes, bundle it well or replace it with a normal one.
Then check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y=> The alarm handling ends.
N=> Go to Step 2.
2. Check the transmit and receive optical power of the optical module
Measure the receive optical power of the local site and the transmit optical power
of the peer one with an optical power meter based on the optical path
corresponding to the "Sub No.".
Check whether the receive optical power is within -35 dBm to -28 dBm and
Check whether the transmit optical power is within -15 dBm to -8 dBm.
Y=> The receive and transmit optical power is normal.Please contact Huawei
Customer Service Center
N=> The measured transmit optical power is low.Please contact Huawei
Customer Service Centero check whether the fiber is in bad contact with the port
Page 31 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 31
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
and whether it is damaged. Verify that the fiber is normal, replace the MCU in the
local site. The alarm handling ends.
N=> The receive optical power is low. Pls contact TEC to check whether the fiber
is in bad contact with the port and whether it is damaged. If yes, securely connect
the fiber or replace it with a normal one. The alarm handling ends.
Page 32 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 32
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:21525-SCCP DSP Unreachable
Alarm Description
This alarm is generated if the handshake between the BSC and the MSC at the SCCP
layer fails.
Impact on System
The signaling interaction and the services between the BSC and the MSC are disrupted.
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. Check the data configurations.
a. Check whether the data configurations of the SS7 signaling points of the
BSC are the same as those of the MSC.
Y => The data configurations of the SS7 signaling points are the same. Go
to c.
N => The data configurations of the SS7 signaling points are different. Go
to b.
b. Ensure that the data configurations of the SS7 signaling points of the BSC
are the same as those of the MSC. Then, check whether the alarm is
cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Go to c.
c. Check whether the data configurations of the SS7 signaling links of the
BSC are the same as those of the MSC.
Y => The data configurations of the SS7 signaling links are the same. Go
to e.
N => The data configurations of the SS7 signaling links are different. Go
to d.
d. Ensure that the data configurations of the SS7 signaling links of the BSC
are the same as those of the MSC. Then, check whether the alarm is
cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
Page 33 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 33
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Go to e.
e. Check whether the data configurations of the SS7 signaling links are
consistent with the physical connections.
Y => The data configurations of the SS7 signaling links are consistent
with the physical connections. Go to 2.
N => The data configurations of the SS7 signaling links are inconsistent
with the physical connections. Go to f.
f. Ensure that the data configurations of the SS7 signaling links are
consistent with the physical connections. Then, check whether the alarm is
cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Go to 2.
2. Check the status of the SCCP DSP and of the MTP3 link.
a. Check whether the SCCP DSP is manually inhibited.
Y => The SCCP DSP is manually inhibited. Go to b.
N => The SCCP DSP is not manually inhibited. Go to c.
b. Uninhibit the SCCP DSP. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Go to c.
c. Check whether the MTP3 link is deactivated.
Y => The MTP3 link is deactivated. Go to d.
N => The MTP3 link is not deactivated. Go to 3.
d. Activate the MTP3 link. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm is not cleared. Go to 3.
3. Check whether the BSC is reset.Inquire the maintenance engineers about whether
the BSC is reset.
Page 34 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 34
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
Y => The BSC is reset. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The BSC is not reset. Go to 4.
4. Log in to the LMT and then choose Alarm Maintenance > Browse Alarm. Check
whether the alarm 21528 Remote SCCP Fault is reported.
Y => The alarm is reported. The SCCP management subsystem of the MSC is
faulty. Contact the maintenance engineers of the MSC. The alarm handling is
complete.
N => The alarm is not reported. Go to 5.
5. Check for the parent alarms.
Page 35 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 35
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
ALARM:21526-SCCP Subsystem Prohibited
Alarm Description
The alarm is reported when the SCCP subsystem is prohibited.
Impact on System
The services of the SCCP subsystem are stopped
Steps to resolve the Alarm
1. In the Brow Alarm window on the LMT, check whether 21525 SCCP DSP
Unreachable is reported.
Y => The SCCP DSP is inaccessible. Handle the alarm according to the
suggestions in 21525 SCCP DSP Unreachable.
N => Go to 2.
2. Check the state of the SCCP subsystem. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If the SCCP subsystem is in the OPERATION ALLOW state, the prohibit
message of the destination point is received. You have to wait for the allow
message of the destination point without any handling.
If the SCCP subsystem is in the OPERATION PROHIBIT state, uninhibit the
subsystem operation.
Y => The alarm is cleared. The alarm handling is complete.
N => The alarm persists. Please contact TEC.
Page 36 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 36
Critical Alarms For Huawei GSM.
Page 37 of 37 ALUMS TEC -RAN. 37
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Digital Profit CourseDocument16 paginiDigital Profit CourseanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- eRAN8.1 Deep Dive - ACH Feature I Ntroduction: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument27 paginieRAN8.1 Deep Dive - ACH Feature I Ntroduction: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDSony SonjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finalized Feature ListDocument8 paginiFinalized Feature ListAkbar Shaukat0% (1)
- LTE PRACH Planning and Configuration GuideDocument30 paginiLTE PRACH Planning and Configuration GuideMahesh PratapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jazan ACP ReportDocument26 paginiJazan ACP ReportUmer AftabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 《NICE3000new电梯一体化控制器用户手册》英文19010735 A00Document367 pagini《NICE3000new电梯一体化控制器用户手册》英文19010735 A00Иван АндреевÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTE BasicsDocument70 paginiLTE BasicsYash MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkDe la EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 LTE eRAN6.0 UL CoMP Feature ISSUE 1.00Document29 pagini4 LTE eRAN6.0 UL CoMP Feature ISSUE 1.00Umair BaqaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- UMTS Troubleshooting Guideline 1 02Document107 paginiUMTS Troubleshooting Guideline 1 02Ankur VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectrum Effect Meeting With Digicel at MWC Feb 28 2022Document34 paginiSpectrum Effect Meeting With Digicel at MWC Feb 28 2022Yadav ShailendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic ParameterDocument9 paginiBasic ParameterSubash Kafle100% (1)
- LTE SwitchesDocument4 paginiLTE Switchesmohamed fadlÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC6900 UMTS Guide To Avoiding Network Problems (V900R012) - 20110524-A-V1.40Document173 paginiBSC6900 UMTS Guide To Avoiding Network Problems (V900R012) - 20110524-A-V1.40Anonymous g8YR8b9Încă nu există evaluări
- Radio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSDe la EverandRadio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSJaana LaihoEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- OWO300050 WCDMA Abnormal Interference Problem Analysis ISSUE 1.00Document71 paginiOWO300050 WCDMA Abnormal Interference Problem Analysis ISSUE 1.00riamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM HuaweiDocument30 paginiGSM HuaweiSri Datta Sameer AchantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Interface Protocol and Signaling Flow 50Document48 pagini3 Interface Protocol and Signaling Flow 50Chidhuro OwenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21CS43 - Module 1Document21 pagini21CS43 - Module 1EMMANUEL RAJARATHNAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ciphering Feature Parameter Description: GSM Bss GBSS14.0Document34 paginiCiphering Feature Parameter Description: GSM Bss GBSS14.0Gunvant ParmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNP Extension: Prerequisites: Radio Network Engineering FundamentalsDocument130 paginiRNP Extension: Prerequisites: Radio Network Engineering Fundamentalsddaann100% (1)
- UMTS Heavy Traffic Precautions and Emergency MeasureDocument28 paginiUMTS Heavy Traffic Precautions and Emergency Measurekara nacimÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRACH Planning11Document2 paginiPRACH Planning11goat55555Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Frequency HoppingDocument9 paginiWhat Is Frequency Hoppingdepeople_arsenal7569Încă nu există evaluări
- Kathrein 738449 Omni Dual-BandDocument1 paginăKathrein 738449 Omni Dual-BandVirgil PeiulescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- RL Re-Establishment SolutionDocument9 paginiRL Re-Establishment Solutionjkpllan3Încă nu există evaluări
- 05 eNodeB O&MDocument25 pagini05 eNodeB O&MHung NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coverage Evaluation For 5G Reduced Capability New Radio (Nr-Redcap)Document12 paginiCoverage Evaluation For 5G Reduced Capability New Radio (Nr-Redcap)pfeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interference Detection UMTSDocument14 paginiInterference Detection UMTSAmit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRAN13.1 CloudAIR Feature Description (Digicel)Document44 paginiSRAN13.1 CloudAIR Feature Description (Digicel)Luis Carlos SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oeo106060 Lte Eran3.0 Handover Feature Issue1.00Document76 paginiOeo106060 Lte Eran3.0 Handover Feature Issue1.00Sami DohaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM SystraDocument84 paginiGSM SystraJm RoxasÎncă nu există evaluări
- RL FailureDocument2 paginiRL FailureGunawan HendroÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZXUR 9000 UMTS (V4.14.10.14) Radio Network Controller Radio Parameter ReferenceDocument955 paginiZXUR 9000 UMTS (V4.14.10.14) Radio Network Controller Radio Parameter ReferencePantheraLeoSkTauÎncă nu există evaluări
- RET Antenna TD-LTE Maintenance GuideDocument24 paginiRET Antenna TD-LTE Maintenance Guidehawdang nureeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC6900 UMTS Parameter Reference (V900R012C01 - 03)Document931 paginiBSC6900 UMTS Parameter Reference (V900R012C01 - 03)snsingh_ecÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Sectorization Sector SplitDocument8 pagini3G Sectorization Sector SplitAmos JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSDPA Throughput OptimizationDocument4 paginiHSDPA Throughput OptimizationroniÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMA AnalysisDocument17 paginiTMA AnalysissamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Search Procedures in LTE SystemsDocument6 paginiCell Search Procedures in LTE Systemshassan abousalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC6910 GU V100R016C00SPC650 Parameter ReferenceDocument597 paginiBSC6910 GU V100R016C00SPC650 Parameter ReferenceMuntazir Mehdi0% (1)
- ZGO-04-04-002 Load Dependent Intelligent TRX Shutdown Feature Guide ZXUR 9000 (V12.2.0) - V1.10 - 20130516Document37 paginiZGO-04-04-002 Load Dependent Intelligent TRX Shutdown Feature Guide ZXUR 9000 (V12.2.0) - V1.10 - 20130516Nosherwan LatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Zong .SSV ReportDocument12 pagini3G Zong .SSV ReportFaise JanÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Smart AntennaDocument8 paginiWhat Is A Smart AntennaRockstar_rohithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radio Link Budget - WDocument29 paginiRadio Link Budget - WAhmed El ShafieÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Optimization Tools You Use?Document17 paginiWhat Are The Optimization Tools You Use?uttam kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcatel BSS Parameter DictionaryDocument1.278 paginiAlcatel BSS Parameter DictionaryrajasapramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Propagation For LTE Product-LTE RRU Channel TroubleshootingDocument11 paginiPropagation For LTE Product-LTE RRU Channel TroubleshootingSedjali Ali-Mustapha100% (1)
- Inter-PLMN Handover: The ProblemDocument2 paginiInter-PLMN Handover: The ProblemmaheshwankhedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft PowerPoint - OEO106010 LTE eRAN6.0 Idle Mode Behavior ISSUE 1Document26 paginiMicrosoft PowerPoint - OEO106010 LTE eRAN6.0 Idle Mode Behavior ISSUE 1javadiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Frequency PlanningDocument10 paginiGSM Frequency PlanningIftikhar AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- T3109, RLT and SACCH Multiframe Related Problem 27062006Document3 paginiT3109, RLT and SACCH Multiframe Related Problem 27062006Salman ZaheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huawei GSM Grfu: Wireless Case and TrainingDocument35 paginiHuawei GSM Grfu: Wireless Case and TrainingChristopher AiyapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RRU ECM Report - E202203291840-01-1Document31 paginiRRU ECM Report - E202203291840-01-1Délsio CabáÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samsung MBS (LTE) Counter Description For SLR 3 1 - V 03 00Document419 paginiSamsung MBS (LTE) Counter Description For SLR 3 1 - V 03 00Sunil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Frequency PlanningDocument54 paginiGSM Frequency Planningspuki210467% (3)
- ZTE LTE + Volte Radio Network Functionality (5 Days)Document5 paginiZTE LTE + Volte Radio Network Functionality (5 Days)vikasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Control HWII and HWIII AlgorithmsDocument48 paginiPower Control HWII and HWIII AlgorithmsFaisal Ahmad JafriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionDe la EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gonda Rigger Site Visit TrackingDocument236 paginiGonda Rigger Site Visit TrackinganandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jan.20 MappingDocument103 paginiJan.20 MappinganandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jan.20 MappingDocument103 paginiJan.20 MappinganandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated TRT MappingDocument12 paginiUpdated TRT MappinganandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- UP East Audit Bahraich CMPDocument2 paginiUP East Audit Bahraich CMPanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- UP East Audit Bahraich CMPDocument2 paginiUP East Audit Bahraich CMPanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated TRT MappingDocument12 paginiUpdated TRT MappinganandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gonda Rigger Site Visit TrackingDocument236 paginiGonda Rigger Site Visit TrackinganandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partner Incentive Structure UpdatedDocument1 paginăPartner Incentive Structure UpdatedanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis Report For TASR Degradation of Allhabad GSM BSC2Document5 paginiAnalysis Report For TASR Degradation of Allhabad GSM BSC2anandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utter Pradesh East AUDIT 2020Document9 paginiUtter Pradesh East AUDIT 2020anandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis Report For TASR Degradation of Allhabad GSM BSC2Document5 paginiAnalysis Report For TASR Degradation of Allhabad GSM BSC2anandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Frequency Allocation Plan-2011 - Page No 237 & 238Document277 paginiNational Frequency Allocation Plan-2011 - Page No 237 & 238suresh5254Încă nu există evaluări
- GSM TimerDocument10 paginiGSM Timerdimond_teaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course 22Document1 paginăCourse 22luckycoolariesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 418111000LE4.0 - V1 - LTE End-to-End Solution OverviewDocument666 pagini418111000LE4.0 - V1 - LTE End-to-End Solution OverviewanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investor Portal - RedemptionDocument1 paginăInvestor Portal - RedemptionanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ravi Shankar Kushwaha: Email: Contact NoDocument2 paginiRavi Shankar Kushwaha: Email: Contact NoanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE LKG Syllabus For MathsDocument4 paginiCBSE LKG Syllabus For MathsanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced 3G and 4G Wireless MobileDocument2 paginiAdvanced 3G and 4G Wireless MobileApoorva AakarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ravi Shankar Kushwaha: Email: Contact NoDocument2 paginiRavi Shankar Kushwaha: Email: Contact NoanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Frequency Allocation Plan-2011 - Page No 237 & 238Document277 paginiNational Frequency Allocation Plan-2011 - Page No 237 & 238suresh5254Încă nu există evaluări
- IrectDocument16 paginiIrectBhargav MosaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- FreqspecDocument2 paginiFreqspecSachin GhodkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epf 10CDocument4 paginiEpf 10Csandee1983Încă nu există evaluări
- Anand SinghhhhhDocument1 paginăAnand SinghhhhhanandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tra.I: Telec:::Omreg J ' OR ..AUT OR X ( S) - 110002Document7 paginiTra.I: Telec:::Omreg J ' OR ..AUT OR X ( S) - 110002anandkusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Configuration: ENE040613040002 HUAWEI BSC6000Document72 paginiData Configuration: ENE040613040002 HUAWEI BSC6000Thirupathi SubbaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18cs43 Os Module1Document46 pagini18cs43 Os Module1Shan MpÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCA New Syllabus 25 ReduceDocument27 paginiBCA New Syllabus 25 ReducePawan SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colibri Arm Som Pxa270 Technical Reference ManualDocument1.246 paginiColibri Arm Som Pxa270 Technical Reference ManualАртемÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calibrating The ADE7753 For Watt, VAR, RMS and VA MeasurementsDocument40 paginiCalibrating The ADE7753 For Watt, VAR, RMS and VA MeasurementsOoal GonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab MicroprocessorsDocument45 paginiLab MicroprocessorsSweetsoulUroojMalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec54-Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument11 paginiEc54-Microprocessors and Microcontrollersbaluchandrashekar2008Încă nu există evaluări
- Freescale KL16P64M48SF5 DatasheetDocument56 paginiFreescale KL16P64M48SF5 Datasheetspas2014Încă nu există evaluări
- TinyosDocument15 paginiTinyosYankur YiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pi PolonesDocument47 paginiPi PolonesSultan Backdoor100% (1)
- ES RX63N Reprint Soft Proof 2013-09-30Document468 paginiES RX63N Reprint Soft Proof 2013-09-30Felipe NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- C200H ASCII Units Operation - ManualDocument307 paginiC200H ASCII Units Operation - ManualcoronaqcÎncă nu există evaluări
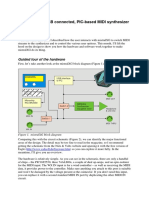
- Mistralxg - A Usb Connected, Pic-Based Midi Synthesizer: Let'S Get Technical!Document9 paginiMistralxg - A Usb Connected, Pic-Based Midi Synthesizer: Let'S Get Technical!CristobalzqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tech Talks Discover The Security Features of Secure VaultDocument27 paginiTech Talks Discover The Security Features of Secure Vaultsanjeev sanjeevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual - MOVI-PLC® SyncCrane Application - SEW Eurodrive (PDFDrive)Document120 paginiManual - MOVI-PLC® SyncCrane Application - SEW Eurodrive (PDFDrive)A-selam IbraÎncă nu există evaluări
- At91sam75 PDFDocument27 paginiAt91sam75 PDFValdenor CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arm NewDocument347 paginiArm Newvenu4a1Încă nu există evaluări
- U3 PIC 18F Microcontroller InterruptsDocument59 paginiU3 PIC 18F Microcontroller Interruptsmadhukar v nimbalkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALC202 (&a) Data Sheet - 1.28Document42 paginiALC202 (&a) Data Sheet - 1.28Daniel Nepomuceno RayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- m220 Service ManualDocument49 paginim220 Service ManualDave SharpÎncă nu există evaluări
- msp430g2553 PDFDocument72 paginimsp430g2553 PDFNguyen Tuan DanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIBGUARD Installation LIT78 220 032019 enDocument54 paginiVIBGUARD Installation LIT78 220 032019 enCường LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec8691 Iq R17Document2 paginiEc8691 Iq R17Hema HoneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAC Modul 2Document18 paginiSAC Modul 2Jepri MarpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oslectureset 1 SPR 20Document102 paginiOslectureset 1 SPR 20Anigrah RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grundfos Dosing Pump DDA DDC DDEDocument44 paginiGrundfos Dosing Pump DDA DDC DDEAndrew KeelingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens SW Using Hypervisor For Infotainment and AUTOSAR Consolidation White Paper tcm27-95958Document12 paginiSiemens SW Using Hypervisor For Infotainment and AUTOSAR Consolidation White Paper tcm27-95958Truc LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- LM629 AN-693 Programming Guide PDFDocument33 paginiLM629 AN-693 Programming Guide PDFBruno SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Microcontroller and ApplicationsDocument40 paginiJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Microcontroller and ApplicationsAkash BÎncă nu există evaluări