Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Annaunivqp
Încărcat de
Shankar0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
28 vizualizări2 paginiElectron Devices
Titlu original
annaunivqp
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
RTF, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentElectron Devices
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca RTF, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
28 vizualizări2 paginiAnnaunivqp
Încărcat de
ShankarElectron Devices
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca RTF, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
http://jagadeeshinfotech2all.blogspot.
com/2009/06/anna-university-random-number-
enquiry.html
http://www.mycrickethighlights.com/india-vs-new-zealand-2nd-test-day-5-highlights-2010-
hyderabad/
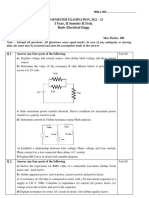
B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION Third Semester Electrical and Electronics
Engineering
EC 253 — ELECTRON DEVICES Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks
Answer ALL questions.PART A — (10 ? 2 = 20 marks)
1. An electron is injected perpendicularly into a uniform magnetic field of flux
density 0.01 Wb/m2 with an initial speed of 107 m/s. What will be the radius of the
circular path that the electron describes?
2. An ideal Germanium diode has a reverse saturation current of 20 ? A. Find the
dynamic resistance for a forward bias of 0.1 V.
3. What is Hall effect? Give any two applications.
4. What are hybrid parameters?
5. Define diffusion current.
6. Give any two ways by which the transistors are protected from overheating due
to high power operation.
7. What are the advantages of FETs?
8. Mention any two applications of SCR.
9. What is an optoelectronic coupler?
10. Draw the basic structure of a CRT.
PART B — (5 ? 16 = 80 marks)
11. (i) Explain about magnetic deflection in a CRT. Derive the expression for
deflection sensitivity. (10) D 033 2 D 033
(ii) Find the speed of an electron after it has moved through a potential difference of
10,000 V. What would be the percentage change in its mass at this speed? (6)
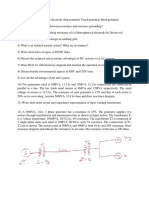
12. (a) (i) Explain the origin of depletion layer capacitance and diffusion capacitance
and discuss the importance of each. (8)
(ii) What is a Schottky diode? What is its application? (8) Or
(b) (i) You are given two different Ge diodes with their data at forward bias as
follows : VD(on)1 = 0.7 V at 10 mA VD(on)2 = 0.6 V at 0.1 mA. If these diodes are
placed in a series circuit and a current of 1 mA is
made to flow in them (forward bias), what will be the sum of voltage drops across
them? (8)
(ii) Explain with relevant diagrams, the function of a Zener diode. Mention its
important applications. (8)
13. (a) (i) Draw the hybrid ? model of a transistor in CE configuration and discuss
about each component of the model. (10)
(ii) Draw the Ebers–Moll model for a pnp transistor. (6)Or
(b) (i) With appropriate diagrams, discuss about various switching times of a
transistor. (8)
(ii) Compare the three configurations of a transistor. (8)
14. (a) Explain the function of depletion type MOSFET. Or
(b) (i) Describe the operation of UJT. What is its main application? (10)
(ii) Draw the low frequency small signal JFET model. (6)
15. (a) With neat sketches, discuss about the basic construction and operation of a
laser diode. Name the different types of lasers. Or (b) What is a photo diode? With
proper characteristic curves and relevant diagrams, explain the operation of the
device. What are its applications?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- VDD VrefDocument2 paginiVDD VrefSureshKumar SaravananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsDe la EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2353 HVE April May 2011 PDFDocument3 paginiEE2353 HVE April May 2011 PDFDevie MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsDe la EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTEE7302 Nov-2021Document2 paginiPTEE7302 Nov-2021imman46920Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionDe la EverandElectrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (4)
- Question Paper Code: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 paginiQuestion Paper Code: (10×2 20 Marks)Gokul NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksDe la EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Physics 200 Question Mission 100 Class 12 THDocument48 paginiPhysics 200 Question Mission 100 Class 12 THNARENDER YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inter Material Modelpapers Iindyear em 3 - Physics - 2nd - Year - emDocument3 paginiInter Material Modelpapers Iindyear em 3 - Physics - 2nd - Year - emcharithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sree Sastha Institute of Engineering and Technology: Model ExamDocument2 paginiSree Sastha Institute of Engineering and Technology: Model ExamthirukoilurÎncă nu există evaluări
- bt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulDocument30 paginibt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulAnonymous nTxB1EPvÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Year Que NewDocument3 pagini1st Year Que Newbalusasi_skgÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1Document2 paginiBEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1mr.prashant.cseÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Physics EM4Document2 pagini2nd Physics EM4karthik chandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 paginiII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electronic Devices and CircuitsViswa ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdf&rendition 1Document43 paginiPdf&rendition 1kajal aggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee 1402 - HveDocument6 paginiEe 1402 - HveckjammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 paginiR09 Set No. 2anji513Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument6 paginiElectrical and Electronics EngineeringsrihariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample 3Document3 paginiSample 3Sujeev GyawaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set No. 1: Cosφ Cosφ.Cos (φ−β) wL RDocument8 paginiSet No. 1: Cosφ Cosφ.Cos (φ−β) wL RViswa ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13836paper 12 FebDocument5 pagini13836paper 12 FebAseem ShibeÎncă nu există evaluări
- rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 paginirr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- 9a02308 Electrical Mechines IDocument4 pagini9a02308 Electrical Mechines IsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec1403 Microwave EngineeringDocument3 paginiEc1403 Microwave EngineeringsubhazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question PapersDocument6 paginiQuestion Papersgunasekar3538Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics 2006 Set 1: Subjective TestDocument29 paginiPhysics 2006 Set 1: Subjective TestAkshit ChanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 paginiRr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- NR-220402-Electrical TechnologyDocument8 paginiNR-220402-Electrical TechnologytemesgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 paginiWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 Electronic Devices and CircuitsUr's Lovely NagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 paginiQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.gokulchandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr220402 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 paginiRr220402 Electrical TechnologySrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- HveDocument7 paginiHveLahari Dalavai0% (1)
- RR310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument2 paginiRR310202 Electrical MeasurementssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 paginiQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microwave EngineeringDocument5 paginiMicrowave EngineeringHarikrishna KhariduÎncă nu există evaluări
- HY - Class XII - 2015-2016 - Class XII - 2016-2017Document3 paginiHY - Class XII - 2015-2016 - Class XII - 2016-2017Rijty SagartonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr410209 High Voltage EngineeringDocument7 paginiRr410209 High Voltage EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- rr222104 Elctrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument8 paginirr222104 Elctrical and Electronics EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR 220402 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 paginiNR 220402 Electrical TechnologySrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- Electrical Meas May 2012Document8 paginiElectrical Meas May 2012Rama raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 SP 12 Physics 08Document3 pagini2015 SP 12 Physics 08maruthinmdcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 paginiRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- Questions and Bits To Students II MidDocument11 paginiQuestions and Bits To Students II Middeepak reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Engg-IDocument6 paginiElectrical Engg-IXYZÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 Basic Electrical Engineering: CS/B.TECH (OLD) /SEM-2/EE-201/2012Document7 pagini2012 Basic Electrical Engineering: CS/B.TECH (OLD) /SEM-2/EE-201/2012abhrajitsahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements EE42 EE402 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAM 4TH SEM AUG 2017Document2 paginiElectrical and Electronics Measurements EE42 EE402 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAM 4TH SEM AUG 2017RT PRAJWAL KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pagini9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- M 063Document3 paginiM 063Karthik JiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ii Pu Physics QPDocument5 paginiIi Pu Physics QPHarshith HachhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- MID PaperDocument2 paginiMID PaperMusic WorldÎncă nu există evaluări
- End Sem 20-21Document2 paginiEnd Sem 20-21Soumya Ranjan NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Et Prsolutions08Document8 paginiEt Prsolutions08BajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Thomas College of Engineering & Technology Kozhuvalloor: Time: 2 Hrs Series Exam - II Max. Marks 60Document2 paginiSt. Thomas College of Engineering & Technology Kozhuvalloor: Time: 2 Hrs Series Exam - II Max. Marks 60syulmnmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1 2013 EM2 and EM3 MARCH-1Document4 paginiTest 1 2013 EM2 and EM3 MARCH-1BONGINKOSI DINGAANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 paginiRr210303 Electrical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- R7410207-High Voltage EngineeringDocument4 paginiR7410207-High Voltage EngineeringsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006Document5 paginiCBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006venkithebossÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama-IIIsem-Network Security-783301Document2 paginiSathyabama-IIIsem-Network Security-783301ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama-Software Quality and Assurance-IIIsem-683E05-ITE02Document2 paginiSathyabama-Software Quality and Assurance-IIIsem-683E05-ITE02ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter No. Title Page NoDocument61 paginiChapter No. Title Page NoShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- JQuery Tutorial - Joshua PelletierDocument8 paginiJQuery Tutorial - Joshua PelletierShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter No. Title Page NoDocument61 paginiChapter No. Title Page NoShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama IIIsem Webservices 783303Document2 paginiSathyabama IIIsem Webservices 783303ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathayabama-IIIsem-Mobile Networking-583302-683302-783302Document2 paginiSathayabama-IIIsem-Mobile Networking-583302-683302-783302ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- sathyabama-IIsem-Advanced Internet Technology-683203-783202Document2 paginisathyabama-IIsem-Advanced Internet Technology-683203-783202ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- sathyabama-IIsem-Distributed Computing-683201-783201Document2 paginisathyabama-IIsem-Distributed Computing-683201-783201ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- J2EE IIIsem 583305 ITE03Document2 paginiJ2EE IIIsem 583305 ITE03ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- sathyabma-IISem-Data Structure and Algorithm - 6C0501-7C0501Document2 paginisathyabma-IISem-Data Structure and Algorithm - 6C0501-7C0501ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2352-Unit 2Document32 paginiIT 2352-Unit 2ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satthyabama-Isem-Data Comunication and Computer Networks 6C0500-7C0500Document2 paginiSatthyabama-Isem-Data Comunication and Computer Networks 6C0500-7C0500ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama-Advance Database-Isem-783103Document2 paginiSathyabama-Advance Database-Isem-783103ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama-MTech-IT-Isem-Fundamental of Computer Engineering - 683101-783101Document2 paginiSathyabama-MTech-IT-Isem-Fundamental of Computer Engineering - 683101-783101ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama IIsem OOAD 7C0503Document2 paginiSathyabama IIsem OOAD 7C0503ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- sathyabama-IIsem-Data Mining and Data Warehousing 683E03Document3 paginisathyabama-IIsem-Data Mining and Data Warehousing 683E03ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama - Isem-C# and .Net 683E04-ITE01Document3 paginiSathyabama - Isem-C# and .Net 683E04-ITE01ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sathyabama-Datamining and Datawarehousing-731301Document2 paginiSathyabama-Datamining and Datawarehousing-731301ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecturer Notes On IT 2353 UNIT IVDocument37 paginiLecturer Notes On IT 2353 UNIT IVShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecturer Notes On IT 2353 UNIT IIIDocument30 paginiLecturer Notes On IT 2353 UNIT IIIShankar100% (3)
- Sathyabama University: (Established Under Section 3 of UGC Act, 1956)Document2 paginiSathyabama University: (Established Under Section 3 of UGC Act, 1956)ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2353 Unit IV 2marksDocument19 paginiIT 2353 Unit IV 2marksShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2353 Unit V 2marksDocument6 paginiIT 2353 Unit V 2marksShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2353 Unit III 2marksDocument18 paginiIT 2353 Unit III 2marksShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2353 Unit III 2marksDocument18 paginiIT 2353 Unit III 2marksShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 2358Document63 paginiCS 2358ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2353 Unit I 2marksDocument22 paginiIT 2353 Unit I 2marksShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 2358Document63 paginiCS 2358ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 2353 Unit II 2marksDocument30 paginiIT 2353 Unit II 2marksShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Can Literary Spaces Support Neurodivergent Readers and WritersDocument2 paginiHow Can Literary Spaces Support Neurodivergent Readers and WritersRenato Jr Bernadas Nasilo-anÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endometab Exam 2018Document8 paginiEndometab Exam 2018teabagmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogeological Survey and Eia Tor - Karuri BoreholeDocument3 paginiHydrogeological Survey and Eia Tor - Karuri BoreholeMutonga Kitheko100% (1)
- Schneider Contactors DatasheetDocument130 paginiSchneider Contactors DatasheetVishal JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business CombinationsDocument18 paginiBusiness Combinationszubair afzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital SLR AstrophotographyDocument366 paginiDigital SLR AstrophotographyPier Paolo GiacomoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ymrtc LogDocument26 paginiYmrtc LogVinicius Silveira0% (1)
- Project Manager PMP PMO in Houston TX Resume Nicolaas JanssenDocument4 paginiProject Manager PMP PMO in Houston TX Resume Nicolaas JanssenNicolaasJanssenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session4 Automotive Front End DesignDocument76 paginiSession4 Automotive Front End DesignShivprasad SavadattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Essential Books For Active TradersDocument6 pagini10 Essential Books For Active TradersChrisTheodorou100% (2)
- Frequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 paginiFrequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFNarendra AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Resist ChartDocument13 paginiChem Resist ChartRC LandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoSiO2 For Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Comparison...Document5 paginiCoSiO2 For Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Comparison...Genesis CalderónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Japanese GardensDocument22 paginiJapanese GardensAnmol ChughÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIM L: 111iiiiiiiDocument54 paginiIIM L: 111iiiiiiiJavier GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectDocument55 paginiCh06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectJosh ChamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRAND AWARENESS Proposal DocumentDocument11 paginiBRAND AWARENESS Proposal DocumentBuchi MadukaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschDocument28 paginiInnovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschacairalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Samsung Galaxy S Duos GT-S7562Document151 paginiManual Samsung Galaxy S Duos GT-S7562montesjjÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEN and CENELEC Position Paper On The Proposal For CPR RevisionDocument15 paginiCEN and CENELEC Position Paper On The Proposal For CPR Revisionhalexing5957Încă nu există evaluări
- Bag Technique and Benedict ToolDocument2 paginiBag Technique and Benedict ToolAriel Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Zahid Imran CVDocument4 paginiZahid Imran CVDhia Hadj SassiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audi R8 Advert Analysis by Masum Ahmed 10PDocument2 paginiAudi R8 Advert Analysis by Masum Ahmed 10PMasum95Încă nu există evaluări
- NHM Thane Recruitment 2022 For 280 PostsDocument9 paginiNHM Thane Recruitment 2022 For 280 PostsDr.kailas Gaikwad , MO UPHC Turbhe NMMCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bushcraft Knife AnatomyDocument2 paginiBushcraft Knife AnatomyCristian BotozisÎncă nu există evaluări
- MV Lec PDFDocument102 paginiMV Lec PDFJonas Datu100% (1)
- Feds Subpoena W-B Area Info: He Imes EaderDocument42 paginiFeds Subpoena W-B Area Info: He Imes EaderThe Times LeaderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac221 and Ac211 CourseoutlineDocument10 paginiAc221 and Ac211 CourseoutlineLouis Maps MapangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Laminar and Turbulent Flow - MITWPU - HP - CDK PDFDocument13 pagini1 - Laminar and Turbulent Flow - MITWPU - HP - CDK PDFAbhishek ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista de Precios Agosto 2022Document9 paginiLista de Precios Agosto 2022RuvigleidysDeLosSantosÎncă nu există evaluări