Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Risk Management Medication Safety 4
Încărcat de
ethernalxDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Risk Management Medication Safety 4
Încărcat de
ethernalxDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Systems Thinking 239
pump. However, because this therapeutic intervention combines inherently error-prone
devices, and narcotics, serious unintended outcomes have frequently occurred.
Fortunately, by identifying specific issues, risks associated with this technology
can be reduced. Table 7.2 summarizes some of the issues surrounding the use of PCA
pumps and appropriate solutions.
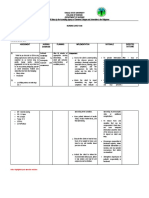
TABLE 7.2. Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA) Problems and Safety
Recommendations.
Problem Description Safety Recommendations
PCA by proxy When another person (health Warn patients, family members, and
professional, family member) visitors about the dangers of PCA by
administers a dose of medication proxy.
instead of the patient’s dosing Place warning labels on activation
themselves. buttons that state “FOR PATIENT USE
Can lead to oversedation, ONLY.”
respiratory depression, and Keep PCA flowsheets at the bedside
death. Patients must control to document PCA doses and patient
the PCA, but a sedated patient monitoring.
cannot press the button, thereby
overdosing.
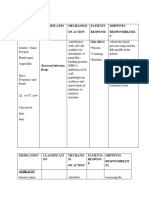
Improper Only patients who have the Check patient allergies, which
patient selection mental alertness and sufficient should be visible on the MAR, before
and education cognitive, physical, and initiating PCA.
psychological ability should use a Educate patients preoperatively about
PCA pump PCA use.
Can lead to inadequate pain Establish patient selection criteria.
control or oversedation.
In general, infants, young children,
Teaching patients during the and confused patients are not suitable
immediate postoperative period candidates to use a PCA pump.
is ineffective if the patient is too
groggy to understand. This has
often led to poor pain control in
the first twelve hours following
surgery.
(Continued)
c07.indd 239 3/3/09 3:08:22 PM
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- MDCT and MR Imaging of Acute Abdomen: New Technologies and Emerging IssuesDe la EverandMDCT and MR Imaging of Acute Abdomen: New Technologies and Emerging IssuesMichael PatlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atient Controlled Nalgesia: Iii Acute PainDocument6 paginiAtient Controlled Nalgesia: Iii Acute PainBoy GantengÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Step Clinical Mastery: Elevate Your Practice as a Nurse Practitioner and NP StudentDe la Everand2-Step Clinical Mastery: Elevate Your Practice as a Nurse Practitioner and NP StudentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Management Medication Safety 5Document1 paginăRisk Management Medication Safety 5ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- The COAT & Review Approach: How to recognise and manage unwell patientsDe la EverandThe COAT & Review Approach: How to recognise and manage unwell patientsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Pca PP Revised 6 4 14 v6Document12 paginiPca PP Revised 6 4 14 v6api-244230664Încă nu există evaluări
- Step 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionDe la EverandStep 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADM HinderDocument6 paginiADM Hindermaryrose menderoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Documentation: The Analgesia Flow Sheet: Stephanie Ricketts, RN N693 Fall 2014Document15 paginiDocumentation: The Analgesia Flow Sheet: Stephanie Ricketts, RN N693 Fall 2014mochkurniawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pca PP Revised 7 7 14 v7Document12 paginiPca PP Revised 7 7 14 v7api-244230664Încă nu există evaluări
- Patient Controlled AnalgesiaDocument26 paginiPatient Controlled AnalgesiaSabah AlungalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitor Alarm Fatigue Standardizing Use of Physiological Monitors andDocument11 paginiMonitor Alarm Fatigue Standardizing Use of Physiological Monitors andVera AntunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ULUAVNIV ProtocolDocument10 paginiULUAVNIV ProtocolsatishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Prioritization Delegation and Assignment 3rd Edition Lacharity Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 paginiDwnload Full Prioritization Delegation and Assignment 3rd Edition Lacharity Solutions Manual PDFwrithemuride8y4w5100% (8)
- Anaesthesia and Sedation Outside TheatresDocument15 paginiAnaesthesia and Sedation Outside Theatresمحمد زينÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Controlled Analgesia CA2048 v7.1Document11 paginiPatient Controlled Analgesia CA2048 v7.1AQSA AHMED SIDDIQUIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Controlled Analgesia CA2048 v7.1Document11 paginiPatient Controlled Analgesia CA2048 v7.1AQSA AHMED SIDDIQUIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cummings2021 Article AducanumabAppropriateUseRecommDocument13 paginiCummings2021 Article AducanumabAppropriateUseRecommRenata Mara Geriatra0% (1)
- Cap 1Document4 paginiCap 1Sirbu CristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jco 21 01532Document4 paginiJco 21 01532niluhputu asrinidewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Guidelines: Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Updated Recommendations From The ATS and IDSADocument4 paginiPractice Guidelines: Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Updated Recommendations From The ATS and IDSAcarolina101812Încă nu există evaluări
- 2014.04.17 PoltechDTPA SPCHDocument2 pagini2014.04.17 PoltechDTPA SPCHLuis Fernando RicardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bedah Buku "Reporting and Learning Systems For Medication Errors: The Role of Pharmacovigilance Centres"Document7 paginiBedah Buku "Reporting and Learning Systems For Medication Errors: The Role of Pharmacovigilance Centres"Noor KevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weaning From Mechanical Ventilation in Intensive Care UnitsDocument2 paginiWeaning From Mechanical Ventilation in Intensive Care UnitsKinesiólogos UPC HPMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute PainDocument4 paginiAcute PainRuffy AbdulazisÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCA Con Tramadol o RemiDocument5 paginiPCA Con Tramadol o RemiChurrunchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ID Checklist RATIONALEDocument42 paginiID Checklist RATIONALEAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAOÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP May00 Sedat PDFDocument9 paginiHP May00 Sedat PDFSaurabh SatheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigger DrugsDocument2 paginiTrigger DrugsTalitha PuspaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Procedure and Lead Placement Guide PediatricsDocument6 paginiECG Procedure and Lead Placement Guide PediatricsMSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eugenio Preeclampsia NCPDocument2 paginiEugenio Preeclampsia NCPBethrice MelegritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarterlyactionagenda: Problem Recommendation Organization Assessment Action Required/ AssignmentDocument7 paginiQuarterlyactionagenda: Problem Recommendation Organization Assessment Action Required/ AssignmentRandy M AlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Original2-2Document8 pagini03 Original2-2Ana ValladaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Better End of Life Care.3 PDFDocument1 paginăBetter End of Life Care.3 PDFmasdika09Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study of Case Presentation 2Document6 paginiDrug Study of Case Presentation 2banana cueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medication Safety Di OK Dan ICU FINALDocument48 paginiMedication Safety Di OK Dan ICU FINALAkhmad Safi'iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apnea of Prematurity. 2016. AAPDocument7 paginiApnea of Prematurity. 2016. AAPmemoaranedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radprot Rebyuwer BushongDocument7 paginiRadprot Rebyuwer Bushongmaxineanne.alberto.mnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholesterol GuidelinesDocument2 paginiCholesterol GuidelinesJuan Miguel PangilinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Drug Study RubricDocument2 pagini7 Drug Study Rubricزياد- 90Încă nu există evaluări
- Kontrol Anes PasienDocument4 paginiKontrol Anes Pasienzidni fatayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Background: Result:: Published by DiscoversysDocument4 paginiBackground: Result:: Published by DiscoversysWilliam OmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The SUP-ICU Trial: Does It Confirm or Condemn The Practice of Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis?Document6 paginiThe SUP-ICU Trial: Does It Confirm or Condemn The Practice of Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis?Valentina Vasco YepesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation:perfusion Lung Scintigraphy - What Is Still Needed? A Review Considering Technetium-99m-Labeled Macro-Aggregates of AlbuminDocument42 paginiVentilation:perfusion Lung Scintigraphy - What Is Still Needed? A Review Considering Technetium-99m-Labeled Macro-Aggregates of AlbuminAyuRosemeiliaDewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pca Current ConceptDocument13 paginiPca Current ConceptAida TantriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contrast Media Administration Guidelines by The ACR (American College of Radiology) Version 6 - 2008Document92 paginiContrast Media Administration Guidelines by The ACR (American College of Radiology) Version 6 - 2008radiology_resources100% (25)
- 9202 5019RevE Field Service ManualDocument212 pagini9202 5019RevE Field Service ManualrdzptecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sedation in The Icu JournalDocument6 paginiSedation in The Icu JournalPriscila FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lehnes Pharmacology For Nursing Care 2015 9e Test BankDocument6 paginiLehnes Pharmacology For Nursing Care 2015 9e Test Bankngaphuonghh40Încă nu există evaluări
- Sham Controls in Medical Device Trials: PerspectiveDocument2 paginiSham Controls in Medical Device Trials: PerspectiveAymen BekirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotik ProfilaksisDocument2 paginiAntibiotik ProfilaksisAdel ZilviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remifentanil PCA For Labour Guideline (2) - Aneurin Bevan Guideline 2015Document6 paginiRemifentanil PCA For Labour Guideline (2) - Aneurin Bevan Guideline 2015Claire PollingtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertensive NCPDocument3 paginiHypertensive NCPjgaitera23223Încă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet CCJMDocument1 paginăWorksheet CCJMapi-651287771Încă nu există evaluări
- Postoperative Pain Relief Measures: Kathleen Rice Simpson, PHD, RNC, FaanDocument1 paginăPostoperative Pain Relief Measures: Kathleen Rice Simpson, PHD, RNC, FaanindielectuallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scott 2014Document12 paginiScott 2014Atif MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template Continued On Page 2: Dose-Dense Ac (Doxorubicin/Cyclophosphamide) CourseDocument2 paginiTemplate Continued On Page 2: Dose-Dense Ac (Doxorubicin/Cyclophosphamide) CourseJaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analgesia Guidelines PaediatricDocument23 paginiAnalgesia Guidelines PaediatricsyahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maravilla AttitudeofNursesDocument30 paginiMaravilla AttitudeofNursesSevered AppleheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valbenazine CFU - 2020Document2 paginiValbenazine CFU - 2020gene flowersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork 2Document1 paginăSteelwork 2ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 38Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 38ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 35Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 35ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 37Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 37ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 36Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 36ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 39Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 39ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 41Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 41ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 34Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 34ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 31Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 31ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 29Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 29ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 33Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 33ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 30Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 30ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 32Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 32ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 28Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 28ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 22Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 22ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 29Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 29ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 26Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 26ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 25Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 25ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 19Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 19ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 27Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 27ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 24Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 24ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 21Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 21ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 23Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 23ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 20Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 20ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 16Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 16ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 14Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 14ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 17Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 17ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 18Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 18ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 15Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 15ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Building 13Document1 paginăSteelwork Building 13ethernalxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult Lead PoisoningDocument14 paginiAdult Lead PoisoningyhonangelÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Would We Know If Psychotherapy Were Harmful?: What Do We Mean by Harm?Document13 paginiHow Would We Know If Psychotherapy Were Harmful?: What Do We Mean by Harm?CoordinacionPsicologiaVizcayaGuaymasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self-Concealment and Attitudes Toward Counseling in University StudentsDocument7 paginiSelf-Concealment and Attitudes Toward Counseling in University StudentsMaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checklist of Nonverbal Pain IndicatorsDocument41 paginiChecklist of Nonverbal Pain IndicatorsantipaticoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rudolfo S. Agustin JR.: Ragus003@odu - EduDocument2 paginiRudolfo S. Agustin JR.: Ragus003@odu - EduRudolfo AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mentor Interview QuestionsDocument3 paginiMentor Interview Questionsapi-377093974Încă nu există evaluări
- Thesis 2Document70 paginiThesis 2Angeline Alpure MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nihms579455 PDFDocument78 paginiNihms579455 PDFMASIEL AMELIA BARRANTES ARCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lange Q&A: Radiography ExaminationDocument18 paginiLange Q&A: Radiography ExaminationSamuel JeebanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aherrera NotesDocument213 paginiAherrera NotesVerna Santiago71% (7)
- 4 MU Calc1Document47 pagini4 MU Calc1Azaleea GeorgianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Assessment of Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument10 paginiAssessment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Assessment of Community-Acquired PneumoniaannisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Safety Update ReportDocument28 paginiPeriodic Safety Update ReportnidhisaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terapi CMLDocument7 paginiTerapi CMLAnnisa Dwi AndrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and RepairDocument6 paginiFactors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and RepairJoseph Arnold AlmonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 3: Functional DiagramsDocument10 paginiSection 3: Functional DiagramsHatman ManhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broncho, Second YearDocument68 paginiBroncho, Second YearHampson MalekanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health Concepts: Classified Examination For Critical Test AnalysisDocument5 paginiMental Health Concepts: Classified Examination For Critical Test AnalysisDebbie Marie BaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ancient Techniques of AcupressureDocument3 paginiThe Ancient Techniques of AcupressureunlimitivÎncă nu există evaluări
- Black Church Leaders Attitudes About Seeking Mental Health Services - Role of Religiosity and SpiritualityDocument12 paginiBlack Church Leaders Attitudes About Seeking Mental Health Services - Role of Religiosity and SpiritualitymizbigspendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desain Pengembangan Karir FTDocument39 paginiDesain Pengembangan Karir FTasma hayatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument8 paginiGuillain Barre SyndromeStephanie AureliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThyroidectomyDocument52 paginiThyroidectomyWindelyn Gamaro100% (4)
- Melodic Intonation TherapyDocument6 paginiMelodic Intonation Therapyrocio100% (1)
- Menstrual Cycle Associated Changes in Agility in Amateur Female AthletesDocument39 paginiMenstrual Cycle Associated Changes in Agility in Amateur Female Athletesvishnu priyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument56 paginiAcute Gastroenteritisneil052298% (46)
- Nuero RehabilitationDocument127 paginiNuero RehabilitationPrajeesh ValayamkunnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHFS Drug InformationDocument10 paginiAHFS Drug InformationMika FebryatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OsteomyelitisDocument13 paginiOsteomyelitisKim Enrico JumarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decompensated HFDocument16 paginiDecompensated HFJessica GarletsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDe la EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (26)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDe la EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDe la EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.De la EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDe la EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingDe la EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningDe la EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDe la EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (170)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDe la EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)