Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Immunology Imunologi: Sumardi, S.Si., M.SC., Apt
Încărcat de
Asiyah0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
29 vizualizări14 paginiImun
Titlu original
1 Immunology and Serology Lecture 1
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentImun
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
29 vizualizări14 paginiImmunology Imunologi: Sumardi, S.Si., M.SC., Apt
Încărcat de
AsiyahImun
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 14
IMMUNOLOGY
Imunologi
Sumardi, S.Si., M.Sc., Apt.
Deskripsi Mata Kuliah
Membahas tentang kedudukan imunologi dalam
bidang kefarmasian:
Molekul pengenal antigen, inisiasi respon imun,
maturasi sel limfosit, sistem komplemen,
imunomodulator, sitokin, imunitas selular dan
humoral, respon imun terhadap patogen,
penyakit yang disebabkan respon imun, antibodi
monoklonal, terapi imunoglobulin intravena,
imunoterapi vaksin dan sera.
Definisi
• Immunology:
– The study of organisms’ body protection from
foreign invading/disease causing microorganisms.
– The study of mechanisms by which an
animals/human body is protected from infectious
agents or foreign substances.
– A science that deals with the immune system and
the cell mediated and humoral aspects of
immunity and immune responses (Merriam
Webster Dictionary)
Definisi
– Study of the molecules, cells, organs,
and systems responsible for the
recognition and disposal of foreign
(nonself) material
– Study of the MECHANISMS that protect
an individual from injury from:
• Exogenous microorganisms – bacteria,
fungi, viruses
• Exogenous chemicals – pollen, poison ivy,
etc.
• Endogenous cells – malignant or senescent
cells
- Bidang ilmu yang mempelajari komponen dan sistem imun serta
responnya.
• IMMUNE RESPONSE: Broad range of defense mechanisms including inflammation,
phagocytosis, antibody synthesis, etc.
IMMUNITY
• Immunis (Latin) for "exempt“ membebaskan
• Immunity: the state of being exempted
(excluded/freed/absolved/excused /relieved).
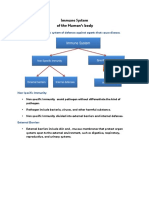
The Immune System
• The immune system is composed of many
interdependent cell types that collectively
protect the body from infectious agents
(bacteria,parasite, fungi, virus) and from the
growth of tumor cells.
The Immune System
• Sistem imun memiliki kemampuan untuk
membedakan materi yang merupakan berasal
dari tubuh sendiri dengan yang darinya.
• In vertebrates a highly specialized receptors
for discriminating between ”self” and
nonself” body components
Serology
• The branch of laboratory medicine that
studies blood serum for evidence of infection
and other parameters by evaluating antigen-
antibody reactions in vitro
• Serology is the scientific study of blood serum.
In practice, the term usually refers to the
diagnostic identification of antibodies in the
serum (possible to detect antigens as well)
Serology
• the study of the non-cellular components of
the blood (serum).
– Antibody production and reactivity
– Complement
Component of
Immune
System
Natural Immunity
• Innate or Inborn immunity
– Non specific
– External Defenses:
• Skin, acid in sweat, mucus membranes, cilia in
respiratory tract, normal flora
– Internal Defenses:
• Non-specific cellular responses
– Cells and soluble factors
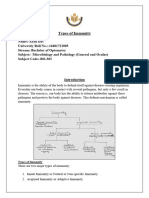
Acquired Immunity
Active
– Allows the body to Recognize, Remember and Respond to
a specific stimulus.
• Example: Your Hepatitis B vaccine(You were give three doses of
attenuated Hep. B virus; your body recognized it as foreign and
produced an anti-hepatitis B antibody.)
Passive
– Antibody mediated immunity received from another
source
• Example: A mothers breast milk has antibody that the baby uses
until he/she can produce their own.
• Example: A gamma (immune) globulin shot provides immunity
when someone travels over seas, but their body did nothing to
develop the immunity.
Cell Mediated vs.Humoral Immunity
Cell Mediated Immunity
• Form of acquired immunity in which T lymphocytes
recognize and react with a stimulus through direct
cell-to-cell interaction of lymphokines.
Humoral Immunity
• Form of acquired immunity in which B Lymphocytes
and plasma cells produce specific antibodies that
recognize and react to a stimulus.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Packrat Cardio QuestionsDocument63 paginiPackrat Cardio Questionscrystalshe100% (1)
- My Sister's KeeperDocument3 paginiMy Sister's Keeperbetsyk1Încă nu există evaluări
- Surgical Services Design Guide PDFDocument465 paginiSurgical Services Design Guide PDFCharles TestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFDocument21 paginiBiology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFMichael John LozanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innate and adaptive immunity defensesDocument63 paginiInnate and adaptive immunity defensesSarvesh Patil100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 paginiCirculatory SystemKumar Sujeet100% (1)
- ImmunologyDocument36 paginiImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- Overview of Immune ResponsesDocument30 paginiOverview of Immune ResponsesVivien KasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology Q4 M7Document19 paginiGeneral Biology Q4 M7Mubin AbdulkarilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is PPT CompleteDocument456 paginiIs PPT CompleteCelso Rodil IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding the Basics of ImmunologyDocument64 paginiUnderstanding the Basics of ImmunologySasidhar VajralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CompilationDocument11 paginiNCP CompilationRene John FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause DiseaseDocument8 paginiThe Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause Diseasemaya100% (2)
- Acute Care TestingDocument222 paginiAcute Care TestingAdel ChaabaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument469 paginiAlzheimer's DiseaseGastón G. Fernández100% (3)
- Immunology For BSCNDocument39 paginiImmunology For BSCNHamas AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 11مناعة الرشيدDocument7 paginiLec 11مناعة الرشيدتجربة أولىÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-7 Defence Mechanisms of The Body, Insta - Husain.z.kmuDocument41 paginiUnit-7 Defence Mechanisms of The Body, Insta - Husain.z.kmusa72562624742Încă nu există evaluări
- BSB - Overview of Immune System - Innate and Adaptive - UndergraduatesDocument70 paginiBSB - Overview of Immune System - Innate and Adaptive - UndergraduatesBumba ArnoldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Veterinary ImmunologyDocument20 paginiVeterinary ImmunologyJennifer Bumagat-BermudezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defence Mechanism of The BodyDocument44 paginiDefence Mechanism of The BodysayafyousafzaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificate on Immunity ProjectDocument19 paginiCertificate on Immunity ProjectHridya UllasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-7 Defence Mechanisms of The Body, P-1Document41 paginiUnit-7 Defence Mechanisms of The Body, P-1abdulsaboor30Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 - Defenses Against Disease - Week8 - DrNyembe - 2022Document26 pagini10 - Defenses Against Disease - Week8 - DrNyembe - 2022Muke MpilwenhleÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIcro - Immunology - Lec.1Document13 paginiMIcro - Immunology - Lec.1زين العابدين محمد عويش مشريÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Gen Bio2 Timothy NicodemusDocument20 paginiPresentation Gen Bio2 Timothy NicodemusTim NicodemusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 paginiLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document52 paginiLecture 1Emmanuel Thon MadingÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMMUNOLOGY ExplainedDocument42 paginiIMMUNOLOGY ExplainedUNO RIPPERSÎncă nu există evaluări
- IS-1 LectureDocument42 paginiIS-1 LectureUNO RIPPERSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument5 paginiInnate and Acquired Immunitydebarajroy1998Încă nu există evaluări
- Zoology6thSem PDFDocument88 paginiZoology6thSem PDFRouf MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immune System ProjectDocument21 paginiImmune System ProjectAvinash BobadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunochemistry 1Document51 paginiImmunochemistry 1RuthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunology ImmunologyDocument136 paginiImmunology ImmunologyZeen_Zeen_Fern_3128Încă nu există evaluări
- Immune SystemDocument56 paginiImmune SystemGerome CausapinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImmunologyDocument8 paginiImmunologyabiyotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunopharmacology - IntroductionDocument51 paginiImmunopharmacology - IntroductionIsrat Jahan Surovy 2225400672Încă nu există evaluări
- Immunology NZDDocument35 paginiImmunology NZDTaonaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunity PPT FinalDocument20 paginiImmunity PPT FinalVarsha SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Biotechnology Boosts ImmunityDocument9 paginiHow Biotechnology Boosts ImmunityAditi ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro Lines of DefenseDocument15 paginiIntro Lines of DefenseGadzikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ayan Das 16401722005 BO-303Document4 paginiAyan Das 16401722005 BO-303Ayan DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Immune FunctionDocument3 paginiAssessment of Immune Functionhalloween candyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro ImmunologyDocument88 paginiIntro ImmunologyJames Carbonell Dela PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penyakit ImunDocument50 paginiPenyakit ImunGuyon S WatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Coordination and Control: Michael A. Tabug, Msc. Shs-InstructorDocument19 paginiChemical Coordination and Control: Michael A. Tabug, Msc. Shs-InstructorMike TabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Immunology: An Overview of the Immune SystemDocument19 paginiClinical Immunology: An Overview of the Immune SystemR Sathish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defence Mechanism of The BodyDocument72 paginiDefence Mechanism of The BodyRawal Rafiq LeghariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Immune DisordersDocument11 pagini4 Immune DisorderscedonuliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 13 Immunity and VaccinationDocument15 paginiUnit 13 Immunity and VaccinationcyumadripÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause DiseaseDocument9 paginiThe Body's System of Defenses Against Agents That Cause DiseasemayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 19-20 - Immunity and Infectious Disesase - UpdatedDocument42 paginiTopic 19-20 - Immunity and Infectious Disesase - UpdatedtnotchwÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 2 Review: The Human Immune System DefenseDocument28 paginiGeneral Biology 2 Review: The Human Immune System DefenseGeorgette MatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMMUNITYDocument36 paginiIMMUNITYDivya AgarawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- FALLSEM2023-24 BBIT305L TH VL2023240100183 2023-04-26 Reference-Material-IDocument23 paginiFALLSEM2023-24 BBIT305L TH VL2023240100183 2023-04-26 Reference-Material-IDrishti BisuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4Document9 paginiLecture 4Smasher AustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inmunidad InnataDocument20 paginiInmunidad InnataANDRÉS FELIPE ARDILA MURILLOÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImmunityDocument27 paginiImmunityMuhammad Fawad100% (1)
- IMMUNITY - (Allied Health Sciences) - Complete - March 2024Document51 paginiIMMUNITY - (Allied Health Sciences) - Complete - March 2024Anania EmmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunology: Combined Class (Mental Health Psichatry, Clinical Anastasia, & Clinical Sciences) Year 2 30/03/2022Document30 paginiImmunology: Combined Class (Mental Health Psichatry, Clinical Anastasia, & Clinical Sciences) Year 2 30/03/2022Derick NKANDU KALUBAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Document41 paginiDasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Olivia NurudhiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Health ScienceDocument12 paginiFaculty of Health ScienceAbdirahman YazinÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMMUNITYDocument19 paginiIMMUNITYMuslimÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImmunoDocument3 paginiImmunoHanah HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boosting the Immune System: Natural Strategies to Supercharge Our Body’s ImmunityDe la EverandBoosting the Immune System: Natural Strategies to Supercharge Our Body’s ImmunityÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Antibody As Drug and Drug Carrier PDFDocument24 pagini7 Antibody As Drug and Drug Carrier PDFAsiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Immunology and Serology - MHC Lecture 2Document18 pagini2 Immunology and Serology - MHC Lecture 2anitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activation of Innate and Adaptive Immune SystemDocument20 paginiActivation of Innate and Adaptive Immune SystemAsiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Immunology and Serology - MHC Lecture 2Document18 pagini2 Immunology and Serology - MHC Lecture 2anitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunology Imunologi: Sumardi, S.Si., M.SC., AptDocument14 paginiImmunology Imunologi: Sumardi, S.Si., M.SC., AptAsiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Antibody As Drug and Drug Carrier PDFDocument24 pagini7 Antibody As Drug and Drug Carrier PDFAsiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- It PDFDocument385 paginiIt PDFCosmina UngurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Manajemen Pelayanan Kesehatan: Artikel PenelitianDocument8 paginiJurnal Manajemen Pelayanan Kesehatan: Artikel PenelitianDiah AdhyaksantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beta Blockers: Selective and Non-Selective TypesDocument22 paginiBeta Blockers: Selective and Non-Selective TypesJewelyn ConolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Test and PAP Smear As Predictors of Outcome in Conservatively Treated Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS) of The Uterine CervixDocument7 paginiHuman Papillomavirus (HPV) Test and PAP Smear As Predictors of Outcome in Conservatively Treated Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS) of The Uterine CervixodivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- XZXZDocument4 paginiXZXZhenpupraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adime Due 10 29Document3 paginiAdime Due 10 29api-437192216Încă nu există evaluări
- IMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamDocument11 paginiIMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamScribdTranslationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDS+Styrene+From+Sigma AldrichDocument7 paginiMSDS+Styrene+From+Sigma AldrichYaumi IstiqlaliyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Footnote To YouthDocument6 paginiFootnote To YouthVanityHughÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Appendicitis in Adults: Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisDocument37 paginiAcute Appendicitis in Adults: Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisDaniela MuñozÎncă nu există evaluări
- SJAMS 43B 750 754 Thesis Tibial PlateauDocument5 paginiSJAMS 43B 750 754 Thesis Tibial PlateauNisheshJainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Casts and Their IndicationsDocument3 paginiTypes of Casts and Their IndicationsPhylum ChordataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enquiry ReportDocument4 paginiEnquiry ReportMeena Koushal0% (1)
- CH 25 Respiration Study GuideDocument2 paginiCH 25 Respiration Study Guide99646qbkdwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Physiology Lab ReportDocument5 paginiRenal Physiology Lab Reportpatricia ankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Low Back Pain Good Clinical Practice GCPDocument341 paginiChronic Low Back Pain Good Clinical Practice GCPTru ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 10 Pharma Companies in India 2022Document8 paginiTop 10 Pharma Companies in India 2022Royal MarathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Negative Feedback Thyroxine and Adrenelin WsDocument2 paginiNegative Feedback Thyroxine and Adrenelin WsEllie AbelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resp 1.02 Hierarchy of O2 Delivery MethodsDocument1 paginăResp 1.02 Hierarchy of O2 Delivery MethodsVin Lorenzo CampbellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hands Only CPRDocument7 paginiHands Only CPRJulisa FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CommonGround 8 26 BrierleyDocument84 paginiCommonGround 8 26 Brierleytuinbroek_94397869Încă nu există evaluări
- Study The Herbalism of Thyme LeavesDocument7 paginiStudy The Herbalism of Thyme Leavespronto4meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4intestinal NematodesDocument41 paginiChapter 4intestinal Nematodesdeneke100% (1)