Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
A Brief History of Life On Earth
Încărcat de
John Lloyd Espinosa0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări3 paginiReviewer on geologic time
Titlu original
Biology 2
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentReviewer on geologic time
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări3 paginiA Brief History of Life On Earth
Încărcat de
John Lloyd EspinosaReviewer on geologic time
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
A Brief History of Life on Earth -widespread forests and swamps
Early Earth Fossil Record Pennsylvanian
-Major events and trends in Earth’s -peat swamps common, with scale
surface environment during the first trees, seed ferns, scouring rushes,
4.0 b.y.: and large dragonflies
Ocean forms, 4.4 b.y. Fossil Record Permian
Oldest bacteria, 3.8 b.y. -Amphibians decline; reptiles and
Blue-green algae, 3.0 b.y. insects increase; first mammal-like
Iron formations, 2.2 b.y. reptiles appear. Nonseed plants
Oxygen buildup, 2.0 b.y. decline.
Eukaryotes, 2.0 b.y. Fossil Record Triassic
Abundant multicelled fossils, 0.6 b.y. -first mammals and dinosaurs
-Planetesimals gathered into larger Fossil Record Jurassic
clusters to make planets; leftover -age of dinosaurs
material formed asteroids and Fossil Record Jurassic and
comets. cretaceous
How Fossils formed -age of dinosaurs
-Mineralization - bones and other -birds appear
hard parts are replaced by minerals Fossil Record Cretaceous
carried in solution by groundwater. -Plesiosaurus infested the beaches
Evolution Fossil Record Cretaceous and
-To explain his observations, Darwin Tertiary
hypothesized that species can adapt -first flowering plants appear
to new conditions through natural Fossil Record Cretaceous and
selection. Tertiary Boundary
Fossil record Precambrian -earth was hit by meteorite and the
-Microbial evidence dinosaurs died
Fossil Record Late Proterozoic Fossil Record Tertiary: Paleocene
-appearance of arthropods -age of mammals, grassland spread
-bacteria and green algae (ancestors Fossil Record Tertiary: Eocene
of plants) were common during this Fossil Record Tertiary: Oligocene
time. -horses, antelopes, cats, creodonts
Fossil Record Cambrian Fossil Record Tertiary: Miocene
-appearance of organisms that had -horses, antelopes, rhinoceri,
hard external skeletons elephants and other mammals.
Fossil Record Ordovician Fossil Record Quaternary:
-adaptation of marine invertebrates Pleistocene
to different conditions. -deer and elephant family
Fossil Record -horses, cats, elephants, bison, dire
-Golden age of cephalopods and wolves
brachiopods (a clam like shellfish) -mammals successfully colonized all
Fossil Record Devonian environments
-Golden age of Fishes -Western Nebraska when first
-land plants became common such humans were appearing
as ferns and club mosses Fossil Record Quaternary
Fossil Record Late Devonian -Hominids diverged from an early
-first seed plants ape-like family.
-naked seed plants developed Fossil Record Quaternary: Holocene
Fossil Record Carboniferous -Homo sapiens sapiens
-age of amphibians
-first winged reptiles and first winged
insects
Fossils Geologic Time URANIUM LEAD METHOD is used
to date rocks older than 10 million
Earth formed along with the solar
years
system 4.6 billion years ago
RUBIDIUM-STRONTIUM METHOD
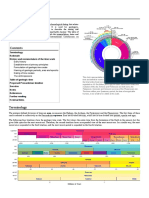
Geologic time scale is the summary
can also be used to date older rocks
of the major events in earth’s history
because of its long half life
-EON largest segment of geologic
POTASSIUM-ARGON METHOD can
time
date older rocks but can also date as
-ERA
young as 50,000 years
-PERIOD
EONS
EPOCH smallest segment of
-Precambrian: earliest span of time
geologic time
-Phanerozoic: everything since Eras,
2 kinds of ages
Periods, Epochs.
-RELATIVE know order of events
ERAS
but not dates
-PALEOZOIC
-ABSOLUTE know dates
-MESOZOIC
Law of Superposition
-CENOZOIC
-in undisturbed sedimentary rocks
PERIODS
the oldest rock layers are at the
-CAMBRIAN
bottom and the youngest are at the
-ORDOVICIAN
top
-SILURIAN
Law of Included Fragments
-DEVONIAN
-if fragments of one type of rock are
-CARBONIFEROUS
found in another rock layer the rock
-MISSIPPIAN
fragments must be older than the
-PENNSYLVANIAN
rock layer in which they are found
-PERMIAN
Faulted and Folded layers
-TRIASSIC
-layers of rock that have been
-JURASSIC
faulted or folded must have been
-CRETACEOUS
faulted or folded must have been
-PALEOGENE
present before the actions of faulting
-NEOGENE
or folding took place
-QUATERNARY
Rock Correlation EPOCHS
-matching of rock layers that can be
-PALEOCENE
seen at the earth’s surface, over a
-EOCENE
large area
-OLIGOCENE
-an OUTCROP is exposed rock
-MIOCENE
layers at the earth’s surface
-PLIOCENE
-KEY BED is a thin, widespread
-PLEISTOCENE
layer, usually of volcanic ash, that
-HOLOCENE
can be used to correlate an exact
The Earth through time
point of time
Proterozoic
Radioactive dating
-no life possible on Earth
-RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES are
-simple, single-celled forms
atoms of elements that give off
of life appeared 3.8 by
radiation from their nuclei
-cyanobacteria begins
-RADIOACTIVE DECAY is the
producing free oxygen
process by which radioactive isotope
-land masses gather to make
changes into a new stable element
up a continent called
RADIOCARBON DATING uses the RODINIA
radioactive isotope carbon-14 found Cambrian
in all living things. -explosion of life
-dominant animals: marine
inverterbrates
-
Evidence
-evidence of common ancestry among
species comes from many sources
-genetic change in a population of
organisms overtime
Evidence of Evolution
-4 types of evidence that scientists have
gathered in support of evolution:
*Fossils
*comparative anatomy and structures
*embryology
*biochemistry (proteins and DNA)
Fossil Evidence
-Earth is 4.6 by
-Fossils in older layers are more
primitive than those in the upper layers
-extinct fossils resemble modern
animals
-shows common ancestry
-Fossil is preserved remains or traces of
an organism that is no longer living
Usually found in sedimentary rocks
Types of Fossils
-permineralization- minerals carried by
water are deposited around a hard
structure
-natural cast-when flowing water
removes all of the original tissue,
leaving an impression
-amber preserved- organisms that
become trapped in tree resin (fossilized
insect)
Impressions- imprints left in a rock
Preserved remains- organisms becomes
encased in material such as ice, tar, ash
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Green HydrogenDocument15 paginiGreen HydrogenG.RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5th Grade 15 Days Lessons MergedDocument66 pagini5th Grade 15 Days Lessons MergedNorma AguileraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth'S History and It'S Geologic Time ScaleDocument40 paginiEarth'S History and It'S Geologic Time ScaleNela RainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dane Rudhyar The Astrology of TransformationDocument58 paginiDane Rudhyar The Astrology of Transformationceudekarnak100% (5)
- Dpp+Module: Class - 12Document31 paginiDpp+Module: Class - 12garu sunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do Fossils Form? The Earth's History in Rocks | Children's Earth Sciences BooksDe la EverandHow Do Fossils Form? The Earth's History in Rocks | Children's Earth Sciences BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument51 paginiGeologic Time ScaleLance Francis DanielesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth History and Geologic TimeDocument1 paginăEarth History and Geologic TimeRemil CastañedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mesozoic EraDocument82 paginiThe Mesozoic EraJessica JulienÎncă nu există evaluări
- David Attenborough’s First Life: A Journey Back in Time with Matt KaplanDe la EverandDavid Attenborough’s First Life: A Journey Back in Time with Matt KaplanEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (13)
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument3 paginiGeologic Time ScaleJohn Andrae MangloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Science Final ReviewerDocument3 paginiEarth and Science Final ReviewerJorge GanzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINALS ELS Made Easy 1Document9 paginiFINALS ELS Made Easy 1Argueza, John Ryan V.Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 17 Geo Notes Earth HistoryDocument4 paginiWeek 17 Geo Notes Earth HistoryGil GameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio ReportingDocument3 paginiBio ReportingJessica ApolonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINALS ELS Made Easy PDFDocument13 paginiFINALS ELS Made Easy PDFheeueuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Bio 2 Pre Lim PDFDocument8 paginiGen Bio 2 Pre Lim PDFMark CagasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth's History and Geologic TimeDocument13 paginiEarth's History and Geologic TimedhonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Quiz 2 ReviewerDocument2 paginiEarth and Life Quiz 2 Revieweririshpajarillaga13Încă nu există evaluări
- Fossils & Geologic TimeDocument32 paginiFossils & Geologic TimeYolanda Jane PagtamaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Geologic HistoryDocument53 paginiEarth Geologic HistoryMarilyn RebatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asma Sadiq Roll NM 47 Topipc Geological Time ScaleDocument14 paginiAsma Sadiq Roll NM 47 Topipc Geological Time ScaleIqra IqraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReviewerDocument5 paginiReviewerRaine DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth AND Life Science: (Grade 11 - Stem & Abm) (Grade 12 - Humss & Gas)Document7 paginiEarth AND Life Science: (Grade 11 - Stem & Abm) (Grade 12 - Humss & Gas)Nhorielyn Joy Disbaro BaltazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of The EarthDocument8 paginiThe Evolution of The EarthChrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE Earth: MYA MYA Precambrean EonDocument1 paginăTHE Earth: MYA MYA Precambrean EonMigolits DalanginÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phanerozoic: Etymology of The Term Proterozoic-Phanerozoic Boundary Eras of The PhanerozoicDocument12 paginiPhanerozoic: Etymology of The Term Proterozoic-Phanerozoic Boundary Eras of The PhanerozoicTheodore PetreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of The EarthDocument7 paginiHistory of The EarthMary JuntillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Chapter 1Document78 paginiEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Chapter 1faith cornejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Sci. Group 1 2Document25 paginiEarth Sci. Group 1 2Zye AgnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Biology 2Document1 paginăGen Biology 2AaliyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 6 Els Earths History GTDocument31 paginiWeek 6 Els Earths History GTChristine CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd QUARTER REVIEWERDocument6 pagini3rd QUARTER REVIEWERlorieferpaloganÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTS ElsDocument94 paginiGTS ElsJie Muska CalejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Ess 17 Presence of FossilsDocument27 pagini5 Ess 17 Presence of FossilsMARIA CAMILA CAMPO GARCIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pateros Catholic School: Senior High School Department SY 2021-2022Document5 paginiPateros Catholic School: Senior High School Department SY 2021-2022Rham Jay SaladoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth HistoryDocument3 paginiEarth HistoryRicarla Faith TuyacÎncă nu există evaluări
- EARTHSCI REVIEWER UnfinishedDocument8 paginiEARTHSCI REVIEWER UnfinishedKipi KipsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Science: Quarter 2: Las 6Document5 paginiEarth Science: Quarter 2: Las 6Maxine ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report BioDocument5 paginiReport BiosharkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 and 8Document49 paginiWeek 7 and 8eugene medinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE-CENOZOIC-ERA SchoolDocument4 paginiTHE-CENOZOIC-ERA SchooljungcolemerjerihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument4 paginiGeologic Time ScaleNctzen ExolÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument31 paginiUntitledFeliks Albert RitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Geologic HistoryDocument12 paginiEarth Geologic HistoryFrancis SugueÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of LifeDocument17 paginiHistory of LifeKienth Vincent LopeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 History of Life On EarthDocument38 paginiModule 2 History of Life On EarthioearngÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 RohithDocument105 pagini1 Rohithsohail mohammad (Style de sohail)Încă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Science Module FinalsDocument5 paginiEarth and Life Science Module FinalsChuck Gil Miguel LaygoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument2 paginiGeologic Time ScaleJaymark HisonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geology - Group 9Document31 paginiGeology - Group 9Grace CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument4 paginiGeologic Time ScaleNika MatammuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument18 paginiGeologic Time ScaletzuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument5 paginiEvolution and Origin of BiodiversityAliahneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12.finding The Age of EarthDocument23 pagini12.finding The Age of EarthIffat KamaalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rock Layer: Timeline of Life in EarthDocument2 paginiRock Layer: Timeline of Life in EarthKaye Angeli VillacrusisÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Geological Time Scale-2015Document9 paginiThe Geological Time Scale-2015StanliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument1 paginăGeologic Time ScaleLeixa EscalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Period: A Division of Geologic History With Spans of No More Than 100 Million YearsDocument5 paginiPeriod: A Division of Geologic History With Spans of No More Than 100 Million YearsStain KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTSDocument14 paginiGTSMariel LolincoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Module 6 Geologic Time ScaleDocument28 pagini2021 Module 6 Geologic Time ScaleYara Jeah Ingay BaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finding The Age of Earth: by Aditi AtmasidhaDocument19 paginiFinding The Age of Earth: by Aditi AtmasidhaIffat KamaalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time Scale: Mesozoic EraDocument2 paginiGeologic Time Scale: Mesozoic EraCrave MeroaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambrian Ordo PaleoDocument2 paginiCambrian Ordo PaleoJanskie BulabogÎncă nu există evaluări
- EWG LUT 100RE All Sectors Global Report 2019 PDFDocument321 paginiEWG LUT 100RE All Sectors Global Report 2019 PDFPai BuabthongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument21 paginiSecond Law of ThermodynamicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Build-Up in A Diesel Tank Exposed To Fire: C H E M I C A L E N G I N E E R I N GDocument6 paginiPressure Build-Up in A Diesel Tank Exposed To Fire: C H E M I C A L E N G I N E E R I N GHenda PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biogeography & EvolutionDocument11 paginiBiogeography & EvolutionDaniel Berry100% (1)
- T Box Wind Power Generation: Vrushali Thok, Minal Kapgate, Prajkta Gawali, Shraddha Kolhe, Ankita SinghDocument6 paginiT Box Wind Power Generation: Vrushali Thok, Minal Kapgate, Prajkta Gawali, Shraddha Kolhe, Ankita Singhrahul.yerrawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 4 Josephine Bakewa A00224059Document7 paginiTutorial 4 Josephine Bakewa A00224059Josephine BakewaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WeCommunities - BrochureDocument6 paginiWeCommunities - BrochurejayanthfunucationÎncă nu există evaluări
- NLSP I - RubberDocument27 paginiNLSP I - RubberbalachandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdsorptionDocument3 paginiAdsorptionali105Încă nu există evaluări
- Tu Dong Nghia Global WarmingDocument1 paginăTu Dong Nghia Global WarmingNguyễn HòaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rocks & Energy Chapter 1 & 2 Environmental Management 0680 Geography GCSE IGCSE O-LevelsDocument108 paginiRocks & Energy Chapter 1 & 2 Environmental Management 0680 Geography GCSE IGCSE O-LevelsIGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Journal: Dong Xu, Penny Xiao, Jun Zhang, Gang Li, Gongkui Xiao, Paul A. Webley, Yuchun ZhaiDocument9 paginiChemical Engineering Journal: Dong Xu, Penny Xiao, Jun Zhang, Gang Li, Gongkui Xiao, Paul A. Webley, Yuchun ZhaiMath And EngineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protok Realnog Fluida-3Document34 paginiProtok Realnog Fluida-3konticvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Chemistry and MineralogyDocument11 paginiFundamentals of Chemistry and MineralogyEvi Intan SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProjectDocument19 paginiProjectAndrea Nicole RocafortÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation of PetroleumDocument19 paginiFormation of PetroleumSajjad AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure in Fluids and Atmospheric PressureDocument4 paginiPressure in Fluids and Atmospheric PressureAditya VijayÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Presentation On: "Multi-Terminal High Voltage Direct Current Transmission"Document22 paginiA Presentation On: "Multi-Terminal High Voltage Direct Current Transmission"Manish Kumar MeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Can SETI Succeed Carl Sagan and Ernst Mayr Debate. (From Planetary Society's Bio Astronomy News, 1995.)Document16 paginiCan SETI Succeed Carl Sagan and Ernst Mayr Debate. (From Planetary Society's Bio Astronomy News, 1995.)joymoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit The Natural World: Environmental Impacts of LoggingDocument7 paginiUnit The Natural World: Environmental Impacts of LoggingnbjnÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypothesisDocument11 paginiHypothesisBaldhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climate Change and The Ocean PowerPointDocument25 paginiClimate Change and The Ocean PowerPointIslay JacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Avaliação Edros 2022 - 7º Ano - ProvaDocument32 pagini1 Avaliação Edros 2022 - 7º Ano - ProvaPauliany MartinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 7 ReviewDocument45 paginiPertemuan 7 ReviewAna Sholikhatus Sa'diyah100% (1)
- Newton's Second LawDocument4 paginiNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Trends of Blade Cooling in Gas TurbinesDocument14 paginiCurrent Trends of Blade Cooling in Gas TurbinesPRAVEENÎncă nu există evaluări