Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fastran Tut 06 Mixing
Încărcat de
Yousaf Saidalavi0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări35 paginifastran
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentfastran
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări35 paginiFastran Tut 06 Mixing
Încărcat de
Yousaf Saidalavifastran
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 35
Turbulent Mixing of Propane and Air
FASTRAN Tutorial 6
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Objectives
This tutorial covers the following subjects:
Setting a model name and title for the problem.
Reading a multi domain, DTF grid, and building a CFD-FASTRAN
model.
Setting fluid properties such as molecular weight.
Activating the turbulent mixing properties
Setting boundary values appropriate for inlets in turbulent mixing
flows.
Setting initial values for the flow field to perform a steady state
mixing simulation.
Choosing a suitable time-integration scheme and setting CFL
numbers.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Problem Description
The problem to be simulated consists of 2D turbulent mixing of
propane into an air stream as shown below.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Model
To start CFD-FASTRAN,
type “CFD-FASTRAN” on
the screen. This action
launches the graphical user
interface.
Load the model
Select File/Open from the
Menu bar
The Open dialog panel opens.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Model
Select the file named
“mixing.DTF” and press
the “Accept” button to
read the file.
The DTF file is read into
CFD-FASTRAN and a
model properties window
appears on the screen as
shown in the figure.
Wireframe outline of the
model appears in the
viewing window after press
OK on the model properties
panel
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Model
Fig 3: Model as shown in CFD-FASTRAN-GUI
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Problem Type
Ensure that the Problem
Type [PT] tab is active so
that the control panel is in
Problem Type setting
mode
Under the modules
activate the Compressible
Flow (Flow) Module and
Reacting/Mixing Fluids
(Chem).
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Model Options
Click on the Model
Options [MO] tab.
The Model Options panel
opens with a tab for setting
Global and Flow
parameters.
From the Global tab do
the following:
In the Title field enter
“Turbulent Mixing of Air and
Propane”.
Polar (Axisymmetric about
X-axis) Non
Axisymmetric
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Model Options
Click on the Flow tab to
activate and set the
following parameters:
Gas Model: Species
Viscous Model: Turbulent
(Navier Stokes)
Viscosity : Kinetic Theory
Conductivity: Kinetic
Theory
Mass Diffusivity: Diffusivity
Model: Fick’s Law
Schmidt Number = 0.5
Turbulent Conductivity =
0.9
Turbulence Model : K
Epsilon (Wall Function)
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Model Options
Click on the Chem tab to
activate and set the
following parameters:
Chemistry Model: Mixing
Solver For: Mixture
Fractions
Species Database: Low
Temp. (300K-6000K)
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure: Open Database
From the Menu Bar
select Tools Database
The Database Manager
pops up
The Database Manager
allows to select/create
species/mixtures and
volume/surface
reactions.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure: Creating Species
Select Database → Species
You will have three folders in
the tree structure: mixing
(current DTF file name),
Local and ESI
We need 3 species: C3H8,
N2 and O2 (the last 2
representing air)
Since these species are
already present in the ESI
database, we will just copy
them to the current DTF
From the ESI folder, select
C3H8, N2 and O2. Copy it by
pressing Ctrl+C
Paste the copied species to
the mixing folder (Ctrl+V) Copy Paste
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure: Create Air Mixture
Select Database → Mixtures
Right Click on the Mixing
Folder to create a New
Mixture
In the Mixture Name field
enter “Mixture1”.
Input → Mass Fraction
From the species list select
O2
In the type-in field below
Mass fraction/Concentration,
type 0.232 and Click “Add”.
Similarly select and add N2
and type in 0.768 as the
mass fraction.
Click “Apply” to save “Mixture 1”.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure: Create Air Mixture
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure: Create Propane Mixture
Right Click on the Mixing
Folder to create a New Mixture
In the Mixture Name field enter
“Mixture2”.
Input → Mass Fraction
From the species list select
C3H8
In the type-in field below Mass
fraction/Concentration, type “1”
and press “Add”.
Click “Apply” to save Mixture 2.
Since this is a mixing problem,
we will not be defining
reactions
Close the Database Manager
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
Click on the Boundary
Condition [BC] tab.
The Boundary Condition
Page is presented and
the Model Explorer
changes to the BC mode
to list all of the boundary
conditions in the currently
active simulation.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
In the explorer window
locate and, while holding
down the CTRL button,
select the following types
for each zone:
Zone 1: Patch # 1,2
Ensure that “Interface”
from the Boundary Menu
is selected. It should
already be selected by
default.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
Set the Outlet Boundary
Condition
In the explorer window
locate and select the
following type:
Zone 1: Patch # 4
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
From the Flow Tab select
“Fixed Pressure” from the
Sub-Type menu and enter
a value of 10000 N/m^2 in
the type-in field
From the Chem Tab,
select “Mixture1” from the
Mixture Name menu.
Click “Apply”
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
Set the Symmetry
Boundary Condition
In the explorer window
locate and select the
following type:
Zone 1: Patch # 5
Zone 3: Patch # 2
Select “Symmetry” from
the Boundary Type Menu.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
Set inlet boundary
conditions for Zone 2
In the explorer window
locate and select the
following type:
Zone 2: Patch # 1
Select the “Inlet” BC from
the Boundary Type Menu.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
From the Flow tab, set the
parameters as shown in
the adjacent figure.
From the Chem tab,
select “Mixture1” from the
“Mixture Name” menu.
Click “Apply”
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
Set inlet boundary
conditions for Zone 3.
In the explorer window
locate and select the
following type:
Zone 3: Patch # 3
Select the “Inlet” BC from
the Boundary Type Menu.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Boundary Conditions
From the Flow tab, set the
parameters as shown in
the adjacent figure.
From the Chem tab,
select “Mixture1” from the
“Mixture Name” menu.
Click “Apply”
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Initial Conditions
Click on the Initial Conditions
[IC] tab.
From the IC Global Setting
section select “Volume by
Volume” from the Initial
Condition option.
Pick all the volumes from the
IC list as shown in the figure.
From the Flow tab set the
parameters as shown in the
adjacent figure.
From the Chem tab, select
“Mixture1” from the Mixture
Name menu.
Click “Apply”
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Solver Controls
Press the Solver Control
[SC] tab to activate the
Solver Control setting
page.
There is a tab for each
major type of solver
control setting. There
are also tabs for the
solver output options
available from this page.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Solver Controls
Under the Control tab for
Simulation do the
following:
Select “Steady State” as
the simulation as a steady
state analysis is being
performed.
Max. No. of Cycles = 1000
Zonal Subcycles = 1
Convergence Crit. = 1E-
008
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Solver Controls
Under the Control tab for
Time Step do the
following:
Time Step Size: Based On
CFL Number
Initial CFL = 0.1
Final CFL = 1
Ramping Cycles = 200
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Solver Controls
Under the Spatial Tab
set the following
parameters:
Flux Splitting: Roe’s FDS
Spatial Accuracy: First
Order
Entropy Fix
Linear Waves
0.2 (Default)
Nonlinear Waves
0.2 (Default)
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Solver Controls
Under the Solvers tab set
the following parameters:
Time Integration:Implicit
Implicit Scheme: Point Jacobi
(Fully Implicit)
Subiterations = 20
Tolerance = 0.0001
Discretization: Backward
Euler
There are no settings
under Relax and Adv.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Output
Click Out tab to open the
Output control panel
Under the Output tab set
the following:
Specified Interval
Cycles/Steps = 100
Same File
There are no settings
under Print, Monitor and
Graphic for this case.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Run
Click Run tab to open the
Run Control Panel
Press the “Start
Simulation” button to start
the solution process
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:Run
Because we have modified
the simulation data during
the solution setup process,
the data must first be
saved to a DTF file before
the solver can start.
Press the “Submit Job
Under Current Name”
button to save the
information and to launch
CFD-FASTRAN using the
same file.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Procedure:View Residuals
We can press the “View
Residuals” and “View
Output” buttons to see
real-time displays of the
residual history and output
file contents.
We are looking for a three
to five-orders of magnitude
drop in the solution
residuals.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
Post Processing
CFD-VIEW can be used to
post-process the results:
Maximum Mach Number =
0.215
Maximum Temperature = 305.9
K
Minimum Temperature = 274 K
This tutorial is now finished.
Copyright © ESI Group, 2010. All rights reserved.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Blast Impact13 CDocument12 paginiBlast Impact13 CYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Modelling of Deflagration Establishing Material Data Into ANSYS Autodyns Powder Burn ModelDocument12 paginiModelling of Deflagration Establishing Material Data Into ANSYS Autodyns Powder Burn ModelAli JavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials: Experimental and Numerical Investigations of High-Speed Projectile Impacts On 7075-T651 Aluminum PlatesDocument15 paginiMaterials: Experimental and Numerical Investigations of High-Speed Projectile Impacts On 7075-T651 Aluminum PlatesYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Explicit Dynamic Analysis of Vehicle Roll Over Crashworthiness Using Ls Dyna Tasitlarin Devrilme Carpmasinin Ls Dyna Kullanilarak Eksplisit Dinamik AnaliziDocument51 paginiExplicit Dynamic Analysis of Vehicle Roll Over Crashworthiness Using Ls Dyna Tasitlarin Devrilme Carpmasinin Ls Dyna Kullanilarak Eksplisit Dinamik Analizihanumantha100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Three-Dimensional, Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Bullet Penetration Through Thin AISI 4340 Steel Target PlateDocument6 paginiThree-Dimensional, Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Bullet Penetration Through Thin AISI 4340 Steel Target PlateYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Lee 2014Document6 paginiLee 2014Yousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Fulltext02 PDFDocument95 paginiFulltext02 PDFYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Samson 30 RWS: The World's Leading Systems Integrated Into An All-In-One SolutionDocument4 paginiSamson 30 RWS: The World's Leading Systems Integrated Into An All-In-One SolutionYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Compressible CFD (CESE) Module Presentation: Zeng Chan Zhang, Kyoung-Su Im, Iñaki ÇaldichouryDocument33 paginiCompressible CFD (CESE) Module Presentation: Zeng Chan Zhang, Kyoung-Su Im, Iñaki ÇaldichouryYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Tutorial 1 Preprocessing, Running LS-DYNA, & PostprocessingDocument64 paginiTutorial 1 Preprocessing, Running LS-DYNA, & PostprocessingYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Three-Dimensional, Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Bullet Penetration Through Thin AISI 4340 Steel Target PlateDocument6 paginiThree-Dimensional, Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Bullet Penetration Through Thin AISI 4340 Steel Target PlateYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Fastran Tut 02 Naca0012Document29 paginiFastran Tut 02 Naca0012Yousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 AdfDocument296 pagini1 AdfYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Fulltext02 PDFDocument95 paginiFulltext02 PDFYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Fastran Tut 04 TankdropDocument70 paginiFastran Tut 04 TankdropYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Autodyn Verberne Pieter 201411 MAS Thesis PDFDocument115 paginiAutodyn Verberne Pieter 201411 MAS Thesis PDFYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Compressible CFD (CESE) Module Presentation: Zeng Chan Zhang, Kyoung-Su Im, Iñaki ÇaldichouryDocument33 paginiCompressible CFD (CESE) Module Presentation: Zeng Chan Zhang, Kyoung-Su Im, Iñaki ÇaldichouryYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fastran Tut 07 ReactingDocument41 paginiFastran Tut 07 ReactingYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of High-Performance Fiber Materials Properties in Simulated and Actual Space EnvironmentsDocument48 paginiComparison of High-Performance Fiber Materials Properties in Simulated and Actual Space EnvironmentsYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Modelling and Simulation of Gun Dynamics Using ANSYS'Document5 paginiFinite Element Modelling and Simulation of Gun Dynamics Using ANSYS'Yousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3d ChimeraDocument32 pagini3d ChimeraYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Fastran Tut 02 Naca0012Document29 paginiFastran Tut 02 Naca0012Yousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fastran Tut 05 StagingDocument79 paginiFastran Tut 05 StagingYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theodore Trevino - Applications of Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian (ALE) Analysis Approach To Underwater and Air Explosion ProblemsDocument198 paginiTheodore Trevino - Applications of Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian (ALE) Analysis Approach To Underwater and Air Explosion ProblemsMallamaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Fastran Tut 01 Cyl2DDocument30 paginiFastran Tut 01 Cyl2DYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pitching Airfoil With FlapDocument2 paginiPitching Airfoil With FlapYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fastran Tut 09 ParallelDocument34 paginiFastran Tut 09 ParallelYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFD-Toolkit V2014.0 User ManualDocument23 paginiCFD-Toolkit V2014.0 User ManualYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Cfd-View v2014.0 User ManualDocument429 paginiCfd-View v2014.0 User ManualYousaf SaidalaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypotestDocument14 paginiHypotestMadhukar SamathamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of EqualityDocument1 paginăProperties of EqualityGia Avereen JanubasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Economics: Ali SalmanDocument11 paginiEngineering Economics: Ali SalmanAli Haider RizviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Fault Signature AnalysisDocument10 paginiMachine Fault Signature AnalysisKotha MahipalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Marine Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument20 paginiAdvanced Marine Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasmahakÎncă nu există evaluări
- ManualDocument376 paginiManualYoseph BirruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verilog HDLDocument74 paginiVerilog HDLgautamsvksÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH 352 Sample Project 1Document10 paginiMATH 352 Sample Project 1Withoon ChinchalongpornÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 6 Set Instruksi, Karakteristik Dan FungsiDocument40 paginiPertemuan 6 Set Instruksi, Karakteristik Dan FungsiRizal AdiwangsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng SP CognatesDocument29 paginiEng SP Cognatescuba_viajesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Enforced ButtDocument2 paginiEnforced ButtSwati DhurpateÎncă nu există evaluări
- JR Maths-Ia Saq SolutionsDocument69 paginiJR Maths-Ia Saq SolutionsKathakali Boys AssociationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reversed CurvesDocument7 paginiReversed CurvesBenidick Santos BernardinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Bearing CalculationDocument47 paginiAir Bearing CalculationtomekzawistowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Journal of Space Syntax (JOSS)Document9 paginiThe Journal of Space Syntax (JOSS)Luma DaradkehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main PaperDocument13 paginiMain PapermdkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital SAT Tests MATH Explanation (Mr. Amr Mustafa)Document196 paginiDigital SAT Tests MATH Explanation (Mr. Amr Mustafa)mr.samirjon.07Încă nu există evaluări
- P1-Set TheoryDocument41 paginiP1-Set TheoryDipanwita DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplex Method Additional ActivityDocument3 paginiSimplex Method Additional ActivityIra Grace De CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
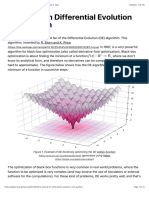
- A Tutorial On Differential Evolution With Python - Pablo R. MierDocument21 paginiA Tutorial On Differential Evolution With Python - Pablo R. MierNeel GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Maths 103 124Document22 paginiDiscrete Maths 103 124Bamdeb DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 13 Moon CalendarDocument24 paginiThe 13 Moon Calendarklatifdg100% (4)
- Polarization WavesDocument37 paginiPolarization WavesNil TaiiayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stratego AlgorithmsDocument74 paginiStratego AlgorithmsbobertstokesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics and Aprobability Q3 - Quarterly AssessmentDocument3 paginiStatistics and Aprobability Q3 - Quarterly AssessmentRomnickCelestinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Methods For Determining The Origin of Vapor Cloud Explosions Case StudyDocument28 paginiAdvanced Methods For Determining The Origin of Vapor Cloud Explosions Case StudyСергей АлексеевÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelim FinalDocument440 paginiPrelim FinalRon AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIBRATION LAB BMM3553 COOPERATIVE LEARNING - Version 1718Document2 paginiVIBRATION LAB BMM3553 COOPERATIVE LEARNING - Version 1718Hassan JabbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Techniques of PL/SQLDocument269 paginiAdvanced Techniques of PL/SQLsunilrguravÎncă nu există evaluări