Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CPAR Lesson
Încărcat de
Anabelle MoyamoyDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CPAR Lesson
Încărcat de
Anabelle MoyamoyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
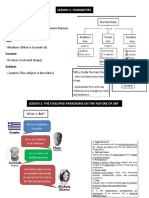
Contemporary Arts Color
- Spring out of the present day, events & - Associated w/our experiences of cold
passion of society. and warmth, and quality light in our
typical environment.
Example:
Values
Diaspora by Antipas Delatovo 2007 in
Oil on Canvas. - Refers to gradations of tone from light
to dark.
Contemporary (Con tempo) – Refers to the
art of the present time. Texture
Contemporary Arts vs. Modern Arts - Refers to how objects & surfaces feel.
- 1800’s up to mid. 20th century Shape
- Discovered that breaking away from - Refers to forms that are 2 & 3
traditional art style started in this dimensional.
period.
Movement
Integrative Art
- Related to line & direction of the eye.
- Interactive & Multi-disciplinary in
nature, consisting of ides & practices Composition
from diff. branches.
- Involves relationship between figures
Humanities and elements.
- Refers to the study of human Principles of Art (Organization of
experience. Element)
Legend & Classic
Design
Lisa Macuja Dancing – Dance - Overall structure of an artform.
- Means by which artists.
Lea Salonga Singining – Music
Harmony – Wholeness of the design.
Cecil Licad Song
Variety (Differences) – It is produced so that
monotony and uniformity.
Subject of Art
Rhythm (Pattern) – Regular repeated pattern.
- Only person, animals, things or issue is
Balance – Distribution of weight.
described or represented in a way.
Formal Balance (Symmetric) – 2 sides
Realism
that are identical.
- Object is done the way it looks. Informal Balance (Asymmetric) – Not
identical yet equal visual weight.
Abstraction
Movement – Convey feelings and emotions.
- Artist break apart a subject rearrange in
a diff. manner. Proportion – Distribution of variables.
Non-objectivism Emphasis Subordination
- No object at all. Gives importance/dominance Gives less
- Pure elements like line, shapes, color To a unit of area. importance to a
etc. unit of area.
Distortion
Content
- Uses imagination or alters the subject.
- Contains the subject matter that carries
Elements of Art the message of the work.
Line Context
- Associated w/the body’s axis as it - Describing the relevant circumstances
moves toward diff. directions. surrounding it.
Form (First Key Element) Installation
- Spectator should be considered in an - An art made indoor outdoors where a
artwork is its form. space is transformed into a three-
dimensional artwork.
New themes in all art forms consist of
Animism – Gods and Goddesses.
certain socially conscious issues which
Bulul – God of rice of the Ifugao’s. have arisen with this period:
Mangyan Basket - Feminism
Pissiyabit (Head Cloth) - Consumerism
Embroidered Jusi & Pina - Multiculturalism
Pakil - Globalization
Philippine Traditional Arts - Health awareness
- Boast of rich songs & dances in the - Migration and so on
regions. (Realistic, Sculpture, Paint)
Filipino Contemporary Artist
Traditional Art
- Still deals with current concerns that
- Culture bound in the sculpture
affect our country.
Traditional Style
- Evident in their adherence to classical The Cultural Center of the Philippines (CCP)
structures & standards.
Contemporary Art - Was established in 1996 through the
- Latter revolves around the artist. Executive Order No. 303.
Philippine Contemporary Art.
- Not bounded by any rule or standard. - Regarded as the premiere showcase of
the arts, it houses several resident
Modernism companies: Philippine Philharmonic
- Art forms evolved into a variety of Orchestra, UST Symphony Orchestra,
expressions & media that turns the Tanghalang Filipino, BAYANIHAN
entire world into a “Creative Upheaval” National Dance Company of the
Example: Philippines, Ramon Obusan
Metall by Louie Cordero Folkloric Group, Philippine Madrigal
Singers, Philippine Ballet Theatre, Ballet
Post Modernism Philippines, and National Music
Competitions for Young Artist.
- First appearance in the Philippine
happened after the world war II and
again during the Martial law era in the
1970’s.
Pastiche
- Most common feature of
postmodernism.
- Refers to the blurring of divisions.
Bricolage
- Also called as assemblage, popularly
used visual arts.
Appropriation
- Also called as borrowing
- Postmodernism finds inspiration in
artworks from the previous periods.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Art App ReviewerDocument5 paginiArt App ReviewerASIANSison, Shekainah May SisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOTES (12-2nd Sem)Document9 paginiNOTES (12-2nd Sem)roushanedelafuente15Încă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument3 paginiArt Appreciation ReviewerJAMILLAH OBENIETAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpar ReviewerDocument3 paginiCpar ReviewerKazuma TaikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contempo Arts Midterms Reviewer PDFDocument2 paginiContempo Arts Midterms Reviewer PDFEarl CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Notes 1Document3 paginiConcept Notes 1Mark PanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPAR ReviewerDocument6 paginiCPAR ReviewerFourEyed PatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary ArtsDocument3 paginiContemporary Artsayah eliviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.7 Subject of Arts and Methods of Presenting SubjectsDocument11 pagini1.7 Subject of Arts and Methods of Presenting SubjectsMECHANICAL ENGINEERINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in CparDocument3 paginiReviewer in CparMariela MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Philippines Arts From The Regions: Prepared By: Ms. Trixie Mae Entrina - NonoDocument43 paginiContemporary Philippines Arts From The Regions: Prepared By: Ms. Trixie Mae Entrina - NonoSylverina FrancoisÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPAR Midterm ReviewerDocument5 paginiCPAR Midterm Reviewerxtraa5272Încă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation Summary NotesDocument2 paginiArt Appreciation Summary NotesToni CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation - Midterm Exam - ReviewerDocument7 paginiArt Appreciation - Midterm Exam - ReviewerAudije, John Michael M.Încă nu există evaluări
- Art App Lecture NotesDocument14 paginiArt App Lecture NotesMA. ERICKAH TINASASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art AppreciationDocument6 paginiArt Appreciationleannanicole.bustamanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpar Reviewer 3RD QDocument5 paginiCpar Reviewer 3RD QRem bea DelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rev in CPARDocument3 paginiRev in CPARLheanne LheanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArtsDocument3 paginiArtslheagomezsisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Is Art Important To Our Society? Characteristics of Contemporary ArtDocument2 paginiWhy Is Art Important To Our Society? Characteristics of Contemporary ArtGroovy모니카Încă nu există evaluări
- 1ST M.E. Reviewer D2Document8 pagini1ST M.E. Reviewer D2Ella CaraanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telos in Greek, Which Translates IntoDocument5 paginiTelos in Greek, Which Translates IntoCarla CarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPAR EditedDocument8 paginiCPAR EditedAro Sanuel AlcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Elements of ArtsDocument5 paginiVisual Elements of ArtsJan Mae EstaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Art Forms FinalDocument9 paginiHistory of Art Forms Finalkevinerrol9Încă nu există evaluări
- AngelaDocument11 paginiAngelaHirajqa LlareuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPAR NotesDocument4 paginiCPAR NotesJahzara Daveigh BolivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Philippine Arts in The Regions Learning Material: Week 5 and 6Document4 paginiContemporary Philippine Arts in The Regions Learning Material: Week 5 and 6sheryn valdejuezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Araling Pilipino ReviewerDocument11 paginiAraling Pilipino ReviewerChristian Jake VerdilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpar Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument3 paginiCpar Reviewer 3RD Quarterangelocamo09Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Art AppreciationDocument6 paginiChapter 4 Art AppreciationJohn Paul BausaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Quarter ReviewersDocument13 pagini1st Quarter ReviewersMyla BlancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Topic Art AppreciationDocument11 paginiSpecial Topic Art Appreciationpulp23Încă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation LectureDocument6 paginiArt Appreciation LectureMariz TrajanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONPHI 3Q Exam ReviewerDocument3 paginiCONPHI 3Q Exam Reviewervince.ortegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Of Inspiration, Making People Achieve Great Things in Life. Between People, To Focus On Common Issues For The Betterment of HumankindDocument9 paginiOf Inspiration, Making People Achieve Great Things in Life. Between People, To Focus On Common Issues For The Betterment of Humankindfrancis bacalangcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conarts ReviewerDocument3 paginiConarts ReviewerAvianna RyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ComArts Week 1 Lesson 1Document22 paginiComArts Week 1 Lesson 1Mary Alexes BejocÎncă nu există evaluări
- AA ReviewerDocument6 paginiAA ReviewerbrylleÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHIL ARTS REVIEWER 1st QuarterDocument23 paginiPHIL ARTS REVIEWER 1st Quarterphoebe porrasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpar NotesDocument11 paginiCpar NotesjohnjesleypogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation: Made Things That Satisfy His NeedsDocument21 paginiArt Appreciation: Made Things That Satisfy His NeedsAngelli SolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conarts ReviewerDocument2 paginiConarts ReviewerAubrey LegaspiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument5 paginiArt Appreciation Reviewersarah gonzagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P1 Long Quiz Reviewer (Art 002)Document21 paginiP1 Long Quiz Reviewer (Art 002)Trisha Mae AcruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEE 12 Chapter 3Document9 paginiGEE 12 Chapter 3Clark Jerome AbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pointers Contemporary ArtsDocument4 paginiPointers Contemporary Artspop upÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpar Quiz2 ReviewerDocument2 paginiCpar Quiz2 ReviewerSABALBORO, Denz ChristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument5 paginiArt Appreciation Reviewerbm1ma.allysaamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art App Midterm ReviewerDocument13 paginiArt App Midterm ReviewerElla Marie LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionDocument5 paginiContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regionjohnahronramos30Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 DomainDocument3 pagini3 DomainAngel Grace LalunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions LASDocument12 paginiContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions LASEnnyliejor YusayÎncă nu există evaluări
- HumanitiesDocument11 paginiHumanitiesCassey Ann PangilinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions 1 1Document88 paginiContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions 1 1John SeñeresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpar ReviewerDocument3 paginiCpar ReviewerMichelyn MacantanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPAR LectureDocument3 paginiCPAR Lecturecasshew02Încă nu există evaluări
- Cpar Lesson 1Document3 paginiCpar Lesson 1Francyne Jhayda EspañolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hodson, Geoffrey - Angels and Archangels (Art)Document3 paginiHodson, Geoffrey - Angels and Archangels (Art)XangotÎncă nu există evaluări
- DDI Au Recruiting For Culture FitDocument20 paginiDDI Au Recruiting For Culture Fitjlg-jlgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competency Framework-Manager AccountsDocument8 paginiCompetency Framework-Manager AccountsAshwary RastogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uid 2M QBDocument20 paginiUid 2M QBSuganya NatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar ComparisonAdjectives1 PDFDocument2 paginiGrammar ComparisonAdjectives1 PDFTeacher MaríaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chaosmosis: An Ethico-Aesthetic ParadigmDocument50 paginiChaosmosis: An Ethico-Aesthetic ParadigmCaetano VillaçaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alanis Obomsawin The Vision of A Native FilmmakerDocument289 paginiAlanis Obomsawin The Vision of A Native Filmmakerirene100% (1)
- 14 Days Prayer For Total HealingDocument137 pagini14 Days Prayer For Total Healingnkugwa6brian80% (5)
- Patricia Benner TFNDocument14 paginiPatricia Benner TFNMenly BalofinosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Thinking Makes Us TiredDocument1 paginăWhy Thinking Makes Us TiredFelipe Augusto BatistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 History Mains 2019Document2 pagini03 History Mains 2019garg1209377Încă nu există evaluări
- Richard L. Crocker - Discant, Counterpoint, and HarmonyDocument22 paginiRichard L. Crocker - Discant, Counterpoint, and Harmonyqvrlenarasegt100% (2)
- Itl 608 - Showcase ReflectionDocument2 paginiItl 608 - Showcase Reflectionapi-449335434100% (2)
- Resume SyntaxDocument8 paginiResume SyntaxKhorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Development - Module 8Document11 paginiPersonal Development - Module 8Benjo RocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graves and CorcoranDocument3 paginiGraves and CorcoranJohn Daemer Halasan KinocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology BooksDocument2 paginiPsychology BooksdeltaserrapapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shame and GuiltDocument524 paginiShame and GuiltitielfilhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Professional Interview Procedures in MalaysiaDocument19 pagini2 - Professional Interview Procedures in Malaysiazahrul azhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- God's Not DeadDocument1 paginăGod's Not DeadLyda Sandstede100% (1)
- For Project Work: Topic: Communication Problem Between Parent and ChildDocument20 paginiFor Project Work: Topic: Communication Problem Between Parent and ChilddlimzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Physics Chapter 14 and 15 Assignment 1Document2 pagini11 Physics Chapter 14 and 15 Assignment 1nellai kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tipping Point SummaryDocument2 paginiTipping Point SummaryAaron Mann100% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument38 paginiSeminar ReportRakesh RoshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP3002/MP4012 Mechanics of Deformable Solids Tutorial 1 - Free Vibration 2009/10 Semester 2Document8 paginiMP3002/MP4012 Mechanics of Deformable Solids Tutorial 1 - Free Vibration 2009/10 Semester 2David SaranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usui's Teacher - The Writings of Tanaka (Extract)Document22 paginiUsui's Teacher - The Writings of Tanaka (Extract)Frank Shortt0% (1)
- The Theatre of The AbsurdDocument16 paginiThe Theatre of The Absurdbal krishanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Archetype and Allegory Journey To The WestDocument113 paginiArchetype and Allegory Journey To The Westmerlin66Încă nu există evaluări
- Total English Intermediate Photocopiable Worksheets PDFDocument118 paginiTotal English Intermediate Photocopiable Worksheets PDFramiona2333% (3)
- Silverman, Isbell - Andean Archaeology II - Art, Landscape, and Society-Springer US (2002)Document294 paginiSilverman, Isbell - Andean Archaeology II - Art, Landscape, and Society-Springer US (2002)foxtrout100% (1)