Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CPAP NIV Evidence Table 2018
Încărcat de
aldiela fitryantoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CPAP NIV Evidence Table 2018
Încărcat de
aldiela fitryantoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Reference Evidence level Key finding, outcomes or recommendations
(I-VII)
Annane D, Orlikowski D, Chevret S, Chevrolet J, & Raphaël J. II Suggests NIV alleviates symptoms of chronic hypoventilation due to
(2007). Nocturnal mechanical ventilation for chronic neuromuscular disease
hypoventilation in patients with neuromuscular and chest wall Comparison of different types of nocturnal ventilation, measuring both short-
disorders. Cochrane database of systematic reviews. Issue 4. term and long-term reversal of daytime hypercapnia, improvement of lung
Art No: CD001941. function and sleep breathing disorders
Pierce, L. (2007). Management of the Mechanically Ventilated VII Clinical examination
Patient. (2nd Ed). Mosby: St Louis. Troubleshooting, airway management and positioning techniques
Pilbeam, S & Cairo, J. (2006). Mechanical Ventilation: VII Identifies differences in paediatric ventilation; allowing for changes to growth
Physiological & Clinical Applications.(4th Ed). Mosby: St Louis. and development
Clinical assessment
Indications and contraindications in using non-invasive mechanical ventilation
Monitoring requirements
Simonds, S. (2006). Recent Advances in Respiratory Care for IV Improvements to quality of life, symptom alleviation and management
Neuromuscular Disease. Chest.130:1879-1886 Physiology
Suresh, S., Wales, P., Dakin, C., Margaret-Anne, H. and V The prevalence of SRBD in DMD is significant. Polysomnography is recommended
Cooper, D. (2005). Sleep-Related Breathing Disorder in in children with symptoms of OSA, or at the stage of becoming
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Disease Spectrum in the wheelchair‐bound. In patients with the early stages of respiratory failure,
Paediatric Population. Journal of Paediatics and Child Health. assessment with polysomnography‐identified sleep hypoventilation and assisted
Sept.41(9-10) pp500-503 in initiating NIV.
Machaalani, R., Evans, C., and Waters, A. (2016). Objective IV Adherence with BiLevel was greater than for CPAP. Over half of our population
Adherence to Positive Airway Pressure Therapy in and continue to utilise PAP therapy 1 year later, and amongst these cases,
Australian Paediatric Cohort. Sleep and Breathing. Dec. 20(4) adequate adherence was maintained.
pp1327-1336
Pugalenthi et al. (2015). Compliance to Non-Invasive V Objective monitoring of CPAP compliance is important in the management of
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Ventilation in Children children with OSA.
with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. European Respiratory
Journal. 46(59)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Endocrine Glands PDFDocument99 paginiEndocrine Glands PDFXochitl ZambranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- PDFDocument342 paginiPDFZae M HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Microbiology and Infection: Original ArticleDocument6 paginiClinical Microbiology and Infection: Original ArticleAkira Masumi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- Varicose Vein and Its Homeopathic Cure - DR Bashir Mahmud ElliasDocument8 paginiVaricose Vein and Its Homeopathic Cure - DR Bashir Mahmud ElliasBashir Mahmud Ellias100% (2)
- Analgesics - New Microsoft Office Power Point PresentationDocument21 paginiAnalgesics - New Microsoft Office Power Point Presentationrozha100% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory: Exercise: Digestive SystemDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology Laboratory: Exercise: Digestive SystemLouise Mica LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Michael H. Antoni, Roselyn Smith-Stress Management Intervention For Women With Breast Cancer-Amer Psychological Assn (2003)Document222 paginiMichael H. Antoni, Roselyn Smith-Stress Management Intervention For Women With Breast Cancer-Amer Psychological Assn (2003)KmoespinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument64 paginiGrowth and DevelopmentRahul Dhaker100% (1)
- Arterial Line Analysis PresentationDocument35 paginiArterial Line Analysis PresentationLisa GilbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory ApplicationDocument38 paginiTheory ApplicationAnusha VergheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tu Syllabus ... BDS PDFDocument90 paginiTu Syllabus ... BDS PDFHitesh karn100% (3)
- Home Quarantine Compliance 2022 1Document1 paginăHome Quarantine Compliance 2022 1Puting KahoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- XII Chemistry CH#11 Notes (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)Document9 paginiXII Chemistry CH#11 Notes (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)salmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maui Medical Dispensary Application Redacted Sec3Document541 paginiMaui Medical Dispensary Application Redacted Sec3melipasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Presentation-Mindy Duran-FinalDocument30 paginiCase Study Presentation-Mindy Duran-Finalapi-278622211Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Adolescent Substance Use Disorder Treatment PDFDocument42 paginiPrinciples of Adolescent Substance Use Disorder Treatment PDFDanilo CozzoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical Considerations From Prisoners inDocument17 paginiEthical Considerations From Prisoners inNino MdinaradzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illich 1982Document5 paginiIllich 1982CsscamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Potential Siddha Mineral Drug Pavala ParpamDocument8 paginiA Potential Siddha Mineral Drug Pavala Parpamjmanuel108yahoo.co.ukÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP in Health 10 Global Health InitiativesDocument10 paginiDLP in Health 10 Global Health InitiativesJoshua MaravillasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adhesive CapsulitisDocument6 paginiAdhesive CapsulitisEllan Giulianno FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Composition II 1Document11 paginiEnglish Composition II 1api-548473407Încă nu există evaluări
- Scid 5 CVDocument26 paginiScid 5 CVZubair Mahmood KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic Resistance Lesson Plan Final ProjectDocument10 paginiAntibiotic Resistance Lesson Plan Final Projectapi-436796283Încă nu există evaluări
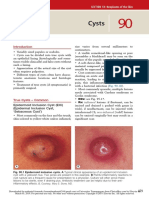
- CystsDocument5 paginiCystsranindita maulyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bril (2002) - Validation of The Toronto Clinical Scoring System For Diabetic PolyneuropathyDocument5 paginiBril (2002) - Validation of The Toronto Clinical Scoring System For Diabetic PolyneuropathyRicky WatariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Marcelia Suryatenggara, Sp. S - How To Choose Your AnalgeticsDocument9 paginiDr. Marcelia Suryatenggara, Sp. S - How To Choose Your AnalgeticsFreade AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating Diagnostics: A Guide For Diagnostic EvaluationsDocument5 paginiEvaluating Diagnostics: A Guide For Diagnostic EvaluationsYanneLewerissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silkworm in NepalDocument11 paginiSilkworm in NepalRitesh Raj Shrestha50% (4)