Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Amoxicillin BP
Încărcat de
kekaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Amoxicillin BP
Încărcat de
kekaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Medical uses
Amoxicillin BP
Amoxicillin is used in the treatment of a number of infections, including acute otitis media,
streptococcal pharyngitis, pneumonia, skin infections, urinary tract infections, Salmonella
infections, Lyme disease, and chlamydia infections.[3][12]
Acute otitis media
Children with acute otitis media who are younger than 6 months of age are generally treated with
amoxicillin or other antibiotic. Although most children with acute otitis media who are older
than two years old do not benefit from treatment with amoxicillin or other antibiotic, such
treatment may be helpful in children younger than two years old with acute otitis media that is
bilateral or accompanied by ear drainage.[13]In the past, amoxicillin was dosed three times daily
when used to treat acute otitis media, which resulted in missed doses in routine ambulatory
practice. There is now evidence that two times daily dosing or once daily dosing has similar
effectiveness.[14]
Respiratory infections
Amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate have been recommended by guidelines as the drug of
choice for bacterial sinusitis and other respiratory infections.[12] Most sinusitis infections are
caused by viruses, for which amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate are ineffective,[15] and the
small benefit gained by amoxicillin may be overridden by the adverse effects.[16] Amoxicillin is
recommended as the preferred first-line treatment for community-acquired pneumonia in adults
by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, either alone (mild to moderate severity
disease) or in combination with a macrolide.[17] The World Health Organization recommends
amoxicillin as first-line treatment for pneumonia that is not "severe".[18] Amoxicillin is used in
post-exposure inhalation of anthrax to prevent disease progression and for prophylaxis.[12]
H. pylori
It is effective as one part of a multi-drug regimen for treatment of stomach infections of
Helicobacter pylori. It is typically combined with a proton-pump inhibitor (such as omeprazole)
and a macrolide antibiotic (such as clarithromycin); other drug combinations are also
effective.[19]
Lyme borreliosis
Amoxicillin is effective for treatment of early cutaneous Lyme borreliosis; the effectiveness and
safety of oral amoxicillin is neither better nor worse than common alternatively-used
antibiotics.[20]
Skin infections
Amoxicillin is occasionally used for the treatment of skin infections,[12] such as acne vulgaris.[21]
It is often an effective treatment for cases of acne vulgaris that have responded poorly to other
antibiotics, such as doxycycline and minocycline.[22]
Infections in infants in resource-limited settings
Amoxicillin is recommended by the World Health Organization for the treatment of infants with
signs and symptoms of pneumonia in resource-limited situations when the parents are unable or
unwilling to accept hospitalization of the child. Amoxicillin in combination with gentamicin is
recommended for the treatment of infants with signs of other severe infections when
hospitalization is not an option.[23]
Prevention of bacterial endocarditis
It is also used to prevent bacterial endocarditis in high-risk people having dental work done, to
prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae and other encapsulated bacterial infections in those without
spleens, such as people with sickle-cell disease, and for both the prevention and the treatment of
anthrax.[3] The United Kingdom recommends against its use for infectious endocarditis
prophylaxis.[24] These recommendations do not appear to have changed the rates of infection for
infectious endocarditis.[25]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Macrolides: AntibioicsDocument14 paginiMacrolides: AntibioicsAbdelrhman AboodaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otitis Media Aguda Update COID 2000Document6 paginiOtitis Media Aguda Update COID 2000Jose MalagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patients at Low Risk Can Usually Be Managed With Oral Antibiotics at HomeDocument15 paginiPatients at Low Risk Can Usually Be Managed With Oral Antibiotics at HomeMimi NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name:-Ibrahim Mohammed Stage:-4 Group-C-Report:-: AmoxicillinDocument7 paginiName:-Ibrahim Mohammed Stage:-4 Group-C-Report:-: AmoxicillinSaif AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amoxicillin: A Beginner's 20-Minute Quick Guide Overview on its Use Cases to Treat Bacterial Infection and Side EffectsDe la EverandAmoxicillin: A Beginner's 20-Minute Quick Guide Overview on its Use Cases to Treat Bacterial Infection and Side EffectsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal To Include Antibacterial Drugs For Treating Upper and Lower Respiratory Infections in ChildrenDocument52 paginiProposal To Include Antibacterial Drugs For Treating Upper and Lower Respiratory Infections in ChildrenAznil FajriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 201060antibiotics and ChildrenDocument2 pagini201060antibiotics and ChildrencillenujmwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amoxicillin DT Product Profile and Supply UpdateDocument7 paginiAmoxicillin DT Product Profile and Supply UpdatebooksdiversÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macrolides PearlsDocument10 paginiMacrolides PearlsRamez AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jase Medical Antibiotic GuideDocument33 paginiJase Medical Antibiotic GuideelectronicoscaldasÎncă nu există evaluări
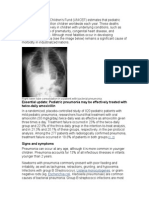
- Essential Update: Pediatric Pneumonia May Be Effectively Treated With Twice-Daily AmoxicillinDocument54 paginiEssential Update: Pediatric Pneumonia May Be Effectively Treated With Twice-Daily AmoxicillinYostesara Maurena SantosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) - Treatment, Complications, and Prevention - UpToDateDocument20 paginiChronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) - Treatment, Complications, and Prevention - UpToDateZulvina FaozanudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infections in PregnancyDocument9 paginiInfections in PregnancyDevi SuryandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amoxicillin: A Broad Spectrum Antibiotic: Review ArticleDocument8 paginiAmoxicillin: A Broad Spectrum Antibiotic: Review ArticlebooksdiversÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmoxicillinDocument8 paginiAmoxicillinMariusNeicuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.editorial Antibiotic Use in Acne VulgarisDocument3 pagini1.editorial Antibiotic Use in Acne VulgarisitaindrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Management For PneumoniaDocument2 paginiMedical Management For PneumoniaSue Elaine100% (1)
- Oral ManifestationsDocument66 paginiOral ManifestationsMiguel DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument45 paginiUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsAbraham TibebuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticDocument25 paginiAntibioticgzmrc6sfrnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Khamlin Hamad Abdal - GroupeaDocument39 paginiKhamlin Hamad Abdal - GroupeaKhamlin NurseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Khamlin Hamad Abdal - GroupeaDocument39 paginiKhamlin Hamad Abdal - GroupeaKhamlin NurseÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmoxicillinDocument3 paginiAmoxicillinElena DenisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Antibiotic Guide A6 105 1048mm February9 2022Document48 paginiEmergency Antibiotic Guide A6 105 1048mm February9 2022Iain HarrisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- RebamipideDocument5 paginiRebamipidejunerubinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric PneumoniaDocument12 paginiPediatric PneumoniaKrystal Migo Denolo ContrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prophylactics of PneumoniaDocument31 paginiProphylactics of PneumoniaJoisy AloorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research ArticleDocument17 paginiResearch ArticleNatanael KindangenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jjournal BagusDocument7 paginiJjournal BagusputerinmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia: Key FactsDocument28 paginiPneumonia: Key FactsAri Widiastuti NiPutuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects On MicrobesDocument12 paginiEffects On MicrobesHabeeb RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.4 CH Imci LearningDocument48 pagini3.4 CH Imci LearningMarion jeptoo RotichÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Essential Guide to Amoxicillin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.De la EverandThe Essential Guide to Amoxicillin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.Încă nu există evaluări
- Untitled Document-2 PDFDocument6 paginiUntitled Document-2 PDFHamssini GantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LRTI and KDDocument14 paginiLRTI and KDjomerdalonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment of Chlamydia Trachomatis InfectionDocument9 paginiTreatment of Chlamydia Trachomatis InfectioneeeeewwwwwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Otitis Media: EtiologyDocument4 paginiAcute Otitis Media: EtiologyMahir FikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indications of Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Dental Practice-ReviewDocument6 paginiIndications of Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Dental Practice-ReviewTayyaba RafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bpac Antibiotics Booklet PDFDocument20 paginiBpac Antibiotics Booklet PDFVenny Tri Pahlevi IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument2 paginiPneumoniaJen Ballesteros100% (1)
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) Treatment, Complications, and PreventionDocument13 paginiChronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) Treatment, Complications, and PreventionchristineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Efficacy of Azithromycin Versus Co-Amoxiclave in Acute Otitis MediaDocument7 paginiClinical Efficacy of Azithromycin Versus Co-Amoxiclave in Acute Otitis MediaAndry YonathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 UpToDate NeumoníaDocument113 pagini18 UpToDate NeumoníaAl DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems Breathing Sputum Fever Uncontrollable Shaking: Symptoms of CAP Commonly IncludeDocument3 paginiProblems Breathing Sputum Fever Uncontrollable Shaking: Symptoms of CAP Commonly Includehush!hushÜ!Încă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics and Its Use in Pediatric Dentistry: A ReviewDocument5 paginiAntibiotics and Its Use in Pediatric Dentistry: A ReviewMayangdevi SPÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO - PneumoniaDocument4 paginiWHO - Pneumoniadyan ayu puspariniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics: Choices For Common InfectionsDocument30 paginiAntibiotics: Choices For Common InfectionsAlfeus GradyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CandidiasisDocument19 paginiCandidiasisTeguh Adi PartamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Essentials: Pediatric Pneumonia MedicationDocument56 paginiPractice Essentials: Pediatric Pneumonia MedicationAnonymous HgX3mN1oÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal DR Nawan 1Document7 paginiJurnal DR Nawan 1muntiir gurusingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- T Trikuria 1Document6 paginiT Trikuria 1Briliant Khoeratun NissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- G AntibioticTherapyDocument3 paginiG AntibioticTherapyJacoboGonzálezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infection ControlDocument12 paginiInfection Controlghufran khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Improve Antifungal StewardshipDocument12 paginiHow To Improve Antifungal StewardshipciaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxoplasmosis Ocular PDFDocument8 paginiToxoplasmosis Ocular PDFSamanta Cadenas100% (1)
- Ijgm 4 421Document3 paginiIjgm 4 421Abu UbaidillahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter OneDocument17 paginiChapter OneBrix RosalijosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Old Diseases Are Coming Back:: Courtesy Of Anti-VaccinatorsDe la EverandOld Diseases Are Coming Back:: Courtesy Of Anti-VaccinatorsEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- (ELT), Foreign Language Teaching (FLT) (#122847) - 104690Document16 pagini(ELT), Foreign Language Teaching (FLT) (#122847) - 104690kekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Pad Construction - SummaryDocument7 paginiWell Pad Construction - SummarykekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Production Equipment - SummaryDocument3 paginiNormal Production Equipment - SummarykekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthworks SummaryDocument3 paginiEarthworks SummarykekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finance TheoryDocument21 paginiFinance TheorykekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Oil and Gas DrillingDocument1 paginăIntroduction To Oil and Gas DrillingkekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aadi Amavasya SpecialDocument5 paginiAadi Amavasya SpecialjyoprasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICMA2011 DigestDocument160 paginiICMA2011 DigestPREEDAIENGINEERINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Financial Regulation Seminar QuestionsDocument2 paginiInternational Financial Regulation Seminar QuestionsNicu BotnariÎncă nu există evaluări
- DefinitionsDocument7 paginiDefinitionsJazmine ButuhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exilis Ultra 360 Brochure Face qNaWU5wmOeC0zuWDocument2 paginiExilis Ultra 360 Brochure Face qNaWU5wmOeC0zuWJohn LuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualities of Effective Business LettersDocument39 paginiQualities of Effective Business Letterskrystel0% (1)
- Development of EIGA Bars For Producing Powder Particles of Ti6Al4V Nanomodified by Gas Atomization (NANOTUN3D European Project)Document1 paginăDevelopment of EIGA Bars For Producing Powder Particles of Ti6Al4V Nanomodified by Gas Atomization (NANOTUN3D European Project)daffaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Writing Business MessagesDocument60 paginiChapter 2 - Writing Business MessagesrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listado de Vehiculos para ChatarrizaciónDocument658 paginiListado de Vehiculos para ChatarrizacióntaycotcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistical Physics Phy632-Tutorial: Sharifah Hafizah Binti Syed Ab AzizDocument26 paginiStatistical Physics Phy632-Tutorial: Sharifah Hafizah Binti Syed Ab AzizSharifahHafizahAl-jufÎncă nu există evaluări
- SQF Edition 8 Quick Start GuideDocument27 paginiSQF Edition 8 Quick Start Guidefourat.zarkounaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument3 paginiAspiration PneumoniaEllen Hennings100% (1)
- R.K. Anand Contempt Delhi HC JudgementDocument112 paginiR.K. Anand Contempt Delhi HC JudgementSampath BulusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracing Changes Through A Thousand YearsDocument27 paginiTracing Changes Through A Thousand YearsPranit PrasoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basso - 2001 - Neurobiological Relationships Between Ambient Ligh PDFDocument11 paginiBasso - 2001 - Neurobiological Relationships Between Ambient Ligh PDFVíctor MJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affiliate Marketing Step by StepDocument27 paginiAffiliate Marketing Step by StepJulia FawcettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everyday Conversation 3CDocument10 paginiEveryday Conversation 3Cjiyoon KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITALY 1940-41: Bersaglieri Support List List OneDocument1 paginăITALY 1940-41: Bersaglieri Support List List OneXijun Liew0% (1)
- Global Davit GMBHDocument8 paginiGlobal Davit GMBHTimothy JacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Mix Asphalt Overlay Splice: (Pavement Termination Detail)Document1 paginăHot Mix Asphalt Overlay Splice: (Pavement Termination Detail)JUAN RULFOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Year 5: MicroorganismsDocument8 paginiScience Year 5: MicroorganismscthanifahÎncă nu există evaluări
- VMGODocument3 paginiVMGOklirt carayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics and Social Responsibilities of Entrepreneurship PDFDocument4 paginiEthics and Social Responsibilities of Entrepreneurship PDFRevuru ArunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Russian Military Intervention in The Syrian Civil War PDFDocument62 paginiRussian Military Intervention in The Syrian Civil War PDFMendiburuFranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bayesian Cost Effectiveness Analysis With The R Package BCEA PDFDocument181 paginiBayesian Cost Effectiveness Analysis With The R Package BCEA PDFNelson Carvas JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline BRM AbasynDocument4 paginiCourse Outline BRM Abasynsadeeq sahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 1b - Selection and Literature Review of A CultureDocument3 paginiPart 1b - Selection and Literature Review of A Cultureapi-535208903Încă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Test Grade 6 TleDocument4 paginiDiagnostic Test Grade 6 TledeguiajericÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Management Practices and Performance of Non-Governmental Organizations Projects in Nairobi City County, KenyaDocument22 paginiProject Management Practices and Performance of Non-Governmental Organizations Projects in Nairobi City County, KenyaAjit Pal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accelerometer With VelocityDocument11 paginiAccelerometer With VelocityAS_865025438Încă nu există evaluări