Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Products Liability Chart
Încărcat de
Kira GearyDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Products Liability Chart
Încărcat de
Kira GearyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
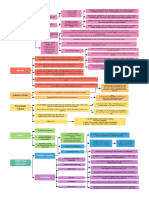
Products Liability
Strict liability: if a product is defective, then there is strict liability—don’t have to show warranty, only that P was using product in a way that it
was intended to be used and their injury was caused by a defect that P was not made aware of. Not necessary to show existence of express
warranty.
Definition Burden on P Notes
Express When an express warranty is made Do not have to show that the product is Requires express misrepresentation of
breach of by a manufacturer and injury is defective; only have to show that P relied material fact (ex. shatter-proof windshield)—
warranty caused to P who relied on that on the representation made by the specific promise made. Not relevant today w/
misrepresentation. manufacturer strict liability.
Implied breach When a manufacturer puts product Only have to show that the product was Usurps express breach of warranty b/c
of warranty into stream of commerce, implied marketed to P, and through that marketing implied warranty that guarantees reasonable
warranty that product is reasonably it is shown that a “warranty” that the safety automatically comes w/ the marketed
safe for use comes w/ that product product would be reasonably safe was product.
established
Design defect When the foreseeable risks of harm P must prove (1) that product was “Risk-Utility Balancing Test”: whether
posed by the product could have defectively designed so as to render it reasonable alt. design could, @ reasonable
been reduced or avoided by the unreasonably dangerous; (2) an cost, reduce foreseeable risks of harm posed
adoption of a reasonable alternative alternative, safer design existed; and (3) by product AND, if so, whether omission of
design by the seller, and the omission the defect was a producing cause of the alt. design rendered the product not
of that design rendered the product injury for which that plaintiff seeks reasonably safe.
not reasonably safe. recovery. State of the art considered, but when met,
not dispositive that it is a safe product.
When not met, dispositive of defect
Manufacturing Exists when a product departs from P must establish that the product deviated Does NOT matter whether the design was
defect its intended design even though all from either the manufacturer’s intended safe or not. Deviation from intended design =
possible care was exercised in the design or from other products of the same manufacturing defect
preparation and marketing of the design. Must also prove that the defect
product. existed when the product left the hands of
the manufacturer.
Instructions or When product is defective b/c of P must show that injury was caused by Defendants able to introduce state-of-the-art:
warnings inadequate instructions or warnings failure to warn, and that the injury they evidence that risk was neither known nor
defect when the foreseeable risks of harm sustained was a foreseeable, knowable knowable
posed by the product could’ve been risk—if debate over whether risk was
reduced or avoided by provision of knowable, only have to show ONE study
reasonable instructions or warnings that shows someone knew something (ex.
AND the omission of those rendered asbestos)
the product not reasonably safe.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Products Liability 3Document46 paginiProducts Liability 3phil_edelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Products Liability Flow ChartDocument7 paginiTorts Products Liability Flow ChartEnragedAcorn100% (1)
- Products Liability Issue/RuleDocument5 paginiProducts Liability Issue/RuleJane SalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E&E Products LiabilityDocument6 paginiE&E Products Liabilitytbolling1Încă nu există evaluări
- Products Liability OutlineDocument108 paginiProducts Liability OutlineFaris YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Products Liability OutlineDocument35 paginiProducts Liability Outlineesquire2014fl100% (3)
- Essay Format Strict Product Liability (MFG)Document2 paginiEssay Format Strict Product Liability (MFG)Harley Meyer100% (1)
- Duplechin Products LiabilityDocument22 paginiDuplechin Products LiabilityMitch WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Products Liability OutlineDocument2 paginiProducts Liability OutlineMayra Villegas100% (1)
- Products Liability OutlineDocument23 paginiProducts Liability OutlineYifei HeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts ChecklistDocument2 paginiTorts ChecklistnegrilledÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Final OutlineDocument37 paginiTorts Final OutlineMichael Seveska100% (1)
- Torts Sample EssayDocument5 paginiTorts Sample Essayjennwyse8208Încă nu există evaluări
- Products Liability ChartDocument1 paginăProducts Liability ChartJay SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts OutlineDocument57 paginiTorts Outlineang3lwings100% (1)
- Bartlett - Contracts Attack OutlineDocument4 paginiBartlett - Contracts Attack OutlinefgsdfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Attack Sheet 1Document1 paginăTorts Attack Sheet 1Micah Carper100% (1)
- Torts I Outline ElementsDocument14 paginiTorts I Outline Elements77bribri77Încă nu există evaluări
- Torts ChecklistDocument2 paginiTorts Checklistdeenydoll4125Încă nu există evaluări
- Torts Attack OutlineDocument1 paginăTorts Attack Outlinebrittany_bisson_2Încă nu există evaluări
- Legal Ethics Checklist QuickListDocument2 paginiLegal Ethics Checklist QuickListDoug SayranianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1L Torts OutlineDocument12 pagini1L Torts Outlineac70119Încă nu există evaluări
- Contracts OutlineDocument18 paginiContracts OutlineSam Levine100% (2)
- Contracts 2 OutlineDocument37 paginiContracts 2 OutlineBrandon YeboahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Awesome Torts OutlineDocument58 paginiAwesome Torts OutlineScott Engstrom100% (1)
- Con Law Outline - Rules and AnalysisDocument11 paginiCon Law Outline - Rules and AnalysisLaura Skaar100% (1)
- Elward Evidence OutlineDocument31 paginiElward Evidence OutlineAnonymous 13FhBKlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts OutlineDocument22 paginiContracts Outlinerealtor.ashley100% (1)
- Defeasible Estates ChartDocument1 paginăDefeasible Estates ChartMrsChuckBassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tort Final Pre WritesDocument5 paginiTort Final Pre WritesMartin Avanesian100% (1)
- Negligence AnalysisDocument1 paginăNegligence AnalysisBrat Wurst100% (3)
- ContractsDocument1 paginăContractsBrat Wurst100% (2)
- Criminal Law MPC v. CL ChartDocument17 paginiCriminal Law MPC v. CL Charttgatga100% (7)
- CONTRACTS SHORT OUTLINE - HendersonDocument20 paginiCONTRACTS SHORT OUTLINE - HendersonSio Mo0% (1)
- Formation of A Contract: OfferDocument19 paginiFormation of A Contract: OfferDavid Jules BakalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts Essay Chart - FaiqDocument4 paginiContracts Essay Chart - FaiqRahimah Faiq100% (6)
- Strict Liability - Torts - FlowchartDocument3 paginiStrict Liability - Torts - Flowchartfranco-44467% (3)
- Frier Contracts Outline 1Document122 paginiFrier Contracts Outline 1oaijf100% (1)
- Fall 18 Sales - OutlineDocument71 paginiFall 18 Sales - OutlineKatlyn Taylor Milligan100% (1)
- Attack Sec. RegDocument5 paginiAttack Sec. RegTroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Procedure II Pre-Writes: InterventionDocument24 paginiCivil Procedure II Pre-Writes: InterventionMorgyn Shae Cooper50% (2)
- Intentional Torts Privileges To Intentional TortsDocument2 paginiIntentional Torts Privileges To Intentional TortsjdfdfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contrascts II Memorize OutlineDocument3 paginiContrascts II Memorize OutlineAndrew BassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts - Attack Outline-2Document5 paginiTorts - Attack Outline-2Leah GaydosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professional Responsibility OutlineDocument38 paginiProfessional Responsibility Outlineprentice brown50% (2)
- Ethics Outline (Modern Rules For Professional Conduct)Document12 paginiEthics Outline (Modern Rules For Professional Conduct)austinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts 1 Rule StatementsDocument8 paginiTorts 1 Rule StatementsNija Anise Bastfield100% (3)
- Fall Civil Procedure Outline FinalDocument22 paginiFall Civil Procedure Outline FinalKiersten Kiki Sellers100% (1)
- Best BA FINAL OUTLINEDocument24 paginiBest BA FINAL OUTLINEHaifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acing BA OutlineDocument64 paginiAcing BA OutlineStephanie PayanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm OutlineDocument40 paginiMidterm OutlineAlejandra Aponte100% (2)
- Contract II Short SheetsDocument10 paginiContract II Short Sheetsbetasteve100% (1)
- Torts (Roadmap)Document5 paginiTorts (Roadmap)Bree Savage100% (3)
- Contracts 1 - OutlineDocument17 paginiContracts 1 - OutlineMarlene MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outline For EssayDocument62 paginiOutline For EssayJames Andrews100% (1)
- Contracts 1 - Quick Issue Spotting GuideDocument8 paginiContracts 1 - Quick Issue Spotting GuideVirginia Crowson100% (1)
- Torts OutlineDocument129 paginiTorts OutlineAmanda FazioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professional Responsibility Attack SheetDocument4 paginiProfessional Responsibility Attack Sheetthanhdra100% (3)
- Corporation Essay ChecklistDocument5 paginiCorporation Essay ChecklistCamille2221Încă nu există evaluări
- ch06 - Business LawDocument4 paginich06 - Business LawHuyền Nguyễn ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Capital Development Authority Ordinance, 1960Document38 paginiThe Capital Development Authority Ordinance, 1960shahid hussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civ QuestionsDocument1 paginăCiv QuestionsRoyalhighness18Încă nu există evaluări
- Uy Vs BirDocument3 paginiUy Vs Birjeanette4hijada100% (1)
- Book 2 Crim Law Ust Golden NotesDocument468 paginiBook 2 Crim Law Ust Golden NotesERWINLAV2000100% (1)
- LEDDA V BPI Case DigestDocument1 paginăLEDDA V BPI Case DigestKatrina Ysobelle Aspi HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 1 - AC Screening Form - RevisedDocument2 paginiForm 1 - AC Screening Form - RevisedPankaj GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Judd V Weinstein Cal Senate Amicus BriefDocument26 paginiJudd V Weinstein Cal Senate Amicus BriefTHROnlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Permanent Savings vs. Velarde DigestDocument2 paginiPermanent Savings vs. Velarde DigestAnonymous 1Ag3X6Încă nu există evaluări
- Gaanan vs. IAC G.R. No. L-69809 October 16, 1986Document2 paginiGaanan vs. IAC G.R. No. L-69809 October 16, 1986John YeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqa Law3 W MS Jun17Document17 paginiAqa Law3 W MS Jun17evansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aaron Barfield Declaration Black Excellence in Cannabis TheftDocument3 paginiAaron Barfield Declaration Black Excellence in Cannabis Theftchristopher king100% (1)
- Ational LAW University Odisha Cuttack: Topic: Law of MaintainanceDocument18 paginiAtional LAW University Odisha Cuttack: Topic: Law of Maintainancearsh singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document3 paginiChapter 1Jover SabaritaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Code Book 4 1156 2270Document225 paginiCivil Code Book 4 1156 2270Donald Abrera MosarbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Procedure of Roman Law - KocourekDocument20 paginiFormula Procedure of Roman Law - KocourekErenÎncă nu există evaluări
- TX Brief of AppellantDocument27 paginiTX Brief of AppellantTheresa Martin100% (1)
- Security Bank Corp. v. Court of AppealsDocument11 paginiSecurity Bank Corp. v. Court of AppealsBea HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurolan, Cristelle R.: (G.R. No. 209330, 11 Jan. 2016)Document5 paginiJurolan, Cristelle R.: (G.R. No. 209330, 11 Jan. 2016)Cristelle Estrada-Romuar JurolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RulesDocument19 paginiRulesVaibhav SanklechaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cindy Chafian TranscriptDocument7 paginiCindy Chafian TranscriptDaily KosÎncă nu există evaluări
- People of The Philippines V. Dionisio Calonge G.R. No. 182793Document2 paginiPeople of The Philippines V. Dionisio Calonge G.R. No. 182793G Carlo TapallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Immigration Commissioners v. Go CallanoDocument2 paginiBoard of Immigration Commissioners v. Go CallanoManuel Rodriguez IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greg Lauer Named To Multi-Million Dollar Advocates Forum Press Release Aug. 2018Document2 paginiGreg Lauer Named To Multi-Million Dollar Advocates Forum Press Release Aug. 2018CHRISTINA CURRIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criminal Law and JurisprudenceDocument12 paginiCriminal Law and JurisprudenceMark Kenneth RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explain The Concept of Nafaqa Under Muslim Law in India: Symbiosis Law School, NOIDADocument4 paginiExplain The Concept of Nafaqa Under Muslim Law in India: Symbiosis Law School, NOIDAFaraz ahmad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- D0005 Training Bond ContractDocument4 paginiD0005 Training Bond ContractApollonia Corleone100% (1)
- Judge Murphy's DecisionDocument95 paginiJudge Murphy's DecisionDan LehrÎncă nu există evaluări
- BACHRACH Vs BRitish American Assurance G.R. No. L-5715 December 20, 1910Document2 paginiBACHRACH Vs BRitish American Assurance G.R. No. L-5715 December 20, 1910Emrico CabahugÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Calcutta: Application Form For Under Graduate ExaminationsDocument1 paginăUniversity of Calcutta: Application Form For Under Graduate ExaminationsAbhiranjan PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporation Law CasesDocument84 paginiCorporation Law CasesOlan Dave LachicaÎncă nu există evaluări