Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ILLUMINATION
Încărcat de
Kartik SinghalDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ILLUMINATION
Încărcat de
Kartik SinghalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ILLUMINATION
An observable property and effect of light, may also refer to:
>Lighting, the use of light sources
>Illumination (image), the use of light and shadow in art
FOOT CANDLE
a foot candle is a measurement of light intensity and is defined
as the illuminance on a one-square foot surface from a uniform
source of light.
The term foot-candle is somewhat archaic, but it is gaining popularity
in many areas, particularly with indoor gardening. This is due to
several factors, including the fact that watts and lumens do not
actually tell an indoor gardener how much light is being delivered to
the plants being grown.
Most of us are accustomed to choosing light bulbs based on wattage –
a 60W bulb should emit X amount of light. We know this based on
experience with that particular wattage. However, wattage is not a
measure of light emission; it’s a measure of energy consumption by the
bulb. Replacing a 60W incandescent bulb with a 60W LED or T5 bulb
would actually generate a significantly greater amount of light.
Because foot-candles measure the amount of light provided to a
specific amount of space, this unit of measurement is actually better
suited for indoor gardening than other options, including lumens or
lux. Really, one foot-candle equates to a single lumen per square
foot of surface space. Based on this knowledge, indoor gardeners can
extrapolate how many candle-feet of light output they will need for
their space.
With the right foot-candle rating in terms of light output, you can
ensure that you’re providing your plants with the optimal light
levels for growth and health.
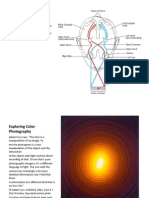
INCADESCENT LIGHT BULB
The incandescent light bulb or lamp is a source of electric light that
works by incandescence, which is the emission of light caused by
heating the filament. They are made in an extremely wide range of
sizes, wattages, and voltages.
An incandescent bulb typically consists of a glass enclosure
containing a tungsten filament. An electric current passes through
the filament, heating it to a temperature that produces light.
Incandescent light bulbs usually contain a stem or glass mount
attached to the bulb's base which allows the electrical contacts to
run through the envelope without gas/air leaks. Small wires
embedded in the stem support the filament and/or its lead wires.
The enclosing glass enclosure contains either a vacuum or an inert
gas to preserve and protect the filament from evaporating.
Incandescent bulbs require no external regulating equipment, have a
very low manufacturing cost, and work well on either alternating
current or direct current. They are also compatible with control
devices such as dimmers, timers, and photo sensors, and can be used
both indoors and outdoors. As a result, the incandescent lamp is
widely used both in household and commercial lighting, for portable
lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, and for
decorative and advertising lighting.
Many incandescent bulbs are scheduled to be phased out of production
by 2014
Advantages & Disadvantages of
Incandescent Light Bulbs
Advantages
Good for lighting small areas.
Cheap for the consumer.
No toxic materials are present.
Safe to handle.
Fast on time.
No flicker.
Disadvantages
Not energy Efficient.
Not good for large areas.
Low lifespan compared to other light bulbs.
FLOURESCENT LAMPS
The fluorescent lamp is a major advancement and a commercial
success in small-scale lighting since the original tungsten
incandescent bulb. These bulbs are highly efficient compared to
incandescent bulbs. Fluorescence is the phenomenon in which
absorption of light of a given wavelength by a fluorescent molecule
is followed by the emission of light at longer wavelengths.
A fluorescent bulb consists of a glass tube with a phosphorus
coating, a small amount of inert gas (usually argon or krypton),
mercury, and a set of electrodes. Contact points on the outside of the
tube carry electricity into the bulb.
Fluorescent lamps are about 2 to 4 times as efficient as incandescent
lamps at producing light at the wavelengths that are useful to
humans. Thus, they run cooler for the same effective light output. The
bulbs themselves also last a lot longer—10,000 to 20,000 hours
versus 1,000 hours for a typical incandescent.
Fluorescent lights need ballasts (devices that control the
electricity used by the unit) for starting and for circuit protection.
Ballasts require energy, and for some type of ballasts, efficiency is
only achieved if the fluorescent lamp is left on for long periods of
time without frequent on-off cycles.
ADVANTAGES OF FLUORESCENT LAMPS
1. More energy efficient than incandescent lamps: When compared to
incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps can produce the same amount
of light or lumens using lesser energy input. Residential and
commercial grade fluorescent tubes and bulbs, including compact
fluorescent lamps or CFL bulbs, can produce 50 to 100 lumens per
watt. Meanwhile, a typical incandescent bulb produces 16 lumens per
watt. This advantage translates to energy efficiency than in turn,
leads to reduced electricity consumption and cost.
2. Longer operational lifespan: Another advantage of fluorescent
lamps over is their lifespan. A typical fluorescent bulb will last 10
to 20 times longer than an incandescent bulb. Specifically,
fluorescent lamps have an operational lifespan of 6000 to 15000
hours while incandescent lamps only have 1000 hours. Due to their
longer operational duration, one of the notable benefits of using
fluorescent lamps involve reduced time and cost associated with
replacement and maintenance.
3. Better light diffusions and distribution: Fluorescent lamps are
bigger light sources than incandescent lamps. Furthermore, most
fluorescent bulbs or tubes readily diffuse light that results in
better distribution of illumination within a particular area. In
contrast, incandescent lamps are smaller light sources, and they
produce undiffused light as evident from glares and uneven
illumination.
4. Less heat emission: Incandescent lamps generate too much excessive
heat because they consume too much energy input. Hence, another
advantage of fluorescent lamps is less heat emission due to their
efficient energy consumption. Typical fluorescent bulbs such as CFLs
convert of 22 percent energy input to visible light while incandescent
lamps only use 5 percent of energy input to produce visible light and
the remaining 95 percent is converted into heat. This advantage
translates further to other benefits such as comfort and reduced
cost from air conditioning and ventilation.
DISADVANTAGES OF FLUORESCENT LAMPS
1. More expensive: Fluorescent lamps are relatively more expensive
than incandescent lamps because they are more complicated to
manufacture. However, considering their energy efficiency and
lifespan, they are arguably more economical in general. Note that
LED lamps are more expensive, but their price is expected to go down
near the level of fluorescent lamps due to better manufacturing
processes and increasing demand.
2. Health and environmental issues: A notable disadvantage of
fluorescent lamps involves susceptibility to chemical leakage that
can contaminate the environment and affect the health of exposed
organisms, including humans. A broken bulb can lead to leakage of a
small amount of mercury. Aside from chemical hazards, fluorescent
tubes and bulbs with magnetic ballasts normally flicker. This
flickering coupled with UV emission might be problematic for
individuals who are sensitive to light, especially those with autism,
epilepsy, chronic headache, lupus, and vertigo, among others.
3. Susceptibility to degradation: Several factors can lead to
inefficiency and wear and tear of fluorescent tubes and bulbs. A
considerable limitation involves switching frequency. Lamps that are
frequently switched on and off rapidly age due to the erosion of the
electron-emitting surface of the cathodes. Operating temperature is
another limitation of fluorescent lamps. Below-freezing
temperature might render these lamps inoperable. Note that because
they emit less heat than incandescent lamps, they are unable to melt
off snow and ice build up.
4. Problems with dimming: Light fixtures based on fluorescent lamps
cannot be connected to dimmer switches made for incandescent lamps.
This is due to the physical and operational differences between these
two types of electric light. Special dimming ballasts and dimmer
switches are required to make fluorescent tubes and bulbs dimmable.
5. Not a better alternative than LED lamps: A comparison with light-
emitting diode or LED lamps will bring forth the limitations of
fluorescent lamps. Although both types of electric light are more
energy efficient and have longer lifespan than incandescent lamps,
LED lamps take these advantages to another level. For example, a
particular type of LED bulb may require 9 watts to produce 900
lumens while a CFL may require 15 watts to produce 600 lumens. LED
lamps also have an operating lifespan of 30000 to 50000 hours.
SOURCES OF LIGHT
ARTIFICIAL LIGHT
First generation – bulbs based on heating of a wire filament
(incandescent lamps) or an arc
A standard modern incandescent lamp is composed of a
glass bulb containing a coil of metal wire, such as tungsten
(W), in a vacuum. Incandescent lamps emit non-ionizing
radiation in the visible light range and do not usually emit
radiation in the ultraviolet (UV) range, except in extreme
conditions of very high power. Additionally this type of
lamp also emits invisible infra-red non-ionizing radiation
which is felt as heat.
The halogen lamp is a type of incandescent lamp filled with
a halogen gas such as iodine (I) or bromine (Br). It emits
visible light and a little UV light. As UV is ionizing radiation
that may cause, with prolonged exposure, burns and skin
cancer, prolonged close exposure to halogen lamps should
be avoided.
The carbon arc lamp comprises two tubular carbon (C)
electrodes connected to an electric voltage source in the
open air. This lamp emits visible light and also UV radiation.
Because of its high intensity it is forbidden to look at its
light source directly.
Second Generation – Gas discharge lamps
Fluorescent lighting is based on electric discharge of a gas
(mercury) leading to emission
n of high-energy photons (usually UV), that impact the
fluorescent coating of the bulb, producing visible light.
The type of radiation emitted by fluorescent tubes and
compact fluorescent lamps (CFL) includes, in addition to
visible light, a small amount of UV radiation in the UVA
range (315-380 nanometers), and even shorter wavelengths
(higher energy) in the UVC range.
Exposure to UV radiation from CFL lamps containing mercury
may be reduced by distancing the lamps from the user by 30
cm or more.
Third generation – Light-Emitting Diode (LED) lamps
A light-emitting diode (LED) consists of a semiconductor
that has undergone doping. An electric current passing
through the diode excites the atoms to high energies. When
the atoms return to lower energy levels, energy in the
form of photons in the visible light range is released.
LED lamps emit visible light and do not emit UV radiation.
NATURAL LIGHT
SUN- the major and most imperative source of natural light present on
earth is sun. The sun is the only natural source that is a massive ball
of fire in which nuclear fusions produce large amount of energy at
the center . sun is the major factor behind the light on earth which
produces heat as well.
Star- star is other factor which produces light even though the
amount of quantity that reaches the earth is small.
Moon- moon is one planet which produces light but not of its own. The
light that moon gives is the result of reflection from the sun because
moon does not have its own light
Artificial sources of light
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Narrow-Band Filter For Satellite Communication SystemsDocument6 paginiNarrow-Band Filter For Satellite Communication SystemsIJICT JournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploring Color PhotographyDocument7 paginiExploring Color Photographyluis_ochoa_17Încă nu există evaluări
- Closed Form Kramers-Kronig Relations To Extract The Refractive Index of MetamaterialsDocument10 paginiClosed Form Kramers-Kronig Relations To Extract The Refractive Index of MetamaterialswerfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Half Value Layer ConceptsDocument1 paginăHalf Value Layer ConceptsPujiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Planner - Physics - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 paginiLecture Planner - Physics - Lakshya JEE 2024Bighnesh worldÎncă nu există evaluări
- EFR 64634 HLX EFR-5/X 64620 HLX: Product Information BulletinDocument2 paginiEFR 64634 HLX EFR-5/X 64620 HLX: Product Information BulletinJJ MMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 - Objective RefractionDocument11 pagini12 - Objective RefractionSumon SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bifocal Add: Image Jump and Image Displacement: Basic Optics, Chapter 24Document45 paginiBifocal Add: Image Jump and Image Displacement: Basic Optics, Chapter 24PAM ALVARADOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson13 Refractive IndexDocument12 paginiLesson13 Refractive IndexGemma WrigleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grand Test 4Document28 paginiGrand Test 4Dr. Pradeep SakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The High-Latitudude IonospehereDocument639 paginiThe High-Latitudude IonospehereSainath Bharadwaj100% (2)
- 3 - High Intensity Discharge Lamps Part 2Document23 pagini3 - High Intensity Discharge Lamps Part 2Miko F. RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9637 Chap01Document30 pagini9637 Chap01gurjarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carl Zeiss Axio Scope A1 Manual ServicioDocument122 paginiCarl Zeiss Axio Scope A1 Manual ServicioDanniel SchaafÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChaDocument34 paginiChachayani sarumahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic MRIDocument274 paginiBasic MRISuresh NarayanaswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nesse - Introduction To Optical Mineralogy - 3th Edition PDFDocument328 paginiNesse - Introduction To Optical Mineralogy - 3th Edition PDFRaúl Iglesias86% (35)
- Shooting Self-Portraits: Short GuideDocument26 paginiShooting Self-Portraits: Short GuideFlorenta Zamfir100% (2)
- LONG PULSE 95 GHZ GYROTRON WITH ROOMDocument7 paginiLONG PULSE 95 GHZ GYROTRON WITH ROOMroeybmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comtec PDFDocument7 paginiComtec PDFgeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A Miniature Rectangular Patch Antenna For Ku Band ApplicationsDocument7 paginiDesign of A Miniature Rectangular Patch Antenna For Ku Band ApplicationsAnonymous 9IlMYYx8Încă nu există evaluări
- 09.ray Optics FDocument92 pagini09.ray Optics FParulÎncă nu există evaluări
- NDT 30P Penetrant Testing 090217 - Notes For Electronic DistributionDocument105 paginiNDT 30P Penetrant Testing 090217 - Notes For Electronic DistributionUlvi Ismayilov100% (6)
- Tubo Fluorescente LED T8Document2 paginiTubo Fluorescente LED T8jahosolaris5512Încă nu există evaluări
- 01 Transmission of Heat 3Document30 pagini01 Transmission of Heat 3Ashok PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bece308l Optical-Fiber-Communications TH 1.0 0 Bece308lDocument3 paginiBece308l Optical-Fiber-Communications TH 1.0 0 Bece308lyv5pgh7z84Încă nu există evaluări
- Progress in Optics. Volume XIV 0444109145 PDFDocument441 paginiProgress in Optics. Volume XIV 0444109145 PDFAlex Zenteno100% (1)
- Bent 4313Document2 paginiBent 4313Shereen LinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospect For Extreme Field ScienceDocument11 paginiProspect For Extreme Field Sciencearohi9Încă nu există evaluări
- OFV-551/552 Fiber-Optic Interferometer: Flexible Vibration MeasurementDocument2 paginiOFV-551/552 Fiber-Optic Interferometer: Flexible Vibration MeasurementguyÎncă nu există evaluări