Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine
Încărcat de
Ariadne MangondatoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine
Încărcat de
Ariadne MangondatoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
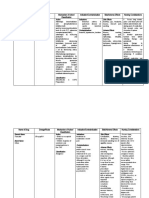
ANTIANXIETY DRUGS
Generic Name: Chlordiazepoxide
Generic Name: Alprazolam Brand Name: Librium
Brand Name: Xanax DRUG CLASSIFICATION
DRUG CLASSIFICATION Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic
Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine
Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine INDICATION
INDICATION Mild to moderate anxiety
Anxiety Withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism
Panic disorders Preoperative apprehension and anxiety
MECHANISM OF ACTION MECHANISM OF ACTION
Unknown. Probably potentiates the effects of GABA, depresses the CNS, and A benzodiazepine that may potentiate the effects of GABA, depress the
suppresses the spread of seizure activity CNS, and suppress the spread of seizure activity
SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS
CNS: sedation, somnolence, difficulty speaking impaired coordination memory CNS: drowsiness, lethargy, ataxia, confusion, extrapyramidal reactions,
impairment, fatigue, depression suicide, mental impairment, ataxia, paresthesia, minor changes in EEG patterns
dyskinesia, hypoesthesia, lethargy, vertigo, malaise, tremor, nervousness, CV: edema
restlessness, agitation, nightmare, syncope, akathisia, mania GI: nausea, constipation
CV: palpitations, chest pain, hypotension GU: menstrual irregularities
EENT: allergic rhinitis, blurred vision, nasal congestion Hema: agranulocytosis
GI: diarrhea, dry mouth, constipation, nausea, increased or decreased appetite, Hepa: jaundice
anorexia, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain Skin: swelling and pain at injection site, skin eruptions
GU: dysmenorrhea, sexual dysfunction, premenstrual syndrome, difficulty urinating Other: altered libido
Meta: increased or decreased weight NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Musculo: arthralgia, myalgia, arm or leg pain, back pain, muscle rigidity, muscle In patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy, monitor
cramps, muscle twitch hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function periodically
Respi: upper respiratory tract infection, dyspnea, hyperventilation Watch for paradoxical reaction in psychiatric patients and
Skin: pruritus, increased sweating, dermatitis hyperactive, aggressive children
Other: influenza, injury, emergence of anxiety between doses, dependence, Use of this drug may lead to abuse and addiction. Don’t
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES withdraw drug abruptly after long-term use because withdrawal
The optimum duration of therapy is unknown symptoms may occur
Don’t withdraw drug abruptly, withdrawal symptoms, including Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness
seizures, may occur. Gradually reduce dosage. Abuse or and coordination until effects of drug are known
addiction is possible Tell patient to avoid use of alcohol while taking drug
Monitor hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function periodically Warn patient drug may my cause psychological and physical
in patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy dependence. Tell patient not to increase dose or abruptly stop the
Closely monitor addiction-prone patients drug because withdrawal symptoms may occur
Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness Warn women to avoid use during pregnancy
and good coordination until effects of drug are known CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES
Tell patient to avoid use of alcohol while taking drug Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in pregnant
Advise patient that smoking may decrease drug’s effectiveness women, especially in first trimester
Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly because withdrawal Use cautiously in elderly patients and in patients with mental
symptoms or seizures may occur depression, history of substance abuse, porphyria, or hepatic or renal
Tell patient to swallow extended-release tablets whole disease
Warn women to avoid use during pregnancy and breast-feeding
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES
Contraindicated to patients hypersensitive to drug or other
benzodiazepines and in those with acute angle-closure glaucoma.
Use cautiously in patients with hepatic, renal, or pulmonary disease or
history of substance abuse
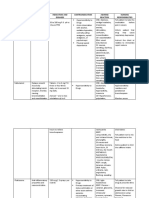
Generic Name: Clonazepam Generic Name: Diazepam
Brand Name: Klonopin Brand Name: Valium
DRUG CLASSIFICATION DRUG CLASSIFICATION
Therapeutic Class: Anticonvulsant Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic
Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine
INDICATION INDICATION
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, atypical absence seizures, Anxiety
akinetic and myoclonic seizures Muscle spams
Restless legs syndrome Adjunct treatment for seizure disorders
MECHANISM OF ACTION Status epilepticus, severe recurrent seizures
Unknown. Probably acts by facilitating the effects of the inhibitory Patients on stable regimens of antiepileptic drugs who
neurotransmitter GABA need diazepam intermittently to control bouts if
SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS increased seizure activity
CNS: drowsiness, agitation, ataxia, behavioral disturbances, confusion, MECHANISM OF ACTION
depression, slurred speech, tremor A benzodiazepine that probably potentiates the effects of GABA,
CV: palpitations depresses the CNS, and suppresses the spread of seizure activity
EENT: abnormal eye movements, nystagmus SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS
GI: anorexia, change in appetite, constipation, diarrhea, gastritis, CNS: drowsiness, dysarthria, slurred speech, tremor, transient amnesia,
nausea, sore gums fatigue, ataxia, headache, insomnia, paradoxical anxiety, hallucination,
GU: dysuria, enuresis, nocturia, urine retention minor changes in EEG patterns, pain
Hema: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia CV: CV collapse, bradycardia, hypotension
Respi: respiratory depression, chest congestion, shortness of breath EENT: diplopia, blurred vision, nystagmus
Skin: rash GI: nausea, constipation, diarrhea with rectal form
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES GU: incontinence, urine retention
Closely monitor all patients for changes in behavior that may Hema: neutropenia
indicate worsening of suicidal thought or behavior or depression Hepa: jaundice
Don’t stop drug abruptly because this may worsen seizures. Call Respi: respiratory depression, apnea
prescriber at once if adverse reactions develop Skin: rash, phlebitis at injection site
Assess elderly patient’s response closely. Elderly patients are Other: altered libido, physical or psychological dependence
more sensitive to drug’s CNS effects NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Monitor patient for oversedation Monitor periodic hepatic, renal and hematopoietic function studies in
To reduce inconvenience of somnolence when drug is used for patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy
panic disorder, giving one dose at bedtime may be desirable Monitor elderly patients for dizziness, ataxia, and mental status
Advise patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities that changes. Patients are at an increased risk of falls
require mental alertness until drug’s CNS effects are known Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness and
Instruct parent to monitor child’s school performance because good coordination until eff3ects of drugs are known
drug may interfere with attentiveness Notify patient that smoking may decrease drug’s effectiveness
Warn patient and parents not to stop drug abruptly because Warn patient not to abruptly stop drug because withdrawal symptoms
seizures may occur may occur
Advise patient that drug isn’t for use during pregnancy or breast- Warn women to avoid use during pregnancy
feeding Instruct patient’s caregiver on the proper use of Diastat rectal gel
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to benzodiazepines and in Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or soy protein;
those with significant hepatic disease or acute angle-closure glaucoma in patients experiencing shock, com, or acute alcohol
Use cautiously in patients with mixed-type seizures because drug may intoxication; in pregnant women, especially in first trimester; and
cause generalized tonic-clonic seizures in infants younger than age 6
Use cautiously in children and in patients with chronic respiratory Contraindicated in patients with acute angle-closure glaucoma
disease, open-angle glaucoma, or a history of drug or alcohol addiction Use cautiously in patients with liver or renal impairment,
Use cautiously in elderly patients. Drug may accumulate due to depression, history of substance abuse, or chronic open-angle
potential decrease in hepatic and renal function glaucoma. Use cautiously in elderly and debilitated patients
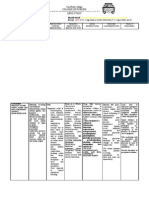
Generic Name: Lorazepam
Brand Name: Ativan Generic Name: Oxazepam
DRUG CLASSIFICATION Brand Name: Serax
Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic DRUG CLASSIFICATION
Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic
INDICATION Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine
Anxiety INDICATION
Insomnia from anxiety Alcohol withdrawal, severe anxiety
Status epilepticus Severe anxiety syndromes; agitation; anxiety associated
MECHANISM OF ACTION with depression
May potentiate the effects of GABA, depress the CNS, and suppress the Anxiety, tension, irritability, agitation
spread of seizure activity MECHANISM OF ACTION
SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS May stimulate GABA receptors in the ascending reticular activating
CNS: drowsiness, sedation, amnesia, insomnia, agitation, dizziness, system
weakness, unsteadiness, disorientation, depression, headache SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS
CV: hypotension CNS: drowsiness, lethargy, dizziness, vertigo, headache, syncope,
EENT: visual disturbances, nasal congestion tremor, slurred speech, changes in EEG patterns
GI: abdominal discomfort, nausea, change in appetite CV: edema
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES GI: nausea
Monitor hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function periodically in Hepa: hepatic dysfunction
patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy Skin: rash
Use of this drug may lead to abuse and addiction. Don’t stop drug Other: altered libido
abruptly after long-term use because withdrawal symptoms may occur NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness and Monitor hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function periodically in
good coordination until effects of drug are known patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy
Tell patient to avoid use of alcohol while taking drug Use of this drug may lead to abuse and addiction. Don’t stop drug
Notify patient that smoking may decrease drug’s effectiveness abruptly because withdrawal symptoms may occur
Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly because withdrawal symptoms Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness or good
may occur coordination until effect of drug are known
Advise women to avoid becoming pregnant while taking drug Tell patient avoid use of alcohol while taking drug
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES Notify patient that smoking may decrease drug’s effectiveness
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug, other Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly because withdrawal symptoms
benzodiazepines, or the vehicle used in parenteral dosage form; may occur
in patients with acute angle-closure glaucoma; and in pregnant Warn women of childbearing age to avoid use during pregnancy
women, especially in the first trimester CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES
Use cautiously in patients with pulmonary, renal, or hepatic Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug; in pregnant
impairment, or history of substance abuse women, especially in the first trimester; and in those with
Use cautiously in elderly, acutely ill, or debilitated patients psychoses
Use cautiously in elderly patients and in those with history of
substance abuse or in whom a decrease in blood pressure might
led to cardiac problems
Generic Name: Temazepam Generic Name: Triazolam
Brand Name: Restoril Brand Name: Halcion
DRUG CLASSIFICATION DRUG CLASSIFICATION
Therapeutic Class: Hypnotic Therapeutic Class: Hypnotic
Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine
INDICATION INDICATION
Short-term treatment (7-10 days) of insomnia Sort-term treatment (7 to 10 days) of insomnia
MECHANISM OF ACTION MECHANISM OF ACTION
Probably acts on the limbic system, thalamus, and hypothalamus of the Unknown. Probably acts on the limbic system, thalamus, and
CNS to produce hypnotic effects hypothalamus of the CNS to produce hypnotic effects
SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS
CNS: complex sleep-related behaviors, drowsiness, dizziness, lethargy, CNS: complex sleep-related behaviors, drowsiness, amnesia, ataxia,
disturbed coordination, daytime sedation, confusion, nightmares, depression, dizziness, headache, lack of coordination, mental confusion,
vertigo, euphoria, weakness, headache, fatigue, nervousness, anxiety, nervousness, physical or psychological dependence, rebound insomnia
depression, minor changes in EEG patterns GI: nausea, vomiting
EENT: blurred vision Other: anaphylaxis, angioedema
GI: diarrhea, nausea, dry mouth NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Other anaphylaxis, angioedema, physical and psychological Monitor patient closely. Anaphylaxis and angioedema may occur
dependence as early as the first dose
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Assess mental status before starting therapy and reduce doses in elderly
Monitor patient closely. Anaphylaxis and angioedema may occur as patient’s; these patients may be more sensitive to drug’s adverse CNS
early as the first dose effects
Assess mental status before starting therapy and reduce doses in elderly Take precautions to prevent hoarding by patients who are depressed,
patient’s; these patients may be more sensitive to drug’s adverse CNS suicidal, or drug-dependent or who have history of drug abuse
effects Don’t stop drug abruptly as this may cause withdrawal
Take precautions to prevent hoarding by patients who are depressed, symptoms. To discontinue drug, follow a gradual dosage-tapering
suicidal, or drug-dependent or who have history of drug abuse schedule
Don’t stop drug abruptly as this may cause withdrawal Warn patient that drug my cause allergic reactions, facial
symptoms. To discontinue drug, follow a gradual dosage-tapering swelling, and complex sleep-related behaviors, such as driving,
schedule eating, and making phone calls while asleep. Advise patient to
Warn patient that drug my cause allergic reactions, facial report these adverse effects
swelling, and complex sleep-related behaviors, such as driving, Tell patient to avoid alcohol during therapy
eating, and making phone calls while asleep. Advise patient to Caution patient to avoid performing activities that require mental
report these adverse effects alertness or physical coordination
Tell patient to avoid alcohol during therapy Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly if taken for 1 month or
Caution patient to avoid performing activities that require mental longer
alertness or physical coordination
Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly if taken for 1 month or CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES
longer Contraindicated in pregnant patients and those hypersensitive to
Tell patient that onset of drug’s effects may take as long as 2 to 2 benzodiazepines
¼ hours Use cautiously in patients with impaired hepatic or renal
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES function, chronic pulmonary insufficiency, sleep apnea, mental
Contraindicated in pregnant patients and those hypersensitive to depression, suicidal tendencies, or history of drug abuse
drug or other benzodiazepines Use cautiously in breast-feeding women
Use cautiously in patients with chronic pulmonary insufficiency,
impaired hepatic or renal function, severe or latent depression,
suicidal tendencies, and history of drug abuse
NONBENZODIAZEPINE
MEDICATION
Generic Name: Buspirone
Brand Name: BuSpar
DRUG CLASSIFICATION
Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic
Pharmacologic Class: Azaspirodecanedione derivative
INDICATION
Anxiety disorders
Traumatic brain injury
MECHANISM OF ACTION
May inhibit neuronal firing and reduce serotonin turnover in cortical,
amygdaloid, and septohippocampal tissue
SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE REACTIONS
CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, nervousness, insomnia, light-
headedness, fatigue, numbness, excitement, confusion, depression,
anger, decreased concentration
CV: tachycardia, nonspecific chest pain
EENT: blurred vision
GI: dry mouth, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal distress
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Monitor patient closely for adverse CNS reactions. Drug is less
sedating than other anxiolytics, but CNS effects may be
unpredictable
Before starting therapy, don’t stop a previous benzodiazepine
regimen abruptly because a withdrawal reaction may occur
Drug shows no potential for abuse and isn’t classified as a
ANTIANXIETY
controlled substance
Teach patient to recognize and immediately report symptoms of
serotonin toxicity
Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness
and good coordination until effects of drug are known
Remind patient that drug effects may not be noticeable for
several weeks
Warn patient not to abruptly stop a benzodiazepine because of
risk of withdrawal symptoms
Tell patient to avoid use of alcohol during therapy
Advise patient to take consistently, that is, always with or always without food
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND CAUSES
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and within 14 days of
MAO inhibitor therapy
Drug isn’t recommended for patients with severe hepatic or renal
impairment
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- SBAR ExamplesDocument2 paginiSBAR ExamplesAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wounded HealerDocument2 paginiWounded HealerNuka Vardidze100% (2)
- Non-Addictive Painkillers: Recent Research and Development Braden Royer Dubois Area High School Honors Biochemistry Mr. KeithDocument11 paginiNon-Addictive Painkillers: Recent Research and Development Braden Royer Dubois Area High School Honors Biochemistry Mr. Keithapi-318355342Încă nu există evaluări
- By Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra RanchiDocument31 paginiBy Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra Ranchiexcel pro100% (1)
- MorphineDocument2 paginiMorphineKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Sedative-Hypnotics (SeH) and AnxiolyticsDocument101 paginiSedative-Hypnotics (SeH) and Anxiolyticsmatchees-gone rogueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacokinetics 1: AbsorptionDocument15 paginiPharmacokinetics 1: AbsorptionCecilia GrayebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gabapentin Oi DesDocument11 paginiGabapentin Oi DesLuis Felipe Arteaga ArredondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABADocument10 paginiBarbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABAAvi WerdesheimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Drug Nutrient Interactions: Pamela MasonDocument35 paginiImportant Drug Nutrient Interactions: Pamela MasonRijantono Franciscus MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 paginiName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Movement Disorders ..Document54 paginiApproach To Movement Disorders ..Ihda ParidahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanisms of Drug Interactions: Pharmacodynamics and PharmacokineticsDocument4 paginiMechanisms of Drug Interactions: Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokineticsgowepa9266Încă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Medicine Cases: Case 1Document33 paginiEmergency Medicine Cases: Case 1skeebs23100% (1)
- Adrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDDocument5 paginiAdrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDKeon RicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIH Public Access: Active Emergence From Propofol General Anesthesia Is Induced by MethylphenidateDocument16 paginiNIH Public Access: Active Emergence From Propofol General Anesthesia Is Induced by Methylphenidate'-dooublleaiienn Itouehh IinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Interaction: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK & DR - Dr.Tri Widyawati MSCDocument39 paginiDrugs Interaction: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK & DR - Dr.Tri Widyawati MSCpsyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Propagation For Home Gardeners: Agriculture and Natural ResourcesDocument6 paginiPlant Propagation For Home Gardeners: Agriculture and Natural ResourceszonetrekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Bioavailability - Clinical Pharmacology - MSD Manual Professional Edition PDFDocument2 paginiDrug Bioavailability - Clinical Pharmacology - MSD Manual Professional Edition PDFRutuja BhujbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ho 1Document3 paginiHo 1Llna HnÎncă nu există evaluări
- SeroquelDocument1 paginăSeroquelE100% (1)
- Part Agents Act NG On The Central Ner Ous System: Liu JuntianDocument89 paginiPart Agents Act NG On The Central Ner Ous System: Liu Juntianapi-19916399Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Analgesics PDFDocument4 pagini1 Analgesics PDFSimranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma Introduction To Pharmacology of CNS DrugDocument5 paginiPharma Introduction To Pharmacology of CNS DrugMica CatanghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indication and DosagesDocument2 paginiIndication and DosagesloveskissesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4853 Medication Worksheet: Student NameDocument8 pagini4853 Medication Worksheet: Student Nameapi-546817891Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Jan 13 PDFDocument8 pagini1 Jan 13 PDFAlejandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Receptor TheoryDocument9 paginiDrug Receptor TheoryFish YanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adrenoceptor - Activating Other Sympathomimetic Drugs PDFDocument43 paginiAdrenoceptor - Activating Other Sympathomimetic Drugs PDFRupal RaghuwanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- StrokeDocument22 paginiStrokeAlex GasnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biodegradation of HydrocarbonDocument5 paginiBiodegradation of HydrocarbonNITI SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychoactive Drug UseDocument1 paginăPsychoactive Drug UsePisay Shehannah Grail MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristics of Compounds That Cross The Blood-Brain BarrierDocument5 paginiCharacteristics of Compounds That Cross The Blood-Brain BarrierHector PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Somniferous Poisons: DR M. Malleswari Asso. Prof Nri Medical CollegeDocument58 paginiSomniferous Poisons: DR M. Malleswari Asso. Prof Nri Medical CollegeSudheera RachamallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xerophilia 2020 26 1Document14 paginiXerophilia 2020 26 1Nacho MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypnotics and Sedatives PDFDocument35 paginiHypnotics and Sedatives PDFSayan Nag100% (1)
- Implementation Toolkit For Clinical Handover ImprovementDocument60 paginiImplementation Toolkit For Clinical Handover ImprovementKhanh LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Targeted Drug DeliveryDocument67 paginiBrain Targeted Drug DeliveryManishMakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study inDocument3 paginiDrug Study inaycee0316Încă nu există evaluări
- Endocannabinoid-CB Receptor SystemDocument7 paginiEndocannabinoid-CB Receptor SystemRobert DinuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Propagation: An Overview of Asexual ReproductionDocument39 paginiPlant Propagation: An Overview of Asexual ReproductionKLT63Încă nu există evaluări
- CNS Stimulant SummaryDocument3 paginiCNS Stimulant SummaryahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Premedication: Moderator: DR - Dinesh Kaushal Presentsd By: DR Rajesh Raman & DR Gopal SinghDocument60 paginiPremedication: Moderator: DR - Dinesh Kaushal Presentsd By: DR Rajesh Raman & DR Gopal Singhramanrajesh83Încă nu există evaluări
- The Name of The Apple: D.J. Mabberley, C.E. Jarvis and B.E. JuniperDocument10 paginiThe Name of The Apple: D.J. Mabberley, C.E. Jarvis and B.E. JuniperKiky Rizqy IsnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyDocument4 paginiCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Interactions in Dentistry: Iyad Abou Rabii DDS, Omfs, Mres, PHDDocument45 paginiDrug Interactions in Dentistry: Iyad Abou Rabii DDS, Omfs, Mres, PHDIyad Abou-Rabii100% (1)
- Analeptic Anti Depression: (Cns Stimulant) andDocument23 paginiAnaleptic Anti Depression: (Cns Stimulant) andMohammad NorzaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study GalaponDocument4 paginiDrug Study GalaponSheryl DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument44 paginiRheumatoid ArthritisBulborea Mihaela100% (1)
- Prescription Opioid Analgesics Rapidly Change The Human BrainDocument8 paginiPrescription Opioid Analgesics Rapidly Change The Human BrainboboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs of Abuse: Rita Dries Senior Lecturer KHK Turnhout - BelgiëDocument32 paginiDrugs of Abuse: Rita Dries Senior Lecturer KHK Turnhout - BelgiëKartikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular DiagnosticsDocument3 paginiMolecular DiagnosticsDante SallicopÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtelectasisDocument28 paginiAtelectasisShikha Acharya100% (1)
- Formulation and Evaluation of Tramadol Hydrochloride Loaded Transferosomal Gel by Thin Film Hydration TechniqueDocument8 paginiFormulation and Evaluation of Tramadol Hydrochloride Loaded Transferosomal Gel by Thin Film Hydration TechniqueIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esr December 2016Document20 paginiEsr December 2016Helton AzevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monoclonal GammopathiesDocument70 paginiMonoclonal GammopathiesElisa Lincă100% (1)
- Medical Emergencies in The Dental Office 6th Edition Malamed Test BankDocument2 paginiMedical Emergencies in The Dental Office 6th Edition Malamed Test BankKieranPenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Acting On Adrenrgic Nervous System: Presented byDocument63 paginiDrugs Acting On Adrenrgic Nervous System: Presented byKiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health Nursing Assignment Sample: WWW - Newessays.co - UkDocument15 paginiMental Health Nursing Assignment Sample: WWW - Newessays.co - UkAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Pharmceutico Analytical Study of Amavatari Rasa - A Herbal FormulationDocument7 paginiA Pharmceutico Analytical Study of Amavatari Rasa - A Herbal FormulationArutpa SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNS Stimulants and PsychotomimeticsDocument29 paginiCNS Stimulants and Psychotomimeticsatom paul100% (1)
- SedativeDocument35 paginiSedativeking_goldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sedative - HypnoticsDocument60 paginiSedative - HypnoticsNurul AinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNS Drug ListDocument13 paginiCNS Drug ListAnaliza Kitongan LantayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharmacologyDocument122 paginiPharmacologyLuis Mejía Ruiz100% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 paginiMethergineKyla VillafrancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development and Characterization of Transdermal Therapeutics System of Tramadol HydrochlorideDocument5 paginiDevelopment and Characterization of Transdermal Therapeutics System of Tramadol HydrochlorideMuhammad SikandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prodrug Design PDFDocument29 paginiProdrug Design PDFmehulpatel100% (1)
- Module # 5 Pharmacology NursingDocument45 paginiModule # 5 Pharmacology Nursingannyeong_123Încă nu există evaluări
- DrUG STUDY PSYCHEDocument52 paginiDrUG STUDY PSYCHELiza MPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antidepressant Drugs: Therapeutic Class: Antidepressant Pharmacologic Class: SSRIDocument31 paginiAntidepressant Drugs: Therapeutic Class: Antidepressant Pharmacologic Class: SSRIBecca SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: PhenothiazineDocument10 paginiTherapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: PhenothiazineMiyuki Bartolaba MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GENS9003/PSYC1023 Abnormal Psychology: Faculty of Science School of PsychologyDocument9 paginiGENS9003/PSYC1023 Abnormal Psychology: Faculty of Science School of PsychologyAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSYC 210 Abnormal Psychology: Introduction To Psychology (PSYC 101) or Equivalent Is Strongly Recommended. StudentsDocument8 paginiPSYC 210 Abnormal Psychology: Introduction To Psychology (PSYC 101) or Equivalent Is Strongly Recommended. StudentsAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Curriculum of The BSN ProgramDocument6 pagini2018 Curriculum of The BSN ProgramAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDocument4 paginiDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health in New Parents Whhat Affect Does Having A Premature BabyDocument5 paginiMental Health in New Parents Whhat Affect Does Having A Premature BabyAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Lack of Sleep Harms Circulation: Published Thu 23 May 2019 by by Isabel GodfreyDocument4 paginiHow Lack of Sleep Harms Circulation: Published Thu 23 May 2019 by by Isabel GodfreyAriadne MangondatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluticasone Propionate - C25h31f3o5s - PubchemDocument51 paginiFluticasone Propionate - C25h31f3o5s - PubchemZuniva AndanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potter: Fundamentals of Nursing, 8 EditionDocument2 paginiPotter: Fundamentals of Nursing, 8 Editionsammm9960% (1)
- Uric Acid Point of Care Device Accuracy AnalysisDocument13 paginiUric Acid Point of Care Device Accuracy AnalysisElectriclatte Health SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bladder IrrigationDocument3 paginiBladder IrrigationRuth GunjalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SulbutiamineDocument1 paginăSulbutiaminezamurd76Încă nu există evaluări
- Keeping Older Adults Safe at Home: Fall Risks Add UpDocument6 paginiKeeping Older Adults Safe at Home: Fall Risks Add UpBj DuquesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF 995644190 PDFDocument150 paginiPDF 995644190 PDFReuben SalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norditropin Travel Letter0611-000348 1v 2Document18 paginiNorditropin Travel Letter0611-000348 1v 2Hary Kernet MerkapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Evaluation - 2021Document12 paginiFinal Evaluation - 2021api-240864098Încă nu există evaluări
- PBL 1 ThyrotoxicosisDocument7 paginiPBL 1 ThyrotoxicosishappyhappylandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atrophic Glossitis: - Margareta Chandra (07120010002) - Renny Surya W (07120010008) - Melda Fitria (07120010012)Document16 paginiAtrophic Glossitis: - Margareta Chandra (07120010002) - Renny Surya W (07120010008) - Melda Fitria (07120010012)Putrisya Rafanael SafageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumer Health: Trained Professional Who Provides People With HealthcareDocument3 paginiConsumer Health: Trained Professional Who Provides People With HealthcareacelÎncă nu există evaluări
- C CA AS SC CL Liin Niiq QU UE E // C CA AS SE ER RE EP PO OR RT TDocument7 paginiC CA AS SC CL Liin Niiq QU UE E // C CA AS SE ER RE EP PO OR RT TG Virucha Meivila IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS20 SolvedDocument2 paginiCS20 SolvedgogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Profession: The United States and Quickly Advanced With The Rise of Trainings For NursesDocument3 paginiNursing Profession: The United States and Quickly Advanced With The Rise of Trainings For NursesMoureneGasperszÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soluvit NinfDocument4 paginiSoluvit NinfNurkholis AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 7 Case Study: Pre-InternshipDocument6 paginiGroup 7 Case Study: Pre-InternshipTrish ShangÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACI Adult Neurological Observation Chart Education PackageDocument101 paginiACI Adult Neurological Observation Chart Education Packagevanphanthuy110Încă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Document6 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Princess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 paginiDaftar Pustakasari murnaniÎncă nu există evaluări