Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Prevention of Home Accidents Among Mothers of Under-Five Children in Community Area Bagalkot
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Prevention of Home Accidents Among Mothers of Under-Five Children in Community Area Bagalkot
Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Volume 4, Issue 11, November – 2019 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
A Study to Evaluate the Effectiveness of Planned
Teaching Programme on Knowledge Regarding
Prevention of Home Accidents among Mothers of
Under-five Children in Community Area Bagalkot
Principal Investigator: Dr. Deelip S. Natekar
Principal BVVS Sajjalashree Institute of Nursing Sciences Bagalkot
Co-Investigators-
1.
Sureshgouda S Patil
Prof & HOD Dept of Pediatric Nsg
SIONS BVV Sangha Bagalkot
2.
Chandrashekhar
3.
Kavita Chalawadi
4.
Darshini Gulannavar
5.
Daneshwari Belagali
6.
Babu Asangi
7.
Bhimappa
Student Nurses
BVVS Sajjalashree Institute of Nursing Sciences Bagalkot
Abstract:- A Quasi-experimental research was undertaken I. INTRODUCTION
to evaluate the effectiveness of PTP on knowledge
regarding prevention of home accidents among the ‘‘Shape the future of Life; Healthy environment for
mothers of under five children. Pre-experimental, one Children’’. They have right to safer, fairer and healthier
group pre-test-post-test method was followed. For this World. There is no task more important than securing their
study 60 mothers were included as participants. Data environment. Children are one third of our future. In order to
collection was done by structured knowledge questionnaire evolve a healthy society, it is important to have healthy
tool. Results revealed as majority 32(53.33%) of mothers children. The under-five group is more vulnerable or special
were in between 21-25 yrs. The relation between pre-test risk group in any population needs special health care because
and post-test scores showed as overall mean difference of of their immaturity and the different stages of growth and
pre-test and post-test was 13.5, Median was 13, Mode was development.1
12, standard deviation was 0.04 and range was 1. The
study concluded that post-test knowledge score is more II. AIMS
than pre-test knowledge score; hence the PTP is found
effective. 1. To determine the knowledge regarding prevention of home
accidents among the mothers of under-five children.
Keywords:- Mothers, Home Accidents, Structured Interview 2. To find out the effectiveness of PTP regarding prevention
Schedule. of home accidents among the mothers of under-five
children.
3. To determine the association between pre-test knowledge
scores and elected demographic variables.
IJISRT19NOV404 www.ijisrt.com 463
Volume 4, Issue 11, November – 2019 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
III. MATERIALS AND METHODS number of under-five children, majority 31 (51.67%) of
them had one under five child, majority 19 (31.67%) of
Pre-experimental, one group pre-test – post-test method was mothers obtained information regarding prevention of
followed, 60 mothers of under-five children were taken for the home accidents in children from family members.
research by following Simple Random Sampling Technique.
The study was carried out in Bagalkot. Structured knowledge SECTION II: Analysis and interpretation of knowledge
questionnaire is used to evaluate the knowledge on prevention scores of mothers regarding prevention of home accidents
of home accidents. The primary aim of the study was to find 1. This study reveals that majority (44.59%) of knowledge
out the effectiveness of PTP. gain is with falls and its prevention, 42.78% of gain in
knowledge was in electric shock and its prevention,
IV. RESULTS knowledge gain in drowning and its prevention was 40%,
knowledge gain in foreign body aspiration and its
SECTION I: Description of Demographic characteristics prevention was 39.99%, knowledge was increased in
of the respondents. poisoning and its preventions 35.63%. and 18.33% of
1. After collection, the data are organized and analyzed with knowledge was increased in trauma due to sharp objects
the help of mean median and percentage, and the socio- and its prevention.
demographic characteristics of the mothers of under-five 2. The deviation between pre-test score and post-test score
children were as follows: majority 32 (53.33%) of mothers showed as overall difference pre-test and post-test in mean
were in between the age group of 21-25 yrs, Considered to was 13.5, Median was 13, Mode was 12, standard
religion, majority 48 (80%) of the mothers belongs to deviation was 0.04 and range was 1.
Hindu religion, 30 (50%) mothers were from nuclear
family. In relation to educational status of mothers SECTION III: Testing hypothesis to evaluate the
maximum numbers 28 (46.47%) of mothers have effectiveness of PTP.
completed their high school education, With regards to the
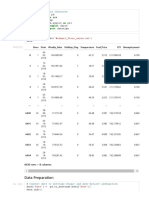
Fig 1:- A Doughnut graph showing Mean difference, Standard error difference and Paired ‘t’ value of knowledge scores of mothers
calculated and tabulated.
SECTION IV: Analysis and Interpretation of data to find There is no any marked significant association exists between
out association between pre-test knowledge scores and these variables and knowledge of mothers.
selected demographic variables.
It reveals that the calculated chi-square value (11.38%) The interpreted chi-square result (48.76%) for
for Age, Religion, Type of family, Occupation, number of educational status of the mother is more than chi-square table
under five children and previous sources of information is less value (12.592). So that H2 is accepted. Significant association
than chi-square table value (12.592). Hence H1 is rejected. seen between knowledge and mothers educational status.
IJISRT19NOV404 www.ijisrt.com 464
Volume 4, Issue 11, November – 2019 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
V. CONCLUSION
Mothers knowledge on prevention of home accidents is
improved after administration of Planned Teaching
Programme.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Same study shall be carried out in extended scale to
generalise study results.
REFERENCES
[1]. Bull JP, Jackson DM, Walton C. Causes and prevention
of domestic burning accidents. Br Med J. 1964 Dec
5;2(5422): 1421-1427. [PMC free article][PubMed].
[2]. Castle OM. Accidents in home. Lancet. 1950 Feb
18;1(6599): 315-319.[PubMed]
[3]. Fisher AJ. Injuries in the aged. Br J Prv Soc Med. 1995
Apr; 9(2): 73-80. [PMC free article][PubMed].
[4]. Dc Fonscka CP, Roberts JL. Invesigating accidents in the
home. Bristol Med Chir J. 1972 Oct; 87(324): 37-51.
[PMC free article][PubMed].
[5]. McNeil WT. Awareness during Anaesthesia. Br Med J.
1969 Mar 15;1 (5645): b715. [PMC free article].
[6]. Maisels DO. Corps BV. Burned Epileptics. Lancet. 1964
Jun 13;1(7346): 1298-1301.[PubMed].
[7]. Neutra R, McFarland RA. Accidents epidemiology and
the design of the residenial environment. Hum Factors.
1972 Oct: 14(5): 405-420.[PubMed].
[8]. Repath E. Home accidents a socio-medical problem.
Community Health (Bristol) 1970 Jul-Aug; 2(1): 12-
17.[PubMed].
IJISRT19NOV404 www.ijisrt.com 465
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Study to Assess the Effectiveness of the Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge Regarding Prevention and Management of Neonates with Hyperbilirubinemia among Mother of Newborn Admitted in HSK Hospital of BagalkotDocument6 paginiA Study to Assess the Effectiveness of the Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge Regarding Prevention and Management of Neonates with Hyperbilirubinemia among Mother of Newborn Admitted in HSK Hospital of BagalkotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test For Special Mental and Physical Abilities and DisabilitiesDocument7 paginiTest For Special Mental and Physical Abilities and DisabilitiesShivani Dhillon100% (2)
- ANM & GNMDocument66 paginiANM & GNMKaran SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka Synopsis Proforma For Registration of Subjects For DissertationDocument14 paginiRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka Synopsis Proforma For Registration of Subjects For Dissertationpavin0% (1)
- Lesson Plan Fonn S.3Document17 paginiLesson Plan Fonn S.3Sandeep MeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newborn ProfileDocument92 paginiNewborn ProfilesarikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: Advanced Nursing Practice Topic: Treatment Aspects: Pharmacological and Pre and Post Operative Care AspectsDocument44 paginiSubject: Advanced Nursing Practice Topic: Treatment Aspects: Pharmacological and Pre and Post Operative Care Aspectsankita100% (1)
- Master of Philosophy Programme in NursingDocument17 paginiMaster of Philosophy Programme in NursingSanjay Kumar SanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Care ConferenceDocument3 paginiPatient Care ConferenceValarmathi0% (1)
- National of Nursing, Barwala, Hisar: Unit PlanDocument3 paginiNational of Nursing, Barwala, Hisar: Unit PlanSumit YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Historcal Evolution of Research in NursingDocument35 paginiAssignment On Historcal Evolution of Research in NursingPoonam Dhatwalia100% (1)
- Effect of Nebulized Suctioning With 3% Hypertonic Saline For Mechanically Ventilated Patient On Airway ClearanceDocument5 paginiEffect of Nebulized Suctioning With 3% Hypertonic Saline For Mechanically Ventilated Patient On Airway ClearanceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breastfeeding QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiBreastfeeding QuestionnaireDr Puteri Nur Sabrina Binti Mohd HanapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Framing Philosophy, Aims and Objectives B.SC - Nursing CourseDocument4 paginiFraming Philosophy, Aims and Objectives B.SC - Nursing CourseRumela Ganguly Chakraborty50% (2)
- Inserviceeducation PPT PBBSCDocument30 paginiInserviceeducation PPT PBBSCkujur mamtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Education BureauDocument13 paginiHealth Education Bureauv_vijayakanth7656Încă nu există evaluări
- Child Abuse AND Battered Child SyndromeDocument90 paginiChild Abuse AND Battered Child SyndromeAmy Lalringhluani ChhakchhuakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Physiological MethodsDocument4 paginiBio Physiological MethodsDelphy VargheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personality DevelopmentDocument25 paginiPersonality DevelopmentmonishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vancouver and Apa StyleDocument8 paginiVancouver and Apa StylePankaj Khatri100% (1)
- Manager Behaviour andDocument11 paginiManager Behaviour andsimmyvashishtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaDocument23 paginiRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaAmit TamboliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Educational Programs in Nursing Course and Program V1Document13 paginiEvaluation of Educational Programs in Nursing Course and Program V1Stephina ImmaculateÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANAGEMENT INFORMATION AND EVALUATION SYSTEM FinalDocument4 paginiMANAGEMENT INFORMATION AND EVALUATION SYSTEM Finalkuruvagadda sagar100% (1)
- EDUCATIONAL PREPARATION, CONTINUING EDUCATION, CAREER OPPURTUNITIES, PROFESSIONAL ADVANCEMENT, ROLES AND SCOPE OF (Autosaved)Document71 paginiEDUCATIONAL PREPARATION, CONTINUING EDUCATION, CAREER OPPURTUNITIES, PROFESSIONAL ADVANCEMENT, ROLES AND SCOPE OF (Autosaved)Mahalakshmi100% (4)
- On National GoalsDocument68 paginiOn National Goalssreedhar muthyala0% (2)
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreDocument18 paginiRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, Bangaloreabdullah khalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Projected Av AidsDocument52 paginiNon Projected Av AidsDeena Melvin100% (2)
- Lumbar PunctureDocument6 paginiLumbar PunctureAnusha VergheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem StatementsDocument42 paginiProblem StatementsAGERI PUSHPALATHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented by Ms. Pallavi CharadeDocument10 paginiPresented by Ms. Pallavi CharadePallavi KharadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Deprivation.Document7 paginiSensory Deprivation.KJ Bindu100% (1)
- Oxygen InsufficiencyDocument70 paginiOxygen InsufficiencydaisyÎncă nu există evaluări
- School of Nursing Science and Research (Sharda University) : Assignment ON Nutritional Problems in CommunityDocument15 paginiSchool of Nursing Science and Research (Sharda University) : Assignment ON Nutritional Problems in CommunitySamjhana Neupane100% (2)
- Group DynamicsDocument21 paginiGroup DynamicsPandiyan Dhyan100% (1)
- Immunization Clinic Report PDFDocument9 paginiImmunization Clinic Report PDFprabha krishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge of Emergency Drugs Among Staff NursesDocument4 paginiEffectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge of Emergency Drugs Among Staff NursesRumela Ganguly ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Rotation PlanDocument5 paginiClinical Rotation PlanamitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope of Nursing Research, EthicsDocument16 paginiScope of Nursing Research, EthicsAmanda ScarletÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Seminar: Computer Application For Patient Care Delivery System and Nursing PracticeDocument18 paginiLong Seminar: Computer Application For Patient Care Delivery System and Nursing Practicepandem soniya100% (2)
- Government College of Nursing, Jodhpur: Presentation ONDocument7 paginiGovernment College of Nursing, Jodhpur: Presentation ONpriyanka0% (1)
- Research ProjectDocument15 paginiResearch ProjectPravalika NatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- History, Principle and Scope of CHNDocument39 paginiHistory, Principle and Scope of CHNArchana100% (1)
- Skill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimenDocument1 paginăSkill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimennetsquadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educational Aims and Objectives-2Document22 paginiEducational Aims and Objectives-2Shruthi Pingula100% (2)
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Simulation Based Learning Programme On Hands-2Document29 paginiA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Simulation Based Learning Programme On Hands-2enam professorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem StatementDocument15 paginiProblem StatementhuylimalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral MedicationDocument11 paginiOral MedicationMayank KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prespective of NSG Edu Global N NationalDocument10 paginiPrespective of NSG Edu Global N NationalAru VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course PlanDocument6 paginiCourse Planmonisha100% (2)
- MICRO TEACHING Physical Examination of ChildrenDocument5 paginiMICRO TEACHING Physical Examination of ChildrenBini Don DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disaster Management Plan, Resources, Drill: Presented byDocument37 paginiDisaster Management Plan, Resources, Drill: Presented byPriyanka Roy100% (2)
- Philosophy of Nursing EducationDocument5 paginiPhilosophy of Nursing Educationamit100% (1)
- Nicu DoccumentationDocument17 paginiNicu Doccumentationchaarvi100% (1)
- Child GuidanceDocument9 paginiChild Guidancegieomson100% (2)
- Research in Continuing EducationDocument25 paginiResearch in Continuing EducationArchana VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indent Verification of Labour RoomDocument4 paginiIndent Verification of Labour RoomRajeshwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anp 1Document11 paginiAnp 1Lekshmi ManuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of VATM On Knowledge Regarding Malnutrition Among Mothers of Under-Five Children Residing at Navanagar of BagalkotDocument5 paginiA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of VATM On Knowledge Regarding Malnutrition Among Mothers of Under-Five Children Residing at Navanagar of BagalkotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Program On Preconception Care PCC Among Women Studying at Selected College, BangaloreDocument4 paginiA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Program On Preconception Care PCC Among Women Studying at Selected College, BangaloreResearch ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDocument6 paginiFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDocument6 paginiStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDocument8 paginiUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Document8 paginiAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDocument7 paginiBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDocument33 paginiCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesDocument8 paginiInsights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDocument2 paginiParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Health Care SystemDocument8 paginiSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyDocument19 paginiSmart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDocument6 paginiImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3Document9 paginiDiabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDocument5 paginiVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareDocument4 paginiCompact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesDocument7 paginiHarnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMDocument8 paginiAir Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningDocument2 paginiPredict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalDocument7 paginiKeywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsDocument6 paginiAn Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsDocument5 paginiParkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolDocument31 paginiThe Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIDocument6 paginiThe Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisDocument8 paginiAdvancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewDocument6 paginiImplications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatDocument16 paginiInvestigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)Document2 paginiDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterDocument11 paginiThe Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubDocument6 paginiFormulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonDocument14 paginiTerracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions On Customer SatisfactionDocument6 paginiThe Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions On Customer SatisfactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Chemical EngineeringDocument124 paginiChemistry Chemical Engineeringjrobs314Încă nu există evaluări
- Titanic Is A 1997 American Romantic Disaster Film Directed, Written. CoDocument13 paginiTitanic Is A 1997 American Romantic Disaster Film Directed, Written. CoJeric YutilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM6 - Mathematics As A Tool - Dispersion and CorrelationDocument18 paginiCM6 - Mathematics As A Tool - Dispersion and CorrelationLoeynahcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sasi EnriquezDocument9 paginiSasi EnriquezEman NolascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTE Self Study - Lfib v3.0Document57 paginiPTE Self Study - Lfib v3.0Jewel AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESL BOOKS - IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 Vocabulary by ESL Fluency - PreviewDocument7 paginiESL BOOKS - IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 Vocabulary by ESL Fluency - Previewanirudh modhalavalasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- French DELF A1 Exam PDFDocument10 paginiFrench DELF A1 Exam PDFMishtiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Storage Center: Command Set 4.1Document174 paginiStorage Center: Command Set 4.1luke.lecheler5443Încă nu există evaluări
- Edci 67200 Abby Carlin Case Study FacilitationDocument9 paginiEdci 67200 Abby Carlin Case Study Facilitationapi-265670845Încă nu există evaluări
- Flow Diagram: Equipment Identification Numbering SystemDocument24 paginiFlow Diagram: Equipment Identification Numbering Systemmkpq100% (1)
- UgvDocument24 paginiUgvAbhishek MatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generative Drafting (ISO) : CATIA TrainingDocument148 paginiGenerative Drafting (ISO) : CATIA TrainingAnonymous 38RNNHWyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yoga Nidra - Text PDFDocument265 paginiYoga Nidra - Text PDFVinod Kumar100% (1)
- UPSC Paper 4 Binder PDFDocument17 paginiUPSC Paper 4 Binder PDFHsis AbedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retail Analysis WalmartDocument18 paginiRetail Analysis WalmartNavin MathadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exalted Signs Sun in AriesDocument6 paginiExalted Signs Sun in AriesGaurang PandyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParallelDocument4 paginiParallelShanntha JoshittaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp#4-Gas TurbineDocument9 paginiExp#4-Gas TurbineLilo17xiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstract On Budgetary ControlDocument22 paginiAbstract On Budgetary ControlIhab Hosny AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm D448Document3 paginiAstm D448Mutyaba Johnson100% (5)
- Sample Intern PropDocument7 paginiSample Intern PropmaxshawonÎncă nu există evaluări
- DonnetDocument12 paginiDonnetAsia SzmyłaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical EngineeringDocument26 paginiChemical EngineeringAnkit TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- استخدام الشبكة الإدارية في السلوك القيادي بحث محكمDocument22 paginiاستخدام الشبكة الإدارية في السلوك القيادي بحث محكمsalm yasmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Message Staging and Logging Options in Advanced Adapter Engine of PI - PO 7.3x - 7.4 - SAP Blogs PDFDocument26 paginiMessage Staging and Logging Options in Advanced Adapter Engine of PI - PO 7.3x - 7.4 - SAP Blogs PDFSujith KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innoventure List of Short Listed CandidatesDocument69 paginiInnoventure List of Short Listed CandidatesgovindmalhotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOS Physical ScienceDocument1 paginăTOS Physical ScienceSuzette De Leon0% (1)
- Mission Statement Generator WorksheetDocument9 paginiMission Statement Generator WorksheetMohamed SururrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taylor Linker ResumeDocument2 paginiTaylor Linker ResumeTaylor LinkerÎncă nu există evaluări