Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Agile
Încărcat de
dream4skyDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Agile
Încărcat de
dream4skyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
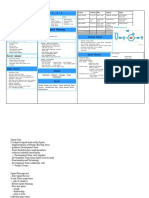
Four Values of Agile Common Agile methodologies Scrum
Scrum 3 pillars - Transparency -> Inspection -> Adaptation
Extreme Programming (XP)
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools. Kanban 5 fundamental values - focus, courage, openness, commitment and
Lean product development respect
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation. Feature-driven development
Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) Sprints - time limited mini project in which the team releases a
Working software over comprehensive documentation. Crystal Family of methods potentially releasable product with a duration of 1 month or less.
Responding to change over following a plan. Scrum Team Roles:
Development Team - self organizing, cross functional team who
build the product increments during each sprint.
12 Principles of Agile Manifesto
Product Owner - manages and prioritizes back log with the
assistance of scrum master and developers, make sure all have a
Satisfy customer through early and continuous delivery of working software. shared understanding of the project goals.
Welcome changes even in a later stage of development for the customer's competitive advantage.
Deliver working software frequently with a preference to shorter timescale. Scrum Master - Servant leader to the development team, meeting
Business and development team must work together daily throughout the project. facilitator, team coaching, helps the organization to adopt scrum
Motivate individuals by giving them the environment and support they need and trust them. practices.
Face to face conversation is more effective and efficient to and within the development team.
Working software is the primary measure of progress. Scrum Activities:
Sustainable development - sponsors, developers and users must maintain a constant pace.
Technical excellence and good design enhances agility. Product backlog refinement - The team discusses and updates the
Simplicity - maximize the amount of work not done - do only what the customer need. items in backlog.
Self-organizing teams - provides best architecture, requirements and design.
Reflect and adjust at regular intervals to become more effective. Sprint Planning Meeting -> Daily Scrum -> Sprint review -> Sprint
retrospectives -------- Inspection and adaptation (2 pillars).
Sprint planning meeting - defines the sprint goal based on the
estimates from dev team, product owner presents the updated
backlog.
Daily Scrum - scrum master facilitates this meeting primarily for the
dev team to sync their work and report any issues.
Scrum of scrums - multiple Serum teams might need to coordinate
their work (Scrum of scrums of scrums)
Sprint Review - includes development team, the product owner, and
the Scrum Master (and potentially other stakeholders). The team
demos the increment work to the product owner, decides whether it
is done.
Sprint Retrospective - primarily for development team to do their
final "inspect and adapt". Timing is after sprint review but before
next sprint planning.
Scrum Artifacts:
Product Increment - which the dev team builds during a sprint that
the team and the product owner needs to define what is "done" and
share this understanding.
Product backlog - single source of all work - prioritized list (by
product owner) of all work that includes features, functions,
requirements, quality attributes, non-functional requirements,
enhancements and fixes. This process is called as backlog
refinement" or "grooming the backlog" - done be dev team and
product owner.
Sprint backlog - highly visible view of the work being undertaken,
only be updated by dev team, subset of product backlog, the team
develops a plan on how to achieve it.
Agile Page 1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Minh ChauDocument12 paginiMinh ChauMinh ChâuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Agile Software Development Master: Scrum Guide For BeginnersDe la EverandScrum Agile Software Development Master: Scrum Guide For BeginnersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum: Agile Framework for High Quality DeliveryDocument2 paginiScrum: Agile Framework for High Quality DeliverydfdgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Summary BookDocument15 paginiScrum Summary BookAlin-Iustinian ToderitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum SummaryDocument2 paginiScrum SummaryEnda MolloyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Guide NotesssDocument7 paginiScrum Guide NotesssHelen MylonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheat Sheet - Scrum Aide Memoire (04.2013)Document1 paginăCheat Sheet - Scrum Aide Memoire (04.2013)Saw' cenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Master Exam Simulator (Mock Test) - 420 Questions - Volkerdon - The Best Solution to Prepare fDocument1 paginăScrum Master Exam Simulator (Mock Test) - 420 Questions - Volkerdon - The Best Solution to Prepare fKonrad ChabrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- IevolveDocument15 paginiIevolvedeepakyadav91100Încă nu există evaluări
- ScrumDocument1 paginăScrumHã DiãÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Classes Must Be Substitutable For Their Base or Parent Classes". This Principle Ensures That Any Class That Is TheDocument1 paginăChild Classes Must Be Substitutable For Their Base or Parent Classes". This Principle Ensures That Any Class That Is TheSahil GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScrumDocument25 paginiScrumMursaleen UmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDLC - Agile Methodology - Scrum - NotepubDocument5 paginiSDLC - Agile Methodology - Scrum - NotepubNote PubÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - PSK+I+Course+PresentationDocument175 pagini1 - PSK+I+Course+PresentationmordmckeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to the Agile ApproachDocument11 paginiIntroduction to the Agile ApproachYan Kusyanto MuritnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum FundamentalsDocument5 paginiScrum FundamentalsMatias SchulzÎncă nu există evaluări
- S OverviewofScrumFrame 1Document7 paginiS OverviewofScrumFrame 1mxiixmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glosario de Términos Scrum (Inglés)Document1 paginăGlosario de Términos Scrum (Inglés)yoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Cheat Sheet 2022Document1 paginăScrum Cheat Sheet 2022oumaima idhikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognizant Information For Task 3Document14 paginiCognizant Information For Task 3Jackson Tom100% (1)
- Agile and Scrum Reference HandoutDocument2 paginiAgile and Scrum Reference HandoutPriscilla Joyce PriscillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCRUM Konrad ChabrosDocument36 paginiSCRUM Konrad ChabrosKonrad ChabrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Course PresentationDocument81 paginiScrum Course PresentationSanyam SehdevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Notes: Roles EventsDocument6 paginiScrum Notes: Roles EventsLucio Pelição DiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Handbook enDocument12 paginiScrum Handbook enDummy AccountÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCRUMDocument13 paginiSCRUMTayabaa Shaik100% (2)
- ScrumDocument12 paginiScrumGul Raiz RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case-Study Intarlinks-Reboot July2017v3Document10 paginiCase-Study Intarlinks-Reboot July2017v3NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGADC Refresher - Part 1Document53 paginiIGADC Refresher - Part 1Biju P NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile ScrumDocument29 paginiAgile ScrumEristiar Tarigan Bre Ndia100% (1)
- Chapitre VDocument15 paginiChapitre VIlyes ArabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile SummaryDocument6 paginiAgile SummaryAli AsgharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8 - Agile Software DevelopmentDocument15 paginiLecture 8 - Agile Software DevelopmentSufyan AbbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginnings of Scrum: Scrum Is An Agile Software Development MethodologyDocument19 paginiBeginnings of Scrum: Scrum Is An Agile Software Development MethodologyZipel SnakhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum at A GlanceDocument13 paginiScrum at A GlanceRobert HeritageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile Testing and Scrum Model ExplainedDocument3 paginiAgile Testing and Scrum Model ExplainedBlesslin JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Williams PDFDocument9 paginiWilliams PDFVarsha DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Popular Agile MethodDocument4 paginiPopular Agile MethodMichael FredyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScrumDocument38 paginiScrumSubramanian KumarappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum in NutshellDocument5 paginiScrum in NutshellrjsinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum in TestingDocument39 paginiScrum in TestingDeepak GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Intro To AgileDocument43 pagini1 - Intro To Agileluciana.nascimentoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile Methodology: Janessa Marielle CruzDocument34 paginiAgile Methodology: Janessa Marielle CruzJanessa CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum v2Document24 paginiScrum v2marioaladro1Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Agile and Scrum MethodologyDocument8 paginiIntroduction to Agile and Scrum MethodologyAnil YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Glossary PSMDocument1 paginăScrum Glossary PSMPeshin KunalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research On Agile Project Management With Scrum MethodDocument4 paginiResearch On Agile Project Management With Scrum MethodUmer FarooqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum Guide SummaryDocument12 paginiScrum Guide SummaryTran Huu Tan100% (1)
- Ict Project Management Using Scrum Day1Document56 paginiIct Project Management Using Scrum Day1Dark LordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Se 34Document175 paginiSe 34Project Chores to HomeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course ContentDocument15 paginiCourse ContentLong Phùng PhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile Development: Department of Information and Communication Technology Software EngineeringDocument39 paginiAgile Development: Department of Information and Communication Technology Software EngineeringDIPESH CHATROLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2 Project CyclesDocument26 paginiWeek 2 Project CyclesCamille MarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile ProcessDocument14 paginiAgile ProcessShomirul Hayder SourovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scrum GlossaryDocument6 paginiScrum GlossaryQasim HammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- SE - Ch.05 - SCRUMDocument15 paginiSE - Ch.05 - SCRUMTariqe Bin Abul KhairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lack of Dedicated Cross Functional Teams.: Self-Organizing Functional. ThisDocument7 paginiLack of Dedicated Cross Functional Teams.: Self-Organizing Functional. ThisAhmed ashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile Key With Answers ConsolidatedpdfDocument12 paginiAgile Key With Answers ConsolidatedpdfNitin GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheat SheetDocument3 paginiCheat SheetJoop den HollanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amount Water To DrinkDocument2 paginiAmount Water To DrinkTamer El SaghirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 10 Reasons For IndDocument1 paginăTop 10 Reasons For Inddream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avoided Subjects Discussed in Plain English: Henry StantonDocument31 paginiAvoided Subjects Discussed in Plain English: Henry Stantondream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expense Tracker/Money Management Application SpecificationsDocument1 paginăExpense Tracker/Money Management Application Specificationsdream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Man Who Would Be PrinceDocument3 paginiThe Man Who Would Be Princedream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PythDocument13 paginiPythdream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 27Document17 paginiCH 27Mohammad NizamuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWR report analysis in depth-part 1: Comparing low vs high CPU environmentsDocument24 paginiAWR report analysis in depth-part 1: Comparing low vs high CPU environmentsdream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex13 SampleDocument1 paginăEx13 Sampledream4skyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Facts For Homebooks Stage 7Document3 paginiBasic Facts For Homebooks Stage 7api-311857762Încă nu există evaluări
- Food Conformity BA 550-13Document9 paginiFood Conformity BA 550-13puipuiesperaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Blueprint 1Document3 paginiAdvanced Blueprint 1api-728237431Încă nu există evaluări
- Smarter Washing Solutions: Modular Wash RangeDocument5 paginiSmarter Washing Solutions: Modular Wash RangeSujesh AnÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Electronics Manufacturing Companies in Noida - ElectronicsmediaDocument2 paginiList of Electronics Manufacturing Companies in Noida - ElectronicsmediaBlue Oceon50% (4)
- Presentation SkillsDocument22 paginiPresentation SkillsUmang WarudkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature vs Nurture DebateDocument3 paginiNature vs Nurture DebateSam GoldbergÎncă nu există evaluări
- World MultipleDocument271 paginiWorld MultipleatrkpoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes and Practices Related To Sexuality and Sexual BehaviorDocument35 paginiAttitudes and Practices Related To Sexuality and Sexual BehaviorGalvin LalusinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zeal Institute of Manangement and Computer ApplicationDocument4 paginiZeal Institute of Manangement and Computer ApplicationSONAL UTTARKARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schippers and Bendrup - Ethnomusicology Ecology and SustainabilityDocument12 paginiSchippers and Bendrup - Ethnomusicology Ecology and SustainabilityLuca GambirasioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Machine-Room-Less Elevator: Kone E MonospaceDocument8 paginiThe Machine-Room-Less Elevator: Kone E MonospaceAbdelmuneimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics in ResearchDocument21 paginiEthics in Researchmukku_raviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delivered Voided Application (Surrender Instrument) Returned To at - Sik - Hata Nation of Yamasee MoorsDocument20 paginiDelivered Voided Application (Surrender Instrument) Returned To at - Sik - Hata Nation of Yamasee MoorsMARK MENO©™Încă nu există evaluări
- CA Ashish Dewani - Resume-1Document2 paginiCA Ashish Dewani - Resume-1Payal JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaDocument9 paginiRenal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaFarhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage PDFDocument1 paginăDrainage PDFSwapnil JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cooled Screw Chiller Performance SpecificationDocument2 paginiAir Cooled Screw Chiller Performance SpecificationDajuko Butarbutar100% (1)
- Eccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic PlanDocument95 paginiEccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic Planyayehyirad100% (1)
- A6V12050595 - Valve Actuator DIL-Switch Characteristic Overview - deDocument42 paginiA6V12050595 - Valve Actuator DIL-Switch Characteristic Overview - depolo poloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics Interview QuestionsDocument5 paginiStatistics Interview QuestionsARCHANA R100% (1)
- 5e Lesson Plan s16 - MagnetsDocument6 pagini5e Lesson Plan s16 - Magnetsapi-317126609Încă nu există evaluări
- Exoskeleton Power Requirements Based on Human BiomechanicsDocument54 paginiExoskeleton Power Requirements Based on Human Biomechanicsja2ja1Încă nu există evaluări
- HIBAH PKSM Sps 2021Document9 paginiHIBAH PKSM Sps 2021Gargazi Bin HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthyDocument1 paginăIIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthySathyamoorthy VenkateshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assissment 1Document12 paginiRisk Assissment 1Ibrahim BouzinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ¿Cómo Hacerlo?: Dr. Jorge Ramírez Medina, Dr. Guillermo Granados Ruíz EGADE Business SchoolDocument17 pagini¿Cómo Hacerlo?: Dr. Jorge Ramírez Medina, Dr. Guillermo Granados Ruíz EGADE Business Schoolgalter6Încă nu există evaluări
- Jupiter - The Giant Planet That Destroys CometsDocument2 paginiJupiter - The Giant Planet That Destroys Cometsmaiche amarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid SemDocument1 paginăMid SemvidulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 3.4 The Conditional and Related StatementsDocument11 paginiSection 3.4 The Conditional and Related Statementsmister sparklesÎncă nu există evaluări