Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Modelling Data and Practical Situations
Încărcat de
Shane Rajapaksha0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
21 vizualizări2 paginiDrepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
21 vizualizări2 paginiModelling Data and Practical Situations
Încărcat de
Shane RajapakshaDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Modelling Data and Practical Situations
Models for Data
When we collect a set of data, we often want to describe as accurately as possible a function that
could generate the same points or at least a good approximation of them. To do this, we need to
know what shape the points take, this is best done by plotting the data. If the shape is recognisable, a
model can be easily fit to the data. However, so situations require a combination (sum, difference, or
product) of functions to more accurately describe the model.
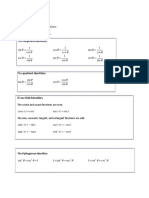
Features that Enable the Recognition of General Forms of Possible Models
Positive Power Model 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 Proportional to the 𝑛th power.
𝑎 Inversely proportional to the 𝑛th power (has asymptotic
Negative Power Model 𝑦 = ⎯⎯⎯
𝑥 behaviour).
Linear Model 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏 Constantly increasing or decreasing.
Polynomial Model Takes the shape of a polynomial.
Sinusoidal (Sine or Cosine) Model Oscillation between two values.
𝑦 = 𝑎 sin 𝑏𝑥 or 𝑦 = 𝑎 cos 𝑏𝑥
Exponential Model 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑒 Increasing or decreasing exponentially (decreasing has
asymptotic behaviour).
Logarithmic Model 𝑦 = 𝑎 log 𝑏𝑥 Slow growth or decay, or data ranges over orders of
magnitude .
Example VCAA 2000 Exam 1 Question 4
𝑥 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
𝑦 1.7 3.2 1.5 0.5 1.2 2.6 3.4 2.3
The data in the above table would be best modelled using a circular function.
Example VCAA 2001 Exam 1 Question 12
The relationship between two quantities, 𝑥 and 𝑦, is
represented graphically as shown below.
If 𝒂 is a negative real constant, the equation relating 𝑥
and 𝑦 is most likely to be of the form 𝑦 = 𝑒
Models using Combinations of Functions
Example VCAA 2014 Exam 2 Question 3
In a controlled experiment, Juan took some medicine at 8 pm.
The concentration of medicine in his blood was then
measured at regular intervals. The concentration of medicine
in Juan’s blood is modelled by the function
5
𝑐(𝑡) = ⎯⎯𝑡𝑒 ⎯⎯⎯, 𝑡 ≥ 0, where 𝑐 is the concentration of
2
medicine in his blood, in milligrams per litre, 𝑡 hours after 8
pm. Part of the graph of the function 𝑐 is shown below.
Example VCAA 2006 Sample Exam 2 Question 5
A small object is oscillating up and down at the end of a vertical spring. The object is ℎ metres
3𝜋𝑡
above its starting point at time 𝑡 seconds, where ℎ = 0.5 1 − 𝑒 . cos ⎯⎯⎯ , and 𝑡 > 0.
2
Piecewise Function / Hybrid Function
A function that takes the shape of different functions at different sections of its domain.
Example VCAA 2007 Exam 2 Question 2
Tasmania Jones is attempting to recover the lost Zambeji diamond. The diamond is buried at a point
4 km into Death Gorge, which is infested with savage insects. In order to recover the diamond,
Tasmania will need to run into the gorge, dig up the diamond and return the same way that he came.
The concentration of insects in the gorge is a continuous function of time. The concentration 𝐶,
insects per square metre, is given by
𝜋(𝑡 − 8)
𝐶(𝑡) = 1000 cos ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ 2
+ 2 − 1000 8 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 16
8000 0 ≤ 𝑡 < 6 or 16 < 𝑡 ≤ 24
where 𝑡 is the number of hours after midnight. The graph of 𝐶 has been graphed for 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 24.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Multiplication and Division: Learning From HomeDocument38 paginiMultiplication and Division: Learning From HomeShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staistics Exam G8Document8 paginiStaistics Exam G8Shane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 StatisticsDocument23 paginiGrade 7 StatisticsShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whole Numbers - Burton Morewood PDFDocument44 paginiWhole Numbers - Burton Morewood PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Line Q Ns DecimalDocument2 paginiLine Q Ns DecimalShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MASA Resource - Year 7 Assessment Tasks For NumberDocument44 paginiMASA Resource - Year 7 Assessment Tasks For NumberShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 Maths Revision Practice BookletDocument31 paginiYear 5 Maths Revision Practice BookletShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- H No Plane Solns PDFDocument20 paginiH No Plane Solns PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Line Q Ns DecimalDocument2 paginiLine Q Ns DecimalShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nap00031 PDFDocument61 paginiNap00031 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 19 PDFDocument17 paginiGrade 7 Exam 19 PDFShane Rajapaksha0% (1)
- H Angles GBR 2011-11-29Document36 paginiH Angles GBR 2011-11-29Shane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- H Polygons Solns PDFDocument24 paginiH Polygons Solns PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Fractions Student Booklet PDFDocument44 pagini7 Fractions Student Booklet PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 927 24635589 NZL H Directed Numbers NZL PDFDocument40 pagini927 24635589 NZL H Directed Numbers NZL PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 15 PDFDocument14 paginiGrade 7 Exam 15 PDFShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Grade 7 Exam 17 PDFDocument15 paginiGrade 7 Exam 17 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 21 PDFDocument16 paginiGrade 7 Exam 21 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 13 PDFDocument14 paginiGrade 7 Exam 13 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 12 PDFDocument13 paginiGrade 7 Exam 12 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 11 PDFDocument16 paginiGrade 7 Exam 11 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 13 PDFDocument14 paginiGrade 7 Exam 13 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DN Seriesh S PDFDocument16 paginiDN Seriesh S PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 7 PDFDocument14 paginiGrade 7 Exam 7 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 3 PDFDocument12 paginiGrade 7 Exam 3 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2535 18923329 NZL H Area and Perimeter NZL PDFDocument40 pagini2535 18923329 NZL H Area and Perimeter NZL PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 16 PDFDocument11 paginiGrade 7 Exam 16 PDFShane RajapakshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Exam 10 PDFDocument16 paginiGrade 7 Exam 10 PDFShane Rajapaksha100% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Linear Programming PDFDocument3 paginiLinear Programming PDFmelissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSIR September 2022 Question PaperDocument24 paginiCSIR September 2022 Question PaperShatabbdi SsinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Reciprocity Theorem For Domino TilingsDocument9 paginiA Reciprocity Theorem For Domino TilingsYannick NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA1032 Syllabus 14S2Document2 paginiMA1032 Syllabus 14S2Ishan DewpuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labsheet 1 (Int)Document3 paginiLabsheet 1 (Int)mail meÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSA Roadmap - +330 ProblemsDocument16 paginiDSA Roadmap - +330 ProblemsAhmed KhairyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Lecture Notes - Part2 PDFDocument18 paginiTrigonometry Lecture Notes - Part2 PDFDezzalyn D. Gabriel100% (1)
- Uwu Onichan OWODocument4 paginiUwu Onichan OWOMiguel Angel CarballoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Functions (COMPLETE)Document86 paginiLinear Functions (COMPLETE)Girish SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculus For JEEDocument157 paginiCalculus For JEERaghavan ARÎncă nu există evaluări
- P3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersDocument3 paginiP3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersSheikh HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Substitution: Jzfa20Document12 paginiTrigonometric Substitution: Jzfa20Samuel SmallmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sum and Difference FormulasDocument23 paginiSum and Difference FormulasHelpful PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DERIVATIVES (Formula)Document2 paginiDERIVATIVES (Formula)Geojanni PangibitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Riemann Integral PDFDocument4 paginiRiemann Integral PDFhimanshu AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equations Reducible To Variables SeparableDocument4 paginiEquations Reducible To Variables SeparablebenrasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- FunctionsDocument29 paginiFunctionsncsko neugesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition:: Adjacent Edges (Incident)Document11 paginiDefinition:: Adjacent Edges (Incident)Abdul BasitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmDocument15 paginiDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmswathisaipragnyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 2 Analysis and Transmission of SignalsDocument42 paginiChapter - 2 Analysis and Transmission of SignalsTemesgen MollaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roughdraft 3Document16 paginiRoughdraft 3api-670141117Încă nu există evaluări
- 11 - Quadratic Forms and EllipsoidsDocument21 pagini11 - Quadratic Forms and EllipsoidsMatheus DomingosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parallel Test - Q1 - GEN MATHDocument3 paginiParallel Test - Q1 - GEN MATHEmma SarzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simultaneous Linear EquationsDocument37 paginiSimultaneous Linear EquationsAnonymous J1Plmv8Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter3 STDocument99 paginiChapter3 STHoang TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths QE Teacher NotesDocument19 paginiMaths QE Teacher NotessashaankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rational Function and Irrational Function: LessonDocument15 paginiRational Function and Irrational Function: LessonMatthew RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 247A Notestodd-KempDocument109 pagini247A Notestodd-KempAnastasisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Algebra PyqDocument3 paginiLinear Algebra PyqsuryanshchauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set Theory and Relations - MaterialDocument46 paginiSet Theory and Relations - MaterialRavi teja NalamÎncă nu există evaluări