Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Calculations Based On Fuel Analysis
Încărcat de
Brille Adrian FernandoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentCalculations Based On Fuel Analysis
Încărcat de
Brille Adrian FernandoCALCULATIONS BASED ON FUEL ANALYSIS
____________________________________________________
• From the complete analysis of the fuel, the theoretical oxygen and the calorific value
can be determined.
Calorific Value
- the energy contained in a fuel or food, determined by measuring the heat produced
by the complete combustion of a specified quantity of it. This is usually expressed in
joules per kilogram.
• If data on air (% excess air or amount of air supplied) is given together with the degree
of completion of the reaction, the following can be calculated:
a. Analysis (Orsat or Complete) of the products of combustion called the flue gases
or the stack gases. These gases are normally CO2, CO, SO2, H2, free O2, N2 and H2O.
▪ Orsat analysis – water is not included
▪ Complete analysis – water is included
b. Air – fuel ratio
c. Stack gas – fuel ratio
𝑭𝒓𝒆𝒆 𝑶𝟐 = 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑂2 + 𝑂2 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑢𝑛𝑏𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑡 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑢𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒
𝐶𝑂 𝐻2
= 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑂2 + +
2 2
𝑵𝟐 = 𝑁2 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑎𝑖𝑟 + 𝑁2 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑓𝑢𝑒𝑙
𝑯𝟐 𝑶 = 𝑚𝑜𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑓𝑢𝑒𝑙 + 𝑚𝑜𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑎𝑖𝑟 + 𝐻2 𝑂 𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑒𝑑 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑢𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑓𝑢𝑒𝑙
__________________________________________________________________________
EXAMPLE: Pure ethane is burned completely in 20 % excess air. Air is supplied at 25°C, 740
torrs and is substantially dry.
Calculate:
a. Orsat analysis of the products of combustion
b. kg dry air supplied / kg of fuel gas
c. cubic meters of air / kg ethane
d. cubic meters of the products of combustion measured at 400°C , 100 kPa / kg ethane
e. Partial pressure of water in the products of combustion
NOTES ON STOICHIOMETRY OF FUEL COMBUSTION (CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEERS)
Engr. Reden E. Nolasco
SOURCE: STOICHIOMETRY OF FUEL COMBUSTION AND RELATED PROCESS INDUSTRIES BY EVELYN LAURITO
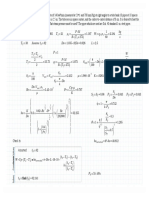
SOLUTION:
Basis: 1 kgmole ethane or 30 kg ethane
Air Stack gas
25 °C 400°C
740 torrs 100 kPa
20 % excess air BURNER
Fuel
C2H6
𝑎𝑡 𝐶𝑎𝑟𝑏𝑜𝑛 = 2
𝑎𝑡 𝐻𝑦𝑑𝑟𝑜𝑔𝑒𝑛 = 6
𝑎𝑡 𝐻 6
𝑇ℎ𝑒𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑂2 = 𝑎𝑡 𝐶 + 𝑎𝑡 𝑆 + − 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑂2 = 2 + 0 + − 0 = 3.5 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
4 4
𝐸𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑂2 = 3.5 × 0.2 = 0.7 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
𝑂2 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑎𝑖𝑟 = 3.5 + 0.7 = 4.2 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
79
𝑁2 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑎𝑖𝑟 = 4.2 ( ) = 15.8 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
21
𝐶𝑂2 𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑒𝑑 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑡 𝐶 = 2 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
𝑎𝑡 𝐻 6
𝐻2 𝑂 𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑒𝑑 = = = 3 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
2 2
𝐶𝑂 𝐻2
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑒 𝑂2 = 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑂2 + + = 0.7 + 0 + 0 = 0.7 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
2 2
a. Orsat analysis of combustion products
Gas Moles %
CO2 2 10.81
O2 0.7 3.78
N2 15.8 85.41
TOTAL 18.5 100
NOTES ON STOICHIOMETRY OF FUEL COMBUSTION (CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEERS)
Engr. Reden E. Nolasco
SOURCE: STOICHIOMETRY OF FUEL COMBUSTION AND RELATED PROCESS INDUSTRIES BY EVELYN LAURITO
b. kg dry air / kg fuel
𝑘𝑔
𝑘𝑔 𝑑𝑟𝑦 𝑎𝑖𝑟 (4.2 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 + 15.8 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒) (29 )
𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
= = 𝟏𝟗. 𝟑𝟑𝟑𝟑 𝒌𝒈 𝒅𝒓𝒚 𝒂𝒊𝒓/ 𝒌𝒈 𝒇𝒖𝒆𝒍
𝑘𝑔 𝑓𝑢𝑒𝑙 30 𝑘𝑔
NOTE : The molecular weight is approximately 29 kg/ kg mole or 29 g / mole.
c. m3 dry air / kg ethane
𝑚3 760 𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑠 273.15 + 25 𝐾
3
𝑚 𝑑𝑟𝑦 𝑎𝑖𝑟 (4.2 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 + 15.8 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒) (22.4 )( )( )
𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 740 𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑠 273.15 𝐾
=
𝑘𝑔 𝑒𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑒 30 𝑘𝑔
𝟑
= 𝟏𝟔. 𝟕𝟒𝟎𝟔 𝒎 𝒅𝒓𝒚 𝒂𝒊𝒓/ 𝒌𝒈 𝒆𝒕𝒉𝒂𝒏𝒆
d. m3 of the products of combustion measured at 400°C , 100 kPa / kg ethane
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑢𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑠 = 18.5 + 3 = 21.5 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
𝑚3 101.325 𝑘𝑃𝑎 273.15 + 400 𝐾
3
𝑚 𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑐𝑘 𝑔𝑎𝑠 (21.5 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒) (22.4 )( )( )
𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 100 𝑘𝑃𝑎 273.15 𝐾
=
𝑘𝑔 𝑒𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑒 30 𝑘𝑔
= 𝟒𝟎. 𝟎𝟖𝟔 𝒎𝟑 𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒄𝒌 𝒈𝒂𝒔 /𝒌𝒈 𝒆𝒕𝒉𝒂𝒏𝒆
e. Partial pressure of water in the products of combustion
𝑃𝑤 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
=
𝑃𝑡 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠
3 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
𝑃𝑤 = 100 𝑘𝑃𝑎 ( ) = 𝟏𝟑. 𝟗𝟓𝟑𝟓 𝒌𝑷𝒂
21.5 𝑘𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒
NOTES ON STOICHIOMETRY OF FUEL COMBUSTION (CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEERS)
Engr. Reden E. Nolasco
SOURCE: STOICHIOMETRY OF FUEL COMBUSTION AND RELATED PROCESS INDUSTRIES BY EVELYN LAURITO
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Drop and Hardness Tests of GreasesDocument17 paginiDrop and Hardness Tests of GreasesJohn Mace VidamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drying ExamplesDocument6 paginiDrying ExamplesIsabelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument18 paginiShell and Tube Heat ExchangertatvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra and Geometry FormulasDocument2 paginiAlgebra and Geometry FormulasKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combustion Calculation: 165472 Power Plant EngineeringDocument43 paginiCombustion Calculation: 165472 Power Plant Engineeringluiz0carlos0martinel100% (2)
- Combustion CalculationsDocument6 paginiCombustion CalculationsMauro FerrareseÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05-Chem Eng Tools 2016Document11 pagini05-Chem Eng Tools 2016Hazel Raditya MizumareruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conradson Carbon Residue ApparatusDocument2 paginiConradson Carbon Residue Apparatusvasudeva yasasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multicomponent Distillation CalculationsDocument5 paginiMulticomponent Distillation CalculationsPatricia DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch140: Chemical Process Industries Case StudyDocument4 paginiCh140: Chemical Process Industries Case StudymarkkkkkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crystallization FormationDocument32 paginiCrystallization FormationMALIK ZARYABBABAR100% (1)
- Boiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerDocument22 paginiBoiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerZeshan AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- FLR - Performance of A Tubular CondenserDocument12 paginiFLR - Performance of A Tubular CondenserNazario Emil LintagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material and Energy Balance DiagramDocument16 paginiMaterial and Energy Balance DiagramcvkalyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample ProblemsDocument18 paginiSample ProblemsEggy ThreekingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive Analysis of Pumps and Heat Exchanger Insulation ThicknessDocument20 paginiCompetitive Analysis of Pumps and Heat Exchanger Insulation Thicknessfrankizzta0% (3)
- Lec 6 Combustion of Liquid and Solid FuelsDocument51 paginiLec 6 Combustion of Liquid and Solid FuelsEli EliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fermenter design specificationsDocument38 paginiFermenter design specificationsMilton Dela Rosa JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Thermodynamics: Note 6 Applications of Thermodynamics To Flow ProcessesDocument24 paginiAdvanced Thermodynamics: Note 6 Applications of Thermodynamics To Flow ProcessesHasif D. MüllerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium Hydroxide Production From Seawater Desalination Brine: Process Design and Energy EfficiencyDocument38 paginiSodium Hydroxide Production From Seawater Desalination Brine: Process Design and Energy EfficiencyjuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Fuels Group 7 & 8Document91 paginiSolid Fuels Group 7 & 8Jowel MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Fuels W:oDocument3 paginiSolid Fuels W:oShane PatulotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bank of Tubes (Gas) T&E: Air Is Blown at A Rate of 140 M /min (Measured at 21 C and 700 MM HG) at Right Angles To A Tube Bank 10 Pipes at 10 SpacesDocument1 paginăBank of Tubes (Gas) T&E: Air Is Blown at A Rate of 140 M /min (Measured at 21 C and 700 MM HG) at Right Angles To A Tube Bank 10 Pipes at 10 SpacesRenzel ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScrubbersDocument5 paginiScrubbersleoboyaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Tables in Excel (By IIT, Mumbai)Document14 paginiSteam Tables in Excel (By IIT, Mumbai)myself_riteshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bare and Lagged Pipes PDFDocument11 paginiBare and Lagged Pipes PDFlee diquiatcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas TurbineDocument14 paginiGas Turbineاحمد الربيعي100% (1)
- Flue-Gas-Analysis SimuDocument5 paginiFlue-Gas-Analysis SimuBernadette BoncolmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsDocument4 pagini3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsbackseeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Weekly Exam5Document4 paginiExam Weekly Exam5Gab LibetarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checal2 LauritoDocument1 paginăChecal2 LauritoGarcia RaphÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bry MomentumDocument13 paginiBry MomentumBryan ManaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- BangbangDocument5 paginiBangbangAutumn JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMTD Correction FactorDocument3 paginiLMTD Correction FactorAKSHAY BHATKARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 EvaporationDocument134 paginiChapter 9 EvaporationTÚ Cao Ngọc ThiệnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pump NPSH Calculation: Sample Problem StatementDocument2 paginiPump NPSH Calculation: Sample Problem Statementelectrifier_surenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 1 Workshop HandoutDocument2 paginiChap 1 Workshop HandoutHenry RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire Tube & Water Tube BoilerDocument9 paginiFire Tube & Water Tube BoilerZaib Rehman100% (3)
- Solid FuelsDocument5 paginiSolid FuelsPritamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument21 paginiVolumetric Properties of Pure FluidsIR Ika EtyEtyka Dora100% (1)
- YYF Lecture 6 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Cont Single Stage 110814Document9 paginiYYF Lecture 6 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Cont Single Stage 110814Pravin NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap3-2e SO2 Absorption ExampleDocument8 paginiChap3-2e SO2 Absorption Exampledarkelf_riderÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Vegetable Oil and BiofuelsDocument15 pagini3 - Vegetable Oil and BiofuelsVenus Abigail GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Condensers PDFDocument7 paginiSurface Condensers PDFing_julio_siviraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial SheetsDocument11 paginiTutorial SheetsKAMARAJU SAI VAMSHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical For Practice MidtermDocument3 paginiNumerical For Practice MidtermSiddhant SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Azucarera de Tarlac Sugar MillDocument4 paginiCentral Azucarera de Tarlac Sugar MillRay RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychrometry ProblemsDocument33 paginiPsychrometry Problems19R21A0334 MATTA SHASHANKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reynolds ExperimentDocument3 paginiReynolds ExperimentShary MosqueraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Assessment #1 PDFDocument1 paginăSummative Assessment #1 PDFCYBER DOMINGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handling of Gaseous Fuels: Caroline P. Mirandilla Catherine C. Glorioso Josua Royce S. RuzolDocument16 paginiHandling of Gaseous Fuels: Caroline P. Mirandilla Catherine C. Glorioso Josua Royce S. RuzolRonald Andrei DaguioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ps1-Che171 Chemical Reaction Engineering 1Document2 paginiPs1-Che171 Chemical Reaction Engineering 1Cha CanceranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Table English PDFDocument9 paginiSteam Table English PDFBruce DoyaoenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Problems On Gas TurbineDocument9 paginiReview Problems On Gas TurbinejehadyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHE 402 - FR Heat Loss in Bare and Lagged PipesDocument8 paginiCHE 402 - FR Heat Loss in Bare and Lagged PipesHirizza Junko YamamotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combustion Engineering - Topic 1-4Document8 paginiCombustion Engineering - Topic 1-4JosafatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overall Assessment CHE 252 2020Document3 paginiOverall Assessment CHE 252 2020Enoch AffulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 11 Solutions - ENB222Document11 paginiWeek 11 Solutions - ENB222Don Wook WonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Fuels Classification and AnalysisDocument49 paginiLiquid Fuels Classification and AnalysisMaejelou Nayre MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsDe la EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Principles of Steel Design Example 3-10Document5 paginiChapter 3 Principles of Steel Design Example 3-10Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Principles of Steel Design Example 4-18 4-19 4-20Document8 paginiChapter 4 Principles of Steel Design Example 4-18 4-19 4-20Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- T-Test: Research in Daily Life 2 G12 - Stem, Abm, Humms Apayao State College 3 Quarter, 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Document30 paginiT-Test: Research in Daily Life 2 G12 - Stem, Abm, Humms Apayao State College 3 Quarter, 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-2Document16 paginiChapter 1-2Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimension Stone AfghanistanDocument26 paginiDimension Stone AfghanistanwerewaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainability 13 02861Document25 paginiSustainability 13 02861Jinxin ZhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnergiesDocument20 paginiEnergiesBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewerage Planning and Wastewater Treatment For Sabang, Puerto GaleraDocument55 paginiSewerage Planning and Wastewater Treatment For Sabang, Puerto GaleraPEMSEA (Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia)Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Module 2Document8 paginiPhysics Module 2Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- One-Way ANOVA Introduction (39Document31 paginiOne-Way ANOVA Introduction (39Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geosciences: Monitoring Groundwater Change in California's Central Valley Using Sentinel-1 and GRACE ObservationsDocument21 paginiGeosciences: Monitoring Groundwater Change in California's Central Valley Using Sentinel-1 and GRACE ObservationsBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Availability and Land Subsidence in The Central Valley, California, USADocument10 paginiWater Availability and Land Subsidence in The Central Valley, California, USABrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Module 1Document9 paginiPhysics Module 1Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Problem Set #1 (Unit Measurement, Unit Conversion & Significant Figures)Document6 paginiPhysics Problem Set #1 (Unit Measurement, Unit Conversion & Significant Figures)Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workbook in Integral Calculus 1-2Document23 paginiWorkbook in Integral Calculus 1-2Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3-4 Gec Chapter 3 PROBLEM SOLVING AND REASONINGDocument10 paginiWeek 3-4 Gec Chapter 3 PROBLEM SOLVING AND REASONINGBrille Adrian Fernando0% (1)
- Workbook in Integral Calculus 1-2Document23 paginiWorkbook in Integral Calculus 1-2Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Module 2Document8 paginiPhysics Module 2Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pink and Blue FreshDocument9 paginiPink and Blue FreshBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4. Lesson 01 Information Technology in Education: ObjectivesDocument3 paginiWeek 4. Lesson 01 Information Technology in Education: ObjectivesBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brief History, Nature and Recent Development of The Game: Lesson 1Document8 paginiBrief History, Nature and Recent Development of The Game: Lesson 1Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1008171282044654types of ComputersDocument1 pagină1008171282044654types of ComputersBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3. Lesson 01 Information Technology in Education: ObjectivesDocument3 paginiWeek 3. Lesson 01 Information Technology in Education: ObjectivesBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Technology in Everyday Life: Lesson ObjectivesDocument4 paginiInformation Technology in Everyday Life: Lesson ObjectivesBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 01 Information Technology in Everyday Life: ObjectivesDocument4 paginiLesson 01 Information Technology in Everyday Life: ObjectivesBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Module 1Document9 paginiPhysics Module 1Brille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Clutch Ch.6 - ThermochemistryDocument23 paginiChemistry - Clutch Ch.6 - ThermochemistryBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Calculus Worksheet Chap 1: Limits and Their Properties SectionDocument1 paginăMath Calculus Worksheet Chap 1: Limits and Their Properties SectionBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Calculus: Derivatives ExplainedDocument13 paginiDifferential Calculus: Derivatives ExplainedBrille Adrian FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetrahydrofuran: Technical InformationDocument3 paginiTetrahydrofuran: Technical InformationNavieenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cutting Fluid Types and Their Importance in MachiningDocument7 paginiCutting Fluid Types and Their Importance in Machiningcm_chemical81Încă nu există evaluări
- NPCA Ultra High Performance ConcreteDocument19 paginiNPCA Ultra High Performance ConcreteGeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urban Engineering Course Outline - Final Year (First Semester)Document6 paginiUrban Engineering Course Outline - Final Year (First Semester)Arif SamoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product14 File1 0 Product Pages - Buildex ScrewDocument4 paginiProduct14 File1 0 Product Pages - Buildex ScrewKoko Putra AriadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Engineering SlidesDocument30 paginiEnvironmental Engineering SlidesDurka AghnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cmos Process FlowDocument25 paginiCmos Process FlowSHAIK MUSTHAFAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wrb-Air Barrier - Parex Usa Weatherseal Spray and Roll OnDocument3 paginiWrb-Air Barrier - Parex Usa Weatherseal Spray and Roll Onsaffronbuilders9Încă nu există evaluări
- Indice categorie di accessori nauticiDocument56 paginiIndice categorie di accessori nauticiJohn FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isocure: Concrete Curing AgentDocument1 paginăIsocure: Concrete Curing AgentshafiullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hints & Solutions: NSEJS - STAGE-I (2016-17) Paper Code: Js-530Document11 paginiHints & Solutions: NSEJS - STAGE-I (2016-17) Paper Code: Js-530Bhuvnesh MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lava Plus High Translucency Zirconia BrochureDocument4 paginiLava Plus High Translucency Zirconia BrochureMario MlinarićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low-Bias Transport in Graphene:an IntroductionDocument57 paginiLow-Bias Transport in Graphene:an IntroductionLIAKMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM D635 Flammability Test of FibreGrid GRP MaterialDocument9 paginiASTM D635 Flammability Test of FibreGrid GRP MaterialDr. Ahmed Abdel-HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstracts Book EWWM2014Document276 paginiAbstracts Book EWWM2014azilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023宣传册最终版 修改3Document16 pagini2023宣传册最终版 修改3CAMILA ESTAY TORRESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminum-Clad Steel Stranded Conductor For Earth WireDocument14 paginiAluminum-Clad Steel Stranded Conductor For Earth WireMohamed AhmiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clean Surfaces and Floors Lesson Explains TechniquesDocument47 paginiClean Surfaces and Floors Lesson Explains TechniquesEmerson Cruz0% (1)
- Atterburg Limits Tests: Liquid Limit L.L T - 89Document7 paginiAtterburg Limits Tests: Liquid Limit L.L T - 89Saif JanÎncă nu există evaluări
- API STD 2000 Tank Venting Rate Calculation Using Latest MethodDocument15 paginiAPI STD 2000 Tank Venting Rate Calculation Using Latest MethodHyungTae JangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesoon Equipment Catalogue 2015Document28 paginiLesoon Equipment Catalogue 2015Jason PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Handbook Standard For Portable Fire ExtinguishersDocument205 pagini10 Handbook Standard For Portable Fire ExtinguishersJosesin SinsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Cost SummaryDocument19 paginiBridge Cost SummaryShashank SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antacid Lab Effectiveness AnalysisDocument42 paginiAntacid Lab Effectiveness Analysisumesh123patilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Health and Vessel Sanitation Preventive Procedure Instruction #11Document1 paginăEnvironmental Health and Vessel Sanitation Preventive Procedure Instruction #11VizitiuAnisoaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-stage centrifugal pumps for clean water applicationsDocument6 paginiMulti-stage centrifugal pumps for clean water applicationsazze bouzÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFM56-5B 2 PDFDocument40 paginiCFM56-5B 2 PDFMohsen Peykaran100% (1)
- Belt Road Capital Management: Method Statement For Installation Pipe Sleeve BRCM-CFU-ET&S-GENERAL-MS-1003Document8 paginiBelt Road Capital Management: Method Statement For Installation Pipe Sleeve BRCM-CFU-ET&S-GENERAL-MS-1003Dong Vanra100% (1)
- Silicato de CalcioDocument2 paginiSilicato de Calciop_pr01Încă nu există evaluări
- Interactions and Incompatibilities of Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument24 paginiInteractions and Incompatibilities of Pharmaceutical ExcipientsEmmanuel Vachon LachanceÎncă nu există evaluări